Full Answer
What do inflamed cells in urine mean?
Factors that make this more likely include:
- Age. Many men older than 50 have occasional hematuria due to an enlarged prostate gland.
- A recent infection. Kidney inflammation after a viral or bacterial infection (post-infectious glomerulonephritis) is one of the leading causes of visible urinary blood in children.
- Family history. ...
- Certain medications. ...
- Strenuous exercise. ...
What cells cause the inflammatory response?
- Cystitis: an inflammation of the bladder
- Bronchitis: an inflammation of the bronchi
- Otitis media: an inflammation of the middle ear
- Dermatitis: a disease where the skin is inflamed
What cells are involved in inflammation?
There are several types, with some recognised in different conditions:
- Langhans Giant Cell in tuberculosis.
- Foreign-body Type Giant Cell.
- Touton Giant Cell in fat necrosis.
What are the types of inflammatory cells?
- Usually > 90% neutrophils.
- Septic, suppurative inflammation is the term used if bacteria are seen.
- You can't assume that something is non-septic just because bacteria are not seen cytologically. ...
- More than one type of inflammatory cell is present.
- Usually comprised predominantly of neutrophils with 10-50% macrophages and/or lymphocytes.

What shows the inflammation in urine test?
Microscopic evidence of white blood cells (WBCs) merely provides evidence of urinary tract inflammation or degeneration. The most common causes include renal inflammation or degeneration, ureteral infection or obstruction, and cystitis.
How do you get rid of inflammation in the urinary tract?
Cystitis can be painful, but you can take steps to ease your discomfort:Use a heating pad. A heating pad placed on your lower abdomen can soothe and possibly minimize feelings of bladder pressure or pain.Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of fluids to keep yourself hydrated. ... Take a sitz bath.
Does abnormal cells in urine mean cancer?
Abnormal cells in the urine may be a sign of inflammation of the urinary tract or cancer of the kidney , ureters, bladder, or urethra.
Can inflammation cause urinary problems?
When you have interstitial cystitis, the walls of your bladder become irritated and inflamed (shown right), compared with those of a normal bladder (shown top). Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-STISH-ul sis-TIE-tis) is a chronic condition causing bladder pressure, bladder pain and sometimes pelvic pain.
What are the 5 classic signs of inflammation?
Based on visual observation, the ancients characterised inflammation by five cardinal signs, namely redness (rubor), swelling (tumour), heat (calor; only applicable to the body' extremities), pain (dolor) and loss of function (functio laesa).
What are the symptoms of inflammation of the bladder?
Bladder infections can lead to inflammation of the bladder (cystitis). Symptoms include pain and burning with urination, increased frequency of urination and sometimes abdominal pain. The inflammation usually improves after a course of antibiotics.
What are the warning signs of bladder cancer?
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms and SignsBlood or blood clots in the urine.Pain or burning sensation during urination.Frequent urination.Feeling the need to urinate many times throughout the night.Feeling the need to urinate, but not being able to pass urine.Lower back pain on 1 side of the body.
What urine test shows cancer?
Urine cytology is a test to look for abnormal cells in your urine. It's used with other tests and procedures to diagnose urinary tract cancers, most often bladder cancer. Your doctor might recommend a urine cytology test if you have blood in your urine (hematuria).
How do you rule out bladder cancer?
A sample of your urine is analyzed under a microscope to check for cancer cells in a procedure called urine cytology. Imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as computerized tomography (CT) urogram or retrograde pyelogram, allow your doctor to examine the structures of your urinary tract.
Does bladder inflammation go away?
There is no cure for bladder pain syndrome. But your doctor will try different treatments to figure out how to improve your symptoms. The first treatment many people try includes steps you can take at home. Sometimes, by changing what you eat, you can make your symptoms go away.
How long does it take for bladder inflammation to go away?
In most cases, cystitis will resolve itself after 3 days . If a person has cystitis that does not begin to ease within 3 days, they should contact a doctor for medical advice.
Can you have bladder inflammation without infection?
Interstitial cystitis (IC)/bladder pain syndrome (BPS) is a chronic bladder health issue. It is a feeling of pain and pressure in the bladder area. Along with this pain are lower urinary tract symptoms which have lasted for more than 6 weeks, without having an infection or other clear causes.
What is the most common type of inflammation in the urinary system?
Inflammation is one of the most frequently diagnosed lesions of the urinary bladder. Inflammation may be acute, suppurative, chronic, chronic-active, or granulomatous, depending on the predominant cell type or cell response involved. In acute inflammation, the predominant infiltrating cell is the neutrophil, though fewer macrophages and lymphocytes may also be present. There may also be evidence of edema and hyperemia. The neutrophil is also the predominant cell type in suppurative inflammation; however, the neutrophils are aggregated, and many of them are degenerative (suppurative exudate). Lymphocytes predominate in chronic inflammation; lymphocytes also predominate in chronic-active inflammation, but there are also a significant number of neutrophils—both lesions contain macrophages. Diagnosis of granulomatous inflammation, another form of chronic inflammation, requires the presence of a significant number of aggregated, large, activated macrophages, epithelioid macrophages, or multinucleated giant cells.
Which cell type is most likely to be present in acute inflammation?
In acute inflammation, the predominant infiltrating cell is the neutrophil, though fewer macrophages and lymphocytes may also be present. There may also be evidence of edema and hyperemia. The neutrophil is also the predominant cell type in suppurative inflammation; however, the neutrophils are aggregated, and many of them are degenerative ...
What does it mean when you have yeast in your urine?
Antibiotics can usually treat these conditions. Cells that appear abnormal in your urine may also indicate inflammation in the urinary tract or cancer of the bladder, kidney, ureter, or urethra.
What is the procedure for cytology of urine?
What is the procedure for urine cytology? There are two ways to obtain the cells needed for a cytology exam. Your doctor can collect a sample during a cystoscopy, which is an examination of the inside of the bladder, or you can provide a clean catch urine sample.
What does a cytology test show?
Your doctor may order a urine cytology exam if you have any of these symptoms: unexplained blood in your urine. burning during urination. persistent pain during urination. The test also monitors those who’ve had urinary tract infections or cancer or who are at high risk for bladder cancer.
What is cytology in a lab?
Cytology is the examination of cells from the body under a microscope. In a urine cytology exam, a doctor looks at cells collected from a urine specimen to see how they look and function. The test commonly checks for infection, inflammatory disease of the urinary tract, cancer, or precancerous conditions. It’s important to note that this test ...
Why do you need a biopsy after urine cytology?
Sometimes a biopsy is necessary after abnormal results from urine cytology to clarify a diagnosis.
How to clean urethra before a urine test?
You will use special cleansing cloths to clean the skin around your urethra prior to the test. You will need to urinate a small amount into the toilet, and then stop the flow of urine. Then you will urinate into the sterile container until reaching the desired level. You may then finish urinating into the toilet.
What is a clean catch urine sample?
Clean catch urine sample. A clean catch urine sample is easy, noninvasive, and carries no risk. Otherwise known as a midstream urine sample, you can do a clean catch urine sample in a doctor’s office or in the comfort of your own home. Your doctor’s office will provide a special container to collect the sample.
Why do we do urine cytology?
Why it's done. Urine cytology is used with other tests and procedures to diagnose cancers of the urinary tract , including: It's generally used for people who have signs or symptoms of urinary tract cancer, such as blood in the urine. Urine cytology can best detect larger and more-aggressive urinary tract cancers.
What does a positive urine cytology test mean?
Positive. A positive result indicates that cancer cells were found in your urine. A urine cytology test can't be used alone to diagnose cancer. If atypical or cancerous cells are detected, your doctor will likely recommend a cystoscopy procedure and a CT scan to further examine your bladder and urinary tract.
What is the male urinary system?
Male urinary system. Your urinary system — which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra — removes waste from your body through urine. Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen, produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. Urine cytology is a test to look for abnormal cells in your urine.
What is the name of the doctor who examines urine?
Your urine sample is sent to a lab for testing by a doctor who specializes in examining body tissues (pathologist). The pathologist analyzes cells from the urine sample under a microscope, notes the types of cells and looks for signs in the cells that might indicate cancer.
Can a urine cytology test detect bladder cancer?
It's used with other tests and procedures to diagnose urinary tract cancers, most often bladder cancer. Your doctor might recommend a urine cytology test if you have blood in your urine (hematuria). For people who've been diagnosed with bladder cancer and have undergone treatment, a urine cytology test can help detect a recurrence.
Who will send urine cytology results to?
Results. The pathologist will send the results of your urine cytology test to your doctor, who will report the results to you. Ask your doctor how long you can expect to wait for your results. Different labs have different ways of describing the results of a urine cytology test.
Is urine cytology dangerous?
Risks. Risks of urine cytology testing depend on how your urine is collected. Most often, people undergoing the test urinate into a sterile container, which carries no risk. Collecting urine by inserting a hollow tube (catheter) into your urethra carries a risk of urinary tract infection.
What are the symptoms of UTI?
Patients with this form of UTI are defined by their presenting symptom complex: symptoms of lower urinary tract inflammation (i.e., dysuria, frequency, urgency, or suprapubic discomfort) in the absence of signs and symptoms of vaginitis (vaginal discharge or odor, pruritus, dyspareunia, external dysuria without frequency, and vulvovaginitis on examination). Therapy for this form of UTI has three objectives: eradication of the lower UTI that is producing symptoms, identification of the minority of patients (∼30%) who have silent renal infection and require more intensive therapy, and eradication of uropathogenic clones from the vaginal and gastrointestinal reservoirs that could produce rapid reinfection of the urinary tract.52,53
What causes proteinuria in the prerenal system?
Other prerenal causes of proteinuria include increases in normal inflammatory proteins (e.g. , from chronic inflammation or infection) or abnormal protein ( e.g., from myeloma). Postrenal protein increases are most typically the result of UTI or inflammation.
What causes white blood cells in cows?
The most common causes include renal inflammation or degeneration, ureteral infection or obstruction, and cystitis. Contamination of free-catch samples by normal lochia or abnormal uterine or vaginal discharges is common in postpartum cows. The finding of 1 to 5 WBCs per high-power field should be considered normal in urine samples obtained from cattle. Tubular degeneration caused by nephrosis or nephritis must be differentiated from lower urinary tract infection (UTI) or inflammation as either may have an increased number of leukocytes in the urine. Gross pyuria is observed most commonly in pyelonephritis or cystitis in cattle. Urine samples demonstrated to have gross or microscopic pyuria should be submitted for bacterial culture; ideally, such samples should be obtained with aseptic preparation and bladder catheterization. In calves, pyuria and cystitis are commonly associated with umbilical remnant infection.
Is proteinuria a marker of renal injury in cats?
124,211 Preliminary studies also suggest that proteinuria may predict the development of azotemia in normal geriatric cats. It is unclear whether proteinuria is a marker or a mediator of renal injury in the cat, and the pathologic mechanisms remain unclear. 210 As with Cr, the source of the proteinuria must be determined before attributing significance to the value. Additionally, persistence of proteinuria must be confirmed because transient physiologic events (e.g., fever, excessive physical activity) may cause nonrenal proteins to spill into the urine. Other prerenal causes of proteinuria include increases in normal inflammatory proteins (e.g., from chronic inflammation or infection) or abnormal protein (e.g., from myeloma). Postrenal protein increases are most typically the result of UTI or inflammation. Once persistence and renal origin have been verified, localizing the protein as being glomerular, interstitial, or tubular remains difficult. However, because the latter two are less likely to cause significant proteinuria, the veterinarian can assume that UPC elevations are associated with alterations in glomerular integrity or hyperfiltration associated with a decline in the number of functional nephrons. 143 Because the significance of microalbuminuria in cats is unclear, UPC remains the test of choice. 97
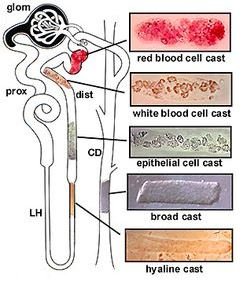
What type of tissue is found in urine?
Types of epithelial cells in urine. Epithelial cells are one of four basic types of animal tissue, which include connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue types generally line the cavities and surfaces of blood vessels and organs throughout the body, including the mucous membranes and urogenital tracts.
Why do I have RBCs in my urine?
RBCs in the urine can be a result of urinary tract or kidney diseases, medications, trauma, intense exercise, or even smoking. White blood cells (WBCs): Finding a few white blood cells in the urine (0-5/HPF) is considered within normal limits and is a typical finding when contaminated with vaginal secretions.
What is a urinalysis test?
A urinalysis is generally the routine test for evaluating urinary tract pathology. If an abnormality is found, further testing may be indicated. Once such additional test is to look at the urine sample under a microscope. This allows for a more detail look at the urinary sediment and the cells that reside therein.
Why do epithelial cells shed?
Epithelial cells have a limited lifespan, which results in them sloughing off to make room for newer cells to take their place. This shedding of cells commonly occurs to the skin and even to various organs of the urinary tract, such as the balder, leading to small amounts of epithelial cells to be found in the urine. If the level of epithelial cells was to be increased or originate from the kidneys, it could signal an abnormality that is worth investigating.
How to keep kidneys running?
Fluids: Drinking plenty of water is a great solution overall to keep the kidneys running properly. Staying hydrated helps to improve urine output, which in turn can help flush out any bacteria present and clear out accumulated waste products. It is recommended to drink between eight to ten glasses of water each day.
What is the name of the disorder where the kidneys are damaged?
Nephrotic syndrome: A kidney disorder characterized by kidney damage and the excretion of too much protein in the urine. It is usually caused by damage to the clusters of small blood vessels in the kidneys normally responsible for filtering out waste and excess water from your blood.
What is squamous epithelial cells?
Squamous: Also known as flat cells due to their shape and they typically come from vaginal or distal urethral epithelium. Finding squamous epithelial cells in urine at the normal range is generally not of any concern. However, having high levels could be indicative of possible vaginitis or urethritis.
What causes inflammation in the urinary tract?
Inflammation in your body triggers the release of leukocytes. That inflammation can come from an injury, infection, or disease. Interstitial nephritis and cystitis are two conditions that cause inflammation in your urinary tract.
What does it mean when you have too many leukocytes in your urine?
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Kidney Stones. Inflammation. If your doctor tests your urine and finds too many leukocytes, it could be a sign of infection . Leukocytes are white blood cells that help your body fight germs. When you have more of these than usual in your urine, it's often a sign of a problem somewhere in your urinary tract.
What does it mean when you pee more?
Cystitis is inflammation of your bladder, often from a urinary tract infection, but the bladder can also be inflamed without infection ( interstitial cystitis ). If you have either one of these problems, you may notice symptoms like: Increased urge to pee. Peeing more often than usual. Blood in your urine. Fever.
How do you know if you have a UTI?
More than half of women and about 1 in 5 men will get a UTI at some point in their lives. Signs that you have one are: 1 Pain or burning when you pee 2 You need to go more often than usual 3 Cloudy or foul-smelling urine 4 Pain in your belly, back, or side 5 Nausea and vomiting
What are the symptoms of interstitial nephritis?
Blood in your urine. Fever. Nausea and vomiting. Keep in mind that if you have interstitial nephritis, there often aren't any symptoms until the disease is very advanced. Call your doctor if you have these symptoms. If an infection is to blame, you'll get antibiotics.
How long does it take for a UTI to clear up?
Pain in your belly, back, or side. Nausea and vomiting. Your doctor can treat a UTI with antibiotics. A few days to a week on these drugs should clear up the infection. How long you stay on the medicine depends on how severe your infection is, how often you get UTIs, and any other medical problems you have.
What are the stones that block the flow of urine?
Kidney Stones. Kidney stones are crystals that form when calcium and other minerals build up in your urine. They can be as small as a pea or as big as a golf ball. Larger kidney stones can block the flow of urine. Kidney stones cause symptoms such as: Sharp pain in your belly, side, back, or groin.
