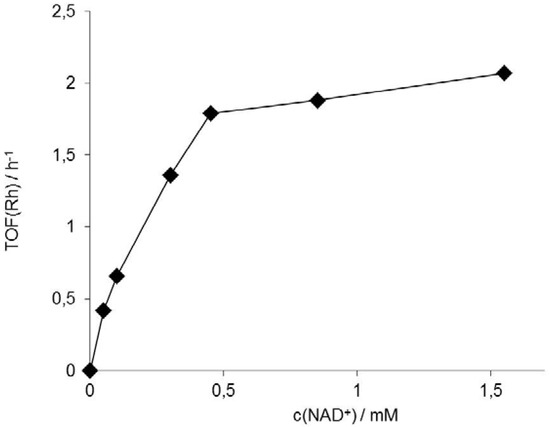
NAD + and FAD are two coenzymes that are required for the catalytic reactions occuring during metabolic reactions. These coenzymes function as electron carriers to the electron transport chain, which ultimately releases energy for ATP Adenosine triphosphate is a complex organic chemical that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of i…Adenosine triphosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a cofactor found in all living cells. The compound is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. Nicotina…
What are NAD+ and FAD and what is their function?
What are NAD+ and FAD and what is their function? the reduced form of NAD+. Has 1 proton and 2 electrons, THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH... YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE... Cell Energy--Photosynthesis and Cellular Respirati…
What is the function of FADH2 and NADH in respiration?
Functions. FADH2 and NADH are created from FAD and NAD+ through reduction-oxidation reactions in the Krebs cycle during respiration as seen below: This cycle gives off small amounts of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, and produces these compounds, FADH2 and NADH. The Krebs cycle is like a wheel.
What is the role of FADH2 in redox reactions?
These redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions play a crucial role in energy generation. Similar to NADH, FADH2 is the reduced form of FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), a co-enzyme. This oxidized form FAD, accepts two electrons and two hydrogen atoms to form FADH2.
What are NAD+ and NADP+ and how are they related?
-NAD+ (NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE) -NADP+ (NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE OHOSPHATE). -The MOST important ELECTRON CARRIERS are NAD+ and a closely related molecule NADP+. How do ELECTRON CARRIERS NAD+ and NADP+ carry energy?
See more
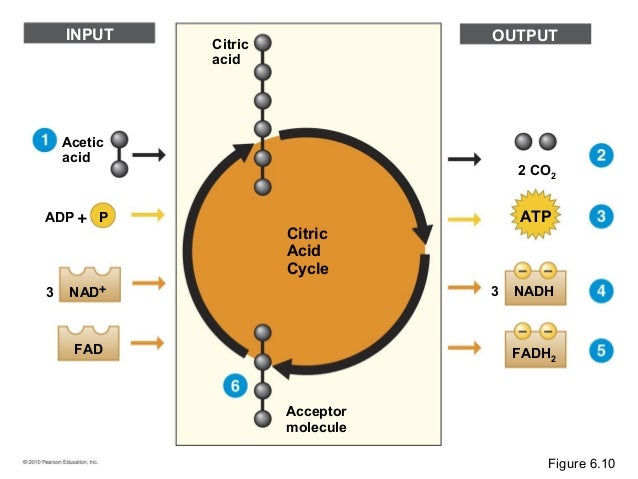
What are NADH and FADH2 in terms of their function?
NADH: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain. FADH2: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain.
What is NADH and what is its function?
NADH stands for "nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) + hydrogen (H)." It occurs naturally in the body and plays a role in generating energy. The NADH produced by the body is involved in making energy in the body. Taking NADH supplements might affect blood pressure and have other effects.
What is the function of NAD NADH FAD and FADH?
NADH and FADH2 that act as electron carriers give away their electrons to the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain refers to a group of chemical reactions in which electrons from high energy molecules like NADH and FADH2 are shifted to low energy molecules (energy acceptors) such as oxygen.
What is the function of FAD and FADH2?
An important mechanism in cellular respiration is the transfer of energy to the molecule flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) to convert it to FADH2 This is a process of reduction which stores the energy in high electron states in the FADH2.
What is FAD in biology?
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a cofactor for cytochrome-b5 reductase, the enzyme that maintains hemoglobin in its functional reduced state, and for glutathione reductase, an enzyme that also protects erythrocytes from oxidative damage.
Where is FAD used?
Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase uses FAD to transfer reducing equivalents to NAD. It also serves in the processes like nucleotide biosynthesis, beta-oxidation of fatty acids, amino acid catabolism, as well as the synthesis of other cofactors such as CoA, CoQ, and heme groups.
What is the function of NADH and FADH2 quizlet?
What is the purpose of NADH and FADH2 in Cellular Respiration? They are used to make ATP in the electron transport chain.
What is the difference between NADH and FAD?
The main difference between NADH and FADH2 is that every NADH molecule produces 3 ATP molecules during oxidative phosphorylation whereas every FADH2 molecule produces 2 ATP molecules. Furthermore, NADH transfers electrons to Cytochrome complex I while FADH2 transfers electrons to Cytochrome complex II.
What is the role of NADH Nadph and FADH2?
Basically, the NADH and FADH2 molecules are affixed with electrons and are transferred to the inner membrane of the mitochondria. They travel down the electron transport chain, releasing the electrons that they once had. The end result is loads of energy, approximately 34 ATP (energy molecule).
What is the difference between NADH and FADH2?
➢ The main difference between NADH and FADH2 is that every NADH molecule produces 3 ATP molecules during oxidative phosphorylation whereas every FADH2 molecule produces 2 ATP molecules. FADH2 transfers electrons to Cytochrome complex II. Krebs cycle.
What is FAD and why is it important?
Fads come fast and fade away A fad is any form of behavior that is intensely followed by a population for a short period of time. The behavior will rise relatively quickly and fall relatively quickly once the perception of novelty is gone. There are some great fads out there!
How are NADH and FADH2 related?
Answer and Explanation: NADH and FADH2 are both high-energy electron carriers used in cellular respiration to deliver electrons to the electron transport chain. The difference between the two is the amount of ATP that can be produced from the elctrons they carry.
What is meant by NADH?
Definition. Abbreviation for the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Supplement.
Is NADH the same as Vitamin B3?
NADH is one of the active forms of Vitamin B3. Many people have heard of NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) which is the oxidized form of NADH because it's been associated with an increased lifespan. But most people don't realize that it's the reduced form – NADH – that is most likely to be deficient in people.
What is the function of the coenzyme NADH?
NADH functions as an energy-rich electron transfer coenzyme, which generates almost three ATPs for every NADH to NAD+ oxidation event, whereas NAD+ functions as a sink for electrons.
What is the importance of NADH in metabolism?
The role of NADH in metabolism is to act as an electron carrier, shuttling electrons from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to the electron transport chain.
What is the function of NADH and FADH2?
Function of NADH and FADH2. NADH and FADH in our body plays a crucial role in cellular energy production. The food that is consumed cannot be directly used as a source of energy. Metabolism that involves a series of chemical reactions, help to convert energy from food into energy that can be easily used by our body.
What is NADH in biology?
Get in touch with us and we'll talk... Let's Work Together! NADH is the reduced version of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( NAD), which is essentially a co-enzyme form of niacin (vitamin B3) , present in all living cells. The enzyme is present in all livings organisms including plants. NAD +, the oxidized version of niacin, ...
What is FADH2?
Similar to NADH, FADH2 is the reduced form of FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), a co-enzyme. This oxidized form FAD, accepts two electrons and two hydrogen atoms to form FADH2. These conversions also assist in cellular energy production.
Did You Know?
Every cell has a mitochondrion―the energy factory of the cell. However, the brain cells may contain more than one mitochondrion, since they are involved in lot of processing and require more energy to perform multiple tasks.
Why is the ratio of NADP+ to NADPH kept low?
In contrast, the ratio of NADP+ to NADPH is kept LOW to ensure that there is plenty of NADPH to act as a REDUCING agent in ANABOLIC PATHWAYS.
Which group transfers to CoA?
3. C2 group transferred to CoA: forms acetyl CoA (makes the two carbons much reactive; occurs on E2)