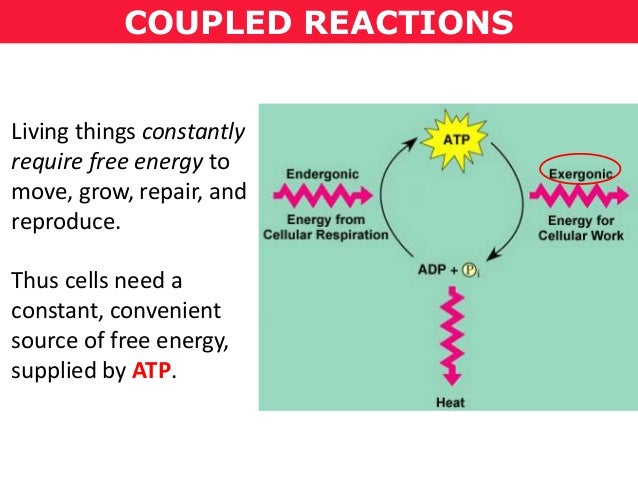
Here are some more examples of exergonic and endergonic reactions: Exergonictic: voila! – spontaneous release of gas from a can of paint Energonictic: heaving a weight – requires energy (usually exerted by muscle) to move Exergonic reactions are always good for releasing energy, while endergonic reactions need the energy to happen.
What is the difference between endothermic and endergonic?
Endergonic and endothermic are both related to heat that is absorbed. The difference is that endothermic is the relative change in enthalpy whereas endergonic is the relative change in free energy of the system.
What is one example of an endothermic reaction?
One of the best examples of an endothermic reaction is the chemical process of dissolving table salt in water. If you pour salt into a bowl or container of water, the salt will automatically dissolve on its own. This chemical process will lower the temperature of the water in the container, consuming some of the energy from the water.
Do endergonic reactions absorb more energy than they release?
Exergonic vs. Endergonic reactions: exergonic release more energy than they absorb. Endergonic reactions absorb more energy than they release.Exergonic reactions release energy while endergonic reactions absorb energy. What are endergonic reactions?
Is an endergonic reaction spontaneous or not?
Endergonic reactions are not spontaneous. Examples of endergonic reactions include endothermic reactions, such as photosynthesis and the melting of ice into liquid water. If the temperature of the surroundings decreases, the reaction is endothermic. An exergonic reaction may be called a spontaneous reaction or a favorable reaction.

What are the examples of endergonic reaction?
An endergonic reaction is one that requires free energy to proceed. An example of an endergonic reaction of biological interest is photosynthesis. Photosynthetic organisms conduct this reaction by using solar photons to drive the reduction of carbon dioxide to glucose and the oxidation of water to oxygen.
What is an example of exergonic reaction?
Exergonic reactions occur spontaneously (no outside energy is required to start them). Examples of exergonic reactions include exothermic reactions, such as mixing sodium and chlorine to make table salt, combustion, and chemiluminescence (light is the energy that is released).
What are endergonic and exergonic reactions in biology?
Complete answer: An exergonic reaction is a type of spontaneous reaction where there is 'release ' of free, here free energy is negative (less than zero). On the contrary, endergonic reactions are the reactions where energy enters the system, the free energy here is positive (greater than 0).
What are exergonic reactions?
An exergonic reaction (such as cellular respiration) is a reaction that releases free energy in the process of the reaction. The progress of the reaction is shown by the line. Activation energy (1) slows down the reaction.
Is photosynthesis an example of exergonic reaction?
Photosynthesis is an endergonic (energy-consuming) process. Cellular respiration is an exergonic (energy-releasing) process.
Is digestion exergonic or endergonic?
All digestive reactions are hydrolytic reactions. They are exergonic processes that do not require energy but release it.
Is muscle contraction endergonic or exergonic?
Muscle contraction (an endergonic reaction) is powered by the exergonic breakdown of ATP. usable energy. ATP breakdown is coupled with muscle contraction. Electron carriers also transport energy within cells.
How do you know if a reaction is endergonic or exergonic?
In an exergonic reaction, energy is released to the surroundings. The bonds being formed are stronger than the bonds being broken. In an endergonic reaction, energy is absorbed from the surroundings. The bonds being formed are weaker than the bonds being broken.
Which type of reaction is always exergonic?
catabolic reactionsThe process is an exergonic process in which the energy is released due to the breaking of the bonds of the larger complex molecules. Thus, catabolic reactions are always exergonic reactions.
Is a light stick always exergonic?
Glow sticks give off light but not heat. Because energy is released, the glow stick reaction is an example of an exergonic (energy-releasing) reaction. However, it is not an exothermic (heat-releasing) reaction because heat isn't released. You can think of exothermic reactions as a type of exergonic reaction.
What are endergonic and exergonic reactions quizlet?
exergonic reaction. a spontaneous chemical reaction, in which there is a net release of free energy. endergonic reaction. a non-spontaneous chemical reaction, in which free energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Why is photosynthesis an endergonic reaction?
This diagram shows that photosynthesis is an endergonic reaction because it takes in energy. Carbon for making carbon compounds (such as sugar) comes from the atmosphere. Plants make carbon-based molecules from raw inorganic compounds. Plants use the organic carbon compounds as “food” and to build cell parts.
Which type of reaction is always exergonic?
catabolic reactionsThe process is an exergonic process in which the energy is released due to the breaking of the bonds of the larger complex molecules. Thus, catabolic reactions are always exergonic reactions.
Which is an exergonic process?
An exergonic process is one which there is a positive flow of energy from the system to the surroundings. This is in contrast with an endergonic process. Constant pressure, constant temperature reactions are exergonic if and only if the Gibbs free energy change is negative (∆G < 0).
What is an exergonic reaction quizlet?
exergonic reaction. a spontaneous chemical reaction, in which there is a net release of free energy.
Is a light stick always exergonic?
Glow sticks give off light but not heat. Because energy is released, the glow stick reaction is an example of an exergonic (energy-releasing) reaction. However, it is not an exothermic (heat-releasing) reaction because heat isn't released. You can think of exothermic reactions as a type of exergonic reaction.
What is an endergonic and exergonic reaction?
She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Endergonic and exergonic are two types of chemical reactions, or processes, in thermochemistry or physical chemistry. The names describe what happens to energy during the reaction.
What type of reaction absorbs energy from its surroundings?
Endergonic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings.
What is the term for the reaction that releases more light and heat than it took to start a fire?
For example, it takes energy to start a fire, but once combustion starts, the reaction releases more light and heat than it took to get it started. Endergonic reactions and exergonic reactions are sometimes called reversible reactions.
How to absorb heat from an endothermic reaction?
Endothermic reactions offer good examples, as they absorb heat. Mix together baking soda (sodium carbonate) and citric acid in water. The liquid will get cold, but not cold enough to cause frostbite.
What happens when the temperature of the surroundings decreases?
If the temperature of the surroundings decreases, the reaction is endothermic.
Is rust an exergonic reaction?
You cannot tell how quickly a reaction will occur based on whether it is endergonic or exergonic. Catalysts may be needed to cause the reaction to proceed at an observable rate. For example, rust formation (oxidation of iron) is an exergonic and exothermic reaction, yet it proceeds so slowly it's difficult to notice the release of heat to the environment.
Is endergonic entropy positive?
The change in the standard Gibbs Free Energy (G) of an endergonic reaction is positive (greater than 0). The change in entropy (S) decreases. Endergonic reactions are not spontaneous. Examples of endergonic reactions include endothermic reactions, such as photosynthesis and the melting of ice into liquid water.
Why do exergonic reactions occur spontaneously?from biologydictionary.net
Because this type of reaction releases energy rather than consuming it, it can occur spontaneously , without being forced by outside factors. In chemistry terms, exergonic reactions are reactions where the change in free energy is negative. Free energy measures the total amount of energy available in a system; negative changes mean ...
How do exergonic reactions release energy?from study.com
Exergonic reactions are chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat. Typically, this energy is released when bonds are broken.
What chemical reaction releases energy?from study.com
chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat. Catabolic. in humans, molecules are being broken down into smaller components. Free energy. energy available to do work. Gibbs free energy. another term for free energy. Spontaneous reaction. bonds that contain energy will break easily to release heat.
What do gasoline, sugar, and lipids have in common?from study.com
Do you know what gasoline, sugar, and lipids have in common? Each of these chemicals provides energy for various systems. Whether it's powering a car for driving or powering animal systems for living, these chemicals, and many others, store energy in their bonds that can be used once released. In order to release this energy, these chemicals must undergo exergonic reactions.
What is catabolic reaction?from study.com
More specifically, in humans, these reactions are called catabolic, which means that the molecules are being broken down into smaller components. By breaking these bonds, systems (such as the human body or the car example above) can receive the energy need to perform their functions. 3:02.
What are the chemical bonds in living things?from biologydictionary.net
For living things, the chemical bonds in molecules such as sugars, proteins, and fats can be used as energy storage. This can be seen in metabolism, where sugars, proteins, and fats are created by consuming energy from photosynthesis or cellular respiration.
Can organisms harness energy from glucose?from biologydictionary.net
Less efficient organisms may only be able to harness enough energy from the breaking of glucose’s bonds to produce a few molecules of ATP – but this is still sufficient to sustain life!
What are some examples of endergonic processes?
These include (a) a compost pile decomposing, (b) a chick hatching from a fertilized egg, (c) sand art being destroyed, and (d) a ball rolling down a hill. (credit a: modification of work by Natalie Maynor; credit b: modification of work by USDA; credit c: modification of work by “Athlex”/Flickr; credit d: modification of work by Harry Malsch)
Which chemical reactions release energy?
Exergonic reactions release energy; endergonic reactions require energy to proceed. Image credit: OpenStax Biology. The same is true for the chemical reactions involved in cell metabolism, such as the breaking down and building up of proteins into and from individual amino acids, respectively.
What happens to reactants in a closed system?
Reactants within a closed system will undergo chemical reactions in both directions until a state of equilibrium is reached. This state of equilibrium is one of the lowest possible free energy and a state of maximal entropy. Energy must be put into the system to push the reactants and products away from a state of equilibrium.
What is the energy storing reaction?
Thus, we can think of the products of these reactions as energy-storing molecules. These chemical reactions are what we refer to as endergonic reactions , and they are non-spontaneous. An endergonic reaction will not take place on its own without the addition of free energy.
Why are chemical reactions called spontaneous reactions?
These reactions are also referred to as spontaneous reactions, because they can occur without the addition of energy into the system. Understanding which chemical reactions are spontaneous and release free energy is extremely useful for biologists, because these reactions can be harnessed to perform work inside the cell.
What does negative G mean in chemistry?
In other words, reactions that release energy have a ∆G < 0. A negative ∆G also means that the products of the reaction have less free energy than the reactants , because they gave off some free energy during the reaction.
Why are chemical reactions always moving towards equilibrium?
In a living cell, chemical reactions are constantly moving towards equilibrium, but never reach it. This is because a living cell is an open system. Materials pass in and out, the cell recycles the products of certain chemical reactions into other reactions, and chemical equilibrium is never reached. In this way, living organisms are in ...
What Are Endergonic Reactions?from study.com
Chemical reactions are occurring all around you and inside you. Even as you watch this lesson your stomach is using acid to break down food molecules for digestion; and outside your window, trees and flowers are undergoing photosynthesis, the process plants use to convert sunlight into usable energy. All chemical reactions involve energy.
What is the most common example of how living things move energy?from biologydictionary.net
Protein synthesis is a more typical example of how living things move energy, and add it to reactions to allow new chemical bonds to form.
Is fatty acid anabolism endergonic?from biologydictionary.net
So is fatty acid anabolism, in which the energy from food is stored in fat molecules. In general, reactions that involve creating new chemical bonds are endergonic. The chemical bonds “store” the reaction energy until they are broken, at which point some of the energy that was put into the initial reaction is released.
Is a reaction spontaneous?from study.com
These reactions are not spontaneous. They require work or an input of force - often in the form of energy - to get started. Sometimes the initial energy required to get the reaction started is all the energy that is required, while other times the reaction continues to absorb energy throughout the entire process.
Is catabolism exergonic or anabolic?from biologydictionary.net
In general, “catabolic” reactions are exergonic and involve breaking down larger units into smaller ones, while “anabolic” reactions are endergonic and involve synthesizing smaller units to form larger units.
Gibbs Free Energy
Countless reactions are taking place in the small space inside our cells. Catabolism, which is the breakdown of molecules, and anabolism, which is the synthesis of molecules, are continuously taking place inside the cells. Both of these processes revolve around energy.
What is an Endergonic Reaction?
As explained previously, some reactions take place spontaneously, while some reactions require energy from another source to proceed ahead. Such reactions of the latter type that absorb energy to proceed ahead are known as endergonic reactions. The term " en dergonic" means " energy inward ," meaning energy is entering the system.
Examples of Endergonic Reactions
There are ample examples of endergonic reactions, such as the ones that follow.
Why do exergonic reactions occur spontaneously?
Because this type of reaction releases energy rather than consuming it, it can occur spontaneously , without being forced by outside factors. In chemistry terms, exergonic reactions are reactions where the change in free energy is negative. Free energy measures the total amount of energy available in a system; negative changes mean ...
How does exergonic energy move?
This is done by breaking the chemical bonds in the sugar or fat, and passing its energy in the form of electrons or another currency to a new molecule.
What is the process of putting energy into chemical bonds?
In these constructive reactions where complex molecules are created, the organism uses energy harvested from photosynthesis or cellular respiration and puts that energy into chemical bonds. These creative parts of metabolism are called “ anabolism .”.
How do enzymes work in exergonic reactions?
The enzymes work by bringing the substrate molecule (such as a fat or sugar to be metabolized) into an ideal arrangement for the reaction to begin. This lowers the activation energy of the ...
What is the process of converting sugar into ATP?
Glycolysis is the first process used by prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike to turn energy stored in sugar into ATP. For eukaryotes, glycolysis is only the first step in a process that leads to cellular respiration; for prokaryotes, glycolysis may be the only means they have of obtaining ATP from glucose.
What are the chemical bonds in living things?
For living things, the chemical bonds in molecules such as sugars, proteins, and fats can be used as energy storage. This can be seen in metabolism, where sugars, proteins, and fats are created by consuming energy from photosynthesis or cellular respiration.
Can organisms harness energy from glucose?
Less efficient organisms may only be able to harness enough energy from the breaking of glucose’s bonds to produce a few molecules of ATP – but this is still sufficient to sustain life!