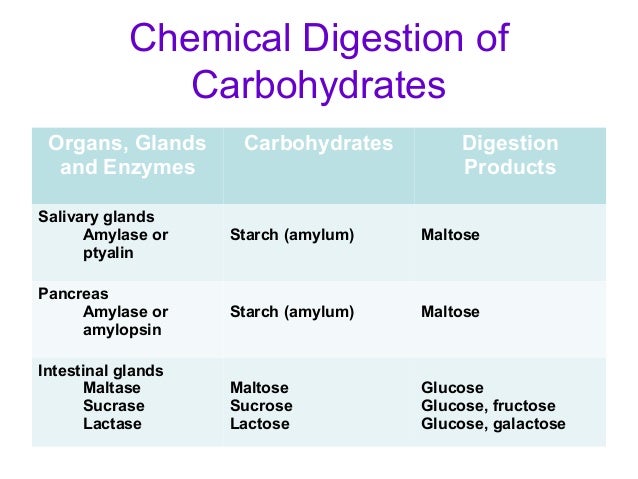
Length of Fatty Acids
- Fatty acids with aliphatic chains of five or lesser carbons are called short-chain fatty acids (SCFA). Example: butyric acid
- Fatty acids with aliphatic chains of 6 to 12 carbons are called medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA). Example: capric acid
- Fatty acids with aliphatic chains of 13 to 21 carbons are called long-chain fatty acids (LCFA). Example: oleic acid
What foods contain fatty acid?
Trans-fatty acids are manufactured fats that prevent products from melting at room temperature. They can be found in variety of food products such as margarine, cooking oil, baked goods like cakes, cookies, fried foods like French fries, doughnuts, fried chicken, among others.
What are the different types fatty acids?
Where are they found?
- Saturated fats. Saturated fat is found mostly in foods from animals and some plants.Saturated fats are usually solid at room temperature.
- Foods from animals. ...
- Foods from plants. ...
- Polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. ...
- Polyunsaturated fats. ...
- Monounsaturated fats. ...
What types of essential fatty acids are there?
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is the most common omega-3 fatty acid in your diet. ...
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) Your body uses eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to produce signaling molecules called eicosanoids, which play numerous physiological roles and reduce inflammation ( 9 ). ...
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)
How many different types of fatty acids are there?
What are the 3 main types or categories of fatty acids? There are three types of fatty acids: saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated. The basic difference between each of these is the number of carbon atoms with or without two hydrogen atoms bonded to them.
What are fatty acids?
Sources of fatty acids include fruits, vegetable oils, seeds, nuts, animal fats, and fish oils. Essential fatty acids, such as omega-3 fatty acids, serve important cellular functions.
What are fatty acids give two examples Class 11?
1 Answer. Fatty acids are compounds which has a carboxyl group attached to an R group. The R group could be a methyl (- CH3), or ethyl (- C2Hs) or higher number of – CH2 groups (1 carbon to 19 carbons). Eg; Palmitic acid, Arachidonic acid.
What are three examples of fatty acids?
There are three main types of fatty acids: saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated. All fatty acids are chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms.
What is fatty acid and its types?
Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides. Long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 13 to 21 carbons. Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 22 or more carbons.
What is fatty acid formula?
Fatty acids are organic compounds that have the general formula CH3(CH2)nCOOH, where n usually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an even number. There are two types of fatty acids: saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids.
What are fatty acids function?
Function of Fatty Acids. Fatty acids have important roles in: 1) signal-transduction pathways; 2) cellular fuel sources; 3) the composition of hormones and lipids; 4) the modification of proteins; and 5) energy storage within adipose tissue (specialized fat cells) in the form of triacylglycerols.
What are 2 types of fatty acids?
There are two types of fatty acids: saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids. Both types consist mainly of simple chains of carbon atoms bonded to one another and to hydrogen atoms. The two types of fatty acids differ in how many hydrogen atoms they contain.
What are example of fats?
Some examples of foods that contain fats are butter, oil, nuts, meat, fish, and some dairy products.
How many fatty acids are there?
More than 300 different fatty acids are known, many with unusual fatty acids with chain lengths from 8-C to > 22-C, and some with an unusual number of double bonds and oxidations or epoxidations.
How are fatty acids named?
Fatty acids can be named in many ways. symbolic name: given as x:y Δ a,b,c where x is the number of C's in the chain, y is the number of double bonds, and a, b, and c are the positions of the start of the double bonds counting from C1 - the carboxyl C. Saturated fatty acids contain no C-C double bonds.
What are essential fatty acids Class 11?
What are essential fatty acids ? Fatty acids which are not synthesized by the body but are important and have to be taken as a part of the diet. There are three essential fatty acids e.g. linoleic acid, linolenic acid and arachidonic acid. These are essential for growth and good health.
What is fatty acid class 10th?
What are fatty acids? Carboxylic acids containing long chain of carbon atoms are fatty acids. They are used as mild acids in foods, cold drinks, drugs, perfumes and are chief constituents of washing soaps.
What is meant by fatty acids write two important uses of it in human body shaala?
Following are the uses of fatty acids: Progesterone, estrogen, testosterone and aldosterone are hormones produced from fatty acids. Phospholipids are molecules formed from fatty acids. They form the basic structure of the cell membrane and are essential for the functional ability of a cell.
What are the components of fatty acids?
Introduction to Fatty Acid. Fatty acids in plants, animals, and microorganisms make the essential components of lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells). A fatty acid generally consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the chain length and at one end of the chain and at the other end ...
What are fatty acids used for?
They are used not only in the manufacture of various food products, for instance, but also in soaps, detergents, and cosmetics. Soaps are fatty acid salts of sodium and potassium.
What is Omega 3 fat?
They are a class of fatty acids found in fish oils that reduce cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoproteins) levels in the blood, especially in salmon and other cold-water fish. (The "bad" cholesterol is LDL cholesterol.)
What are the most commonly distributed fatty acids?
The 16- and 18-carbon fatty acids, better known as palmitic acid and stearic acid, are among the most commonly distributed fatty acids. In the lipids of most species, both palmitic and stearic acids exist. Palmitic acid makes up as much as 30 percent of body fat in animals. It accounts for between 5 and 50 percent of the lipids in vegetable fats, ...
Why are fatty acids essential?
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that must be consumed by humans and other animals because they are required by the body for good health but can not be synthesized. Fatty acids needed for biological processes are referred to by the term "essential fatty acid" but do not include fats that only serve as fuel.
How are fatty acids classified?
In many ways, fatty acids are classified: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by the content of even vs odd carbon, and by linear vs branched.
What are soaps made of?
Soaps are fatty acid salts of sodium and potassium. Some skincare items contain fatty acids, which can help keep the look and function of the skin healthy. Fatty acids are also commonly marketed as dietary supplements, particularly omega-3 fatty acids.
What are fatty acids?
Fatty Acids Definition. Fatty acids are comprised of hydrocarbon chains terminating with carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids and their associated derivatives are the primary components of lipids. The length and degree of saturation of the hydrocarbon chain is highly variable between each fatty acid, and dictates the associated physical properties ...
What are the functions of fatty acids?
Function of Fatty Acids. Fatty acids have important roles in: 1) signal-transduction pathways; 2) cellular fuel sources; 3) the composition of hormones and lipids; 4) the modification of proteins; and 5) energy storage within adipose tissue (specialized fat cells) in the form of triacylglycerols.
How are fatty acids used as energy?
When used as an energy source, fatty acids are released from triacylglycerol and processed into two-carbon molecules identical to those formed during the breakdown of glucose; moreover, the two-carbon molecules generated from the breakdown of both fatty acids and glucose are used to generate energy via the same pathways.
How do fatty acids affect the liver?
In particular, these fatty acids increase the uptake of circulating LDL by the liver, and reduce leukocyte activation and platelet reactivity, lymphocyte proliferation, and blood pressure .
How do fatty acids get into the body?
The metabolism of fatty acids involves the uptake of free fatty acids by cells via fatty acid-binding proteins which transport the fatty acids intracellularly from the plasma membrane. The free fatty acids are then activated via acyl-CoA and transported to: 1) the mitochondria or peroxisomes to be converted into ATP and heat as a form of energy; 2) facilitate gene expression via binding to transcription factors; or 3) the endoplasmic reticulum for esterification into various classes of lipids that can be used as energy storage.
Why are fatty acids important?
When stored in this form, fatty acids are important sources of thermal and electrical insulation, as well as protection against mechanical compression. Fatty acids are the preferred form of energy storage over glucose because they produce approximately six times the amount of usable energy. Storage in the form of triacylglycerol molecules consists ...
What are some examples of biological signaling pathways?
Following the dietary intake of polyunsaturated lipids, the products of lipid peroxidation can function as the precursors of powerful signaling mediators. Some examples of such signaling include eicosanoid production, the peroxidation of LDL, ...
What are the different types of fatty acids?
On a molecular level, fatty acids are long chains of carbon atoms with some hydrogen atoms attached. Small differences in structure make a big difference in how fatty acids behave. There are four types of fatty acids: 1 Saturated: The carbon chains of saturated fats have no open spots on their chain for hydrogen atoms. That is why they are called saturated. They raise LDL cholesterol (the "bad" cholesterol) and increase the risk of heart disease 2 Monounsaturated : These fatty acids are missing one of their hydrogen atoms due to one double bond between carbon molecules. Sometimes called MUFAs, monounsaturated fats are healthier than saturated fats. 3 Polyunsaturated: These fatty acids are missing more than one of their hydrogen atoms. Sometimes called PUFAs, these fatty acids have significant health benefits. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids belong to this group. 4 Trans fats : This type of fat is rare in nature but has been widely used in processed foods. Trans fats are created by adding hydrogen molecules to unsaturated fats to make them shelf-stable. Trans fats are generally unhealthy, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates their use in food products.
Why do we need fatty acids?
Why You Need Fatty Acids. Foods With Fatty Acids. Fat is made up of building blocks called fatty acids. This is true of both the fat in food and the fat in our bodies. When you eat a food containing fat, your body breaks it into fatty acids. On a molecular level, fatty acids are long chains of carbon atoms with some hydrogen atoms attached.
Why are omega 3s and omega 6s considered essential fatty acids?
The omega-3s and omega-6s are especially important. They are known as essential fatty acids because the body cannot manufacture them. They must be consumed in food.
What are the benefits of fatty acids?
The benefits of fatty acids are found mainly in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats: Heart Health. One of the best things you can do for your heart is to replace saturated fats in your diet with unsaturated fats. Healthier fats reduce your cholesterol levels and cut your risk of heart attack and stroke.
What is the best source of Omega 3?
Fatty fish is one of the best sources of omega-3s. Older adults who eat a lot of fish show less cognitive decline than those who eat a diet high in saturated fats. Healthy Pregnancies. Pregnant women need a good supply of omega-3s to ensure normal development of their babies.
Why are Omega 3 and Omega 6 important?
Omega-3s and omega-6s are both necessary for skin health. They keep skin elastic and reduce the effect of UV rays on the skin. They also help the skin function as a barrier, keeping moisture in and irritants out. A deficiency of omega fatty acids may cause various skin conditions.
What is the purpose of trans fats?
Trans fats are created by adding hydrogen molecules to unsaturated fats to make them shelf-stable. Trans fats are generally unhealthy, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates their use in food products.
What are fatty acids?
Fatty Acids Definition in Biology :� These are acids occurring in natural triglycerides and are monocarboxylic acids. Fatty acids are composed of long hydrocarbon chains terminated by carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids are basically the primary derivative of lipids.� Chain length from 4 to usually 24C atoms. They contain even number of C atoms majority of fatty acids are those containing 16 and 18 C atoms.� Fatty Acid Structure Described Below.
What are the physical properties of fatty acids?
Physical Properties of Fatty Acid: Saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature. Unsaturated fatty acids are liquid at room temperature. The long chain length of fatty acid has a high melting point than short-chain fatty acids. The solubility of fatty acids decrease due to increase in no. of the methylene group.
What is the bond between fatty acids?
Unsaturated Fatty acids Definitions: These fatty acid have the Double C-C bond. Unsaturated fatty acids are LIQUID at room temperature. If one double bond present in fatty acid it is called Monosaturated or Monoenoic fatty acids. If more than one double bond present in fatty acid it is called� Polysaturated or Polyenoic fatty acid.
Why does butter smell rancid?
This rancidity is due to the slow hydrolysis of fats. In case of fats like Butter results in the liberation of short chain fatty acids. Which have odor and taste? Hydrolysis of fats may be hastened by Bacterial contaminants which produce enzyme lipase. Rancidity also results in a loss of certain essential dietary constituents such as vitamins A and E, Carotenes and linoleic acid.
What is the name of the alkane that is used to decompose fats?
By boiling with strong alkanes such as NaOH, the fats are readily decomposed into Glycerol and salts of constituent fatty acids (Soap).
Which fats have the ability to add halogens?
Neutral fats containing unsaturated fatty acid s have the ability to add halogens. The degree of halogenation is an index of the unsaturated fatty acid content of fats.
How to hydrolyze fats?
This can be accomplished by heating fats with water at high temperature and pressure. The hydrolysis of ingested fats is efficiently accomplished by enzyme Lipase present in pancreatic juice.
What is the most common type of fatty acid found in animal fats?
Stearic Acid. You’re most likely to find stearic acid in animal fats such as meats, lard and butter. It has 18 carbon atoms and is known to lower LDL cholesterol more than other fatty acids. Systematic Name: octadecanoic acid.
What is the numeric name of fatty acids?
Each fatty acid has a numeric name that represents the number of carbon atoms within the saturated fatty acid chain. Here are examples of saturated fats with their common name, systematic name, numeric name (or lipid number), and foods in which they are found.
How are trans fats produced?
Trans fats are not found naturally in foods; instead, they are produced by adding hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils. Trans fats almost always raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol, making them unhealthier than even the richest saturated fat.
Why is saturated fat called saturated fat?
They are called "saturated" because there are no double bonds between the fatty acid chain and the carbon atoms, meaning the carbon atoms are fully filled or saturated with hydrogen atoms (unlike “unsaturated fats”). Keep reading for examples ...
What is the smallest medium chain fatty acid?
One of the smallest medium-chain fatty acids is caproic acid. Caproic acid is found in plant and animal oils and waxes, various aged cheeses and wine grapes.
Why is proprionic acid used in food?
Proprionic acid is often used as a food preservative because it inhibits mold and bacteria growth. However, this short-chain saturated fatty acid is also found in dairy and soy products.
What is butyric acid?
Butyric Acid. Butyric acid is a short-chain fatty acid, which is a fatty acid that contains fewer than six carbon atoms. It’s made in your gut when fiber breaks down and helps with the digestive process. Small amounts of butyric acid are also found in dairy products, such as butter, milk and parmesan cheese, as well as goat’s and sheep’s milk.
What Are Essential Fatty Acids?
Essential fatty acids are required for the body to perform vital health functions. They play important roles in the body’s immune response, metabolism, heart health, and cognitive function.
Which fatty acids are not produced independently?
The most important fatty acids are linoleic acids (omega-6) and alpha-linolenic acids (omega-3), which the body can not produce independently.
How to get more Omega 3?
Eating fatty fish is one of the most common ways to add a high amount of omega-3 to your diet (as long as you’re not vegetarian). Again, these are not the only sources of omega-3, just popular choices.
What is the ratio between omega 6 and omega 3?
In the U.S., the ratio between omega-6 and omega-3 is closer to 16:1 (omega-6:omega-3).
Why is it important to include essential fatty acids in your diet?
Essential fatty acid foods are vital to include in your diet since the body can not synthesize in the body. You’ve probably heard of omega-3 before
What is the most fatty fish?
1. Salmon . Salmon is probably the most fatty fish source for omega-3 containing approximately 2,260 mg in 3.5 ounces. It is also an incredibly nutrient-dense food. Salmon has a high amount of protein, vitamin D, vitamin B, and selenium. 2.
What is Omega 3?
Omega-3 is most commonly talked about during the consumption of fish, such as salmon. It provides several benefits to the body, including lowering triglyceride levels, inflammation, and improving cognitive function.

Fatty Acids Examples
- The 16- and 18-carbon fatty acids, better known as palmitic acid and stearic acid, are among the most commonly distributed fatty acids. In the lipids of most species, both palmitic and stearic acids exist. Palmitic acid makes up as much as 30 percent of body fat in animals. It accounts for between 5 and 50 percent of the lipids in vegetable fats, w...
Essential Fatty Acids
- Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that must be consumed by humans and other animals because they are required by the body for good health but can not be synthesized. Fatty acids needed for biological processes are referred to by the term "essential fatty acid" but do not include fats that only serve as fuel. In the sense of being a distilled essence, essential fatty acid…
Here Is An Example of Two Essential Fatty Acids
- Linoleic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid) and alpha-linolenic acid are not synthesized by many species (an omega-3 fatty acid). However, for cellular processes and the development of other essential omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, certain fatty acids are needed. Thus, they are called essential fatty acids since they need to be taken in via the diet. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids derived …
Classification of Fatty Acids
- In many ways, fatty acids are classified: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by the content of even vs odd carbon, and by linear vs branched. 1. Fatty acids with aliphatic tails of five or fewer carbons are short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) (e.g. butyric acid). 2. Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with 6 to 12 carbon aliphatic tails that are capable of forming medium-chain trigly…
List of Unsaturated Fatty Acids
- Crotonic acid.
- Myristoleic.
- Palmitoleic acid.
- Oleic acid.
Applications of Fatty Acids
- A large variety of commercial uses are available for fatty acids. They are used not only in the manufacture of various food products, for instance, but also in soaps, detergents, and cosmetics. Soaps are fatty acid salts of sodium and potassium. Some skincare items contain fatty acids, which can help keep the look and function of the skin healthy. Fatty acids are also commonly m…
Did You Know?
- They are a class of fatty acids found in fish oils that reduce cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoproteins) levels in the blood, especially in salmon and other cold-water fish. (The "bad" cholesterol is LDL cholesterol.) Trans fatty acids (trans fats) are made to solidify liquid oils by hydrogenation. They increase the shelf life of oils and are found in some margarine, crackers, co…
Fatty Acids Definition
Function of Fatty Acids
- Fatty acids have important roles in: 1) signal-transduction pathways; 2) cellular fuel sources; 3) the composition of hormones and lipids; 4) the modification of proteins; and 5) energy storage within adipose tissue (specialized fat cells) in the form of triacylglycerols.
Types of Fatty Acids
- Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Monounsaturated fatty acids contain one carbon-carbon double bond, which can be found at different positions throughout the fatty acid chain. The majority of monounsaturated fatty acids are between 16 and 22 carbons in length, and contain a cis double bond, meaning that the hydro… - Saturated
Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen, and most are straight hydrocarbon chains with an even number of carbon atoms. The most common fatty acids contain 12–22 carbon atoms.
Fatty Acid Structure
- Fatty acids are composed of carbon chains containing a methyl group at one end and a carboxyl groupat the other. The methyl group is termed the omega (ω) and the carbon atom situated next to the carboxyl group is termed the “α” carbon, followed by the “β” carbon, etc. Fatty acid molecules also have two chemically distinct regions: 1) a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain, …
Quiz
- 1. Unsaturated fatty acids and saturated acids are distinguished based on: A. The length of the hydrocarbon chain. B. The number of carbons in the fatty acid chain. C. The presence of a double bond in the hydrocarbon chain. D.The lack of a hydrophilic phosphate group. 2. Which of the following is NOT a function of fatty acids: A. Immune regulation B. Cell membrane C. Gene expre…