5 Functional Pre-Requisites of Human Society | Sociology
- (1) The first and basic functional pre-requisites of human society are food, clothing, shelter, security and defence against the dangers of outer environment. ...
- (2) Co-ordination of human actions is another functional pre- requisite of human society. ...
- (3) Division of labour is another functional pre-requisite of human society. ...
- (4) Procreation is another important functional pre-requisite of society. ...
Full Answer
What are the four functional prerequisites of a society?
Functional prerequisites may also refer to the factors that allow a society to maintain social order. On the other hand, Parsons argued any successful social system has four functional prerequisites: Adaptation; Goal attainment; Integration; Pattern maintenance; Adaptation – To survive, any society needs the basics of food and shelter.
What do you mean by functional prerequisites?
Functional prerequisites. Jump to navigation Jump to search. In sociological research, functional prerequisites are the basic needs (food, shelter, clothing, and money) that an individual requires to live above the poverty line. Functional prerequisites may also refer to the factors that allow a society to maintain social order.
When is a function a prerequisite to society?
OF A SOCIETY The performance of a given function is prerequisite to a society if in its absence one or more of the four conditions dis- solving a society results. This can be demonstrated clearly in some cases. Less clearly, but still convincingly, the non- 8 It is worth re-emphasizing that a given society
What are the prerequisites of society logically?
prerequisites of a society logically pre- cedes the development of a scheme of structural prerequisites-which tell how the functional prerequisites may be met -in actuality the theoretic development of the two approaches is indivisible. 3 Neither the nature of the dependence of our
What are the 5 functional prerequisites of society?
(1) The first and basic functional pre-requisites of human society are food, clothing, shelter, security and defence against the dangers of outer environment. Sufficient provision must be made for the fulfillment of the above basic needs of man.
Which of the following is a functional prerequisite of a social system?
He argued that any social system has four basic functional prerequisites: adaptation, goal attainment, integration and pattern maintenance. These can be seen as problems that society must solve if it is to survive.
What are functional prerequisites quizlet?
Functional prerequisites are. tasks that a society or relatively permanent group must accomplish if it is to survive. organized patterns of beliefs and behavior centered on basic social needs.
What are the 4 functional imperatives of structural functionalism?
Parsons broke structural functionalism down into four functional imperatives all social structures must have to exist: adaptation, goal attainment, integration, and latency.
What are the key concepts of functionalism?
Functionalism is the doctrine that what makes something a thought, desire, pain (or any other type of mental state) depends not on its internal constitution, but solely on its function, or the role it plays, in the cognitive system of which it is a part.
What are the basic requirements of society?
A traditional list of immediate "basic needs" is food (including water), shelter and clothing. Many modern lists emphasize the minimum level of consumption of "basic needs" of not just food, water, clothing and shelter, but also sanitation, education, and healthcare.
Which of the following is considered a functional prerequisite?
In sociological research, functional prerequisites are the basic needs (food, shelter, clothing, and money) that an individual requires to live above the poverty line.
What is the meaning of term Gesellschaft in social science?
Gemeinschaft (German pronunciation: [ɡəˈmaɪnʃaft]) and Gesellschaft ([ɡəˈzɛlʃaft]), generally translated as "community and society", are categories which were used by the German sociologist Ferdinand Tönnies in order to categorize social relationships into two dichotomous sociological types which define each other.
Which type of group is most important for socialization?
The primary group is usually made up of significant others, those individuals who have the most impact on our socialization. The best example of a primary group is the family.
What are the basic assumptions of structural functionalism?
Structural functionalism. Assumptions: The conceptual assumptions underlying the approach can be divided into two basic areas: the social system is the prior causal reality and the system parts are functionally interrelated, all social phenomena have functions for the larger social system.
What is Durkheim's theory of functionalism?
Functionalism is basic to Durkheim's sociology. Like other functionalists, he focused on the problem of order and the positive effects of social institutions, explaining their existence in terms of their functionally necessary contributions.
What are functional imperatives?
a requirement for the survival of any social system, as communication, control of conflict, or socialization.
What are the three different types of social functioning?
Social workers perform their roles and responsibilities within three interrelated levels of practice: micro, mezzo, and macro. These systems of practice use different methodologies to provide services to diverse populations, but they all operate within the Person-in-Environment (PIE) Theory.
What are the different types of social functioning?
These social functions often involve identity, conversation, sharing, presence, relationships, reputation, and groups.
What is effective social functioning?
-result from the interaction between people and their social and physical environments. What is effective social functioning? -ability to access personal, interpersonal, and institutional resources to deal with problems. -resources are available and accessible.
Which of the following is true for socialization?
In sociology, socialization is the process of internalizing the norms and ideologies of society. Socialization encompasses both learning and teaching and is thus "the means by which social and cultural continuity are attained". ... Humans need social experiences to learn their culture and to survive.
What are functional prerequisites?
Functional prerequisites. In sociological research, functional prerequisites are the basic needs ( food, shelter, clothing, and money) that an individual requires to live above the poverty line. Functional prerequisites may also refer to the factors that allow a society to maintain social order .
What are the four prerequisites for a social system?
On the other hand, Parsons argued any successful social system has four functional prerequisites: Adaptation. Goal attainment. Integration. Pattern maintenance. Adaptation – To survive, any society needs the basics of food and shelter. Having these gives any society control over its environment.
What are the functions of pre-requisites?
What are the main functions of pre-requisites of society ? Society has certain basic needs or necessary conditions, which must be satisfied if it is to survive. These basic needs or necessary conditions of existence of society are known as functional pre-requisites of society. Sociologists differ in their views regarding the identification ...
What are the basic needs of a society?
Food, clothing and shelter are the basic needs for each and everybody of the society. Besides man needs security for protection of its members. Every society has a mechanism of defence.
How can a society function in the absence of a system of production?
No society can function in the absence of a system of production. It involves techniques and organisation. Human beings learn these techniques of production through observation, participation, and instruction. Production has both individual and collective aspect. Man achieves many things through collective effort,
What is the process of determining which persons will occupy what roles at what time for what purposes?
This process is called ‘role allocation’ . Proper allocation of roles between members minimises problem for the society. Otherwise, society may face disintegration.
What are the key ideas of Functionalist perspective?
The key ideas of Functionalist perspective are as follows –. There is such a thing as a social structure that exists independently from individuals. This social structure consists of norms values passed on through institutions which shape the individual –. We should study society scientifically and at the macro level – looking for ...
Who is the founder of functionalism?
You would do well to be able to distinguish between the ideas of Emile Durkheim – one of the founding fathers of Sociology and Talcott Parsons – who developed Functionalism in the 1940s and 50s. Durkheim and Functionalism. Durkheim is one of the founding fathers of Sociology.
What did Durkheim believe about social structures?
Durkheim believed that there was such a thing as a social structure – made up of norms and values. He argued that this structure existed above the level of the individual because norms and values precede the individual – they already exist in society when we are born into it.
Why is socialisation important?
Socialisation is important – individuals need to be regulated for the benefit of everyone. The integration and regulation of individuals is a good thing.
Which theory exaggerates the extent of Value Consensus and Social Order?
3. Functionalism exaggerates the extent of Value consensus and Social Order – Parsons is criticized for assuming value consensus exists rather than actually proving it
Is it hard to achieve solidarity in an advanced industrial society?
Achieving solidarity in advanced industrial society is difficult. Durhkeim argued that solidarity and moral regulation were achieved in different ways in primitive and advanced industrial societies. In the former, solidarity happens automatically, while in the later it is more difficult to achieve.
What are the functional prerequisites of a social system?
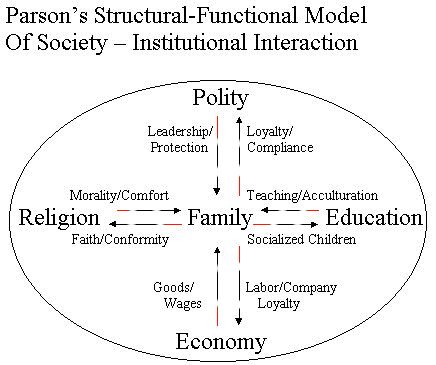
These functional prerequisites are adaptation, goal attainment, integration and latency, which are all necessary responses, in Parsons’ view for the existence and survival of any social system. The institutions and processes, which serve to maintain the existence of the system, are considered to be functional for the system by Talcott Parsons.
What is functionalism in social science?
Functionalism represents the viewpoint that all social systems invariably possess the tendency to evolve and integrate such processes and institutions as elements (parts) of the system , which help in its own self-maintenance. Social systems are basically oriented to evolving such units as components of their form, be it in the shape of processes (such as, in Parsons’ understanding, adaptation, goal-attainment, integration and latency) or as social institutions, such as government, economy, schools, courts, etc. all of which serve to maintain the system as if on purpose. The term teleology refers to this purposiveness of institutions. Teleology is thus an essential characteristic of functionalism. It is based on an analogy with the organic system, for instance the human body. In the human body, processes such as respiration, blood circulation, maintenance of a constant temperature, etc., are intended to maintain the health of the body. As such these processes are Ideological or purposive in nature. Simply stated, teleology is any explanation, which is in terms of the final cause or purpose. For example, it would be teleological to argue that fruits and seeds exist so that animal and birds can eat them in order to live; or that the function of the long tail of monkeys is to help them jump easily from tree to tree.
How does sociology approach social change?
According to Parsons social sciences have yet to formulate a general theory of social change which can take into account both these aspects of social change. But sociology can approach the problem of social change if it delimits its analysis in two respects, first, change must be studied with the help of a set of conceptual categories or paradigms. The conceptual categories that Parsons puts forward for such analyses of change are those of motivational and value orientation, as well as those that relate to the functional prerequisites of the system. Second, social change, according to Parsons, must be studied at a specific historical level rather than in a general form applicable universally to all societies. Parsons, therefore, held the view that for sociologists it is relatively easier to study processes of change within the social system than processes of changes of the social system as a whole.
What is the functionalism of a system?
It is called homeostasis. Functionalism implies that social systems bear resemblance to organic systems such as the human body. The processes and institutions in social systems and the human body possess self-regulatory mechanisms that keep them stable and save it from external threats. A stability of this sort is called homeostasis.
What is the teleological criticism of functionalism?
Besides several criticisms of functionalism, its teleological nature is its logical criticism. As you know, teleology is the explanation for the existence of a process or institution or any object or idea in terms of the purpose it fulfils. Thus, according to this explanation the effect is treated as the cause. This is the principal objection to the functionalist theory. For example, according to this theory, religion exists in societies in order to uphold the moral order of societies. Here the effect of religion
What is Talcott Parsons' critique of social systems?
This Criticism is based on the-functionalist position that members of a social system are socialised from childhood onwards to a common set of beliefs and values, which are specific to that society. Talcott Parsons did not deny the element of value consensus and stability in a social system that results from the functional processes ...
How does Parsons maintain social stability?
In Parsons’ view the stability of a social system is maintained not only through the rules and regulations that society imposed upon its members or through other measures of social control that state enforces upon its citizens but in a more enduring manner, by the internalisation of socially approved values, expected behaviour patterns and codes of social existence. This internalisation takes place in society through the process of socialisation of its members. Child learns from his/her environment in the family and neighbourhood both the expected and prohibited norms and values with respect to different social institutions and social roles. Later on as the person grows older, the school, the college and work-place make the person learn and imbibe other sets of social values and expected behaviour patterns.