
What characteristics identify a metamorphic rock?
When identifying metamorphic rocks, geologists examine and consider the following rock characteristics: structure, grain size, pressure and temperature, and mineral content. Structure indicates the way minerals are oriented in a rock. Contact metamorphic rocks have a crystalline structure, though the minerals are usually randomly arranged.
What are the names of some metamorphic rocks?
metamorphic rocks: Muscovite - hydrous mineral that eventually disappears at the highest grade of metamorphism Biotite - a hydrous mineral that is stable to very high grades of metamorphism. Pyroxene - a non hydrous mineral. Garnet - a non hydrous mineral. Retrograde Metamorphism
What are some facts on metamorphic rock?
What are some fun facts about metamorphic rocks?
- Many metamorphic rocks are made of layers that can be split apart. …
- Magma under the earth sometimes heats rocks, causing them to change. …
- Marble is a type of metaphoric rock made from limestone or chalk and is usually found in the mountains.
What are some examples of metamorphic rocks?
Metamorphic Rocks
- What are some examples of Metamorphic Rocks? There are two types of metamorphic rocks: Foliated Rocks: Examples: Slate, schist, amphibolite, gneiss, migmatite, phyllite, etc. ...
- Write uses of Metamorphic Rocks in everyday life. Quartzite and marbles are most commonly used metamorphic rocks in our day-to-day life. ...
- Write some examples of Sedimentary Rocks. ...
What are metamorphic foliated rocks?
Foliated Metamorphic Rocks Foliated rocks develop a platy or sheet-like structure that reflects the direction that pressure was applied in. Types of foliated metamoprhic rocks include slate, schist, and gneiss.
Where are foliated metamorphic rocks?
Foliated metamorphic rocks are formed within the Earth's interior under extremely high pressures that are unequal, occurring when the pressure is greater in one direction than in the others (directed pressure).
What are 5 foliated metamorphic rocks?
The six types of foliated metamorphic rocks highlighted below (slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, amphibolite, and migmatite) are arranged by the increasing amount of temperature and pressure required for their formation. They are classified based on the nature of their foliation and their crystal size.
What is Nonfoliated metamorphic rock?
Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks lack foliated texture because they often lack platy minerals such as micas. They commonly result from contact or regional metamorphism. Examples include marble, quartzite, greenstone, hornfel, and anthracite.
What are the characteristics of foliated metamorphic rocks?
Foliated rocks are a type of metamorphic rock that has a characteristic banded (or striped) pattern. Due to extreme heat and pressure, rock minerals will flatten to create parallel layers needed to form the striped patterns in foliated rocks. Foliation describes a metamorphic rock whose minerals are aligned in layers.
What foliation means?
/ˌfəʊ.liˈeɪ.ʃən/ a process in which rocks divide into thin layers that can be separated, or the layers themselves: Pressure concentrated in opposing directions often causes foliation in rocks. The presence of foliation is a clue to metamorphic rocks.
What are the 3 main types of metamorphic rocks?
The heat generated by the magma chamber has changed these sedimentary rocks into the metamorphic rocks marble, quartzite, an hornfels.
How foliated metamorphic rocks are formed?
Foliated metamorphic rocks are formed within the Earth's interior under extremely high pressures that are unequal, occurring when the pressure is greater in one direction than in the others (directed pressure).
What are three types of foliated rock?
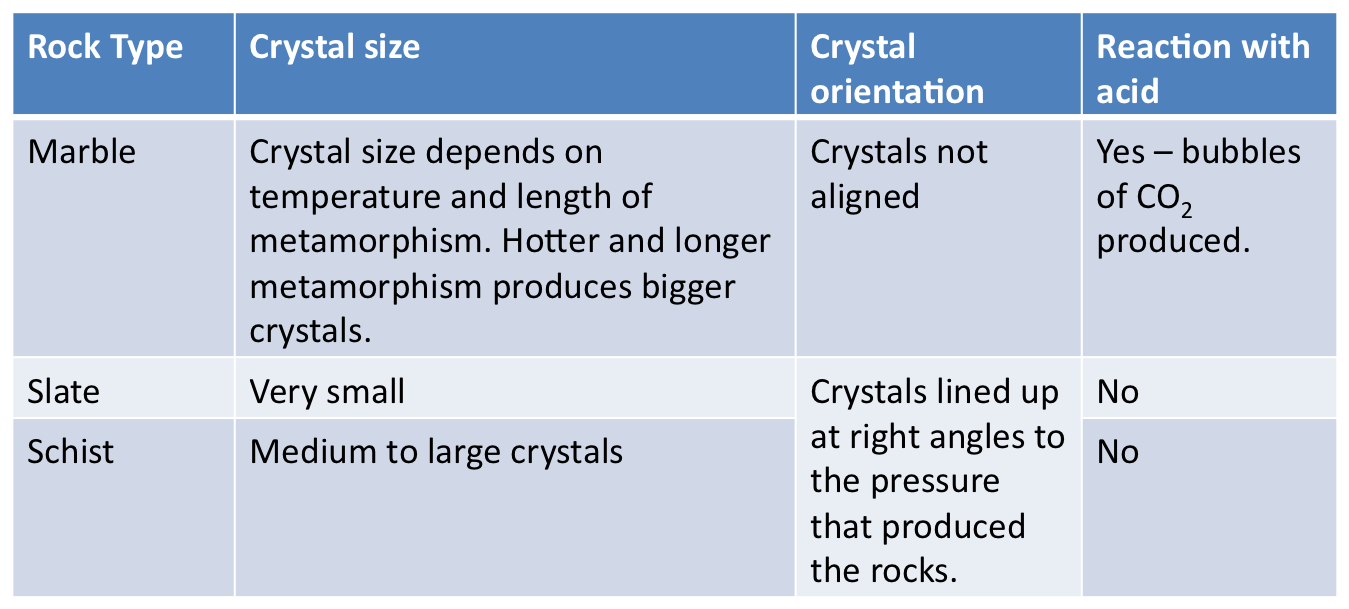
There are three types of foliated rocks: slate, schist, and gneiss.
What is the difference between foliated and non-foliated rock?
Foliated metamorphic rocks have bands or visible layers in the rock pattern. This is created through direct pressure and heat. Some examples of this are slate and gneiss. Non-foliated metamorphic rocks do not have bands or visible layers.
What is the definition of non-foliated?
Metamorphic rocks are broadly classified as foliated or non-foliated. Non-foliated metamorphic rocks do not have aligned mineral crystals. Non-foliated rocks form when pressure is uniform, or near the surface where pressure is very low.
What is foliated and non-foliated rock?
Foliated rocks have platy or elongate minerals aligned in roughly parallel planes or in wavy bands or planes. Nonfoliated rocks may show colored bands that reflect minute impurities in the rock, but the dominant minerals show no visible alignment.
Will foliated metamorphic rocks form in mountain ranges?
Regional metamorphism covers large areas of continental crust typically associated with mountain ranges, particularly those associated with convergent tectonic plates or the roots of previously eroded mountains.
Are all metamorphic rocks foliated?
There are two main types of metamorphic rocks: those that are foliated because they have formed in an environment with either directed pressure or shear stress, and those that are not foliated because they have formed in an environment without directed pressure or relatively near the surface with very little pressure ...
What are the 3 main types of metamorphic rocks?
The heat generated by the magma chamber has changed these sedimentary rocks into the metamorphic rocks marble, quartzite, an hornfels.
How do you tell if a metamorphic rock is foliated or Nonfoliated?
Foliated rocks have platy or elongate minerals aligned in roughly parallel planes or in wavy bands or planes. Nonfoliated rocks may show colored bands that reflect minute impurities in the rock, but the dominant minerals show no visible alignment.
Why are there bands on foliated metamorphic rocks?
This occurs due to heat and pressure given on a single plane of axis, one direction, where the re-crystallization of the minerals in the rock are elongated along that axis.
What is the main characteristic of metamorphic rocks?
This heat and pressure changes the rock into a denser form, which is the main characteristic of metamorphic rock. This denser form makes metamorphic rocks more difficult to erode or break down. Keep in mind metamorphic rocks are not igneous or sedimentary rocks that are melted (This by definition would be an igneous rock).
How are metamorphic rocks identified?
Metamorphic rocks are identified by their denser, stronger form, which was caused by intense heat and pressure but not enough to melt the rock into magma. The minerals that are in the rock can show some very colorful variations, this at times can be coloring with banding or layering.
What is the role of fluids in metamorphic rocks?
Sedimentary rocks will hold the most fluids, but most rocks do hold some kind of water. This fluid can help with the mixing of minerals locally or even transferring minerals too far off places.
What type of rock is foliated?
The foliated metamorphic rock will show the banding and layering of the different mineral colors that exists in the rock. Some foliated metamorphic rock types include schist, gneiss, slate, and phyllite.
What changes occur during the creation of metamorphic rocks?
Some changes that can occur during the creation of metamorphic rocks are the introduction of minerals or rearrangement of minerals during heat and pressurization. ...
Which is harder, sedimentary or metamorphic?
Additionally, note what environment you are in. If you are in mountainous regions, you will likely be finding more metamorphic rocks. If you are in desert regions, you might be finding more sedimentary rocks.
What is the name of the rock that is a medium to high grade metamorphic rock?
Amphibolite is derived from mafic igneous rock. It usually has a dark color and weak foliation. Abundant minerals include hornblende and plagioclase. Amphibolite is a medium- to high-grade metamorphic rock.
How many types of foliated metamorphic rocks are there?
The six types of foliated metamorphic rocks highlighted below (slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, amphibolite, and migmatite) are arranged by the increasing amount of temperature and pressure required for their formation. They are classified based on the nature of their foliation and their crystal size.
What is phyllite in science?
Phyllite by Earth Sciences, University of Newcastle on Sketchfab. Original caption: "Phyllite is a low-grade pelitic metamorphic rock. It is distinguished from lower grade slate by having a higher proportion of newly crystallised minerals, and accordingly, a higher sheen.
What is schist derived from?
Schist is derived from metamorphosed shale, carbonates, or mafic igneous rocks. It exhibits fine- to medium-sized grains. Micas, chlorite, quartz, talc, garnet, hornblende, and graphite are all common in schist. The presence of micas give schist a sparkly appearance, similar to fish scales. Schist is a low- to high-grade metamorphic rock.
What type of rock is gneiss?
Abundant minerals include quartz, feldspars, micas, and hornblende. Gneiss is a high-grade metamorphic rock.
What is the texture of a rock?
The texture of a rock has to do with the arrangement, sizes, and shapes of its crystals. Metamorphism always alters the texture of rock. One type of altered texture is foliation, wherein minerals become grouped in parallel arrangements. This happens because platy minerals such as micas and chlorites become aligned at an angle relative ...
What is slate made of?
Grains of slate are microscopic and are composed mostly of clays, micas, and chlorite. This type of rock often breaks at an angle relative to its original bedding. Slate is a low-grade metamorphic rock.
What is the highest rank of coal?
Anthracite is the highest rank of coal. It has been exposed to enough heat and pressure that most of the oxygen and hydrogen have been driven off, leaving a high-carbon material behind. It has a bright, lustrous appearance and breaks with a semi-conchoidal fracture.
What is a skarn?
Skarn is a rock characterized by its formation rather than its mineral composition. It often forms when carbonate rocks near a magma body are altered by contact metamorphism and metasomatism. Various minerals, gems, and even precious metals can sometimes be found in skarn.
What is phyllite made of?
Phyllite is a foliated metamorphic rock that is made up mainly of very fine-grained mica. The surface of phyllite is typically lustrous and sometimes wrinkled. It is intermediate in grade between slate and schist. The specimen shown above is about two inches (five centimeters) across.
What is mariposite in mining?
It can refer to green mica minerals, or metamorphic rocks that contain enough green mica to impart a green color. Gold prospectors learned that gold could be found in areas where these green rocks were present. This is because mariposite is an ore of gold.
What are some examples of nonfoliated rocks?
Examples of nonfoliated rocks include: hornfels, marble, novaculite, quartzite, and skarn. Photographs and brief descriptions of some common types of metamorphic rocks are shown on this page. Gneiss is a foliated metamorphic rock that has a banded appearance and is made up of granular mineral grains. It typically contains abundant quartz ...
How big is soapstone?
It is about two inches (five centimeters) across. Soapstone is a metamorphic rock that consists primarily of talc with varying amounts of other minerals such as micas, chlorite, amphiboles, pyroxenes, and carbonates. It is a soft, dense, heat-resistant rock that has a high specific heat capacity.
What are some examples of foliated metamorphic rocks?
Examples of foliated rocks include: gneiss, phyllite, schist, and slate. Non-foliated metamorphic rocks do not have a layered or banded appearance. Examples of nonfoliated rocks include: hornfels, marble, novaculite, quartzite, ...
What is the difference between foliated and nonfoliated metamorphic rocks?
The major differences between foliated and nonfoliated metamorphic rocks are in the areas of texture, appearance and the type of pressure applied during recrystallization. The pressure applied to the reforming rock causes the differences in the way the rock looks once recrystallized and determines whether it will be foliated or nonfoliated.
Why are foliated and nonfoliated rocks considered metamorphic?
Both foliated and nonfoliated rocks begin their lives as either sedimentary, igneous or another metamorphic rock. Due to geological changes, a metamorphic rock of the foliated or nonfoliated type will be created. These geological changes can be due to heat and temperature from the recrystallizing rock being found deep within the earth's crust.
What is slate metamorphic?
A fourth type of foliated metamorphic rock is called slate . Slate exhibits slaty foliation , which is also called cleavage. In geology, cleavage refers to the tendency of a rock to break parallel to the alignment of the tiny mica minerals it is composed of. This means that slate breaks into thin layers, which have economic value as tiles and blackboards. The protolith for slate is shale, and sometimes fossils that were present in the original rock can be seen in freshly sheared layers of slate.
What is a foliation called?
One kind of foliation is called gneissic banding , which looks like bands of light and dark layers. Any rock that contains more than one kind of mineral can be the protolith for gneiss , which is the name for a metamorphic rock that exhibits gneissic banding.
What are the types of foliated metamorphic rocks?
A rock list of types of foliated metamorphic specimens includes gneiss, schist, phyllite and slate. Specific patterns of foliation depend on the types of minerals found in the original rock, the size of the mineral grains and the way pressure is applied to the rock during metamorphosis.
What is quartzite made of?
A second type of nonfoliated metamorphic rock, quartzite , is composed mostly of silicon dioxide. The protolith for quartzite is quartz , and because quartz is stable under high pressure and high temperatures, metamorphism of this rock simply causes the reorganization of its crystals. A very hard rock, quartzite is often used to make kitchen countertops and floor tiles.
What are foliated rocks?
Foliated rocks are most often formed from mudstones and contain "fine-grained" or "platy" minerals that are usually too small to see with the naked eye; although some can be seen without aid. Examples of foliated rocks are slate, phyllite and schist.
