Types of Synovial Joints
- 1. Plain Joints ...
- 2. Pivot joints ...
- 3.Condyloid joints Condyloid Joints are also said to be Ellipsoidal joints of the body. ...
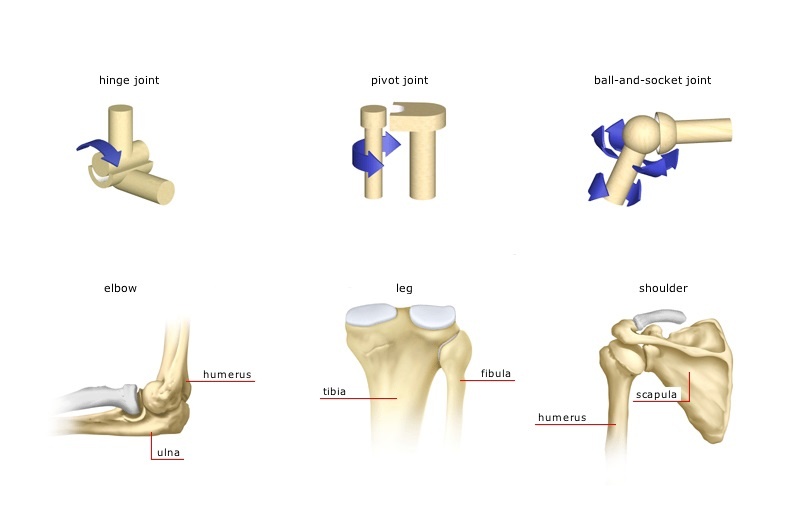
- 4.Hinge joints Hinge Joints are those which help in fitting the rounded end of one bone into the hollow end of another bone in the human body. ...
- 5.Ball & socket joints Ball & socket joint is also referred to as Universal joints. ...
- 6.Saddle Joint ...
What are the 3 structural types of synovial joints?
Types of synovial jointsHinge - these can be found in the elbow, knee and ankle. ... Ball and socket - these types of joint can be found at the shoulder and hip and allow movement in almost every direction. ... Pivot - this joint can be found in the neck between the top two vertebrae.
What are the names of the 4 types of synovial joints and describe them?
The different types of synovial joints are the ball-and-socket joint (shoulder joint), hinge joint (knee), pivot joint (atlantoaxial joint, between C1 and C2 vertebrae of the neck), condyloid joint (radiocarpal joint of the wrist), saddle joint (first carpometacarpal joint, between the trapezium carpal bone and the ...
What are the synovial joints?
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces.
What are the 6 types of freely moving synovial joints?
The six types of freely movable joint include ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot and gliding.
What are the 7 types of joint?
Types of freely movable jointsBall and socket joint. Permitting movement in all directions, the ball and socket joint features the rounded head of one bone sitting in the cup of another bone. ... Hinge joint. ... Condyloid joint. ... Pivot joint. ... Gliding joint. ... Saddle joint.
What are the 7 main movements of synovial joints?
Synovial joints allow bones to slide past each other or to rotate around each other. This produces movements called abduction (away), adduction (towards), extension (open), flexion (close), and rotation. There are six types of synovial joints. Some are relatively immobile but more stable than mobile joints.
What are synovial joints and their functions?
Synovial joints allow for movement. Where the bones meet to form a synovial joint, the bones' surfaces are covered with a thin layer of strong, smooth articular cartilage. A very thin layer of slippery, viscous joint fluid, called synovial fluid, separates and lubricates the two cartilage-covered bone surfaces.
What are the 5 parts of the synovial joint?
Synovial joints share important structural components: subchondral bone, hyaline cartilage, a joint cavity, synovial lining, articular capsule, and supporting ligaments.
What are synovial joints quizlet?
Synovial joints. those in which the articulating bones are separated by a fluid-containing joint cavity. This arrangement permits freedom of movement, and all synovial joints are freely movable diarthroses. Most joints fall into this class.
What are the 5 types of joints and give an example of each?
Immovable joints- Example: Bones of the skull box. Partially movable joints- Example: Joints between the ribs and breast bone.Gliding joint- Between the bones of the wrist.Hinge joint- Example: Present in the elbow.Pivot Joint- Example: Joint between axis vertebrae and atlas.More items...•
What are the 4 main types of joints?
What are the different types of joints?Ball-and-socket joints. Ball-and-socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, allow backward, forward, sideways, and rotating movements.Hinge joints. ... Pivot joints. ... Ellipsoidal joints.
What are the 4 classification of joints?
The structural classification divides joints into bony, fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints depending on the material composing the joint and the presence or absence of a cavity in the joint.
What are the 4 types of joints and examples?
What are the different types of joints?Ball-and-socket joints. Ball-and-socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, allow backward, forward, sideways, and rotating movements.Hinge joints. ... Pivot joints. ... Ellipsoidal joints.
What are the types of joints and explain?
There are three types of joints in the structural classification: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints. Fibrous joints are joints in which bones are joined by dense connective tissue that is rich in collagen fibers. These joints are also called sutures. The joints between bones of the cranium are fibrous joints.
What are the 4 classification of joints?
The structural classification divides joints into bony, fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints depending on the material composing the joint and the presence or absence of a cavity in the joint.
What are the different types of synovial joints quizlet?
ball-and-socket, condyloid, gliding, hinge, pivot, and saddle.
What is the function of the synovial joint?
All joints have different purposes. Fibrous joints provide strength and fuse two bones together. Cartilaginous joints provide structure and support...
What are the 6 characteristics of synovial joints?
Synovial joints must meet the following criteria: They must be where two or more bones meet and the bones must have cartilaginous ends They must...
Which joints are synovial joints?
All mobile (diarthrosis) joints are synovial joints. Synovial joints are classified by the fact that they are mobile when compared to fibrous joint...
What are the 6 types of synovial joints?
Synovial joints are described based on how they move and the anatomy of the joint. The six joint types are saddle, pivot, hinge, ball and socket, c...
What are the different types of synovial joints?
Different types of joints allow different types of movement. Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
What are saddle joints?
Saddle Joints. Saddle joints are so named because the ends of each bone resemble a saddle, with concave and convex portions that fit together. Saddle joints allow angular movements similar to condyloid joints but with a greater range of motion. An example of a saddle joint is the thumb joint, which can move back and forth and up and down, ...
What is a ball and socket joint?
Ball-and-socket joints possess a rounded, ball-like end of one bone fitting into a cuplike socket of another bone. This organization allows the greatest range of motion, as all movement types are possible in all directions. Examples of ball-and-socket joints are the shoulder and hip joints (Figure 7).
Where are planar joints found?
Planar joints are found in the carpal bones in the hand and the tarsal bones of the foot, as well as between vertebrae (Figure 2). Figure 2. The joints of the carpal bones in the wrist are examples of planar joints. (credit: modification of work by Brian C. Goss)
What is an example of a hinge joint?
Figure 3. The elbow joint, where the radius articulates with the humerus, is an example of a hinge joint. (credit: modification of work by Brian C. Goss)
What is hinge joint?
Hinge Joints. In hinge joints, the slightly rounded end of one bone fits into the slightly hollow end of the other bone. In this way, one bone moves while the other remains stationary, like the hinge of a door. The elbow is an example of a hinge joint. The knee is sometimes classified as a modified hinge joint (Figure 3).
What is the shape of a bone end?
A cylindrical bone end fits into a trough shaped surface on another bone to form a hinge joint. A round end of one bone fits into another bone's ring, surrounded by a ligament to form a pivot joint, as in the joint between the Atlas and Nexus axis.
What are some examples of plane joints?
So the plane joint permits gliding movement. The examples of plane joint are intercarpal joints, intertarsal joints, joints between articular processes of vertebrae.
Why are synovial joints called synovial joints?
They are called synovial joint because is filled with synovial fluid which acts as lubricants. It is also interesting to know that there are 6 types of synovial joints in our body. But our body also has numerous immovable joints which do not allow any movement. In this article, we are concerned about the movable joints / synovial joints, ...
How many types of synovial joints are there?
What are the types of synovial joints? There are a total of 7 types of synovial joints in the human body. These joints allow movement which is why it is also known as movable joints. Actually, the articulating surface of this type of joint is filled with a special lubricating fluid known as synovial fluid. This fluid provides lubrication ...
What are the two types of joints?
Types of joints in human body. Whenever two or more bones meet they form a joint. The human body has broadly two types of joint, one is immovable joint and another is movable joint.
Why is cartilage smooth?
Smooth cartilage allows friction-less movement and this smoothness is further enhanced by body lubricants. Our movable joints are also lubricated and filled with fluid known as synovial fluid and this is why we call this joint as synovial Joint.
Which synovial joint is the most movable?
The last on the list of types of synovial joints is the most movable of all the types. As the name suggests the ball and socket joint consists of a ball that fits into the socket a cup-shaped socket. The spherical ball fits into the cup-shaped socket and that’s why it allows movement in almost all direction. It gives great freedom of movement.
What is the purpose of immovable joints?
However, there are other joints whose purpose is to maintain the structure of the body parts by not allowing movement, they are fixed and do not take part in any kind of movement. These are immovable joints.
What is pivot joint?
The pivot joint, also known as rotary joint, allows for rotational movement. Pivot joints are indicated as joint letter A on our illustration. This type of joint can be found between your neck vertebrae. For instance, when you turn your head side-to-side, it's due to the rotary motion permissible in pivot joints.
How many types of synovial joints are there in the human body?
If you've ever heard of someone having hip replacement surgery, it's likely centered on repairing this joint. Lesson Summary. Our bodies contain six types of synovial joints. Synovial joints are the most movable type of joint found in the human body.
What is saddle joint?
Our thumb is a classic example of a saddle joint in action. Thumbs can move using a hinge-like motion but can also rock side to side. This is because of a saddle joint. In fact, it's the saddle joint that makes our thumbs opposable, a trait that allows us to firmly grasp objects with our hands.
What are the six types of synovial joints?
Synovial joints and the human body. As shown on this illustration, the six types of synovial joints include the pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints. These joints are found throughout the body; however, some locations serve as better examples than others.
Where are the saddle and plane joints located?
Saddle and plane joints are found in your hands. The saddle joint makes your thumb opposable, while the plane joints allow your small wrist bones to shift in relation to one another. Condyloid joints form the connection between your lower arm and wrist. Ball-and-sockets joints are located in your shoulders and hips.
Where are synovial joints found?
Joints are formed where bones come together. The six types of synovial joints are the pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints. Pivot joints are found in your neck vertebrae, while hinge joints are located in your elbows, fingers, and knees. Saddle and plane joints are found in your hands.
Where do condyloid joints form?
These joints form where the head of one or more bones fits in an elliptical cavity of another . You'll find this type of connection in your wrist where it connects the radius, or lower arm, and carpal, or wrist, bones.
What is the fluid that lubricates joints called?
All joints in the human body contain synovial fluid. Also called synovia, the fluid is very thick and lubricates the joint. This, in turn, allows for easier movement.
What is a fibrous capsule?
A fibrous joint capsule is a ligamentous sac surrounding the articular cavity of any freely moveable joint. It is attached to the bone and completely exposes the joint. A joint capsule is also composed of an inner synovial membrane and an outer fibrous membrane.
What is the synovial joint of the scapula?
This is a synovial joint that is formed by the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus. It is also called a humeral joint or a shoulder joint.
What is the ball and socket?
A type of synovial joint. Here, the spheroidal or rounded surface of one bone (the ball) moves within a depression that is cup-shaped (the socket) on another bone. This allows for great freedom of movement as compared to other types of joints. The ball-and-socket joint is also called the spheroidal or poly-axial joint.
What is a condyloid joint?
Condyloid joints have an irregular surface at the point where the bones move past one another. In essence, the joint is very similar to the two bowls nested together. A good example of a condyloid joint is the radio-carpal joint in the wrist.
Which joint is the most mobile?
Synovial joints are the most common and most mobile joints in mammals. Their freely moveable characteristic means they enable mammals to make large movements and they also provide stability in the body.
What type of joint is a synarthrosis?
This is a type of synarthrosis whereby the bones are united by cartilage, providing only a little flexible movement. There are two types of cartilaginous joints: the symphysis and the synchondrosis.
What is the purpose of synovial joints?
Synovial joints allow for smooth movements between the adjacent bones. The joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that defines a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage.
How does cartilage prevent friction?
Friction between the bones at a synovial joint is prevented by the presence of the articular cartilage, a thin layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the entire articulating surface of each bone. However, unlike at a cartilaginous joint, the articular cartilages of each bone are not continuous with each other. Instead, the articular cartilage acts like a Teflon ® coating over the bone surface, allowing the articulating bones to move smoothly against each other without damaging the underlying bone tissue. Lining the inner surface of the articular capsule is a thin synovial membrane. The cells of this membrane secrete synovial fluid (synovia = “a thick fluid”), a thick, slimy fluid that provides lubrication to further reduce friction between the bones of the joint. This fluid also provides nourishment to the articular cartilage, which does not contain blood vessels. The ability of the bones to move smoothly against each other within the joint cavity, and the freedom of joint movement this provides, means that each synovial joint is functionally classified as a diarthrosis.
What is the most common type of joint in the body?
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body ( [link] ). A key structural characteristic for a synovial joint that is not seen at fibrous or cartilaginous joints is the presence of a joint cavity. This fluid-filled space is the site at which the articulating surfaces of the bones contact each other.
What is the fluid filled space between the bones?
This fluid-filled space is the site at which the articulating surfaces of the bones contact each other. Also unlike fibrous or cartilaginous joints, the articulating bone surfaces at a synovial joint are not directly connected to each other with fibrous connective tissue or cartilage.
Why do my hips hurt so bad?
The most common cause of hip disability is osteoarthritis, a chronic disease in which the articular cartilage of the joint wears away, resulting in severe hip pain and stiffness.
How do ligaments help bones?
Outside of their articulating surfaces, the bones are connected together by ligaments, which are strong bands of fibrous connective tissue. These strengthen and support the joint by anchoring the bones together and preventing their separation. Ligaments allow for normal movements at a joint, but limit the range of these motions, thus preventing excessive or abnormal joint movements. Ligaments are classified based on their relationship to the fibrous articular capsule. An extrinsic ligament is located outside of the articular capsule, an intrinsic ligament is fused to or incorporated into the wall of the articular capsule, and an intracapsular ligament is located inside of the articular capsule.
Which joint allows the body to move?
The six types of synovial joints allow the body to move in a variety of ways. (a) Pivot joints allow for rotation around an axis, such as between the first and second cervical vertebrae, which allows for side-to-side rotation of the head. (b) The hinge joint of the elbow works like a door hinge.
Why are saddle joints called saddle joints?
Saddle joints are so named because the ends of each bone resemble a saddle, with concave and convex portions that fit together. Saddle joints allow angular movements similar to condyloid joints but with a greater range of motion. An example of a saddle joint is the thumb joint, which can move back and forth and up and down, but more freely than the wrist or fingers (see the figure below).
What is RA in the body?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the synovial joints of the hands, feet, and cervical spine. Affected joints become swollen, stiff, and painful. Although it is known that RA is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, the cause of RA remains unknown. Immune cells from the blood enter joints and the synovium causing cartilage breakdown, swelling, and inflammation of the joint lining. Breakdown of cartilage causes bones to rub against each other causing pain. RA is more common in women than men and the age of onset is usually 40–50 years of age.
How to diagnose RA?
Rheumatologists can diagnose RA on the basis of symptoms such as joint inflammation and pain, X-ray and MRI imaging, and blood tests. Arthrography is a type of medical imaging of joints that uses a contrast agent, such as a dye, that is opaque to X-rays. This allows the soft tissue structures of joints—such as cartilage, tendons, and ligaments—to be visualized. An arthrogram differs from a regular X-ray by showing the surface of soft tissues lining the joint in addition to joint bones. An arthrogram allows early degenerative changes in joint cartilage to be detected before bones become affected.
What is a ball and socket joint?
Ball-and-socket joints possess a rounded, ball-like end of one bone fitting into a cuplike socket of another bone. This organization allows the greatest range of motion, as all movement types are possible in all directions. Examples of ball-and-socket joints are the shoulder and hip joints (see the figure below).
How to treat RA?
There is currently no cure for RA; however, rheumatologists have a number of treatment options available. Early stages can be treated with rest of the affected joints by using a cane or by using joint splints that minimize inflammation. When inflammation has decreased, exercise can be used to strengthen the muscles that surround the joint and to maintain joint flexibility. If joint damage is more extensive, medications can be used to relieve pain and decrease inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin, topical pain relievers, and corticosteroid injections may be used. Surgery may be required in cases in which joint damage is severe.
What are the different types of synovial joints?
Different types of joints allow different types of movement. Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
What is an example of a hinge joint?
The elbow joint, where the radius articulates with the humerus, is an example of a hinge joint. (credit: modification of work by Brian C. Goss)
