Key Takeaways: Isotopes
- Isotopes are samples of an element with different numbers of neutrons in their atoms.
- The number of protons for different isotopes of an element does not change.
- Not all isotopes are radioactive. Stable isotopes either never decay or else decay very slowly. ...
- When an isotope decays, the starting material is the parent isotope. The resulting material is the daughter isotope.
How do you identify isotopes?
How do you identify isotopes? Look up at the atom on the periodic table of elements and find out what its atomic mass is. Subtract the number of protons from the atomic mass. This is the number of neutrons that the regular version of the atom has. If the number of neutrons in the given atom is different, than it is an isotope.
What are the most common uses for isotopes?
Uses of Unstable Isotopes
- Carbon dating. Every organic material is composed of a certain percentage of carbon. ...
- As tracers. Radioisotopes of phosphorus are used to trace the uptake of phosphorus in plants. ...
- Agriculture. ...
- Winery. ...
- Medical applications of radioisotopes. ...
What are the examples of isotopes and their uses?
Examples of isotopes are O-16, O-17 and O-18. These isotopes can be used in forensics, but are even more accurate in their ability to tell whether a certain rock originated on Earth, Mars or even an asteroid. Oxygen isotopes can also tell how the oceans have been heating up or cooling down over eons. Carbon has 15 isotopes, and carbon-14 is ...
How do you find isotopes?
How do you determine isotopes? Subtract the atomic number (the number of protons) from the rounded atomic weight. This gives you the number of neutrons in the most common isotope.

What is an isotope easy definition?
An isotope is one of two or more species of atoms of a chemical element with the same atomic number and position in the periodic table and nearly identical chemical behavior but with different atomic masses and physical properties. Every chemical element has one or more isotopes.
What is an isotope meaning for kids?
Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons. Changing the number of neutrons in an atom does not change the element. Atoms of elements with different numbers of neutrons are called "isotopes" of that element.
What is isotope and example?
Isotope → Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but differ in numbers of neutrons. Isotopes are different forms of a single element. Example - Carbon 12 and Carbon 14 are both isotopes of carbon, one with 6 neutrons and one with 8 neutrons.
How do isotopes work?
An isotope is one of two or more forms of the same chemical element. Different isotopes of an element have the same number of protons in the nucleus, giving them the same atomic number, but a different number of neutrons giving each elemental isotope a different atomic weight.
How do you remember isotopes?
Isotones are atomic species that share the same number of neutrons and differ in the number of protons....A mnemonic that can be used to differentiate isotones from isotopes and isobars is as follows:same Z (number of protons) = isotopes.same A (number of nucleons) = isobars.same N (number of neutrons) = isotones.
Which of the following best describes isotopes?
Which of the following best describes an isotope? Structurally variant atoms, which have the same number of protons (and electrons), but differ in the number of neutrons they contain.
Why isotopes are formed?
Isotopes can either form spontaneously (naturally) through radioactive decay of a nucleus (i.e., emission of energy in the form of alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons, and photons) or artificially by bombarding a stable nucleus with charged particles via accelerators or neutrons in a nuclear reactor.
Why do atoms have isotopes?
Neutrons exist to stabilize the nucleus – without them, the nucleus would consist of nothing but positively-charged protons in close proximity to one another. Because there are different ways of stabilizing the protons, there are different isotopes.
What are atoms kids definition?
Atoms are the smallest building blocks of matter and make up everything around us. Every atom has a center called a nucleus, which is made of particles called protons and neutrons. Electrons move in electron shells around the nucleus. Atoms can bond to one another to form solids, liquids, or gases.
What is ion for kids?
0:348:45What are Ions? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo an ion is an atom or group of atoms with a net positive or negative charge.MoreSo an ion is an atom or group of atoms with a net positive or negative charge.
What is isotopes quizlet?
isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of an element with the normal number of protons and electrons, but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes have the same atomic number, but different mass numbers.
What does an isotope look like?
3:567:55What are Isotopes? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo this is carbon-12 6 plus 7 protons and neutrons of 13 here 6 plus 8 is carbon 14 here so that'sMoreSo this is carbon-12 6 plus 7 protons and neutrons of 13 here 6 plus 8 is carbon 14 here so that's how we distinguish between these different isotopes. Different types of carbon.
What is an isotope kid definition?
Isotopes are different forms of atoms of an element that have the same number of protons and electrons as each other, but have a different number o...
What is isotope explain with example?
Isotopes are different species of atoms of an element that have different atomic masses. For example, there are three isotopes of carbon: Carbon-12...
What are 2 examples of isotopes?
Some examples of isotopes include: - Isotopes of hydrogen: Hydrogen-1 (protium), Hydrogen-2 (deuterium), and Hydrogen-3 (tritium) - Isotopes of c...
How to determine the number of neutrons in an element?
The number of neutrons can be determined by taking the difference between the atomic mass and the atomic number. The atomic masses of the elements that are reflected in the periodic table are calculated from averages of the different isotopes and their abundance.
What is the difference between isotopes and neutrons?
Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but that have a different number of neutro ns. Since the atomic number is equal to the number of protons and the atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons, we can also say that isotopes are elements with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. Let us take a look at an example.
How to determine neutrons in the periodic table?
The number of neutrons can be determined by taking the difference between the atomic mass and the atomic number. The atomic masses of the elements that are reflected in the periodic table are calculated from averages of the different isotopes and their abundance. There are two types of isotopes: stable and radioactive.
How to find neutrons in hydrogen?
The number of neutrons can be calculated by calculating the difference between the atomic mass and atomic number.
How are cosmogenic isotopes formed?
Cosmogenic isotopes are formed when the atmosphere reacts with the rays emitted from stars or when geological materials on the Earth's surface are irradiated by cosmic rays directly. Carbon-14, chlorine-36 and hydrogen-3, also known as tritium, are all cosmogenic isotopes.
Why are radioactive isotopes useful?
They are typically useful when performing experiments in the environment and in the field of geochemistry. These isotopes can help determine the chemical composition and age of minerals and other geologic objects.
What are elements made of?
Atoms and elements are made of protons, neutrons and electrons. The nucleus is made of protons and neutrons, and the electrons surround the nucleus, as shown in the illustration below. The sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons is equal to the atomic mass.
How are isotopes identified?
It does, however, change the mass of the element. Isotopes are identified by their mass, which is the total number of protons and neutrons. There are two ways that isotopes are generally written.
What is the name of the isotope of hydrogen that has twice the mass of normal hydrogen?
Deuterium (the hydrogen isotope with one neutron) can form water with oxygen. This is called "heavy water" as deuterium has twice the mass of normal hydrogen (protium).
What determines the atomic number of an element?
The number of protons determines the atomic number of the element. Each atom also has the same number of electrons as protons . What is an isotope? Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons.
How to write isotopes?
There are two ways that isotopes are generally written. They both use the mass of the atom where mass = (number of protons) + (number of neutrons). The first way is to put the mass as a superscript before the symbol of the element: Hydrogen is the only element where the isotopes are given specific names.
Which element has zero neutrons?
Hydrogen. Hydrogen is the only element where the isotopes are given specific names. Common hydrogen, which has zero neutrons, is called protium. Hydrogen with one neutron is called deuterium and hydrogen with two neutrons is called tritium. See the picture at the top of the page.
Which element has the fewest number of isotopes?
All elements have a number of isotopes. Hydrogen has the fewest number of isotopes with only three. The elements with the most isotopes are cesium and xenon with 36 known isotopes. Some isotopes are stable and some are unstable.
How many elements have one stable isotope?
Twenty-six elements only have one stable isotope. These elements are called monoisotopic.
How Are Isotopes Named?
Each isotope has a long formal name and a shorter nickname, just like William. But both of these names are based on the isotope's mass.
How many neutrons does carbon 14 have?
Carbon-14 is an example of a radioactive isotope of the element carbon. Carbon-14 starts out with six protons and eight neutrons. Over time, carbon-14's nucleus starts to decay and so do its particles. If one of carbon-14's neutrons decays into a proton, it changes the isotope from carbon-14 to nitrogen-14, a stable isotope with seven protons and seven neutrons.
What are apples like?
These apples are a lot like the isotopes found in chemistry. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons. The number of protons in an atom can tell you what element it is. Atoms with one proton are atoms of the element hydrogen, just like all atoms with two protons are atoms ...
Why are radioactive isotopes unstable?
Radioactive isotopes have unstable nuclei that breakdown causing the isotope to decay into different elements over time. As isotopes decay, they give off energy in the form of radiation, so we say that they are radioactive.
How do you calculate the mass of an atom?
The mass of an atom, also known as its atomic mass, is calculated by adding the number of protons and neutrons in the atom.
What are the three types of radiation?
The three types of radiation are named for the first three letters of the Greek alphabet and are: Alpha emission: Consist of two protons and two neutrons. Beta emission: These are high speed electrons. They have more energy than alpha particles. Gamma radiation: This is pure energy that is emitted from decay.
What is the purpose of radioisotopes?
Radioisotopes are used for determining when something was formed. Carbon-14 is used to determine when a living organism died because, while it lived, Carbon-14 that decayed to Carbon-12 was replaced. When it died, decay occurred without replacement. The rate of decay is constant and known.
What is the mass number of an isotope with 6 protons and 6 neutrons?
For example, an isotope with 6 protons and 6 neutrons is carbon-12 or C-12. An isotope with 6 protons and 7 neutrons is carbon-13 or C-16. Note the mass number of two isotopes may be the same, even though they are different elements. For example, you could have carbon-14 and nitrogen-14. The mass number may be given in the upper left side ...
How many isotopes are there in the periodic table?
There are 250 isotopes of the 90 naturally occurring elements and there are over 3,200 radioactive isotopes, some of which are natural and some synthetic. 1 Every element on the periodic table has multiple isotope forms.
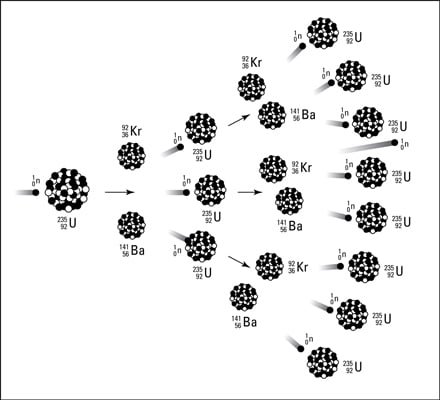
What is the initial isotope of a radioactive reaction?
When radioisotopes undergo radioactive decay, the initial isotope may be different from the resulting isotope. The initial isotope is called the parent isotope, while the atoms produced by the reaction are called daughter isotopes. More than one type of daughter isotope may result.
What is 131 isotope?
An Introduction to Isotopes. Iodine 131 (I-131) is a radioactive isotope used for hyperthyroidism treatment and is stored in a lead box. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
Which isotope has the most protons?
With the exception of hydrogen, the most abundant isotopes of the natural elements have the same number of protons and neutrons. The most abundant isotope of hydrogen is protium, which has one proton and no neutrons.
What is the half life of bismuth 209?
Bismuth-209 is a stable radioactive isotope that undergoes alpha-decay but has a half-life of 1.9 x 10 19 years (which is more than a billion times longer than the estimated age of the universe). Tellurium-128 undergoes beta-decay with a half-life estimated to be 7.7 x 10 24 years.
Why are isotopes different from each other?
The physical properties of isotopes are different from each other because these properties often depend on mass. This difference may be used to separate isotopes of an element from each other by using fractional distillation and diffusion.
Why are isotopes important?
Isotopes are needed for research, commerce, medical diagnostics and treatment, and national security. However, isotopes are not always available in sufficient quantities or at reasonable prices. The DOE Isotope Program addresses this need. The program produces and distributes radioactive and stable isotopes that are in short supply, including byproducts, surplus materials, and related isotope services. The program also maintains the infrastructure required to produce and supply priority isotope products and related services. Finally, it conducts research and development on new and improved isotope production and processing techniques.
How many protons are in carbon?
The number of protons in a nucleus determines the element’s atomic number on the Periodic Table. For example, carbon has six protons and is atomic number 6. Carbon occurs naturally in three isotopes: carbon 12, which has 6 neutrons (plus 6 protons equals 12), carbon 13, which has 7 neutrons, and carbon 14, which has 8 neutrons. Every element has its own number of isotopes.
Which element has the same number of protons and neutrons?
Hydrogen and its two naturally occurring isotopes, deuterium and tritium. All three have the same number of protons (labeled p+) but different numbers of neutrons (labeled n). A family of people often consists of related but not identical individuals. Elements have families as well, known as isotopes. Isotopes are members of a family of an element ...
What is a family of people?
A family of people often consists of related but not identical individuals. Elements have families as well, known as isotopes. Isotopes are members of a family of an element that all have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The number of protons in a nucleus determines the element’s atomic number on the Periodic Table.
What is DOE Explains?
Scientific terms can be confusing. DOE Explains offers straightforward explanations of key words and concepts in fundamental science. It also describes how these concepts apply to the work that the Department of Energy’s Office of Science conducts as it helps the United States excel in research across the scientific spectrum.
Which element has two neutrons?
Hydrogen is the only element whose isotopes have unique names: deuterium for hydrogen with one neutron and tritium for hydrogen with two neutrons.
What are the two main types of isotopes?
There are two main types of isotopes: stable and unstable (radioactive).
What are isotopes and carbon ratios?
An isotope is an atom of an element that naturally occurs with a different number of neutrons. For example, carbon most often has an atomic number of 12 (6 protons and 6 neutrons) and is labeled by scientists as carbon-12 or 12C.
Have carbon ratios shifted?
Before humans began burning fossil fuels, the carbon ratios naturally shifted about 0.03 percent over a couple thousand years. Over the past 150 years (since humans began burning fossil fuels), the carbon isotope signature of the atmosphere has shifted more than 0.15 percent.
About the book author
Alecia M. Spooner teaches Earth and Environmental Sciences at a community college and enjoys developing active-learning science curriculums for adults. Alecia is also the author of Geology For Dummies.
What are the two things that are so similar that it can't be coincidence?
Planets revolving around a star in a solar system, and electrons revolving around a nucleus in an atom ... the two things are so similar that it can't be mere coincidence.
What is the mass number of an element?
(*) The mass number of an element is the number of (protons + neutrons) in the nucleus, as stated above.#N#The key words in the above definition are "mass" and "nucleus," and you'll see why in a moment.#N#The "mass number" is alternatively called the "atomic mass number" and the "nucleon number," for two self-defining reasons:#N#1) It's called the "atomic mass number," as opposed to simply the "mass number," because it represents nearly the entire mass of the entire atom.#N#2) It's called the "nucleon number" because both protons and neutrons reside inside the nucleus of an atom.#N#A nucleon is defined as "any subatomic particle (i.e. a proton or a neutron) that resides in the atomic nucleus ."#N#Both protons and neutrons are nucleons, but electrons aren't, because electrons revolve around, and reside outside of, the atomic nucleus.#N#The mass number of an element is the number of nucleons in the nucleus.#N#Reading 1) and 2), you might deduce that protons and neutrons have a LOT more mass than electrons, and you'd be correct. How much more mass?#N#If a neutron has a mass of 1, then a proton has a mass of nearly .999, but a revolving electron has a negligible mass of only about .0005 - only 1/2000th as much as a proton or a neutron.#N#This is why nearly 100% of the atomic mass is found inside the nucleus.#N#If you go back and read every sentence in both of these posts, it should all be readily understandable, even trivial: It's just a matter of memorizing a few basic terms and their corresponding definitions, all of which are extremely simple.#N#You now know what an isotope, atomic number, mass number, and nucleon are.#N#You now know that the nucleus contains virtually the entire mass of an atom.#N#This thread could be titled, "Things I learned in fifth grade, but then forgot."
How many protons and neutrons are in carbon?
For example, Carbon (with an atomic number of 6) is normally the isotope C-12, with 6 protons + 6 neutrons.
What is the meaning of isotope?
An isotope ( iso - "the same," tope = "place") is a variant.
Elements of elements
When talking about chemistry, the term "elements" does not refer to water, air, fire, or earth. Instead, elements are the “ingredients” that make up the water, air, fire, or earth. The following analogy may help you understand the differences between an element, molecule, and compound.
Inside the atom: Protons and neutrons
Inside the nucleus (core) of the atom are two kinds of particles (pieces of matter). They are called subatomic particles because they are smaller than the atom ( sub = less, lower; as in subscript). These subatomic particles (pieces of an atom) include protons, which are positively charged, and neutrons, which are neutral.
Outside the atom: Electron shells
Atoms are surrounded by electrons, which are negatively charged. Just as batteries need to have the positive and negative poles together to function, an atom is held together (so it can function) by the pull between its positive core (nucleus) and its negative electrons.