
Kinship Terms and Concepts
- Address, Terms of Kin terms used in speaking to a kinsman or kinswoman. ES:12
- Adelphic Polyandry “The marriage of a woman to two or more brothers. Syn. ...
- Affinity “Relationship by marriage ties. ...
- Agamy “The lack of any rule in regard to marriage within or without of a group; it denotes absence of marriage regulations on the part of a social unit.” ...
- Agnatic ...
- Alliance ...
- Alter ...
- Amilateral ...
Full Answer
How to pronounce kinship?
Here are 4 tips that should help you perfect your pronunciation of 'kinship':
- Break 'kinship' down into sounds : [KIN] + [SHIP] - say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them.
- Record yourself saying 'kinship' in full sentences, then watch yourself and listen. ...
- Look up tutorials on Youtube on how to pronounce 'kinship'.
What are the types of kinship system?
Types of Kinship:
- (i) Affinal Kinship: ADVERTISEMENTS: ...
- (ii) Consanguineous Kinship: The bond of blood is called consanguineous kinship. ...
- (i) Classificatory System: ...
- (ii) Descriptive System: ...
- (i) Avoidance: ...
- (ii) Joking Relationship: ...
- (iii) Teknonymy: ...
- (iv) Avunclate:
What is kinship and what are the basis for kinship?
The bond of blood or marriage which binds people together in group is called kinship. According to the Dictionary of Anthropology, kinship system includes socially recognized relationships based on supposed as well as actual genealogical ties. These relationships are the result of social interaction and recognized by society.
What is the definition of the term kinship?
Noun: 1. kinship - a close connection marked by community of interests or similarity in nature or character; "found a natural affinity with the immigrants"; "felt a deep kinship with the other students"; "anthropology's kinship with the humanities"
What is terminologies as a kinship?
Kinship terminologies include the terms of address used in different languages or communities for different relatives and the terms of reference used to identify the relationship of these relatives to ego or to each other.
What are the three types of kinship terminology?
TypesConsanguineal: This kinship is based on blood—or birth: the relationship between parents and children as well as siblings, says the Sociology Group. ... Affinal: This kinship is based on marriage. ... Social: Schneider argued that not all kinship derives from blood (consanguineal) or marriage (affinal).
What is the importance of kinship terminologies?
Kinship provides continuity between the generations. Socialization of child and initial child care is done in a kinship unit. The transference of property and social positions from one generation to the other takes place in kin groups. Kinship defines a universe of persons on whom to depend in normal routine of life.
Why are kinship terminologies important to anthropologists?
it provides an objective, universal perspective on how people are related to one another. B. kinship ties are important to the people anthropologists study; they are a key component of people's everyday social relations.
What are the 5 types of kinship?
According to Dr. Dubey, there are eight such primary kins. They are husband-wife, father-son, mother- daughter, father-daughter, mother-son, younger-elder brothers, younger-elder sisters and sister-brother.
What is kinship and example?
The definition of kinship is a family relationship or other close relationship. An example of kinship is the relationship between two brothers.
What is the most common type of kinship?
In bilateral descent (also referred to as bilineal descent), an individual's kinship is traced through both mother's and father's lines. This is the most common form of descent practiced in the United States today.
What are three major aspects of an individual that are revealed in kinship terms?
In addition to specifying persons in this manner, kinship terms define the biological or quasi-biological relationship between the persons, essentially three in number: (1) biological generation, Le., parent, child, and the deriva- tive “child of my parent” or sibling; (2) mating or marriage, and (3) accidentals ( ...
What is primary secondary and tertiary kinship?
The primary kins of our secondary kins or secondary kins of our primary kins are known as our tertiary kins or third degree kins. For example, your brother-in-law is your secondary kin and his wife or children who are his primary kins become your tertiary kin. These are 151 types of tertiary kins.
What are the types of primary kinship?
Primary Kinship: There are basically eight primary kins—wife father son, father daughter mother son, wife; father son, father daughter, mother son, mother daughter; brother sister; and younger brother/sister older brother/sister.
What is the difference between kinship and classificatory?
He proposed to describe kinship terms and terminologies as either descriptive or classificatory. When a descriptive term is used , it can only represent one type of relationship between two people, while a classificatory term represents one of many different types of relationships.
What is the seventh type of terminological system?
Floyd Lounsbury described a possible seventh, Dravidian, type of terminological system; there is on-going discussion on whether this system is a sub-type of Iroquois or whether it is a distinct system that had been conflated with Iroquois in Morgan’s typology of kin-term systems. Both systems distinguish relatives by marriage from relatives by descent, although both are classificatory categories rather than being based on biological descent. The basic idea is that of applying an even/odd distinction to relatives that takes into account the gender of every linking relative for ego’s kin relation to any given person. A MFBD (C), for example, is a mother’s father’s brother’s daughter’s child. If each female link (M,D) is assigned a 0 and each male (F,B) a 1, the number of 1s is either even or odd; in this case, even. However, variant criteria exist. In a Dravidian system with a patrilineal modulo -2 counting system, marriage is prohibited with this relative, and a marriageable relative must be modulo-2 odd. There exists also a version of this logic with a matrilineal bias. Discoveries of systems that use modulo-2 logic, as in South Asia, Australia, and many other parts of the world, marked a major advance in the understanding of kinship terminologies that differ from kin relations and terminologies employed by Europeans.
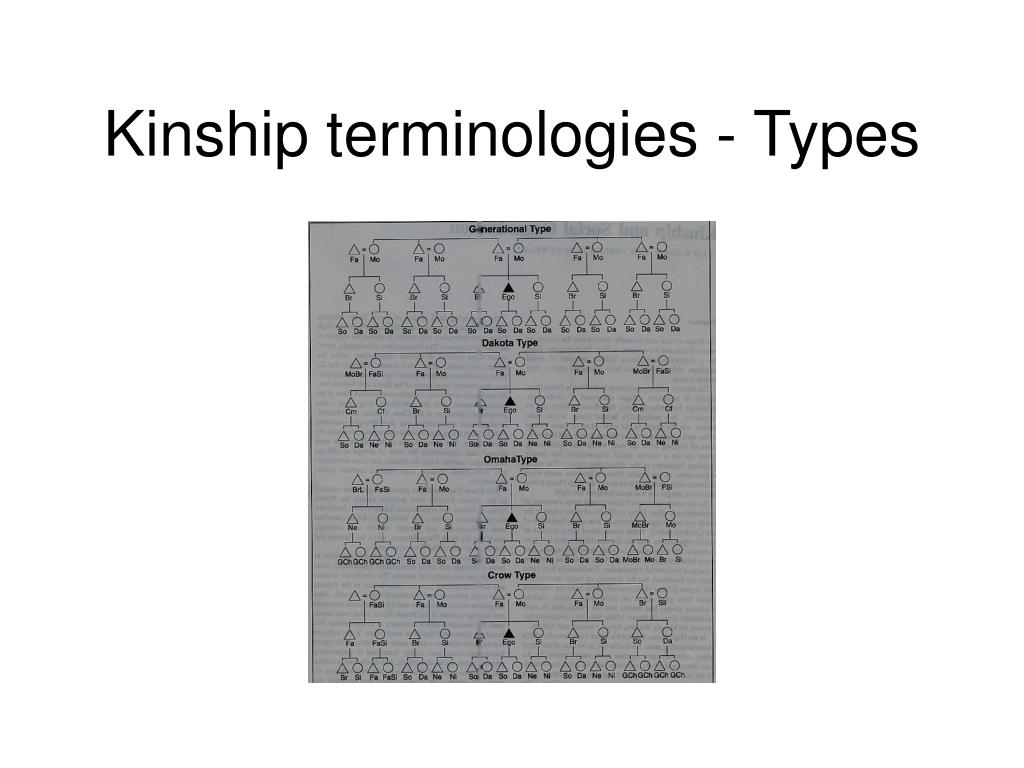
How many kinship terminologies did Morgan identify?
Armed with these different terms, Morgan identified six basic patterns of kinship terminologies:
What is kinship in a language?
Kinship terminology is the system used in languages to refer to the persons to whom an individual is related through kinship. Different societies classify kinship relations differently and therefore use different systems of kinship terminology; for example, some languages distinguish between consanguine and affinal uncles ( i.e. the brothers of one's parents and the husbands of the sisters of one's parents, respectively), whereas others have only one word to refer to both a father and his brothers. Kinship terminologies include the terms of address used in different languages or communities for different relatives and the terms of reference used to identify the relationship of these relatives to ego or to each other.
What is the ego in a kinship diagram?
^ The "ego" is who the person is kin to. In a kinship diagram, the ego is the family member in the center that the others are 'mother', 'father', 'sister', 'brother', 'son', 'daughter' etc. to.
What do Chiricahua children call their grandmother?
Other languages, such as Chiricahua, use the same terms of address for alternating generations. So Chiricahua children (male or female) call their paternal grandmother -ch’iné, and likewise this grandmother will call her son's children -ch’iné. Similar features are seen also in Huichol, some descendant languages of Proto-Austronesian (e.g. Fordata, Kei, and Yamdena ), Bislama, and Usarufa. Terms that recognize alternating generations and the prohibition of marriage within one's own set of alternate generation relatives (0, ±2, ±4, etc.) are common in Australian Aboriginal kinship .
What is a first cousin?
A person's male first cousin could be the mother's brother's son , mother's sister's son, father's brother's son, father's sister's son, and so on; English-speaking societies therefore use the word cousin as a classificatory term.
What is kinship in speech?
Kinship terms are words used in a speech community to identify relationships between individuals in a family (or a kinship unit ). This is also called kinship terminology . A classification of persons related through kinship in a particular language or culture is called a kinship system .
What are lexicalized categories?
"Some of the clearest examples of lexicalized categories are words used to refer to people who are members of the same family, or kinship terms. All languages have kinship terms (e.g. brother, mother, grandmother ), but they don't all put family members into categories in the same way.
What does "father" mean in English?
" [T [he English kinship term 'father' is defined to imply a particular biological relationship. Yet in an actual case the term may be used when the biological relationship is not in fact present."#N#(Austin L. Hughes, Evolution and Human Kinship. Oxford University Press, 1988)
Who is Richard Nordquist?
Dr. Richard Nordquist is professor emeritus of rhetoric and English at Georgia Southern University and the author of several university-level grammar and composition textbooks.
Is it "cousin sister" or "brother"?
"It is not uncommon to hear the term cousin sister or cousin brother, a common mistake that Indian speakers of English make since they are unable to say just 'cousin,' which would be too vague since it does not distinguish gender."
What is the mode of analysis used by anthropologists?
In the United States particularly, anthropologists used this mode of analysis in a variety of domains ranging from kinship terminologies to ethnoscience (as with indigenous plant classification schemes). Classification was seen as a key component of the study of meaning and, as such, a central aspect of culture.
What is the culturalist approach to kinship?
Rather than taking the ideological basis of kinship for granted or assuming it to be of less importance than strategic interests related to status and property, Schneider examined kinship as a cultural system that is based in shared symbols and meanings. This form of analysis became known as the culturalist approach.
What was Lévi Strauss's interest in residence?
All these scholars were concerned mainly with structural aspects of residence—the relations between marriage rules, property transfers, and the constitution of domestic groups. Residence also came to the fore in studies that had a different intellectual origin. In the late 1970s Lévi-Strauss returned to kinship, but this time in a less structuralist guise. He became interested in societies in which the most prominent institutions of kinship did not fit the models provided by either descent or alliance theory.
What is kinship in the West?
It was assumed by many practitioners of both disciplines that kinship was far less important as a social institution in the West and that it was clearly separable from political, economic, and religious life. The 20th-century Western family was viewed as an essentially private, domestic institution dominated by women and without wider political significance. Sociological and historical studies of the Western family tended to concentrate on its economic and instrumental aspects, including the transfer of property at marriage and through inheritance, rather than its ideological or experiential qualities. This version of Western kinship was overturned partly by feminist studies, which subjected relations within the household, the control of property, and the concept of privacy to a sustained analytic scrutiny. The notion of the “private” world of the family as a haven from the “public” world of work and competitive economic relations emerged as an ideological construct that was itself a suitable object of analysis.
What is kinship in anthropology?
While British social anthropologists examined the functions of various social rules and institutions and French structuralists used the regularities that underlay those features in a search for the origins of humanity, American cultural anthropologists explored the idea that behaviour is ordered by social categories.
What was the focus of kinship studies in the 1960s?
During the 1960s and ’70s another direction pursued in kinship studies involved the foregrounding of residence and the household as crucial dimensions of kinship. Marriage often entails a change of residence for one or both partners, and this approach reflected a concern with the interaction between property or economic relations and marriage rules. It was also spurred by research on societies in Polynesia and Southeast Asia in which kinship was reckoned bilaterally rather than unilineally. Finally, studies highlighting residential arrangements were more able than previous approaches to incorporate other anthropological concerns such as gender, rules about symbolic and practical divisions of space, inheritance practices, informal domestic relations, and subjective and experiential aspects of place.
What was the economic significance of kinship in the 1970s?
During the 1970s and ’80s some studies highlighted the economic significance of kinship but began to view as central its more instrumental and strategic aspects —that is, the ways that one or a few individuals could use kinship to advance their personal interests.
What is kinship in social life?
Kinship refers to social relationships that may or may not coincide with biological ones. The terms of kinship can, indeed, correspond to true kinship, with social relationships coinciding with the biological ones (consanguinity or affinity). When social relationships only simulate biological ones, the term we use is pseudo-kinship or fictitious kinship. The third type of kinship is a special form of fictitious kinship created through a ritual, such as godparenthood, adoption, or fraternization. The terms of pseudo-, fictitious, and ritual kinship are identical to the ones of real or true kinship.
Why did anthropologists use abbreviations?
Anthropologists invented abbreviated terms for methodological reasons, namely, simplicity and clarity. In both French and English, where fundamental terms of kinship are morphologically unlike each other, we can achieve what anthropologists envisioned. In English, the abbreviations of the terms of kinship consist of the first letter (or sometimes the first two letters) of the terms:
Why do we use descriptive terms?
To eliminate any chance of confusion, we use each of these terms or a combination to describe only one relative. In the kinship systems of Western societies, individuals use descriptive terms wherever specific terms for each and every relative do not exist.
What are the different types of kinship?
H. Morgan and G. P. Murdock, we now use six categories to classify systems of kinship: Eskimo, Hawaiian, Iroquois, Sudan, Crow, and Omaha . The main criterion for classifying a system is how the Ego uses the same term for different relatives. For instance, the kinship system of Western societies belongs to the Eskimo group, where the brothers of the parents are “uncles” and their sisters, “aunts.” In contrast, in societies belonging to the Hawaiian group of classification, the same people are “fathers” and “mothers,” respectively. Using the same term for different relatives entails a significant similarity in the behavior of Ego toward them, for example, the possibility of marriage.
What are the terms of reference and address?
Terms of address are the ones we use from birth (.Ego) to address our kin, such as “Mum” or “Dad.” Terms of reference are the ones we use to refer to our kin in the third party: “my mother,” or “my father.” As these examples demonstrate, terms of address and terms of reference may be identical. Our use of kinship terms depends on how familiar we are with the relatives involved and the ages and genders of these relatives. Both terms of address and terms of reference exist only with respect to one another: “father” or “mother” implies there is a “son” or “daughter” and vice versa.
Where does kinship occur metaphorically?
We may use terms of kinship metaphorically in cases where neither real, fictitious, nor ritual kinship is in place. For example, the inhabitants of the villages Didima, Karakassi, and Loukaïti (in Peloponnesus, Greece) address each other as cousin, referencing their reminiscence of a common ancestry, even when that relationship is distant.
What is an agnate?
An agnate, then, is a person related by patrilineal descent (RK:147).”. DT. “In Roman law agnati were kin who traced their relationship by descent through males only from a common ancestor, who were under the authority of a single paterfamilias, and who resided together. Agnati could be adopted.
What is an ambilateral group?
“Ambilateral is sometimes used in kinship studies to refer to non-unilineal systems in which an individual may choose to align himself with either of his parental groups. R. Firth argues that “The admission to membershilp through descent from either males or females–or both conjoined–shows that the hapu is not a unilateral group of the strict type. It may be called in fact, an ambilateral group, since both parents are eligible for the purposes of kinship affiliation” (R. Firth, Economics of the New Zealand Maori, Wellington, N.Z.:R. E. Owen 1959, p.112).” GK:22.
What is the meaning of "tangible items of value transferred from the groom or groom's group to the bride?
“Tangible items of value transferred from the groom or groom’s group to the bride’s group, the prestation serving to validate the marriage union. Cf. Brideservice, in which the groom contributes labor and/or services to the bride’s group for validatory purposes.” DT. Contra. “dowry”.
What is avoidance relationship?
Avoidance Relationships. “A pattern of complete avoidance of speech and physical contact between relatives. Murdock (1949:273) suggests that such a technique is an aspect of sex regulation in societies where sexual prohibitions are not strongly internalized in enculturation.”.
What is the apex of the triangle of descendants?
The ancestor/ess from whom descent is traced (the “apex” of the triangle of descendants).
How long does a newlywed couple live with the bride's group?
First the newly wed couple lives with the bride’s group for a time (usually for a year or until the birth of the first child), then residence is shifted definitely to the groom’s group. GPM: 17.
What does Alter mean in kinship?
Alter. “The person to whom a relationship is being indicated; thus, in English kinship terminology, “male Ego refers to his FB as “uncle” and Alter reciprocates with “nephew”. DT. Contra. “Ego”.
How does Dani differ from English?
Dani terminology differs from English both in the words used and the categories constructed by them. Often the particular system of categorization gives clues to a culture's priniciples of social organization and construction of social roles.
What is kinship terminology?
Kinship Terminologies. Kin terms constitute a culture's kinship vocabulary, a catalog of the names that are assigned to relatives, e.g., father, mother, uncle, grandson. Different societies of course use different labels to designate their kin; "uncle" is "oncle" in French and "tio" in Spanish.
What is the Dani term for Uncle?
For example, the Dani term that corresponds to "uncle" is "ami". This category includes a person's mother's brother but not his/her father's brother who is called "opaije", the term that is used for "father". Spanish and English use different words for the same categories.

Overview
Kinship terminology is the system used in languages to refer to the persons to whom an individual is related through kinship. Different societies classify kinship relations differently and therefore use different systems of kinship terminology; for example, some languages distinguish between consanguine and affinal uncles ( i.e. the brothers of one's parents and the husbands of the sisters of one's parents, respectively), whereas others have only one word to refer to both a father and h…
Historical view
Anthropologist Lewis Henry Morgan (1818–1881) performed the first survey of kinship terminologies in use around the world. Though much of his work is now considered dated, he argued that kinship terminologies reflect different sets of distinctions. For example, most kinship terminologies distinguish between sexes (the difference between a brother and a sister) and between generations (the difference between a child and a parent). Moreover, he argued, kinshi…
Tri-relational kin-terms
A unique set of kin-terms common in some Australian Aboriginal languages are tri-relational—also called triangular, ternary, triadic and shared kin-terms—which encapsulate a set of relations between three distinct entities. Broadly, there are two kinds of tri-relational kin-terms. The more common is a Dual Propositus Tri-relational Kin-term which has one referent whose relationship is defined with r…
Group/dyadic kin terms and pronouns
Australian Aboriginal languages tend to have extensive vocabularies for denoting kin-relations, including for referring to and addressing dyads and groups based on their relation to one another and/or to the speaker. For example, see below the complete inventory of group kin-terms in Bardi (note that some but not all of these are assessed with respect to the speaker as well and may thus be considered tri-relational dyadic terms:
Relative age
Some languages, such as Kannada, Telugu, Tamil, Turkish, Sinhalese, Chinese (see Chinese kinship), Japanese, Korean, Khmer, Malayalam, Vietnamese, Tagalog (Filipino), Hungarian, Bulgarian, Nepalese, and Nahuatl add another dimension to some relations: relative age. Rather than one term for "brother", there exist, for example, different words for "older brother" and "younger brother". In Tamil, an older male sibling is referred to as aṇṇā and a younger male sibling as thambi, wherea…
Identification of alternating generations
Other languages, such as Chiricahua, use the same terms of address for alternating generations. So Chiricahua children (male or female) call their paternal grandmother -ch’iné, and likewise this grandmother will call her son's children -ch’iné. Similar features are seen also in Huichol, some descendant languages of Proto-Austronesian (e.g. Fordata, Kei, and Yamdena ), Bislama, and Usarufa. Terms that recognize alternating generations and the prohibition of marriage within one's own …
Dravidian
Floyd Lounsbury described a possible seventh, Dravidian, type of terminological system; there is on-going discussion on whether this system is a sub-type of Iroquois or whether it is a distinct system that had been conflated with Iroquois in Morgan’s typology of kin-term systems. Both systems distinguish relatives by marriage from relatives by descent, although both are classificatory categories rather than being based on biological descent. The basic idea is that of …
Abbreviations for genealogical relationships
The genealogical terminology used in many genealogical charts describes relatives of the subject in question. Using the abbreviations below, genealogical relationships may be distinguished by single or compound relationships, such as BC for a brother's children, MBD for a mother's brother's daughter, and so forth.
• B = Brother
Examples and Observations
- "Bailey was the greatest person in the world. And the fact that he was my brother, and I had no sisters to share him with, was such good fortune that it made me want to live a Christian life just t...
- "Two years later a note arrived from one of her daughters relating that Tata had died in childbirth. It was with one of Tata's sons who'd moved to Omaha that Rocco went to live whe…
- "Bailey was the greatest person in the world. And the fact that he was my brother, and I had no sisters to share him with, was such good fortune that it made me want to live a Christian life just t...
- "Two years later a note arrived from one of her daughters relating that Tata had died in childbirth. It was with one of Tata's sons who'd moved to Omaha that Rocco went to live when he was eighteen...
- "My Mom was an illegal alien, born out of wedlock in Mexico . . .. Once I told a neighbor her husband wasn't my real father. I didn't know I wasn't supposed to say this. I was sorry I embarrassed h...
Lexicalized Categories
- "Some of the clearest examples of lexicalized categories are words used to refer to people who are members of the same family, or kinship terms. All languages have kinship terms (e.g. brother, mother, grandmother), but they don't all put family members into categories in the same way. In some languages, the equivalent of the word father is used not only for 'male parent,' but also for …
Kinship Terms in Sociolinguistics
- "One of the attractions that kinship systems have for investigators is that these factors are fairly readily ascertainable. You can, therefore, relate them with considerable confidence to the actual words that people use to describe a particular kin relationship. "There may be certain difficulties, of course. You can ask a particular person what he...
More Difficulties
- "[T[he English kinship term 'father' is defined to imply a particular biological relationship. Yet in an actual case the term may be used when the biological relationship is not in fact present." (Austin L. Hughes, Evolution and Human Kinship. Oxford University Press, 1988)
Kinship Terms in Indian English
- "It is not uncommon to hear the term cousin sister or cousin brother, a common mistake that Indian speakers of English make since they are unable to say just 'cousin,' which would be too vague since it does not distinguish gender." (Nandita Chaudhary, "Mothers, Fathers, and Parents." Semiotic Rotations: Modes of Meanings in Cultural Worlds, ed. by Sunhee Kim Gertz, Jaan Valsi…
Terms of Address and Terms of Reference
Classificatory Terms—Kinship Systems
Descriptive Terms
Abbreviated Terms
Fictitious, Ritual, and Pseudo-Kinship Terminology
- We may use terms of real kinship in social relationships that result from fictitious or ritual kinship. For instance, children who have been breastfed by the same mother are siblings in many societies, but there is usually a more exact definition of this relationship: foster siblings. We may also use similar terms, such as godfather-father in Engli...