
What is the difference between Mycoplasma and Gram positive?
Some key points about Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria:
- The cell wall of gram-positive bacteria is consisting of thick layers of peptidoglycan. ...
- During the gram staining procedure, a gram-positive cell retains the purple-colored stain. ...
- Gram-positive bacteria produce exotoxins, whereas gram-negative bacteria produce endotoxins.
- Gram-negative bacteria cause many infections in humans. ...
How to distinguish Gram positive cocci?
- Beta-hemolysis is complete hemolysis. It is characterized by a clear (transparent) zone surrounding the colonies. ...
- Partial hemolysis is termed alpha-hemolysis. Colonies typically are surrounded by a green, opaque zone. ...
- If no hemolysis occurs, this is termed gamma-hemolysis. There are no notable zones around the colonies. ...
What are rare Gram positive cocci?
rare gram positive cocci lungs Gram-Positive Gram-Positive Anaerobic Cocci SUMMARY Gram-positive anaerobic cocci (GPAC) are a heterogeneous group of organisms defined by their morphological appearance and their inability to grow in the presence of oxygen; most clinical isolates are identified to species in the genus Peptostreptococcus.
What does Gram negative diplococci look like?
gram-negative diplococci (look like kidney beans side by side)
What are examples of gram-positive diplococci?
Examples of gram-positive diplococci are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus spp. Presumably, diplococcus has been implicated in encephalitis lethargica.
What is the disease caused by diplococci?
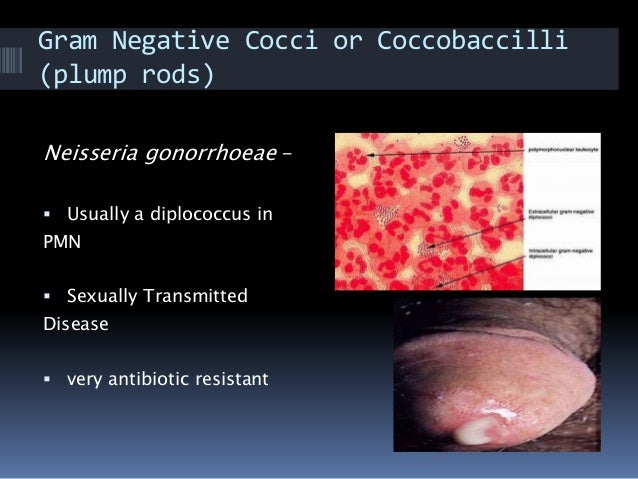
Summary. Gonorrhea infection is a common STI caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a gram-negative diplococcus bacterium that is closely related to other human Neisseria species. Men typically present with a urethral discharge; women are often asymptomatic, but may have vaginal discharge.
What is the meaning of diplococci?
Definition of diplococcus : any of various encapsulated bacteria (such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, a common cause of pneumonia) that usually occur in pairs and that were formerly grouped in a single taxon (genus Diplococcus) but are now all assigned to other genera.
What is the difference between cocci and diplococci?
Cocci may occur as single cells or remain attached following cell division. Those that remain attached can be classified based on cellular arrangement: Diplococci are pairs of cocci (e.g. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae) Streptococci are chains of cocci (e.g. Streptococcus pyogenes).
Is diplococci gonorrhea?
Background. Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the causative agent of gonorrhoea, is a Gram negative, coffee-bean shaped facultative intracellular diplococcus bacterium, the classical sexually transmitted bacteria.
What are the characteristics of diplococci?
Essentially, diplococci bacteria (singular; diplococcus) are rounded/spherical bacteria that occur in pairs. Unlike staphylococci bacteria (which form grape-like clusters and are truly round), some may appear ovoid (elongated) or bean-shaped.
Is Streptococcus pneumoniae gram-positive diplococci?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram-positive, α-hemolytic, lancet-shaped diplococcus and is bile soluble and optochin sensitive.
What causes diplococcus pneumonia?
Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). People with pneumococcal disease can spread the bacteria to others when they cough or sneeze. Symptoms of pneumococcal infection depend on the part of the body affected.
Is Chlamydia gram-negative diplococci?
On the Cover: Methods to detect Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae include microscopy (Gram-stain negative diplococci, lower-left), culture (intracellular inclusions, upper-left), and nucleic acid detection tests (DNA helix, right).
What is the arrangement of diplococci?
coccus arrangement Pairs of cocci are called diplococci; rows or chains of such cells are called streptococci; grapelike clusters of cells, staphylococci; packets of eight or more cells, sarcinae; and groups of four cells in a square arrangement, tetrads.
What are the 3 main types of bacteria?
There are three basic shapes.Spherical: Bacteria shaped like a ball are called cocci, and a single bacterium is a coccus. Examples include the streptococcus group, responsible for “strep throat.”Rod-shaped: These are known as bacilli (singular bacillus). ... Spiral: These are known as spirilla (singular spirillus).
What is the difference between gram-positive cocci and gram-positive bacilli?
In the classical sense, six gram-positive genera are typically pathogenic in humans. Two of these, Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, are cocci (sphere-shaped). The remaining organisms are bacilli (rod-shaped) and can be subdivided based on their ability to form spores.
What is the gram positive diplococcus?
Image 3 is a Gram stain made from a lower respiratory tract specimen. The gram-positive diplococci can be presumptively identified as Streptococcus pneumoniae. Image 3.
What are cocci that occur in pairs called?
Cocci that occur in pairs are referred to as diplococci . Image 2 contains many gram-positive diplococci. Lancet-shaped gram-positive diplococci from a lower respiratory tract specimen could indicate Streptococcus pneumoniae.
What are some examples of gram positive diplococci?
Few showed characteristics of meningitis, endocarditis, and septic arthritis. Examples of gram-positive, diplococci pathogens include S treptococcus pneumoniae and some species in Enterococcus bacteria.
What is a diplococcus?
A diplococcus (plural diplococci) is a round bacterium (a coccus) that typically occurs in the form of two joined cells.
What are some examples of diplococci?
Many of these diplococci bacteria have species (strains) exhibit pathogenic characteristics. Examples of gram-negative, diplococci pathogens would be N.gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. N. gonorrhea is transmitted through copulation with a person who is infected. This bacterium embeds in the reproductive tract tissue in women, causing cervical and uterine infections. Once the membranous tissues within the fallopian tubes are infected, complications in pregnancies will arise. In men, this bacterium infects the urethra. Testing on male subjects, showed apparent bacteria forming colonies within the epithelium and exhibiting signs of damage in these cells. N. meningitidis, also known as meningococcus, can cause bacterial infections on/in the body, i.e. lungs, nasopharynx, or skin, which eventually enters the bloodstream. (web arch) The malignant bacteria within the bloodstream burgeon and often ends in fatality if extreme enough. Another example of a gram-negative, diplococci pathogen is Moraxella catarrhalis. A study of M. catarrhalis was conducted on 58 cases and all presented similar, yet different results. Many cases appeared to have infections within the body: pharyngitis, tracheitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, and otitis. Few showed characteristics of meningitis, endocarditis, and septic arthritis.
How many species of Streptococcus pneumoniae are there?
The species Streptococcus pneumoniae belongs to the genus Streptococcus and the family Streptococcaceae. The genus Streptococcus has around 129 species and 23 subspecies that benefit many microbiomes on the human body. There are many species that show non-pathogenic characteristics; however, there are some, like S. pneumoniae, that exhibit pathogenic characteristics in the human body.
How many species are there in Enterococcus?
The genus Enterococcus belongs to the family Enterococcaceae. This genus is divided into 58 species and two subspecies. These gram-positive, coccoid bacteria were once thought to be harmless to the human body. However, within the last ten years, there has been an influx of nosocomial pathogens originating from Enterococcus bacteria.
Is Neisseria a gram negative species?
This genus, Neisseria, is divided into more than ten different species, but most of them are gram negative and coccoid. The gram-negative, coccoid species include: Neisseria cinerea, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria polysaccharea, Neisseria lactamica, Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria mucosa, Neisseria oralis and Neisseria subflava. Of these Neisseria species, the most common, pathogenic species are N. meningitidis and N.gonorrhoeae.
What is Gram positive diplococcus?
Gram Positive Diplococci Bacteria. Two of the most common Gram-positive diplococcus includes Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus species. Normally, Streptococcus pneumoniae lives as a commensal in the mucosal surfaces of the respiratory system in human beings.
What is a diplococcus?
Essentially, diplococci bacteria (singular; diplococcus) are rounded/spherical bacteria that occur in pairs. Unlike staphylococci bacteria (which form grape-like clusters and are truly round), some may appear ovoid (elongated) or bean-shaped. There are both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria that are responsible for various infections in ...
What does purple mean in a strep?
Generally, they are elongated and may have slightly pointed ends. They also appear purple in color which indicates that they are Gram-positive bacteria (having retained the primary stain).
Where is Streptococcus pneumoniae found?
As mentioned, Streptococcus pneumoniae is commonly found in the mucosal surfaces of the nose and throat where they live as commensalism. Like some of the other diplococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae is characterized by surrounding capsule as well as type I pili that promotes interaction with host cells.
Which type of bacteria is divided in the parallel plane?
For Streptococcus pneumoniae, as is the case with the other diplococci bacteria, division occurs in the parallel plane perpendicular to the long axis. During cell division, the site of division is first marked by ...
How to make a sterile smear?
Procedure. · Place a small amount of the specimen on the glass slide at the center of the glass slide and create a thin smear - a sterile wire-loop can be used. · Allow the slide to air-dry and then heat fix for a few seconds making sure not to overheat.
Can enterococcus cause pneumonia?
However, it can cause community-acquired pneumonia under certain conditions (it's an opportunistic pathogen). Enterococcus species, on the other hand, are normal intestinal flora of human beings and animals. While they are commonly found in the gut and bowel, they can also be found in the mouth.
Abstract
A 5-month-old girl presented with meningitis after receiving amoxicillin for bilateral otitis media. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Gram stain suggested Streptococcus pneumoniae: Gram-positive diplococci with a surrounding clear area indicative of a bacterial capsule. Her CSF and blood cultures grew penicillin-resistant S pneumoniae serotype 35B.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the clinical microbiology laboratory technicians at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta for their technical expertise, the Georgia Emerging Infections Program, and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for serotyping the isolate.
Author notes
Correspondence: Evan J. Anderson, MD, Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Emory Children’s Center, 2015 Uppergate Drive, Atlanta, GA, 30322 ( [email protected] ).
What is Gram positive?
Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria classified by the color they turn in the staining method. Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884. The staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color ...
What is the difference between Gram positive and Gram negative?
Gram-positive organisms have a thicker peptidoglycan cell wall compared with gram-negative bacteria. It is a 20 to 80 nm thick polymer while the peptidoglycan layer of the gram-negative cell wall is 2 to 3 nm thick and covered with an outer lipid bilayer membrane. Epidemiology. Bloodstream infection mortality rates have increased by 78% in just two ...
When was the Gram staining method invented?
Hans Christian Gram developed the staining method in 1884. The staining method uses crystal violet dye, which is retained by the thick peptidoglycan cell wall found in gram-positive organisms. This reaction gives gram-positive organisms a blue color when viewed under a microscope.
What are the different groups of streptococcus bacteria?
Streptococcus bacteria subdivide into Strep. pyogenes (Group A), Strep. agalactiae (Group B), enterococci (Group D), Strep viridans, and Strep pneumonia. Gram-positive bacilli (rods) subdivide according to their ability to produce spores.
What is a gram positive spore-forming rod?
Clostridia is a gram-positive spore-forming rod consisting of C. tetani, C. botulinum, C. perfringens, and C. difficile. C. difficileis often secondary to antibiotic use (clindamycin/ampicillin), PPI use, and recent hospitalization. Treatment involves primarily with oral vancomycin.
What is Listeria monocytogenesis?
Listeria monocytogenesis a gram-positive rod acquired by the ingestion of cold deli meats and unpasteurized dairy products or by vaginal transmission during birth. Listeriacan cause neonatal meningitis, meningitis in immunocompromised patients, gastroenteritis, and septicemia. Treatment includes ampicillin.
Do Gram positive bacteria have blue dye?
Although gram-negative organisms classically have an outer membrane, they have a thinner peptidoglycan layer, which does not hold the blue dye used in the initial dying process. Other information used to differentiate bacteria is the shape. Gram-positive bacteria comprise cocci, bacilli, or branching filaments. NCBI.
What is Gram positive?
Gram-Positive Bacteria Explained in Simple Terms. Gram-positive bacteria are bacteria with thick cell walls. In a Gram stain test, these organisms yield a positive result. The test, which involves a chemical dye, stains the bacterium’s cell wall purple. Gram-negative bacteria, on the other hand, don’t hold the dye.
What is a gram positive bacillus?
Gram-positive bacilli. When gram-positive bacteria are shaped like rods, they’re known as bacilli. Most of these bacteria are typically found on the skin, but some can cause serious medical conditions. Gram-positive bacilli are further categorized based on their ability to make spores.
What bacteria can form spores?
Spore-forming. Bacillus and Clostridia bacteria can form spores, which help the bacteria survive in harsh conditions like high heat. These bacilli are subdivided based on their need for oxygen. Bacillus bacteria need oxygen to survive (aerobic), while Clostridia bacteria don’t ( anaerobic ).
Why do Gram positive bacteria stain purple?
Under a microscope, gram-positive bacteria appear purple-blue because their thick peptidoglycan membrane can hold the dye. The bacteria is called gram-positive due to the positive result. Gram-negative bacteria stain pink-red. Their peptidoglycan layer is thinner, so it doesn’t retain the blue color.
What is Gram stain test?
Gram stain testing is a method for classifying bacteria based on their cell wall. It allows scientists to determine whether an organism is gram-positive or gram-negative. The test, which uses a microscope, was created by Hans Christian Gram in 1884.
What color does Gram negative bacteria stain?
The test, which involves a chemical dye, stains the bacterium’s cell wall purple. Gram-negative bacteria, on the other hand, don’t hold the dye. They stain pink instead. Though both groups of bacteria can cause disease, they require different treatments.
How thick is peptidoglycan?
In gram-positive bacteria, the peptidoglycan is 40 to 80 layers thick. Certain surface appendages. Gram-positive bacteria may have flagella, which help them move. They rarely have hair-like structures called pili.
Can gram negative diplococci cause pneumonia?
Human respiratory tract infections caused by gram- negative diplococci continue to remain significant issues in health care. Although not addressed as frequently as the classical diplococcal pneumonia, the gram-positive Streptococcus pneumoniae (the pneumococcus), infections due to Neisseria meningi …. Human respiratory tract infections caused by ...
Is a gram negative diplococcus gram positive?
Although not addressed as frequently as the classical diplococcal pneumonia, the gram-positive Streptococcus pneumoniae (the pneumococcus), infections due to Neisseria meningitidis (the meningococcus), ...
