Are bisphosphonates really effective?
One class of agents used to treat osteoporosis is the bisphosphonates, which inhibit bone resorption, cause an increase in bone mineral density and reduce the risk of future fractures caused by aging, estrogen deficiency and corticosteroid use. Overall, bisphosphonates have been shown to have a strong safety and tolerability profile.
What medications are bisphosphonates?
What are bisphosphonates?
- ibandronate (Boniva)
- zoledronic acid (Reclast)
- etidronate (Didronel)
What are the uses of bisphosphonates?
- Bisphosphonates, one of the available therapeutic options for the management of osteoporosis, inhibit bone resorption with relatively few side effects. ...
- For the initial treatment of osteoporosis, we suggest oral bisphosphonates ( Grade 2B ). ...
- We suggest either alendronate or risedronate as the initial choice of bisphosphonate ( Grade 2B ). ...
When to start bisphosphonates?
Your doctor may prescribe a bisphosphonate if you:
- Have osteoporosis and have already had a broken bone (fracture). Bisphosphonates help to prevent any further bone fractures.
- Have a low bone density and your doctor thinks you are at risk of getting a bone fracture. ...
- Take long courses (more than three months) of steroids (corticosteroids) - for example, prednisolone tablets. ...

What are the most common bisphosphonates?
Bisphosphonates are usually the first choice for osteoporosis treatment. These include: Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill. Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill.
Which bisphosphonate is best for osteoporosis?
Oral – We suggest alendronate or risedronate as the initial choice of oral bisphosphonate (table 1). We most commonly use alendronate, in part due to direct evidence showing residual fracture benefit in selected patients after completing a five-year course of therapy [1].
What is considered a bisphosphonate?
Listen to pronunciation. (bis-FOS-foh-nayt) A drug or substance used to treat hypercalcemia (abnormally high blood calcium) and bone pain caused by some types of cancer. Forms of bisphosphonates are also used to treat osteoporosis and for bone imaging.
Who should avoid bisphosphonates?
Avoid oral bisphosphonates in patients with esophageal disorders such as achalasia, esophageal stricture, esophageal varices, Barrett's esophagus, inability to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes, history of bariatric surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass).
What is the safest osteoporosis drug 2021?
The guidelines recommend denosumab as an alternative to bisphosphonates for the initial treatment of osteoporosis if they cannot take bisphosphonates or are at high risk of osteoporotic fractures.
What is the fastest way to increase bone density?
Keep reading for tips on increasing bone density naturally.Weightlifting and strength training. ... Eating more vegetables. ... Consuming calcium throughout the day. ... Eating foods rich in vitamins D and K. ... Maintaining a healthy weight. ... Avoiding a low calorie diet. ... Eating more protein. ... Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids.More items...•
What are the two medications that may cause osteoporosis after long term use?
High doses or long-term use of medicines called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can raise the risk of bone loss. PPIs, such as esomeprazole, lansoprazole, and omeprazole, are used for GERD (acid reflux), peptic ulcer, or heartburn. However, getting enough calcium and vitamin D may be enough to lower the risk.
Why you should not take bisphosphonates?
The most common side effects of bisphosphonates are stomach irritation and heartburn, but these problems are often avoided by taking the medication correctly. Other common side effects include: Bone or joint pain, or generalized pain. Muscle cramps or aches.
What are the two main adverse effects of bisphosphonates?
General side effects of bisphosphonates and denosumabFever and flu-like symptoms. ... Low levels of calcium in your blood (hypocalcaemia) ... Bone and joint pain. ... Changes in bowel movements. ... Tiredness and low energy levels. ... Feeling sick. ... Changes to your kidneys. ... Irritation of the food pipe (oesophagus)More items...•
Are bisphosphonates worth the risk?
The higher your fracture risk, the more likely it is that bisphosphonates can help prevent a fracture. The lower your fracture risk, the less likely it is that these medicines can help prevent a fracture. If you have osteoporosis or you have had a fracture, taking bisphosphonates lowers your risk of a fracture.
What is the most common side effect of bisphosphonate?
Side effects for all the bisphosphonates (alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate and zoledronic acid) may include bone, joint or muscle pain. Side effects of the oral tablets may include nausea, difficulty swallowing, heartburn, irritation of the esophagus (tube connecting the throat to the stomach) and gastric ulcer.
What are the alternatives to bisphosphonates?
In recent years, the drug denosumab (Prolia) has emerged as an alternative to bisphosphonates for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Denosumab may be considered a first-line treatment for women with osteoporosis who are at high risk of fracture or in women who can't take bisphosphonates.
Which is better for osteoporosis Fosamax or Prolia?
The bottom line. Fosamax, Prolia, and Boniva are all effective osteoporosis treatments since each one can help lower your risk of fractures. Each also comes with its own risk of side effects.
What is the safest osteoporosis drug 2020?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Evenity (romosozumab-aqqg) to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at high risk of breaking a bone (fracture).
Which is safer Actonel or Fosamax?
The result: After a year of treatment, women taking Actonel had 43% fewer hip fractures and 18% fewer non-spine fractures than women taking Fosamax.
Which drug classification is the most widely used to treat osteoporosis?
The drugs most often used in the treatment of osteoporosis are in the class of bisphosphonates (formerly called diphosphonates).
What is bisphosphonate used for?
Bisphosphonates can be used to reduce the risk of hip and spine fractures in osteoporosis. They may also be used, at different doses, to treat Paget's disease of bone.
How long does bisphosphonate last?
Most specialists limit treatment with oral bisphosphonates to five years (or three years for intravenous zoledronate) to minimise the risks of rare, long-term side-effects. However, some people will need more lengthy treatment.
How to take a sulfate pill?
Take it on an empty stomach with a glass or two of plain tap water. Other drinks may prevent the drug being properly absorbed by the body.
Is bisphosphonate a good medicine?
Bisphosphonates are generally well tolerated. The risk of digestive problems with oral preparations is very much reduced if you carefully follow the instructions that come with your medicine.
Does alcohol interact with bisphosphonates?
Alcohol is unlikely to interact with bisphosphonates. However, heavy drinking is a risk factor for osteoporosis and for having falls so it's recommended that you drink alcohol only in moderation.
Can you take other medications with bisphosphonates?
It's usually fine to take other medicines alongside bisphosphonates, but check with your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new medications. There's no reason why you shouldn't have vaccinations while you're on bisphosphonates.
Can bisphosphonate cause heartburn?
Oral bisphosphonates tend to be poorly absorbed by the body and can cause irritation of the gullet (heartburn), so it's very important that you carefully follow the instructions for taking your medication: Take it on an empty stomach with a glass or two of plain tap water.
How do bisphosphonates work?
Bisphosphonates help prevent your bones from losing calcium and other minerals by slowing or stopping the natural processes that dissolve bone tissue. In doing this, they help your bones remain strong and intact. If you have already developed osteoporosis, these medications may slow the thinning of your bones and help prevent bone fractures (broken bones). In fact, studies have shown that alendronate (Fosamax) and risedronate (Actonel) can lower your risk of fractured vertebrae—bone segments that make up your spine—by 50%. Similar studies demonstrate that these medications can lower the chance of breaking other bones by 30-49%.
What are the usual doses of bisphosphonates, and what should I remember while taking these medications?
Most bisphosphonates are taken anywhere from once a week to once a month. All of these medications come in tablet form except for zoledronic acid (Reclast), which is given intravenously (IV) once per year. Both women and men may take bisphosphonates.
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Bisphosponates such as risedronate (Actonel), alendronate (Fosamax), ibandronate (Boniva), zoledronic acid (Reclast), and pamidronate (Aredia) are used to treat and prevent osteoporosis—or, bone thinning—which occurs when the bones lose calcium and other minerals that help keep them strong and compact. This condition can lead to fractures, bone ...
Why is bisphosphonate used in a drug?
Because a bisphosphonate group mimics the structure of pyrophosphate, it can inhibit activation of enzymes that utilize pyrophosphate. The specificity of bisphosphonate-based drugs comes from the two phosphonate groups (and possibly a hydroxyl at R 1) that work together to coordinate calcium ions.
What is the backbone of bisphosphonate?
All bisphosphonate drugs share a common phosphorus-carbon-phosphorus "backbone": The two PO. 3 ( phosphonate) groups covalently linked to carbon determine both the name "bis phospho nate" and the function of the drugs. Bis refers to the fact that there are two such groups in the molecule.
What is the best bisphosphonate for osteoporosis?
In osteoporosis and Paget's, the most popular first-line bisphosphonate drugs are alendronate and risedronate. If these are ineffective or if the person develops digestive tract problems, intravenous pamidronate may be used. Strontium ranelate or teriparatide are used for refractory disease.
How long does bisphosphonate stay in your system?
After five years of medications by mouth or three years of intravenous medication among those at low risk, bisphosphonate treatment can be stopped. In those at higher risk ten years of medication by mouth or six years of intravenous treatment may be used.
What is the specificity of bisphosphonate?
The specificity of bisphosphonate-based drugs comes from the two phosphonate groups (and possibly a hydroxyl at R 1) that work together to coordinate calcium ions. Bisphosphonate molecules preferentially bind to calcium ions. The largest store of calcium in the human body is in bones, so bisphosphonates accumulate to a high concentration only in bones.
How long does bisphosphonate treatment last?
Long-term treatment with bisphosphonates produces anti-fracture and bone mineral density effects that persist for 3–5 years after an initial 3–5 years of treatment.
How does bisphosphonate affect bone?
Bisphosphonates inhibit the digestion of bone by encouraging osteoclasts to undergo apoptosis, or cell death, thereby slowing bone loss. The uses of bisphosphonates include the prevention and treatment ...
What is the purpose of bisphosphonates?
These drugs are used to treat several conditions associated with bone loss. Bisphosphonates are a group of drugs used to help prevent and treat bone loss. They're prescribed for people with osteopenia (softening of the bones), osteoporosis (brittle and easily broken bones), Paget's disease, and certain bone cancers.
What are the side effects of bisphosphonates?
The most common side effects of bisphosphonates are stomach irritation and heartburn, but these problems are often avoided by taking the medication correctly. Other common side effects include: Bone or joint pain, or generalized pain. Muscle cramps or aches. Nausea, constipation, diarrhea, or other stomach discomfort.
How long do you have to stay upright after taking bisphosphonate?
Have low levels of calcium in your bloodstream. To avoid irritation to your stomach and food pipe, you must remain in an upright position for at least 30 minutes after taking a bisphosphonate by mouth. Boniva requires you to remain upright for 1 hour.
When to take bisphosphonate?
Except for Altevia, all pill forms of bisphosphonates should be taken on an empty stomach before eating breakfast — generally 30 minutes beforehand. Take Boniva on an empty stomach 1 hour before eating; Altevia should be taken after meals.
Can you drink water with bisphosphonates?
Bisphosphonates should be taken with a full glass of water only — no juice, coffee, soda, or flavored beverages.
Can you take bisphosphonates if you are allergic to them?
Warnings and Precautions. Don't take bisphosphonates if you: Are allergic to them. Have disorders of the food pipe (esophagus), including tears, holes, narrowing, or difficulty swallowing. Have severe kidney disease. Can't sit in an upright position for at least 30 minutes. Have low levels of calcium in your bloodstream.
Cancer involving the bone
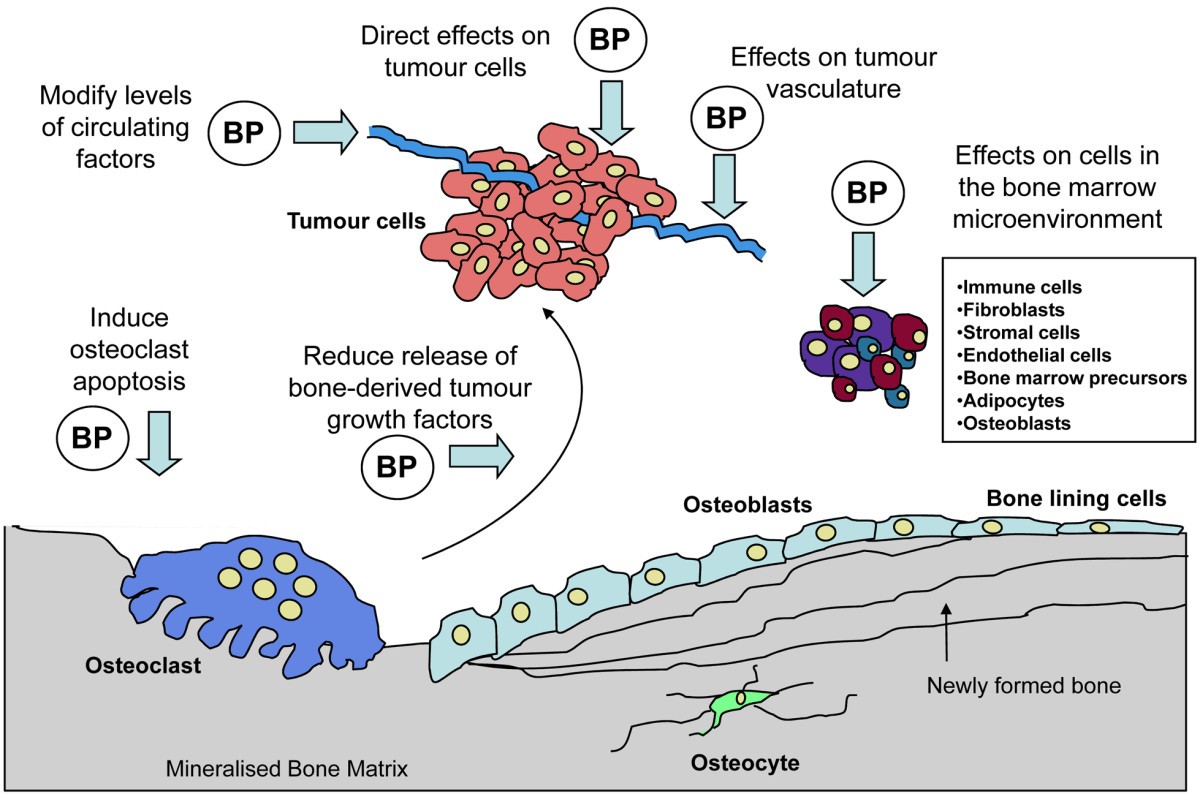
Bisphosphonates are very effective in the treatment of secondary cancer, cancer that has spread to the bones from elsewhere in the body. Cancer affecting the bones usually leads to increased bone destruction and high levels of blood calcium. The bones become fragile and prone to fracture, even on minor trauma.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that renders the bones brittle, fragile and prone to breakage. Osteoporosis is one of the more recent indications for bisphosphonate therapy. Etidronate was the first bisphosphonate approved to treat the condition, followed by alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate and zoledronate.
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Bisphosphonates may also be useful in “brittle bone” disorder or osteogenesis imperfecta. Palmidronate, in particular, has proved to be an effective treatment for this condition.
What is a bisphosphonate?
Bisphosphonate drugs are a class of medications that help prevent bone loss in osteoporosis and other conditions that can weaken the skeleton.
What are the side effects of bisphosphonate?
Rare side effects of bisphosphonate drugs include: 1 Osteonecrosis of the jaw 2 Slight increased risk of cancer of the esophagus 3 Painful, partial or complete fractures in the upper, outer region of the thigh bone (femur) below the hip (extremely rare)#N#Risk is increased with extended use or concomitant steroid treatment or in patients who have diabetes
How long does bisphosphonate last?
Because the medication lasts in the bones for some time after you stop taking it, your doctor might recommend stopping bisphosphonates after three to five years — especially if your overall risk of fracture is low. Your bone density, your age, your history of fractures and other factors determine your risk.
How long should I take bisphosphonates for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates, the most common type of osteoporosis medications, are typically taken for three to five years.
How long do you have to wait to stop taking bisphosphonates?
To reduce the risk of these rare complications, your doctor may recommend that you temporarily stop taking bisphosphonates after 3 to 5 years. This is sometimes called a bisphosphonate holiday. People who have severe osteoporosis may need to wait for 10 years before they stop taking these drugs.
What are the most common sites for osteoporosis fractures?
These drugs help strengthen bones and prevent fractures. The most common sites for osteoporosis fractures are the wrist, hip and spine. A broken hip can result in a severe decline in quality of life and even increases the risk of death.
What are the medications that are used for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates include alendronate (Binosto, Fosamax), ibandronate (Boniva), risedronate (Actonel, Atelvia) and zoledronic acid (Reclast, Zometa).
Can bisphosphonate cause a fracture?
Long-term bisphosphonate therapy has been linked to a rare type of thigh fracture. This injury, known as atypical femoral fracture, is similar to a stress fracture, causing pain that begins subtly and can gradually worsen. If not identified early on, a complete fracture of the thighbone can occur.
What are the side effects of bisphosphonates?
Side effects for all the bisphosphonates (alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate and zoledronic acid) may include bone, joint or muscle pain. Side effects of the oral tablets may include nausea, difficulty swallowing, heartburn, irritation of the esophagus (tube connecting the throat to the stomach) and gastric ulcer.
Can you take bisphosphonates with kidney failure?
All bisphosphonates can affect how the kidneys work and should not be taken by patients who have poor kidney function or kidney failure. Certain blood tests will be done to check your kidney function before starting these medicines.
Can you stop taking bisphosphonate?
Patients taking the oral bisphosphonate tablets should stop taking the drug and contact their healthcare provider immediately if experiencing chest pain, new or worsening heartburn, or difficult or painful swallowing. It is important for patients to report these or other side effects to their healthcare provider.
Can bisphosphonate help with osteonecrosis?
There have been rare reports of osteonecrosis of the jaw with bisphosphonate medicines. Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) occurs when the jaw bone is exposed and begins to starve from a lack of blood. Most cases of ONJ happen after a dental extraction and is associated with cancer treatments (including radiation), infection, steroid use, or potent antiresorptive medications. While ONJ is associated with these conditions, it also can occur without any identifiable risk factors. The risk of ONJ increases with treatment periods longer than 5 years and is estimated to be between 1 in 10,000 and 1 in 100,000 people on osteoporosis treatment each year. Most patients with ONJ who are taking antiresorptive therapy for osteoporosis can be healed with conservative treatment and often do not require surgery. You may wish to have a dental checkup before starting a bisphosphonate medicine. Good oral hygiene and regular dental care is the best way to lower the risk of ONJ.

Overview
Medical uses
Bisphosphonates are used to treat osteoporosis, osteitis deformans (Paget's disease of the bone), bone metastasis (with or without hypercalcemia), multiple myeloma, and other conditions involving fragile, breakable bone.
In osteoporosis and Paget's, the most popular first-line bisphosphonate drugs are alendronate and risedronate. If these are ineffective or if the person develops digestive tract problems, intravenous
Adverse effects
Oral bisphosphonates can cause upset stomach and inflammation and erosions of the esophagus, which is the main problem of oral N-containing preparations, that is ones containing "normal" unbranched chains. This can be prevented by remaining seated upright for 30 to 60 minutes after taking the medication. Intravenous bisphosphonates can give fever and flu-like symptoms after the first infusion, which is thought to occur because of their potential to activate human γδ T cells.
Chemistry and classes
All bisphosphonate drugs share a common phosphorus-carbon-phosphorus "backbone":
The two PO 3 (phosphonate) groups covalently linked to carbon determine both the name "bisphosphonate" and the function of the drugs. Bis refers to the fact that there are two such groups in the molecule.
The long side-chain (R in the diagram) determines the chemical properties, the mode of action an…
Pharmacokinetics
Of the bisphosphonate that is resorbed (from oral preparation) or infused (for intravenous drugs), about 50% is excreted unchanged by the kidney. The remainder has a very high affinity for bone tissue, and is rapidly adsorbed onto the bone surface. Once bisphosphonates are in bone, they have a very long elimination half-life that can exceed ten years.
Mechanism of action
Bisphosphonates are structurally similar to pyrophosphate, but with a central carbon that can have up to two substituents (R and R ) instead of an oxygen atom. Because a bisphosphonate group mimics the structure of pyrophosphate, it can inhibit activation of enzymes that utilize pyrophosphate.
The specificity of bisphosphonate-based drugs comes from the two phosphon…
History
Bisphosphonates were developed in the 19th century but were first investigated in the 1960s for use in disorders of bone metabolism. Their non-medical use was to soften water in irrigation systems used in orange groves. The initial rationale for their use in humans was their potential in preventing the dissolution of hydroxylapatite, the principal bone mineral, thus arresting bone loss. In the 1990s their actual mechanism of action was demonstrated with the initial launch of alendr…
External links
• International Myeloma Foundation article on bisphosphonates