Functional groups are chemical motifs, or patterns of atoms, that display consistent “function” (properties and reactivity) regardless of the exact molecule they are found in. Biological molecules can contain many different types and combinations of functional groups, and a biomolecule’s particular set of groups will affect many of its properties, including its structure, solubility, and reactivity.
What are the characteristics of functional groups?
Key Takeaways: Functional Groups
- In organic chemistry, a functional group is a set of atoms within molecules that function together to react in predictable ways.
- Functional groups undergo the same chemical reactions no matter how large or small the molecule is.
- Covalent bonds link the atoms within functional groups and connect them to the rest of the molecule.
What are functional groups found in biological molecules?
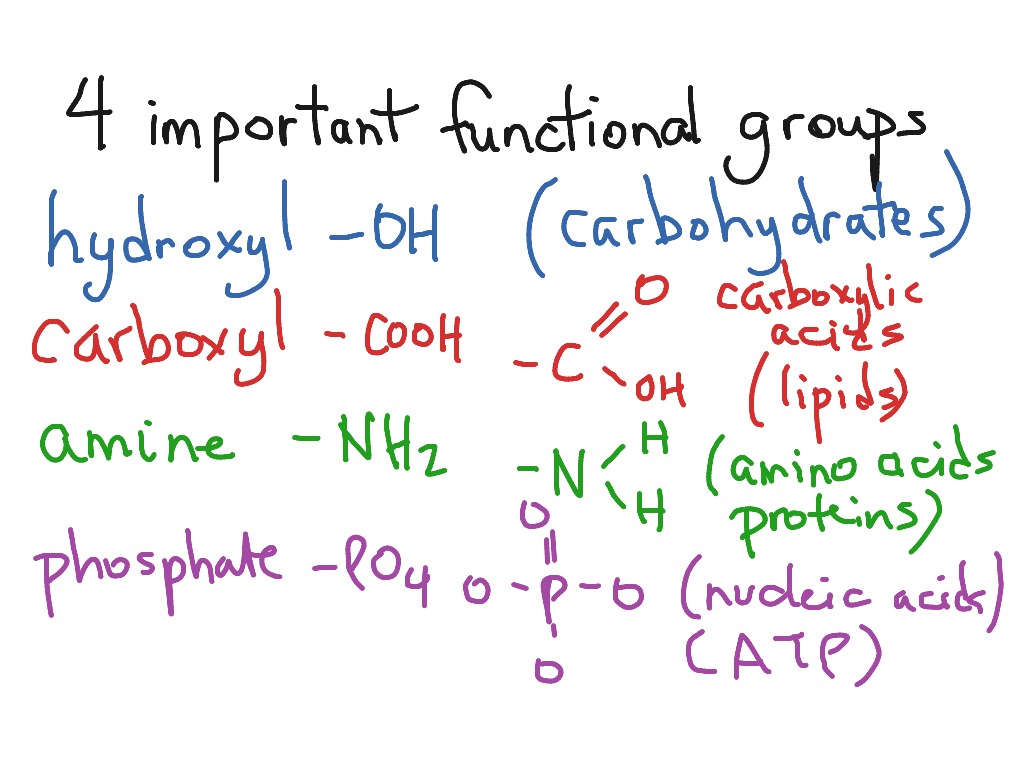
Some of the important functional groups in biological molecules include: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl groups. These groups play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
What is the definition of functional groups?
Functional groups are groups of one or more atoms with distinctive chemical properties regardless of what is attached to them. The atoms of functional groups are bound by covalent bonds with one another and with the rest of the molecule. Functional groups in a coordination complex which bind to a central atom are called ligands.
What are fuctional groups?
Key Points
- Functional groups are collections of atoms that attach the carbon skeleton of an organic molecule and confer specific properties.
- Each type of organic molecule has its own specific type of functional group.
- Functional groups in biological molecules play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.

What are the 6 functional groups in biology?
Hydroxyl, sulfhydryl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino and phosphate groups.
What is a functional group easy definition?
Functional groups are groups of atoms in a compound, such as the hydroxyl group in an alcohol, that determine the chemical behavior of the compound. The part of a compound that reacts with another compound is called the functional group.
What is a functional group and examples?
A functional group in organic chemistry is a collection of atoms within molecules which bind together to react in predictable ways. Examples of functional groups include the group hydroxyl, ketone, amine, and ether.
What is a functional group in biology quizlet?
A functional group is a portion of a molecule that is a recognizable/classified group of bound atoms. In organic chemistry it is very common to see molecules comprised mainly of a carbon backbone with functional groups attached to the chain.
What is a functional group answer?
Functional group may be defined as an atom or group of atoms upon which the properties of a particular organic compound are based.
How do you identify functional groups?
Identification and extraction of functional groupsmark all heteroatoms in a molecule, including halogens.mark also the following carbon atoms: atoms connected by non-aromatic double or triple bond to any heteroatom. atoms in nonaromatic carbon–carbon double or triple bonds. ... merge all connected marked atoms to a single FG.
What are functional groups and why are they important?
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms that is responsible for a particular chemical property of an organic compound. Organic compounds can be classified according to their functional groups. A functional group gives an organic compound a property that is different than it would otherwise have.
What are the 7 major functional groups?
Functional groups in biological molecules play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Functional groups include: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl.
Where are functional groups found?
carbon backboneFunctional groups are groups of atoms that occur within molecules and confer specific chemical properties to those molecules. They are found along the “carbon backbone” of macromolecules.
What are the functional groups of atoms quizlet?
The seven functional groups that are most important in the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, phosphate, methyl groups.
Is alkane a functional group?
Alkane sequences form the inert framework of most organic compounds. For this reason, alkanes are not formally considered a functional group. When a hydrocarbon chain is connected as a substituent to a more fundamental structural unit, it is termed an alkyl group.
What is functional group of aldehyde?
Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds which incorporate a carbonyl functional group, C=O. The carbon atom of this group has two remaining bonds that may be occupied by hydrogen or alkyl or aryl substituents.
What is a functional group in organic chemistry?
Functional groups are specific groupings of atoms within molecules that have their own characteristic properties, regardless of the other atoms present in a molecule. Common examples of functional groups are alcohols, alkenes, alkynes, amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes, ketones, esters, and ethers, among others.
What is functional group write one example as well?
An atom/group of atoms joined in a specific manner which is responsible for the characteristics chemical properties of the organic compounds is called a functional group. Examples are hydroxyl group (-OH), aldehyde group(-CHO), Ketonic group (-CO-),Carboxlic acid group(-COOH) etc.
What is meant by a functional group in an organic compound?
Definition: A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that is bonded to a carbon chain. It defines the chemical property of the organic compound. (i) Ethanol: -OH functional group.
What is the role of functional groups?
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms that is responsible for a particular chemical property of an organic compound. Organic compounds can be classified according to their functional groups. A functional group gives an organic compound a property that is different than it would otherwise have.
What is functional group?
Explanation: A functional group is a collection of atoms in a molecule that are responsible for the characteristic reactions of the compound.
Which functional group gives amino acids their unique properties?
But it is the functional group (the R in the above) that gives the individual amino acids their unique properties. In the image below you will see that the R has been replaced with a collection of other atoms to yield all the different amino acids.
What happens when hydroxyl is attached to a carbon backbone?
Sal says that when Hydroxyl is attached to a carbon backbone it turns the entire molecule into an alcohol. Then later in the video he shows the sugar Fructose, and there are tons of Hydroxyl groups on the molecule.
Does oxygen bind to amino acids?
If oxygen atom binds to the amino group then it does no longer stay as an amino group and we are not speaking about amino acids. Yes, the carboxyl group can give a hydrogen to an amino group. It is called aminotransfer when you create 2 new amino acids between alpha-keto acid and amino acid.
Can the amino group bond with hydrogen?
7:30. , explains that the Nitrogen atom can pick up a hydrogen ion. Therefore one can conclude that both the Carboxyl group and Amino group can bond with a hydrogen atom.
Is fructose a sugar?
In that part of the video, Sal shows that fructose has a carbonyl group. He also says that this makes it into a sugar. This means that no matter how many Hydroxyl groups you have on a molecule, if it has a carbonyl group, it can't be an alcohol anymore, instead, it is classified as a sugar.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What is the sulfhydryl group?
A sulfhydryl group consists of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom. No. A phosphate group consists of a phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygens. The phosphorus shares a double bond with one of the oxygens, and a single bond with each of the other three.
How many hydrogens are in a methyl group?
No. A methyl group consists of a carbon single bonded with three hydrogens.
What are small groups of atoms called?
These small groups of atoms act as a unit, and are called functional groups . Let’s continue using glucose as an example. If you look at carbon number 1, you can see that the carbon, in addition to sharing electrons with a hydrogen atom, is also double bonded to an oxygen.
Is a phosphate a sulfur atom?
A sulfhydryl group consists of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom. Yes. A phosphate group consists of a phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygens. The phosphorus shares a double bond with one of the oxygens, and a single bond with each of the other three.
Is a carboxyl group a carbon?
No. A Carboxyl group has a carbon that’s double bonded to an oxygen, and single bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH) No. An amino group consists of a nitrogen atom with single bonds to two hydrogen atoms. No. A sulfhydryl group consists of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom.
Is a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom?
No. A sulfhydryl group consists of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom.
Is hydroxyl a hydrogen bond?
Yes. A hydroxyl group consists of an oxygen bonded to a hydrogen,
Why is chemistry important?
Chemistry classes are important to the craft of biology and health. Sound understand of chemistry can be the difference between a good biologist and an exceptional one. Unfortunately, the classes are an ocean of irrelevant, or unhelpful facts. For biology and health majors to succeed in chemistry the first skill they must learn is to sort out ...
Why are amino acids important?
Amines are important for maintaining the structure of many macromolecules through electrostatic interactions and H-bonding. Amines can be found in the backbone, and positively charged (when protonated, which is most of the time) R-groups of amino acids, as well as in neurotransmitters and the base pairs of nucleic acids.
Which group of acids are weak?
They are weak acids and donate protons off the -OH group. Carboxylic acids are ubiquitous in biology and include amino acids, fatty acids, acetic acid, and many others. Carboxyl groups are also susceptible to nucleophilic attack, especially when modified in an enzymatic pocket.
What are phosphorus groups?
Phosphate groups consist of a phosphorous atom attached to four oxygen, with a net negative charge ranging from -1 to -2 depending on what it is attached to, or -3 when in a free form. Phosphate groups are hugely important to biological systems for many reasons: They are vital structural units for nucleic acids, and biological membranes; they have a perfectly balanced reduction potential to make them excellent intermediaries in red-ox reactions; Their large size, and electronegativity can cause deformations in the 3D structure of proteins which make them the primary way to control enzymatic function, and cell signaling. Unfortunately, it is unlikely that this functional group will even be mentioned in your organic chemistry class. I highly recommend spending some time outside of class to learn a little about the mechanisms and reactions that this functional group can undergo.
Why are hydroxyl groups important?
In biology the important role of hydroxyl groups mostly has to do with their ability to form hydrogen bonds. The polarity of the functional group and the ability to form two simultaneous H-bonds increase the water solubility of any molecule that has a hydroxyl group attached to it.
Where can you find thiols in chemistry?
The most common place students will see thiols is in the amino acid cysteine. Two cysteines can form a sulfur-sulfur bonds which give additional 3D structure to the protein. Not all organic chemistry classes will talk about sulfur bridges, and enzymatic functions of thiols will only be covered in biochemistry.
What are the carbonyl groups in sugar?
Carbonyl Group. Carbonyl groups include aldehydes and ketones, which consist of an oxygen double bonded to a primary or secondary carbon. Every sugar has a carbonyl group, and they are often targeted by enzymes as the site for making or breaking carbon-carbon bonds.