
not present
| Disease | Gene/Defect | Inheritance | Clinical Features |
| Achondroplasia | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGR ... | Autosomal dominant (normal parents can ... | Short limbs relative to trunk, prominent ... |
| Cystic Fibrosis | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator ... | Autosomal Recessive (most common geneti ... | Pancreatic insufficiency due to fibrotic ... |
| Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | Dystrophin (DMD) - deletions | X-linked recessive | Gradual degeneration of skeletal muscle, ... |
| Hypercholesterolemia | LDL receptor (commonly) | Autosomal dominant (haploinsufficiency) ... | Impaired uptake of LDL, elevated levels ... |
What is the difference between dominant and recessive genes?
Jun 10, 2020 · A dominant gene means that a single allele can control whether the disease develops. If both parents are unaffected and they each pass on a defective gene causing their child to be affected, then the genetic disorder is autosomal recessive. The parents are called carriers. Click to see full answer.
What are some examples of dominant disorders?
A dominant allele produces a dominant phenotype in individuals who have one copy of the allele, which can come from just one parent. For a recessive allele to produce a recessive phenotype, the individual must have two copies, one from each parent. An individual with one dominant and one recessive allele for a gene will have the dominant phenotype.
Are your genes Recessive or dominant?
Dec 25, 2012 · There are two types of disorders based on the type of Gene. Dominant – Only one copy of the gene is enough to transfer the disorder. In Recessive – Two copies of the gene are required to transfer the disorder from parent to child.
What are 4 examples of recessive traits?
Dominant And Recessive. A dominant gene means that a single allele can control whether the disease develops. If only one parents (usually affected) passes on an autosomal, defective gene which results in the child having a genetic disorder, then the disorder is called autosomal dominant. A recessive gene means that there is enough normal protein product to function …
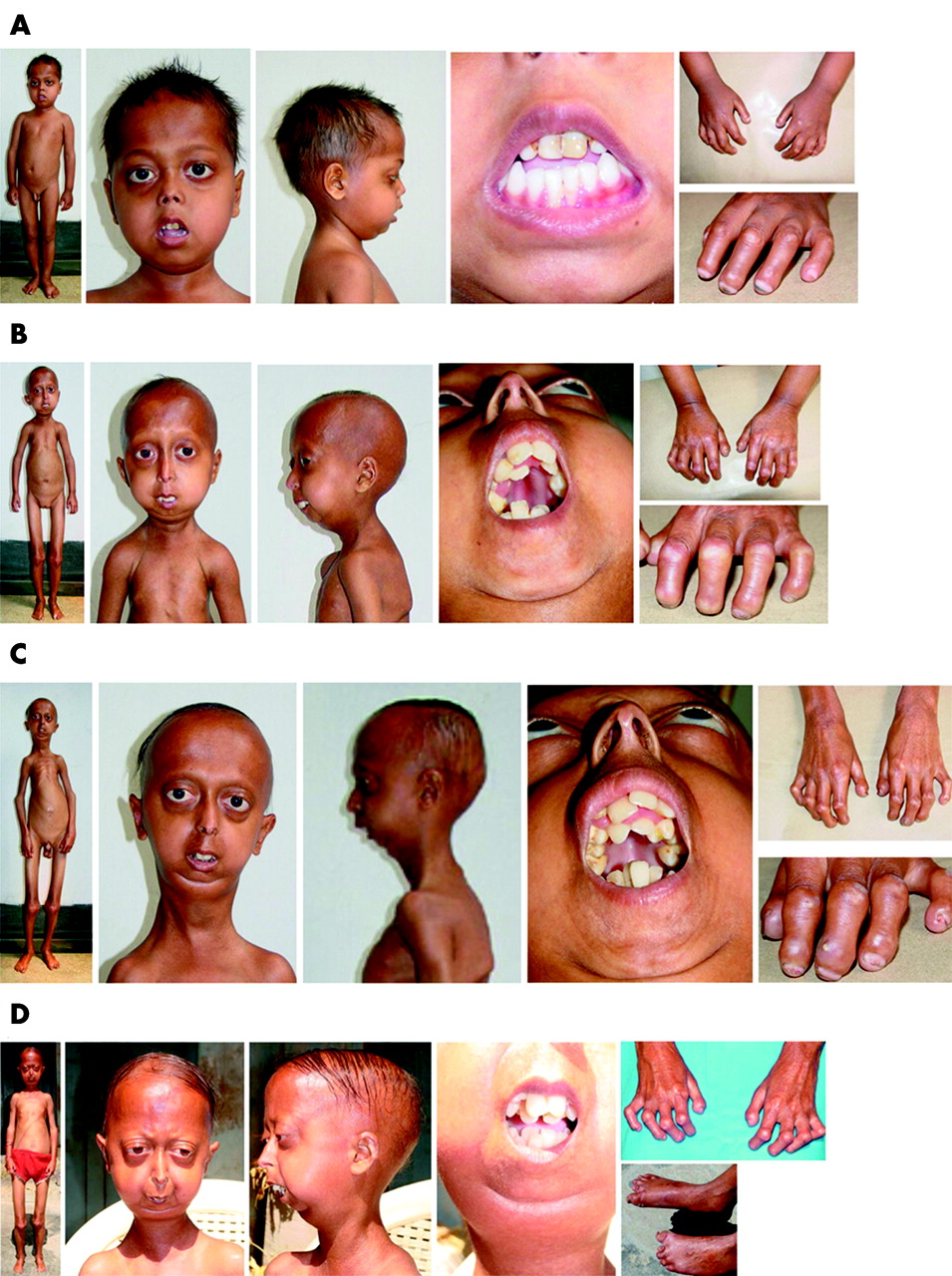
What are examples of dominant and recessive disorder?
What are the different ways a genetic condition can be inherited?Inheritance patternExamplesAutosomal dominantHuntington disease, Marfan syndromeAutosomal recessivecystic fibrosis, sickle cell diseaseX-linked dominantfragile X syndromeX-linked recessivehemophilia, Fabry disease4 more rows•Apr 19, 2021
What is a recessive disorder?
Print. To have an autosomal recessive disorder, you inherit two mutated genes, one from each parent. These disorders are usually passed on by two carriers. Their health is rarely affected, but they have one mutated gene (recessive gene) and one normal gene (dominant gene) for the condition.
What are the dominant disorders?
Huntington's disease and Marfan syndrome are two examples of autosomal dominant disorders. Mutations to BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes — which have been associated with breast cancer — also are transmitted in this pattern.
What is the difference between dominant and recessive inherited disorders?
Recessive genes are said to be inherited in either an autosomal recessive or X-linked pattern. If two copies of the abnormal gene are present, disease may develop. However, if only one abnormal gene is needed to produce a disease, it leads to a dominant hereditary disorder.Jan 28, 2020
What gene is dominant?
If the alleles of a gene are different, one allele will be expressed; it is the dominant gene. The effect of the other allele, called recessive, is masked.
What is an example of a recessive trait?
Examples of Recessive Traits For example, having a straight hairline is recessive, while having a widow's peak (a V-shaped hairline near the forehead) is dominant. Cleft chin, dimples, and freckles are similar examples; individuals with recessive alleles for a cleft chin, dimples, or freckles do not have these traits.Apr 28, 2017
What are three examples of diseases that are recessive?
Examples of autosomal recessive disorders include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease.
Why are some disorders dominant?
Dominant inheritance means an abnormal gene from one parent can cause disease. This happens even when the matching gene from the other parent is normal. The abnormal gene dominates. This disease can also occur as a new condition in a child when neither parent has the abnormal gene.Jan 28, 2020
Is sickle cell dominant or recessive?
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern , which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations.
What are dominant and recessive traits class 10?
Complete Answer: - Dominant refers to the relationship between two versions of a gene. If the alleles (two versions of each gene) of a gene are different, one allele will be expressed as Dominant gene while the other allele effect is called recessive.
How do you know if a trait is dominant or recessive?
For example, if a trait tends to be directly passed from parent to child, then the odds are pretty good that the trait is a dominant one. If a trait skips generations or pops up out of nowhere, then the odds are pretty good that it is recessive.Jun 3, 2010
Why are genes dominant or recessive?
Dominant and recessive genes. The most common interaction between alleles is a dominant/recessive relationship. An allele of a gene is said to be dominant when it effectively overrules the other (recessive) allele.
The terms are confusing and often misleading
Dominant and recessive inheritance are useful concepts when it comes to predicting the probability of an individual inheriting certain phenotypes, especially genetic disorders. But the terms can be confusing when it comes to understanding how a gene specifies a trait.
Inheritance patterns
Sickle-cell disease is an inherited condition that causes pain and damage to organs and muscles. Instead of having flattened, round red blood cells, people with the disease have stiff, sickle-shaped cells. The long, pointy blood cells get caught in capillaries, where they block blood flow.
Protein function
If we look at the proteins the two alleles code for, the picture becomes a little more clear. The affected protein is hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying molecule that fills red blood cells. The sickle-cell allele codes for a slightly modified version of the hemoglobin protein.
Dominant alleles are not better than recessive alleles
Mode of inheritance has nothing to do with whether an allele benefits an individual or not. Take rock pocket mice, where fur color is controlled mainly by a single gene. The gene codes for a protein that makes dark pigment. Some rock pocket mice have dark fur, and some have light fur.
What is the role of autosomal dominant and recessive disorders?
Autosomal dominant and recessive disorders play a major role in determining the transfer of disease from parents to children. These are also used to determine any Hereditary gene which can be passed on to children leading to passing on the disorder from parent to child.
What happens if a child has autosomal recessive disorder?
If the disorder is Autosomal recessive there should be transfer of both affected genes from both the parents to cause the disease. If gene from only one parent is transferred then the child becomes a carrier but does not get the disease.
How many copies of a gene are needed to transfer a disorder from parent to child?
There are two types of disorders based on the type of Gene. Dominant – Only one copy of the gene is enough to transfer the disorder. In Recessive – Two copies of the gene are required to transfer the disorder from parent to child.
What is the difference between a dominant and recessive gene?
Dominant And Recessive. A dominant gene means that a single allele can control whether the disease develops. If only one parents (usually affected) passes on an autosomal, defective gene which results in the child having a genetic disorder, then the disorder is called autosomal dominant. A recessive gene means that there is enough normal protein ...
What happens if a mother passes on a recessive X-linked gene?
If the mother passes on a recessive X-linked gene, then all her sons will be affected and all her daughters will be carriers. Understanding the mechanisms by which genetic disorders are inherited are very important for interpreting recurrence risks.
What is the genetic disorder of sickle cell anemia?
The parents are called carriers. For example, sickle-cell anemia is a recessive disorder characterized by abnormal hemoglobin production.
What is the genetic defect of sickle cell carriers?
The genetic defect involves a gene that produces hemoglobin. Although sickle-cell carriers produce, in part, abnormal hemoglobin, although they usually do not experience clinical manifestations since the normal hemoglobin produced from the normal gene is enough to function normally.
What is codominance in biology?
In codominance, both gene variants are expressed at the same time, representing a third phenotype. For example, a flower with alleles that can produce either white or red in the homozygote form will produce both colors in the heterozygote form expressed as spotted flowers.
Is a white phenotype recessive or dominant?
A white and a red phenotype are neither dominant nor recessive. If a flower is heterozygous and carries genes that produce both the white color and the red color, the flower color results in pink. Another variation is codominance. In incomplete dominance, the phenotype is a blending of the two different gene effects.
Can X-linked genetic disorders be inherited?
Like autosomal disorders, X-linked genetic diseases also can be inherited by dominant and recessive mechanisms. X-linked dominant means that if the father passes on the defective gene on his only X chromosome, all his offspring (which will be females) will be affected.
What is autosomal recessive disorder?
What are Autosomal Recessive Disorders? An autosomal recessive disorder is a genetic disorder in which two copies of an abnormal gene are responsible for the development of a disease. The recessive inheritance means both mutated copies of a gene must be abnormal (recessive) to cause the disease.
What is the difference between autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive?
The key difference between autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive disorders is that, in autosomal dominant disorders, one altered copy of a gene is enough to cause the disease while , in autosomal recessive disorders, both altered copies of the gene are needed to cause the disease.
What are some examples of autosomal dominant disorders?
The popular examples of autosomal dominant disorders are Huntington disease, tuberous sclerosis, Myotonic dystrophy and neurofibromatosis.
How many copies of the disease-associated mutation are needed to cause the disease in autosomal recessive disorder
A single copy of the disease-associated mutation is enough to cause the disease in autosomal dominant disorder. Two copies of the disease-associated mutation are needed to cause the disease in autosomal recessive disorder. Thus, this is the key difference between autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive disorders.
What is autosomal dominant condition?
Autosomal dominant conditions sometimes show reduced penetrance. It means although only one copy is needed to develop the disease, not all individuals who inherit the mutation will be affected by the disease. For example, in conditions such as tuberous sclerosis, people may be minimally affected.
How many copies of a gene do you need to be affected by a disorder?
A person needs only one mutated copy of the gene to be affected by this type of disorder. The affected person has a 50% chance of having an affected child with one mutated copy (dominant) of the gene. The same person also has a 50% chance of an unaffected child with two normal copies (recessive) of the gene. Each affected person usually has one ...
What is Dr. Samanthi Udayangani's degree?
Dr.Samanthi Udayangani holds a B.Sc. Degree in Plant Science, M.Sc. in Molecular and Applied Microbiology, and PhD in Applied Microbiology. Her research interests include Bio-fertilizers, Plant-Microbe Interactions, Molecular Microbiology, Soil Fungi, and Fungal Ecology.
Are most genetic disorders recessive or dominant?
Most genetic disorders that result in sterility or childhood death are caused by recessive mutations, DNA sequence variants that are harmless when a person carries only one copy.
Why are genetic diseases usually recessive?
Genes come in pairs. One gene in each pair comes from the mother, and the other gene comes from the father. Recessive inheritance means both genes in a pair must be abnormal to cause disease. People with only one defective gene in the pair are called carriers.
Is dominant or recessive more common?
Dominant traits are the most common traits in a population. When people hear the word “dominant”, often they incorrectly believe that the majority of the population expresses this trait. Describing a trait as dominant does not mean it is the most common; it means that it is expressed over the recessive trait.
Are single gene disorders recessive or dominant?
Single-gene diseases run in families and can be dominant or recessive, and autosomal or sex-linked. Pedigree analyses of large families with many affected members are very useful for determining the inheritance pattern of single-gene diseases. Table 1 includes some examples of single-gene diseases.
How is a recessive gene inherited?
Autosomal recessive inheritance is a way a genetic trait or condition can be passed down from parent to child. A genetic condition can occur when the child inherits one copy of a mutated (changed) gene from each parent. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive condition usually do not have the condition.
Are all genetic diseases recessive?
It is estimated that all people carry about 20 recessive genes that cause genetic diseases or conditions. Usually a person does not know they carry a recessive gene unless they have the disease in their family, or if they have had an affected child.
What is recessive genetic disorder?
To have an autosomal recessive disorder, you inherit two mutated genes, one from each parent. These disorders are usually passed on by two carriers. Their health is rarely affected, but they have one mutated gene (recessive gene) and one normal gene (dominant gene) for the condition.
What is a recessive allele?
Recessive alleles are the genes that do not show the trait. If a person has one copy of the brown eye allele (dominant) and one copy of the blue eye allele (recessive) then that person is considered to be a of the blue eye allele, since they would have brown eyes but still have the blue eye trait that is not shown.
What is the dominant allele?
Dominant alleles are seen as an uppercase of a letter; for example, B. Recessive alleles are seen as a lower case of a letter; b. In order for a person to show the dominant trait, one of the person’s parents must have the dominant trait (which is an uppercase letter). Remember that human cells carry 2 copies of each chromosome, ...
How many sets of alleles are dominant?
With that being said, there are 2 sets of alleles that can be dominant or recessive. If a person carries a. set of alleles (both uppercase and lower case letter of the gene) then the person will show the dominant trait (being that there is an uppercase letter present). For example, the brown eye allele is dominant, B.
What are some examples of different versions of a gene?
The coloring of the blue and brown eyes is an example of different versions of a gene. Different versions of a gene are called . Alleles can be considered dominant or recessive, with dominant being the trait that is observed or shown and recessive being the trait is not seen. Dominant alleles are seen as an uppercase of a letter; for example, ...
What is a sex-linked gene?
Sex-linked genes are genes that are inhererited through the X chromosome. Remember that a biological female carries 2 sets of X chromosomes (XX) and a biological male carries one set of the X and one set of Y chromosomes (XY). If the offspring is a boy, the X chromosome comes from the mother and the Y comes from the father.
What is it called when you have two copies of the alleles that are both dominant?
When you have two copies of the alleles that are both dominant, this is called. codominance. . For example, if the dominant trait is red for flowers and another dominant trait is white, then the flower will have both red and white as the dominant traits are expressed equally. If a person carries two copies of the brown eye allele, ...
Where does the X chromosome come from?
If the offspring is a boy, the X chromosome comes from the mother and the Y comes from the father. If the offspring is a girl, one of the X chromosomes comes from the mother and the other X chromosome comes from the father. In some genetic diseases that are caused by sex-linked genes, for example. haemophila.
