What are lipid-derived hormones?
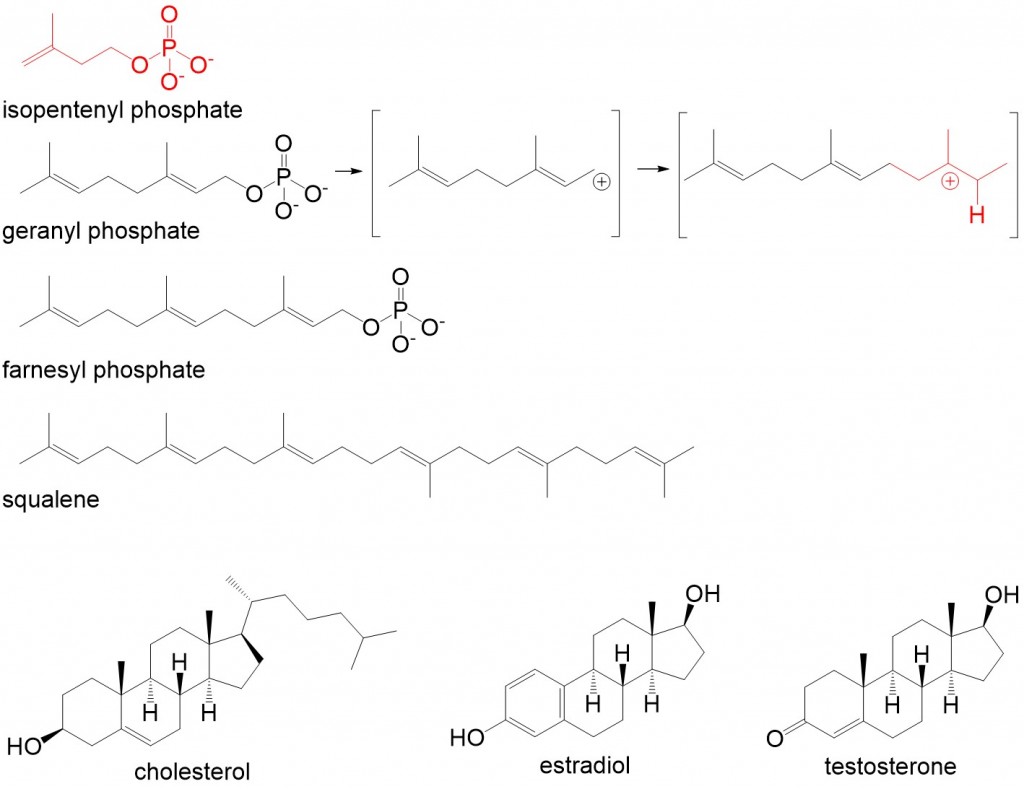
Lipid-Derived Hormones (or Lipid-soluble Hormones) Most lipid hormones are derived from cholesterol and thus are structurally similar to it, as illustrated in the figure below. The primary class of lipid hormones in humans is the steroid hormones. Chemically, these hormones are usually ketones or alcohols; their chemical names will end in “-ol”...
What hormones are derived from cholesterol in the cell membrane?
The cholesterol in the cell membrane provides the necessary degree of integrity for the function of the cell. All of the steroidal hormones are derived from cholesterol: progesterone, cortisol, DHEA, testosterone, estradiol, pregnenolone.
Is cholesterol a steroidal hormone?
Cholesterol & Hormones. All of the steroidal hormones are derived from cholesterol: progesterone, cortisol, DHEA, testosterone, estradiol, pregnenolone. It is not unreasonable to consider that low cholesterol concentrations may be a cause of steroidal hormone deficiencies, in many cases.
Which of the following is a lipid compound?
All may be classified as lipids or lipidic compounds: Vitamin D, Vitamin E, omega 3, 6 and 9, Vitamin A, Vitamin K, phosphatidyl nutrients, cholesterol, steroidal hormones (all derived from the cholesterol lipid).
What hormones are produced from cholesterol?
All classes of steroid hormones, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex hormones, are derivatives of cholesterol. Synthesis occurs in the placenta and ovaries (estrogens and progestins), testes (testosterone), and adrenal cortex (cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens).
What lipids are hormones?
The main class of lipid-derived hormone is the steroids which are derived from cholesterol and the eicosanoids. Steroid hormones include testosterone, estrogen and cortisol. Testosterone and estrogen are important regulators of reproductive function, secreted by both the testes and the ovaries.
What hormone regulates cholesterol?
thyroid hormoneHDL CHOLESTEROL A number of key proteins involved in HDL metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport are regulated by thyroid hormone. Specifically, CETP, hepatic lipase, LCAT, and SR-B1 are increased by thyroid hormone (168,169,171,174,179-186).
What are the 3 types of steroid hormones?
More than 30 steroids are produced in the adrenal cortex; they can be divided into three functional categories: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens.
What are the 4 types of hormones?
Summarylibid-derived hormones.amino acid-derived hormones.peptide hormones.glycoprotien hormones.
What are the 3 types of hormones?
Types of HormonesThe three types of hormones are steroid hormones, peptide hormones and amino acid derivatives.The different types of hormones will have different mechanisms of action due to their distinct chemical properties.
Which hormone is produced from cholesterol quizlet?
Aldosterone, testosterone, and progesterone are all steroids derived from cholesterol. Cortisol is another steroid that is released by the adrenal cortex and is involved in stress adaptation.
Is cortisol made from cholesterol?
Cortisol, a glucocorticoid (steroid hormone), is produced from cholesterol in the two adrenal glands located on top of each kidney. It is normally released in response to events and circumstances such as waking up in the morning, exercising, and acute stress.
What are the 7 hormones?
Pituitary glandAdrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotropin).Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).Growth hormone (GH).Luteinizing hormone (LH).Prolactin.Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
What are the 5 steroid hormones?
There are five major classes of steroid hormones: testosterone (androgen), estradiol (estrogen), progesterone (progestin), cortisol/corticosterone (glucocorticoid), and aldosterone (mineralocorticoids).
What are the 5 types of hormones?
Let's take a closer look at five important hormones and how they help you function well.Insulin. The fat-storage hormone, insulin, is released by your pancreas and regulates many of your metabolic processes. ... Melatonin. ... Estrogen. ... Testosterone. ... Cortisol.
Are all steroids made from cholesterol?
All steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol. They are transported through the bloodstream to the cells of various target organs where they carry out the regulation of a wide range of physiological functions.
Are all hormones made of lipids?
Although there are many different hormones in the human body, they can be divided into three classes based on their chemical structure: lipid-derived, amino acid-derived, and peptide hormones (which includes peptides and proteins).
Is cholesterol a hormone?
Cholesterol is a very important steroid to the body. It's formed in the liver, brain tissue, bloodstream, and nerve tissue. It's a precursor to certain hormones, such as testosterone. This means the body needs cholesterol to create these hormones.
How do lipids act as hormones?
Lipid-derived hormones, known as steroid hormones, are important chemical messengers and include testosterone and estrogens. At an organismal level triglycerides stored in adipose cells serve as energy-storage depots and also provide thermal insulation.
Are hormones proteins or lipids?
Chemically, hormones may be classified as either proteins or steroids. All of the hormones in the human body, except the sex hormones and those from the adrenal cortex, are proteins or protein derivatives.
What are the lipids and metabolism?
Lipids & Metabolism: Fats, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol & Hormones. You may have noticed that over the years there have been many products promoting health. Consider that many of the most recommended and studied nutrients and nutritional supplements have something in common: lipids.The effect that lipids and lipidic compounds have in ...
What are the lipids in the cell membrane?
Its significant to address that all biological cellular membranes are comprised of lipids. The balance of lipids (most ly phospholipids and cholesterol) within the membranes of cells account for the membrane’s integrity and fluidity. Simply stated, a cell membrane whose lipidic composition is compromised, is a cell whose functions are compromised.
What is the cell membrane composed of?
Simply stated, a cell membrane whose lipidic composition is compromised, is a cell whose functions are compromised. Though the cytosplasm of human cells is mostly water, there are concentrations of lipids that make up its composition. The inner mitochondrial membrane is comprised of lipids, such as cardiolipin and cholesterol.
Why are lipids important in nutrition?
Because of their essential role in a multitude of biological functions, lipid therapies have a wide range of applicability for a number of situations. Ongoing nutritional research, which encompasses the importance of lipids in therapeutics will potentially save many people’s lives as well as reduce human suffering.
Which fatty acid is involved in the inflammatory response?
For example, lipid eicosanoid signaling molecules are involved in the inflammatory response. Arachadonic acid, an omega 6 fatty acid is a major lipid that results in the inflammatory cascades. Of course, there is the omega 3 fatty acids, which are known to block the eicosanoid-derived E2 prostaglandins. The 3 major eicasanoid molecules are all ...
Why do saturated fats have a greater degree of resilience?
Whereas, saturated fats possess a far greater degree of resilience due to the lack of double bonds between carbon atoms.
Is cardiolipin a lipid?
A cancer researcher Thomas Seyfried, PhD presents a compelling argument in his recent book “Cancer As A Metabolic Disease”, that abnormal inner mitochondrial lipids such as cardiolipin are at the root of damaged oxidative phosphorylation in cancer cell mitochondria.
What is the name of the protein that moves cholesterol and other fats throughout the body?
These tiny particles, called lipoproteins (lipid plus protein), move cholesterol and other fats throughout the body. Cholesterol and other lipids circulate in the bloodstream in several different forms. Of these, the one that gets the most attention is low-density lipoprotein— better known as LDL, or "bad" cholesterol.
What is the purpose of cholesterol?
The Harvard Special Health Report Managing Your Cholesterol explains cholesterol as a waxy, whitish-yellow fat and a crucial building block in cell membranes. Cholesterol also is needed to make vitamin D, hormones (including testosterone and estrogen), and fat-dissolving bile acids.
Why is LDL considered bad?
LDL is known as "bad" cholesterol because it delivers cholesterol to tissues and is strongly associated with the buildup of artery-clogging plaque.
What are the different types of cholesterol?
Cholesterol and other lipids circulate in the bloodstream in several different forms. Of these, the one that gets the most attention is low-density lipoprotein— better known as LDL, or "bad" cholesterol. But lipoproteins come in a range of shapes and sizes, and each type has its own tasks. They also morph from one form into another. These are the five main types: 1 Chylomicrons are very large particles that mainly carry triglycerides (fatty acids from your food). They are made in the digestive system and so are influenced by what you eat. 2 Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles also carry triglycerides to tissues. But they are made by the liver. As the body's cells extract fatty acids from VLDLs, the particles turn into intermediate density lipoproteins, and, with further extraction, into LDL particles. 3 Intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) particles form as VLDLs give up their fatty acids. Some are removed rapidly by the liver, and some are changed into low-density lipoproteins. 4 Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles are even richer in pure cholesterol, since most of the triglycerides they carried are gone. LDL is known as "bad" cholesterol because it delivers cholesterol to tissues and is strongly associated with the buildup of artery-clogging plaque. 5 High-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles are called "good" cholesterol because some of them remove cholesterol from circulation and from artery walls and return it to the liver for excretion.
How much cholesterol does the liver produce?
In fact, cholesterol production is so important that your liver and intestines make about 80% of the cholesterol you need to stay healthy. Only about 20% comes from the foods you eat. (See illustration.) If you eat only 200 to 300 milligrams (mg) of cholesterol a day (one egg yolk has about 200 mg), your liver will produce an additional 800 ...
Why are HDL particles considered good cholesterol?
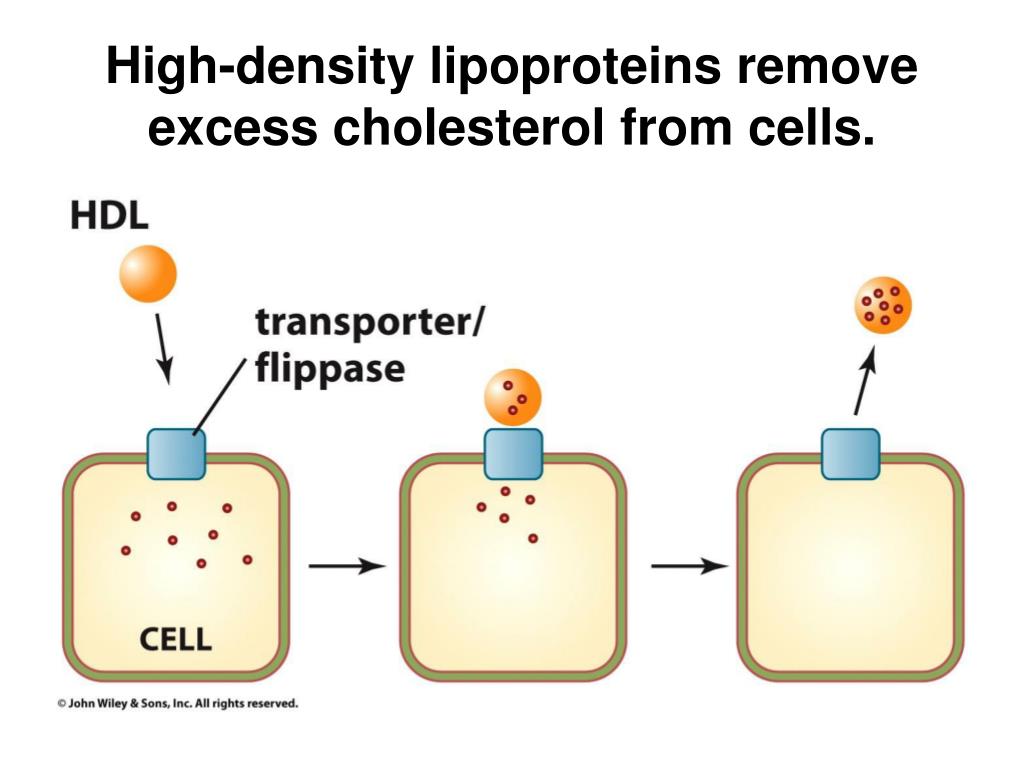
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles are called "good" cholesterol because some of them remove cholesterol from circulation and from artery walls and return it to the liver for excretion. – By Julie Corliss. Executive Editor, Harvard Heart Letter.
What are chylomicrons made of?
Chylomicrons are very large particles that mainly carry triglycerides (fatty acids from your food). They are made in the digestive system and so are influenced by what you eat. Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles also carry triglycerides to tissues. But they are made by the liver.
How does HDL transport cholesterol to the liver?
The HDL then transports the cholesterol to the liver either directly by interacting with hepatic SR-B1 or indirectly by transferring the cholesterol to VLDL or LDL, a process facilitated by CETP. Cholesterol efflux from macrophages to HDL plays an important role in protecting from the development of atherosclerosis.
What is reverse cholesterol transport?
Reverse cholesterol transport begins with the formation of nascent HDL by the liver and intestine. These small HDL particles can then acquire cholesterol and phospholipids that are effluxed from cells, a process mediated by ABCA1 resulting in the formation of mature HDL.
What is the structure of lipoproteins?
STRUCTURE OF LIPOPROTEINS (2) Lipoproteins are complex particles that have a central hydrophobic core of non-polar lipids, primarily cholesterol esters and triglycerides. This hydrophobic core is surrounded by a hydrophilic membrane consisting of phospholipids, free cholesterol, and apolipoproteins (Figure 1).
How many classes of lipoproteins are there?
Plasma lipoproteins can be divided into seven classes based on size, lipid composition, and apolipoproteins (chylomicrons, chylomicron remnants, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL, and Lp (a)). Chylomicron remnants, VLDL, IDL, LDL, and Lp (a) are all pro-atherogenic while HDL is anti-atherogenic.
What are the components of lipoproteins?
Lipoproteins are complex particles with a central core containing cholesterol esters and triglycerides surrounded by free cholesterol, phospholipids, and apolipoproteins, which facilitate lipoprotein formation and function.
What are the functions of apolipoproteins?
Apolipoproteins have four major functions including 1) serving a structural role , 2) acting as ligands for lipoprotein receptors , 3) guiding the formation of lipoproteins, and 4) serving as activators or inhibitors of enzymes involved in the metabolism of lipoproteins.
Why are lipids insoluble in water?
Because lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are insoluble in water these lipids must be transported in association with proteins (lipoproteins) in the circulation. Large quantities of fatty acids from meals must be transported as triglycerides to avoid toxicity.
Which hormone stimulates the development of the follicles in the ovaries of females?
The hormone that stimulates the development of the follicles in the ovaries of females is the X hormone.
Which cells secrete insulin?
The X cells in the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas are responsible for secreting insulin.
What is it called when a young person has too little growth hormone?
If a young person suffers from too little growth hormone as a result of abnormal development of the pituitary gland, the resulting condition is. Dwarfism. A special group of cells that secretes the hormone insulin directly into the bloodstream is called: Islets of Langerhans.
What is X thyroid?
X is the condition in which the thyroid gland does not secrete sufficient thyroxine.
How to convert mmol/l to mg/dl?
To convert from mmol/L to mg/dL multiply by 88.57396; To convert from mg/dL to mmol/L, multiply by 0.01129. Cholesterol levels are tested through blood cholesterol or lipid panel tests, and are recommended every 5 years between the ages of 20 and 45 and after more frequently.
How to get mg/dL to mmol/l?
To get from mg/dL to mmol/L multiply by 0.02586.