21 Feedback Loops
- Feedback. Feedback is a situation when the output or response of a loop impacts or influences the input or stimulus.
- Positive Feedback. In a positive feedback mechanism, the output of the system stimulates the system in such a way as to...
- Negative Feedback. Most biological feedback systems are negative feedback systems. Negative feedback occurs when a...
How does negative feedback loop work in the body?
21 Feedback Loops Feedback. Feedback is a situation when the output or response of a loop impacts or influences the input or stimulus. Positive Feedback. In a positive feedback mechanism, the output of the system stimulates the system in such a way as to... Negative Feedback. Most biological ...
What are examples of positive feedback in the human body?
What are feedback loops in the body? A feedback loop is a biological occurrence wherein the output of a system amplifies the system (positive feedback) or inhibits the system (negative feedback). Feedback loops are important because they allow living organisms to maintain homeostasis. Click to see full answer.
How well does your organization use feedback loops?
Typically, we divide feedback loops into two main types: positive feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes additional change in the same direction.For... negative feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes change in …
How does feedback help maintain homeostasis?
Oct 01, 2016 · The human body is governed by a wide range of feedback loops. These systems maintain a careful balance of everything from the amount of water in your cells to the amount of hormones released into your bloodstream. Feedback loops are always running in the background of our lives, but they influence our bodies and minds in profound ways.

What are three examples of feedback loops in the body?
- Thermoregulation (if body temperature changes, mechanisms are induced to restore normal levels)
- Blood sugar regulation (insulin lowers blood glucose when levels are high ; glucagon raises blood glucose when levels are low)
What is an example of a feedback loop?
What type of feedback loop has many examples in the human body?
A typical example of a negative feedback mechanism in the human body is the regulation of body temperature via endotherms. When the body's temperature rises above normal, the brain sends signals to various organs, including the skin, to release heat in the form of sweat.Jan 13, 2022
What is the most common feedback loop in the body?
What are the feedback loops and how they work in human brain?
What is an example of a negative feedback loop in the human body?
What is a feedback loop in biology?
Why are feedback loops important?
What's an example of your body displaying homeostasis?
What are positive and negative feedback loops?
What are the two feedback loops that maintain homeostasis?
What is a feedback loop in climate?
What is feedback loop?
Feedback is a situation when the output or response of a loop impacts or influences the input or stimulus. Typically, we divide feedback loops into two main types: positive feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes additional change in the same direction.For example, an increase in the concentration of a substance causes ...
What is positive feedback loop?
positive feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes additional change in the same direction.For example, an increase in the concentration of a substance causes feedback that produces continued increases in concentration. negative feedback loops, in which a change in a given direction causes change in the opposite direction.For ...
How does the hypothalamus respond to heat?
When body temperature rises, the hypothalamus initiates several physiological responses to decrease heat production and lose heat: 1 Widening of surface blood vessels (vasodilation) increases the flow of heat to the skin and get flushed. 2 Sweat glands release water (sweat) and evaporation cools the skin.
Why are positive feedback loops unstable?
Positive feedback loops are inherently unstable systems. Because a change in an input causes responses that produce continued changes in the same direction, positive feedback loops can lead to runaway conditions.
Is positive feedback harmful?
In most cases, positive feedback is harmful, but there are a few instances where positive feedback, when used in limited fashion, contributes to normal function. For example, during blood clotting, a cascade of enzymatic proteins activates each other, leading to the formation of a fibrin clot that prevents blood loss.
Is thrombin a positive or negative feedback loop?
But if we just consider the effects of thrombin on itself, it is considered a positive feedback cycle. Although some may consider this a positive feedback loop, such terminology is not universally accepted. Negative feedback loops are inherently stable systems.
Is a positive feedback loop a runaway process?
As noted, there are some physiologic processes that are common ly considered to be positive feedback, although they may not all have identifiable components of a feedback loop.
What is the key characteristic of a feedback loop?
All feedback loops have one key characteristic: the output from one cycle becomes the input for the next cycle. In other words, all feedback loops measure something and that measurement becomes the starting point for the next cycle of behavior. Data improves awareness and awareness is the first step to behavior change.
What is the purpose of feedback loops?
Effective feedback loops help you make comparisons that are personal and relevant. Adjustment is the action that closes the feedback loop. Adjustments should be made as quickly as possible. The more rapid the change, the tighter the feedback loop.
How does feedback work in the human body?
These systems maintain a careful balance of everything from the amount of water in your cells to the amount of hormones released into your bloodstream. Feedback loops are always running in the background of our lives, but they influence our bodies and minds in profound ways.
Is feedback loops only at the core of biology?
In extreme cases, things spiral out of control — like the growth of Robert Wadlow. Here’s the important part: Feedback loops are not only at the core of human biology, but also at the center of human behavior.
Where is feedback loop?
Feedback loops are not only at the core of human biology, but also at the center of human behavior. Like the biological processes mentioned above, psychological feedback loops often run unnoticed in the background of our daily lives.
What is balancing feedback loop?
Generally speaking, balancing feedback loops are associated with maintaining equilibrium or oscillating around a desired level. Meanwhile, reinforcing feedback loops are associated with continuous increases or decreases. Let’s break down each type and discuss how to use it to improve your habits. 1.
How to use feedback loops to improve habits?
Let’s break down each type and discuss how to use it to improve your habits. 1. Balancing Feedback Loops . Balancing feedback loops pull behavior back on track and help to stabilize a system around a desiredlevel. These systems can be very effective at both moderating bad habits and kickstarting good habits.
What is feedback loop?
Feedback loop is defined as a system used to control the level of a variable in which there is an identifiable receptor (sensor), control center (integrator or comparator), effectors, and methods of communication. We use the following terminology to describe feedback loops:
What is homeostasis and feedback loops?
Homeostasis and Feedback Loops. Homeostasis relates to dynamic physiological processes that help us maintain an internal environment suitable for normal function. Homeostasis is not the same as chemical or physical equilibrium. Such equilibrium occurs when no net change is occurring: add milk to the coffee and eventually, ...
When a stimulus, or change in the environment, is present, is feedback loops respond to keep systems functioning near
When a stimulus, or change in the environment, is present, feedback loops respond to keep systems functioning near a set point, or ideal level . Feedback is a situation when the output or response of a loop impacts or influences the input or stimulus. Typically, we divide feedback loops into two main types:
What is positive feedback?
In a positive feedback mechanism, the output of the system stimulates the system in such a way as to further increase the output. Common terms that could describe positive feedback loops or cycles include “snowballing” and “chain reaction”. Without a counter-balancing or “shut-down” reaction or process, a positive feedback mechanism has the potential to produce a runaway process. As noted, there are some physiologic processes that are commonly considered to be positive feedback, although they may not all have identifiable components of a feedback loop. In these cases, the positive feedback loop always ends with counter-signaling that suppresses the original stimulus.
How does a negative feedback loop maintain homeostasis?
This is an important example of how a negative feedback loop maintains homeostasis is the body’s thermoregulation mechanism. The body maintains a relatively constant internal temperature to optimize chemical processes. Neural impulses from heat-sensitive thermoreceptors in the body signal the hypothalamus.
Can negative feedback cause high glucose levels?
Thus, failure of the negative feedback mechanism can result in high blood glucose levels, which have a variety of negative health effects. Let’s take a closer look at diabetes. In particular, we will discuss diabetes type 1 and type 2. Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin, resistance to insulin, or both.
What is the process of maintaining internal conditions in the body called?
This ensures that the tissue will have enough oxygen to support its higher level of metabolism. Maintaining internal conditions in the body is called homeostasis (from homeo-, meaning similar, and stasis, meaning standing still).
What is negative feedback loop?
A negative feedback loop, also known as an inhibitory loop, is a type of self-regulating system. In a negative feedback loop, increased output from the system inhibits future production by the system.
What does it mean when the body needs a way to slow down the factory?
It does this through a negative feedback loop. What that means is that the speed of production is sensitive to the amount of Product X. When it starts to build up, production slows.
What is homeostasis in the human body?
Homeostasis is defined as a system's tendency towards stability. Homeostasis is very important in the human body. Many systems have to self regulate in order for the body to stay in optimal ranges for health. 3 . Some systems that regulate through negative feedback to achieve homeostasis include: Blood pressure.
What is the function of feedback in the body?
Feedback also regulates your internal body temperature, which is critical to cel lular processes. Your hypothalamus, another important component of the endocrine system, sits above the roof of your mouth and tells your brain when you get too hot or too cold.
Why does the body not use positive feedback?
Your body does not often employ positive feedback because it doesn't like extreme conditions. Therefore, since negative feedback maintains appropriate conditions in your body, it's the most common type of feedback mechanism. Let's look at an example to see how this works.
What are the two types of feedback mechanisms?
There are two types of feedback mechanisms: negative and positive . Negative feedback mechanisms are the most common because they attempt to maintain a target level. In contrast, positive feedback mechanisms are amplifications away from a target level.
Why are negative feedback mechanisms the most common?
Negative feedback mechanisms are the most common because they attempt to maintain a target level. In contrast, positive feedback mechanisms are amplifications away from a target level. Don't let these names fool you though - negative feedback is a very good thing when it comes to homeostasis.
How does negative feedback work?
For example, your pancreas (an important gland in your endocrine system) relies on negative feedback to regulate blood glucose levels. An influx of glucose, say from a carbohydrate-heavy dinner, triggers your pancreas to produce a hormone called insulin. Insulin's message to your body is to take up that extra sugar into cells in order to bring your blood sugar back to the target level. Once enough glucose has been taken up by your cells, your pancreas stops secreting insulin. It's negative feedback!
What are the glands that regulate energy?
By now, you should have a good understanding of your endocrine system, which is made of hormone-producing glands that help regulate your energy levels, growth, emotions, ability to reproduce, and more. There are over a dozen glands that make up your endocrine system, including your pancreas, adrenal glands, thyroid, and pituitary gland.
What is the endocrine system?
By now, you should have a good understanding of your endocrine system, which is made of hormone-producing glands that help regulate your energy levels, growth, emotions, ability to reproduce, and more. There are over a dozen glands that make up your endocrine system, including your pancreas, adrenal glands, thyroid, ...
Why is feedback loop important?
Feedback loops are important because they allow living organisms to maintain homeostasis.
When does a positive feedback loop occur?
A positive feedback loop occurs in nature when the product of a reaction leads to an increase in that reaction. If we look at a system in homeostasis, a positive feedback loop moves a system further away from the target of equilibrium.
What is the feedback loop in apples?
Figure 2: The process of apples ripening is a positive feedback loop.
What is negative feedback loop?
A negative feedback loop occurs in biology when the product of a reaction leads to a decrease in that reaction. In this way, a negative feedback loop brings a system closer to a target of stability or homeostasis. Negative feedback loops are responsible for the stabilization of a system, and ensure the maintenance of a steady, stable state.
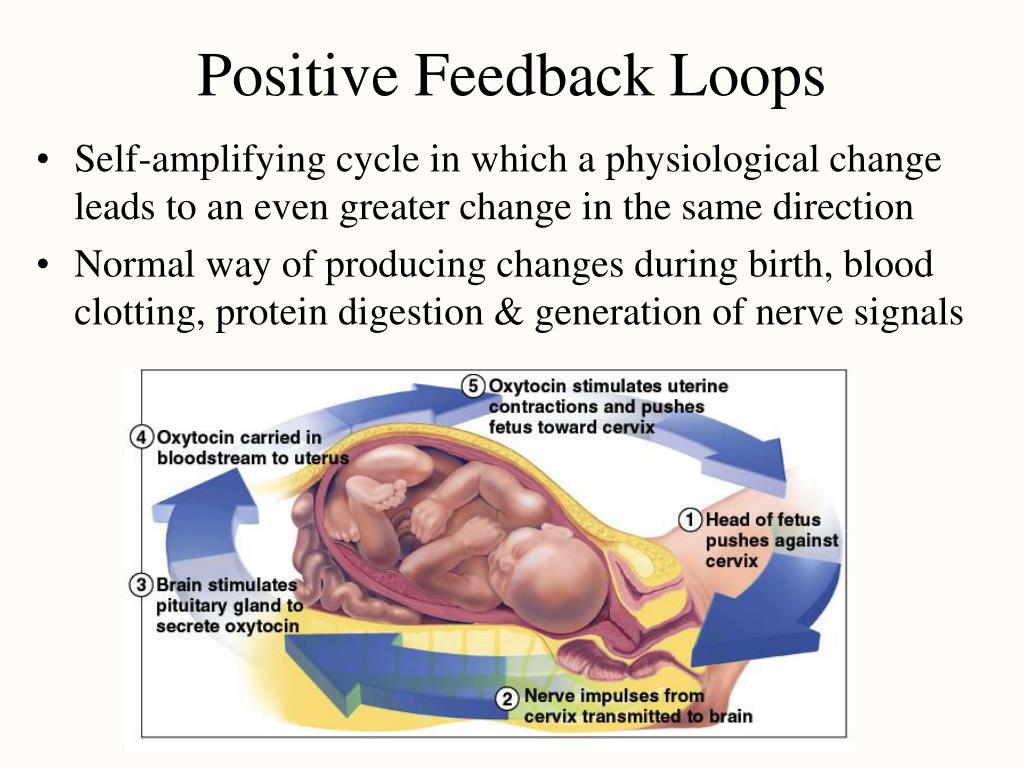
What happens when a baby's head is pushed downwards?
When labor begins, the baby’s head is pushed downwards and results in increased pressure on the cervix. This stimulates receptor cells to send a chemical signal to the brain, allowing the release of oxytocin. This oxytocin diffuses to the cervix via the blood, where it stimulated further contractions.
What are the components of a feedback loop?
Feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they monitor conditions inside and outside the body. Some examples are thermoreceptors and mechanoreceptors. The control center, often in the brain, compares the value the sensor receives to the values in the range.
What are some examples of negative feedback loops?
Other examples of negative feedback loops include the regulation of blood sugar, blood pressure, blood gases, blood pH, fluid balance, and erythropoiesis.
What happens when a condition is out of balance?
When any condition gets out of balance, feedback loops return the body to homeostasis. This is a natural response to changes in the optimal conditions for the body to function. To sense when things are out of balance, bodily functions have set points around which normal values fluctuate within a range. For example, normal human body temperature set ...
Does the body cool itself?
The body does not “cool itself” in the literal sense, meaning it does not turn on an internal air conditioning system or synthesize chemicals that cool the body. The major thermoregulatory negative feedback loop for cooling is when thermoreceptors on the skin detect higher than desired temperatures.
Why is positive feedback important?
Instead of reversing it, positive feedback encourages and intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition, actually driving it farther out of the normal range. This type of feedback is normal for the body, provided there is a definite endpoint.
What is the process of blood coagulation?
When the body is damaged inside or outside, the damaged tissues release factors that cause platelets to adhere to the tissue (the effector) at the site of the wound. The platelets release granules that activate and attract more platelets and cause them to bind to each other. Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin which creates a meshwork that traps blood cells and platelets, forming a clot and stopping the bleeding. The cascade comes to an end when thrombin binds to the cofactor thrombomodulin, activating protein C which inhibits the coagulation cycle.
What are the positive and negative feedback loops?
Positive and Negative Feedback 1 Childbirth is a positive feedback loop. During childbirth, the uterus will contract until the child is born. 2 Blood clotting is another example because platelets will continue to be released to the injury site until the bleeding has stopped.
Is negative feedback loop hard to understand?
Negative feedback loops can be hard to understand. But once you look at examples and how they compare to positive feedback loops, it makes more sense. Dive into more about biological processes by looking at examples of electrolytes.
What is negative feedback?
A negative feedback loop is a reaction that causes a decrease in function. It occurs in response to some kind of stimulus. Often, it causes the output of a system to be lessened; so, the feedback tends to stabilize the system. This can be referred to as homeostasis, as in biology, or equilibrium, as in mechanics.
Is childbirth a positive feedback loop?
Childbirth is a positive feedback loop. During childbirth, the uterus will contract until the child is born. Blood clotting is another example because platelets will continue to be released to the injury site until the bleeding has stopped.
What happens when a human is hungry?
Human metabolism - When a human is hungry, metabolism slows down to conserve energy and allows the human to continue living with less food. Regulation of blood sugar in humans - When blood sugar rises, insulin sends a signal to the liver, muscles, and other cells to store the excess glucose.
What are some examples of hypothalamus?
Explore a few different examples. Human body temperature - The hypothalamus of a human reacts to temperature fluctuations and responds accordingly. If the temperature drops, the body shivers to bring up the temperature and if it is too warm, the body will sweat to cool down due to evaporation. Human blood pressure - When blood pressure increases, ...
/GettyImages-141483854-566348113df78ce161a08b65.jpg)
Homeostasis Terminology
Feedback Loops
- Remember that homeostasis is the maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment. When a stimulus, or change in the environment, is present, feedback loops respond to keep systems functioning near a set point, or ideal level. Feedbackis a situation when the output or response of a loop impacts or influences the input or stimulus. Typically, we divide feedback loops into two …
Positive Feedback
- In a positive feedback mechanism, the output of the system stimulates the system in such a way as to further increase the output. Common terms that could describe positive feedback loops or cycles include “snowballing” and “chain reaction”. Without a counter-balancing or “shut-down” reaction or process, a positive feedback mechanism has the potential to produce a runaway pro…
Negative Feedback
- Most biological feedback systems are negative feedback systems. Negative feedback occurs when a system’s output acts to reduce or dampen the processes that lead to the output of that system, resulting in less output. In general, negative feedback loops allow systems to self-stabilize. Negative feedback is a vital control mechanism for the body’s homeostasis. You saw a…
Diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2
- An important example of negative feedback is the control of blood sugar. 1. After a meal, the small intestine absorbs glucose from digested food. Blood glucose levels rise. 2. Increased blood glucose levels stimulate beta cells in the pancreas to produce insulin. 3. Insulin triggers liver, muscle, and fat tissue cells to absorb glucose, where it is stored. As glucose is absorbed, blood …