
| Stage | Psychosocial Crisis | Basic Virtue |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Trust vs. Mistrust | Hope |
| 2. | Autonomy vs. Shame | Will |
| 3. | Initiative vs. Guilt | Purpose |
| 4. | Industry vs. Inferiority | Competency |
What are the 8 stages of developments according to Erickson?
- Infancy – Basic trust versus mistrust
- Toddler – Autonomy versus shame and doubt
- Preschool-age – Initiative versus guilt
- School-age – Industry versus inferiority
- Adolescence – Identity versus identity confusion
- Young adulthood – Intimacy versus isolation
- Middle age – Generativity versus stagnation
- Older adulthood – Integrity versus despair
What are the 8 stages of Erik Erikson?
unresolution) of each stage forms the characteristics of individual personality and impacts the degree of resolution (or unresolution) of later stages. Erikson defined the following eight developmental stages: trust vs. mistrust, autonomy vs. shame and doubt, initiative vs. guilt, industry vs. inferiority, identity vs. identity
What are Erik Erickson's stages on psychosocial development?
Erikson's Eight Stages of Psychosocial Development
- Trust versus Mistrust.
- Autonomy versus Shame and Doubt.
- Initiative versus Guilt.
- Industry versus Inferiority.
- Identity versus Role Confusion.
- Intimacy versus Isolation.
- Generativity versus Stagnation.
- Integrity versus Despair.
What does Erikson mean by generativity vs stagnation?
Generativity vs Stagnation. Generativity vs Stagnation is stage 7 of Erikson’s 8 stages of personality development and it goes from about 35-55 years, making this the longest stage in the psychosocial theory of personality development, and the primary drive in this stage is procreativity. Erikson defines Generativity as the syntonic quality of adulthood and according to him it refers to “the generation of new beings as well as new products and new ideas”.
See more
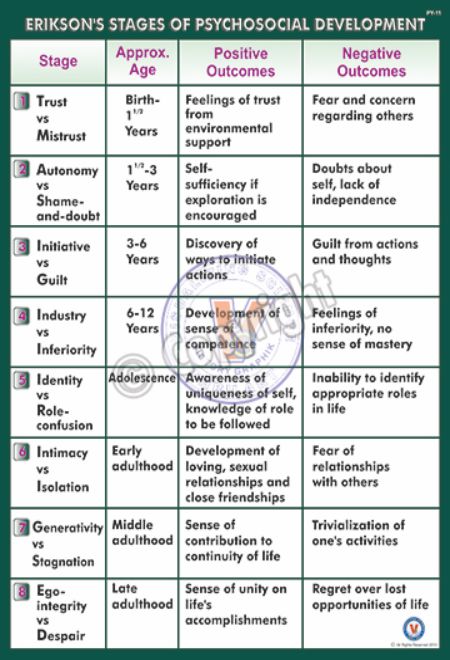
What are the 8 stages of life according to Erikson?
Understanding Erikson's 8 Stages of DevelopmentInfancy – Basic trust versus mistrust.Toddler – Autonomy versus shame and doubt.Preschool-age – Initiative versus guilt.School-age – Industry versus inferiority.Adolescence – Identity versus identity confusion.Young adulthood – Intimacy versus isolation.More items...•
What are the 8 stages of development How do they differ?
The eight stages of development are:Stage 1: Infancy: Trust vs. Mistrust.Stage 3: Preschool Years: Initiative vs. Guilt.Stage 4: Early School Years: Industry vs. Inferiority.Stage 6: Young Adulthood: Intimacy vs. ... Stage 7: Middle Adulthood: Generativity vs. ... Stage 8: Late Adulthood: Ego Integrity vs. ... References:
What are the 8 stages of Erikson's theory quizlet?
Terms in this set (8)Stage 1: Trust V. Mistrust. 1 is a bun. ... Stage 2: autonomy vs. shame and doubt. 1-2 years. ... Stage 3: initiative vs. Guilt. ... Stage 4: industry vs. Inferiority. ... Stage 5: Identity vs. role confusion. ... Stage 6: intimacy vs. isolation. ... Stage 7: generativity vs. stagnation. ... Stage 8: Ego integrity vs. Dispair.
Which of Erikson's eight stages seems most important why?
Erikson believed that the trust vs mistrust stage is the most important period in a person's life because it shapes one's view of the world.
What are the eight 8 stages of human development?
The key components of Erikson's model of human development include stage one, infancy, trust versus mistrust; stage two, toddlerhood, autonomy versus shame and doubt; stage three, preschool years, initiative versus guilt; stage four, early school years, industry versus inferiority; stage five, adolescence, identity ...
What was the main idea behind Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development?
What was the main idea behind Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development? An individual's personality develops throughout the lifespan.
What is the main emphasis of Erik Erikson's theory of development quizlet?
What is Erikson's theory emphasize? The importance of social relationship in human development.
What is Erikson's stage of psychosocial development in early childhood quizlet?
stage of Erikson's theory of psychosocial development takes place during early childhood and is focused on children developing a greater sense of personal control. At this point in development, children are just starting to gain a little bit of independence.
What are the different stages of development?
Developmentalists break the life span into nine stages as follows:Prenatal Development.Infancy and Toddlerhood.Early Childhood.Middle Childhood.Adolescence.Early Adulthood.Middle Adulthood.Late Adulthood.More items...
What are the different stages of human development?
IntroductionInfancy (neonate and up to one year age)Toddler ( one to five years of age)Childhood (three to eleven years old) - early childhood is from three to eight years old, and middle childhood is from nine to eleven years old.Adolescence or teenage (from 12 to 18 years old)Adulthood.
What are the stages of development of human being?
Human development is a predictable process that moves through the stages of infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood.
How are childhood and adolescence different stages?
Adolescence is the time in a young person's life when they transition from childhood into young adulthood and experience physical, behavioral, cognitive, emotional, and social developmental changes.
What is Erikson's theory of child development?
Erikson maintained that personality develops in a predetermined order through eight stages of psychosocial development, from infancy to adulthood....
What happens during trust vs mistrust?
Trust vs. mistrust is the first stage in Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development. During this stage, the infant is uncertain about the wo...
What is autonomy vs shame and doubt?
Autonomy versus shame and doubt is the second stage of Erik Erikson's stages of psychosocial development. This stage occurs between the ages of 18...
What is Initiative vs guilt?
Initiative versus guilt is the third stage of Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development. During the initiative versus guilt stage, children...
What is industry versus Inferiority?
Erikson's fourth psychosocial crisis, involving industry (competence) vs. Inferiority occurs during childhood between the ages of five and twelve....
What is identity vs role confusion?
The fifth stage of Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development is identity vs. role confusion, and it occurs during adolescence, from about 1...
What does intimacy vs isolation mean?
Intimacy versus isolation is the sixth stage of Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development. This stage takes place during young adulthood be...
What is generativity vs stagnation?
Generativity versus stagnation is the seventh of eight stages of Erik Erikson's theory of psychosocial development. This stage takes place during d...
What are Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development?
Erikson's eight stages of psychosocial development include trust vs. mistrust, autonomy vs. shame/doubt, initiative vs. guilt, industry vs. Inferio...
What is ego integrity vs despair?
Ego integrity versus despair is the eighth and final stage of Erik Erikson’s stage theory of psychosocial development. This stage begins at approxi...
What are Erikson's stages of development?
Erik Erikson was a German psychologist who theorized that there's a specific psychological struggle that takes place through the eight stages of a person's life. These struggles, he believed, contribute to your personality throughout your development..
What is the stage of development for young people?
If young people are overwhelmed by expectations and responsibilities at this stage, they may not be able to establish their identity. This leads to confusion about what their needs and goals are. Stage 6 — Young adulthood. At this stage, intimacy and isolation are the focus of development.
What does Erikson mean by "stages you don't master"?
Erikson suggested that these stages may overlap. A stage you don't master may extend into other stages later in life. If a toddler, for example, doesn’t overcome shame and self-doubt, these feelings will continue to impact their development as they move through other stages of childhood.
How many stages of psychosocial protective development are there?
Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science: “The Eight Stages of Psychosocial Protective Development: Developmental Psychology.”
What is the age of stage 7?
Stage 7 — Middle adulthood. The development in this stage is around generativity and stagnation or self-absorption. This stage begins at age 40 and lasts till age 65.
What is the final stage of the developmental process?
The final stage of the developmental process proposed by Erikson centers around ego integrity and despair. This stage begins at age 65 and lasts throughout the rest of your life. If you’re satisfied with your life, you age with grace.
What is the stage 4 of a child's life?
Stage 4 — Early school years. Here, development centers around industry and inferiority. This stage begins at age six and lasts till age 11. During this stage, your child's becoming aware of their individuality. They see accomplishments in school and sports and seek praise and support from those around them..
What is the purpose of each stage of Erikson's theory?
In each stage, Erikson believed people experience a conflict that serves as a turning point in development. 2
What did Erikson believe about personality development?
Much like Sigmund Freud, Erikson believed that personality developed in a series of stages. Unlike Freud's theory of psychosexual stages, however, Erikson's theory described the impact of social experience across the whole lifespan. Erikson was interested in how social interaction and relationships played a role in the development and growth ...
What did Erikson believe about the development of ego identity?
While Erikson believed that each stage of psychosocial development was important, he placed a particular emphasis on the development of ego identity. Ego identity is the conscious sense of self that we develop through social interaction and becomes a central focus during the identity versus confusion stage of psychosocial development.
What did Erikson believe about toilet training?
Erikson believed that learning to control one's bodily functions leads to a feeling of control and a sense of independence.
What did Erikson believe?
Erikson also believed that a sense of competence motivates behaviors and actions. Each stage in Erikson's theory is concerned with becoming competent in an area of life.
What is Erikson's view on conflict?
In Erikson's view, these conflicts are centered on either developing a psychological quality or failing to develop that quality. During these times, the potential for personal growth is high but so is the potential for failure.
How did Erikson's theory differ from many others?
Erikson's theory differed from many others because it addressed development throughout the entire lifespan, including old age. Older adults need to look back on life and feel a sense of fulfillment. Success at this stage leads to feelings of wisdom, while failure results in regret, bitterness, and despair.
What is Erikson's stage?
Studying Erikson’s stages serve as a basis of treatment for different recovery stages of mental illness. [8] For example, the initial stage of trust vs. mistrust parallels the mental illness recovery stage concerning the acceptance of the mental illness and trusting the idea of recovery.
What is the 9th stage of psychosocial development?
A ninth stage was added by Erik Erikson’s wife, Joan Erikson. It considers new challenges experienced with continued aging and incorporates aspects from all previous eight stages of psychosocial development.
What stage does ego identity crystallize?
As an example, the ego identity crystallizes in stage 5, during adolescence. The two opposing qualities are ego identity and confusion/diffusion. Those who develop ego identity yield the virtue of fidelity, while the inability to do so – ego confusion – creates a quality of repudiation.
Who developed the theory of psychosocial development?
Definition/Introduction. Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development is a theory introduced in the 1950s by the psychologist and psychoanalyst Erik Erikson. It built upon Freud’s theory of psychosexual development by drawing parallels in childhood stages while expanding it to include the influence of social dynamics as well as the extension ...
What is an example of engagement with the next generation?
Example: Engagement with the next generation through parenting, coaching, or teaching
What is Erikson's theory of psychosocial development?
The theory differs from many others in that it addresses development across the entire lifespan, from birth through death. 1. At each stage , the individual deals with a conflict that serves as a turning point in development.
What stage of psychosocial conflict occurs during middle adulthood?
Once adults enter the generativity versus stagnation stage that occurs during middle adulthood, the psychosocial conflict becomes centered on the need to create or nurture things that will outlast the individual. 5
What is the major criticism of psychosocial stage theory?
One major criticism of the psychosocial stage theory is that these stages do not necessarily follow a sequential order. People can experience these developmental changes and challenges at different points in their lives. 2
What stage of childhood is industry versus inferiority?
During middle childhood between the ages of about six and eleven, children enter the psychosocial stage known as industry versus inferiority. 1 As children engage in social interaction with friends and academic activities at school, they begin to develop a sense of pride and accomplishment in their work and abilities.
What is the intimacy versus isolation stage?
Dating, marriage, family, and friendships are important during the intimacy versus isolation stage, which lasts from approximately age 19 to 40. By successfully forming loving relationships with other people, individuals are able to experience love and enjoy intimacy.
What is the sixth stage of Erikson's theory?
In the sixth stage of Erikson’s psychosocial development theory, young adulthood takes place between the ages of 18 and 40. During this time, major conflict can arise as we attempt to form longer term commitments outside of our family, with varying degrees of success.
When does Erikson's third stage occur?
Erikson’s third stage of psychosocial development occurs during preschool, between the ages of three and five years. At this point in our psychosocial development – when conflict occurs between initiative and guilt – we learn to assert ourselves and typically begin to direct play and social interactions.
What is the fifth stage of psychosocial development?
According to Erikson (1963), the fifth stage of psychosocial development exists “ between the morality learned by the child, and the ethics to be developed by the adult. ”.
What is the first stage of Erikson's psychosocial model?
Stage 1: Trust Versus Mistrust. In the first stage of Erikson’s psychosocial model, infancy is crucial to our psychosocial development. During our initial 18 months, we are uncertain about the world in which we find ourselves and must develop basic trust.
What age is Erikson's psychosocial theory?
In stage four of Erikson’s psychosocial theory – ages 5 to 12 years – we are immersed in a world of education, learning to read, write, and solve math puzzles (Erikson, 1958, 1963).
What is Erikson's theory of development?
Erik Erikson’s (1958, 1963) psychosocial development theory proposes that our personality develops through eight stages, from infancy to old age. He argued that social experience was valuable throughout life, with each stage recognizable by the specific conflict we encounter between our psychological needs and the surrounding social environment.
How to develop your strengths?
We have many resources at PositivePsychology.com that will help you to explore personal development: 1 Learn to focus on your strengths rather than your weaknesses by Identifying Limiting Beliefs About Personal Strengths. 2 Recognize and grow the strengths required to protect your family using the Family Tree of Strengths worksheet. 3 Use the Exploring Character Strengths guide to identify and reflect on your character strengths. 4 20 Guidelines for Developing a Growth Mindset provides an excellent tool to perceive challenges as a way to grow.
How many developmental stages does Erikson describe?
According to Erikson, a person passes through eight developmental stages that build on each other. At each stage we face a crisis. By resolving the crisis, we develop psychological strengths or character traits that help us become confident and healthy people. Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development gives us a way to view the development ...
What did Erikson believe about the eight stages of psychosocial development?
So take these eight stages as the starting point you use to help your child develop the psychosocial skills they need to become a successful person, but don’t take them as law.
What is Erik Erikson's theory?
Erik Erikson is one name you might notice come up again and again in the parenting magazines you leaf through. Erikson was a developmental psychologist who specialized in child psychoanalysis and was best known for his theory of psychosocial development .
How do children develop their identity?
They form their identity by examining their beliefs, goals, and values.
What does it mean when a child succeeds?
When your child succeeds, they’ll feel industrious and believe they can set goals — and reach them. However, if children have repeated negative experiences at home or feel that society is too demanding, they may develop feelings of inferiority.
How does providing basic needs help a child?
By providing these basic needs, you teach them that they can depend on you. This builds within them the psycholog ical strength of trust. Feeling secure and safe, your infant will be ready to experience the world.
What happens if you don't complete the previous stages?
However, people who didn’t complete the previous stages may have feelings of loss and regret. If they see their lives as unproductive, they become dissatisfied and depressed. Interestingly, this last stage, according to Erikson, is one of flux. People often alternate between feelings of satisfaction and regret.
What is Erikson's theory?
His theory is widely taught in developmental psychology courses in the United States. Stage -based theories of development were popular during Erikson’s era. Yet there is one important difference between Erikson’s theory and other popular models of his time. In Erikson’s theory, a person does not have to successfully complete one stage ...
What is Erikson's theory of biographical case studies?
Erikson based much of his theory of biographical case studies. Seeing the stages play out in a case study can help people understand the concepts at work. Yet the details of Mahatma Gandhi’s development are difficult to apply on a broad scale.
Why is Erikson criticized?
Erikson is often criticized for supporting a limited view of human development . Critics argue Erikson focused too much on childhood, neglecting the development that occurs in adulthood. He admitted a person’s identity could change in adulthood after the adolescent stage.
What did Erikson agree with Freud?
Other critics take issue with his views on gender. Erikson agreed with Freud that personality differences between genders are rooted in biology. He claimed human development also differed by gender. Feminist theorists criticize Erikson for using the male experience as the default template for human development.
What does Erikson mean by isolation?
Isolation: According to Erikson, people who do not develop relationships may become socially isolated. They may develop long-term feelings of loneliness.
What is the main conflict in the infancy stage?
Each stage has a conflict between two opposing concepts. For instance, the infancy stage’s main conflict is trust vs. mistrust. Although people of all ages may experience issues with trust, the infancy stage is where the challenge is most potent.
How long does it take to become a young adult?
It has been defined as anywhere from 20-24 years to 20-40 years.
Who developed the stages of psychosocial development?
Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development is a theory introduced in the 1950s by the psychologist and psychoanalyst Erik Erikson.
What is Freud's theory of psychosexual development?
It built upon Freud’s theory of psychosexual development by drawing parallels in childhood stages while expanding it to include the influence of social dynamics as well as the extension of psychosocial development into adulthood.
