Can you feel lobules during breast exams?
Lobules are the milk-producing glands of the breast. Breast ducts are the thin tubes that carry breast milk from the lobules of the breast to the nipple. How is lobular breast cancer different from other breast cancers? Compared to other types of breast cancer, lobular breast cancer:
What causes lobular breast cancer?
Feb 08, 2022 · What are lobules in the breast? A small part of a lobe in the breast. A breast lobule is a gland that makes milk. Enlarge. Anatomy of the female breast. The nipple and areola are shown on the outside of the breast. Do breast lobules feel like lumps? Adenosis: Small, round lumps, or a lumpy feeling that are caused by enlarged breast lobules.
Does LCIs turn into cancer?
Breasts are made up of lobules (milk-producing glands) and ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple). These are surrounded by glandular, fibrous and …
How serious is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Nov 15, 2021 · Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), also known as lobular neoplasia, is a rare condition in which abnormal cells develop in the milk glands, known as lobules, in the breast. These abnormal cells are not considered to be breast cancer and don’t require any treatment beyond surgical removal.

Does breast cancer start in the lobules?
Lobular breast cancer (also called invasive lobular carcinoma) is a type of breast cancer that begins in the milk-producing glands (lobules) of the breast. It is the second most common type of breast cancer, accounting for about 10% to 15% of all invasive breast cancers.Sep 30, 2019
What is a lobular mass in breast?
What is lobular neoplasia? Lobular neoplasia is a benign (not cancer) condition. Breasts are made up of lobules (milk-producing glands) and ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple). These are surrounded by glandular, fibrous and fatty tissue. This tissue gives breasts their size and shape.
What do breast lobules look like?
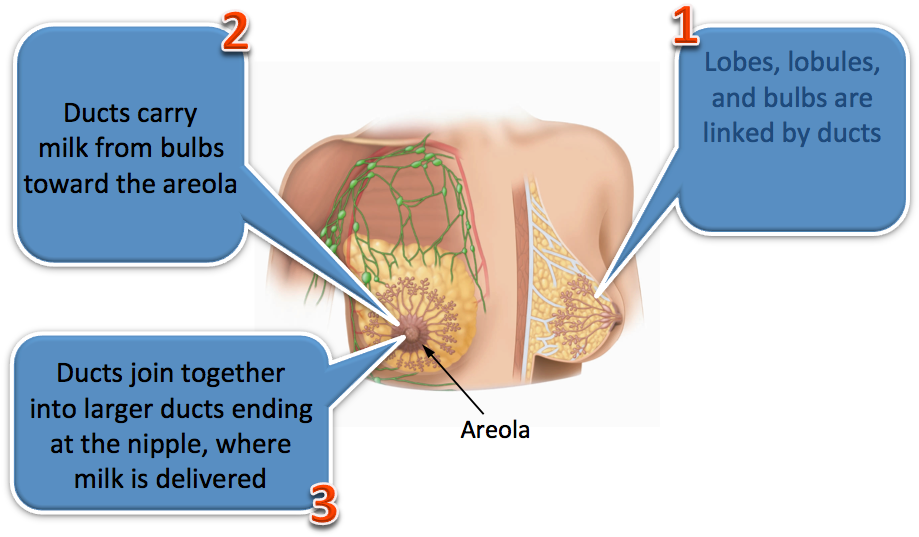
Lobules are arranged in clusters, like bunches of grapes. Ducts are thin tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The nipple is located in the middle of the areola, which is the darker area surrounding the nipple. Breast cancers can form in the ducts and the lobes.
Where are the lobules in the breast located?
Lobes: Each breast has between 15 to 20 lobes or sections. These lobes surround the nipple like spokes on a wheel. Glandular tissue (lobules): These small sections of tissue found inside lobes have tiny bulblike glands at the end that produce milk.Oct 14, 2020
Can breast lobules swollen?
Adenosis is a benign (non-cancerous) breast condition in which the lobules (milk-producing glands) are enlarged, and there are more glands than usual. Adenosis is often found in biopsy samples of women who have fibrocystic changes in their breasts.Jan 25, 2022
What is a lobular tumor?
Overview. Invasive lobular carcinoma is a type of breast cancer that begins in the milk-producing glands (lobules) of the breast. Invasive cancer means the cancer cells have broken out of the lobule where they began and have the potential to spread to the lymph nodes and other areas of the body.May 23, 2020
What is a lobe and lobule?
As nouns the difference between lobe and lobule is that lobe is any projection or division, especially one of a somewhat rounded form while lobule is a small lobe; a subdivision of a lobe.
What muscle is under your breast?
Pectoralis major is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, which makes up the bulk of the chest muscle. It lies under the breast. It serves to flex, extend, and rotate the humerus, the long bone of the upper arm. Pectoralis minor is a thin, triangular muscle located beneath the pectoralis major.
Do you have bones in your breast?
The breasts of an adult woman are milk-producing, tear-shaped glands. They are supported by and attached to the front of the chest wall on either side of the breast bone or sternum by ligaments. They rest on the major chest muscle, the pectoralis major. The breast has no muscle tissue.
How do I know if a lump in my breast is normal?
Breast tissue in and of itself can feel somewhat lumpy and sponge-like, so it can be hard to know if what you're feeling is an actual lump or just normal breast tissue. "A breast lump will feel like a distinct mass that's noticeably more solid than the rest of your breast tissue.Oct 1, 2020
What is breast alveoli?
Alveoli are a few millimeters in size and form cavities in the breast. These cavities fill with milk-creating cells called cuboidal cells, which are surrounded by the myoepithelial cells. When the alveoli combine they are called lobules.
How many lobules do breasts have?
The adult breast Adult women have 15-20 lobes in each breast [1]. Each lobe has 20-40 lobules [2]. Small milk ducts are attached to the lobules. These ducts join together like branches of grape stems, gradually forming larger ducts.
What are lobules in the breast?
A small part of a lobe in the breast. A breast lobule is a gland that makes milk. Enlarge. Anatomy of the female breast. The nipple and areola are shown on the outside of the breast.
Do breast lobules feel like lumps?
Adenosis: Small, round lumps, or a lumpy feeling that are caused by enlarged breast lobules. Sometimes the lumps are too small to be felt. If there is scar-like tissue, the condition may be painful and is called sclerosing adenosis.
Does lobular breast cancer show up on mammogram?
Invasive lobular carcinoma is less likely to be detected on a mammogram than other types of breast cancer are. Still, a mammogram is a useful diagnostic test.
Is lobular breast cancer worse than ductal?
An analysis of the largest recorded cohort of patients with invasive lobular breast cancer (ILC) demonstrates that outcomes are significantly worse when compared with invasive ductal breast cancer (IDC), highlighting a significant need for more research and clinical trials on patients with ILC.
How many lobules do breasts have?
Adult women have 15-20 lobes in each breast [1]. Each lobe has 20-40 lobules [2]. Small milk ducts are attached to the lobules.
Can you feel alveoli in breast?
You have little branches of bud-like glands in the breast, and when you get pregnant these little buds grow out and form ducts and tiny sacs, called alveoli, to hold the milk.” This activity inside your breasts can make them feel tingly, sore, swollen or heavy – all early signs of pregnancy.
Can breast lobules swollen?
Adenosis is a benign (non-cancerous) breast condition in which the lobules (milk-producing glands) are enlarged, and there are more glands than usual. Adenosis is often found in biopsies of women who have fibrosis or cysts in their breasts.
What is lobular neoplasia?
When lobular neoplasia occurs, there’s an increase in the number of cells contained in the lobules, together with a change in their appearance and behaviour. 2. Types of lobular neoplasia. The most common forms of lobular neoplasia are atypical lobular hyperplasia (ALH) and lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS).
What are the glands that carry milk to the nipple?
Breasts are made up of lobules (milk-producing glands) and ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple). These are surrounded by glandular, fibrous and fatty tissue. This tissue gives breasts their size and shape.
How long does lobular neoplasia last?
Although most women diagnosed with lobular neoplasia do not develop breast cancer, your specialist will usually recommend having yearly follow-up mammograms for up to five years. This aims to find any changes as early as possible. Your specialist will discuss which follow-up is best for you.
Does tamoxifen help with lobular neoplasia?
Research has shown that treating women who have lobular neoplasia with tamoxifen (a hormone therapy treatment for breast cancer) can reduce the risk of breast cancer developing . However, any possible benefit of taking tamoxifen needs to be considered against the risks and side effects of this treatment.
Is PLCIS more likely to develop breast cancer?
However, women diagnosed with either condition have a slightly higher risk than the general population of developing breast cancer in either breast. Women diagnosed with PLCIS are slightly more at risk of developing breast cancer than those with ALH or LCIS.
Can lobular neoplasia be treated?
There’s no standard recommended treatment for lobular neoplasia. Your specialist will discuss treatment options with you based on your individual situation. If lobular neoplasia is diagnosed by a core biopsy, your doctor may recommend removing more tissue from the area where the lobular neoplasia was found.
Can lobular neoplasia show up on a mammogram?
Lobular neoplasia doesn’t usually cause any symptoms or show up on a mammogram. It’s usually found during a biopsy or other test being done for another breast symptom or change. For example, when calcifications (small spots of calcium) are detected on a mammogram.
Can you feel lobules in your breast?
Adenosis of the breast is a non-cancerous condition in which the lobules increase in size and number. This can cause the breasts to be painful, and lumps may be felt in the breasts. Adenosis can be seen on mammogram, and these may require a sample of the tissue to be biopsied to make sure it isn’t breast cancer.
What is a lobular mass in breast?
Lobular neoplasia is a benign (not cancer) condition. Breasts are made up of lobules (milk-producing glands) and ducts (tubes that carry milk to the nipple). These are surrounded by glandular, fibrous and fatty tissue. This tissue gives breasts their size and shape.
Does Lobulated mean cancer?
Invasive means that the cancer has “invaded” or spread to the surrounding breast tissues. Lobular means that the cancer began in the milk-producing lobules, which empty out into the ducts that carry milk to the nipple.
Can breast lobules hurt?
Sclerosing adenosis is excess growth of tissues in the breast’s lobules. This often causes breast pain. While these changes in the breast tissue are very small, they may show up on mammograms as calcifications and can make lumps.
Do breast lobules swell?
The lobules in your breasts can become enlarged and contain more glands than usual. Intraductal papillomas. Small tumors can form in your nipple’s milk ducts.
Can cysts be lobular?
Cysts are fluid filled and develop secondary to dilatation of the terminal ductal lobular unit (TDLU). They are commonly multiple, bilateral and may wax and wane in size.
Should Lcis be removed?
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), also known as lobular neoplasia, is a rare condition in which abnormal cells develop in the milk glands, known as lobules, in the breast. These abnormal cells are not considered to be breast cancer and don’t require any treatment beyond surgical removal.
What happens to the lobules of breast as a woman ages?
Humans. As a woman ages, breast lobules involute and the number and size of acini per lobule in the breast decreases. The intralobular stroma is initially replaced by collagen followed by a gradual replacement of both glandular tissue and collagen by fatty tissue (Hutson et al., 1985 ).
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is an uncontrolled growth of epithelial cells originating in the ducts or breast lobules Carbone et al (1993). The disorder includes early, noninvasive breast cancer, such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS), breast cancer that has invaded the surrounding breast stroma (primary invasive breast cancer); and breast cancer that has spread to the draining lymph nodes or to distant organs (advanced or metastatic breast cancer). The disease is differentiated from benign breast pathologies, such as fibroadenoma, fibrocystic disease, or benign hyperplasia.
What is fibroadenomas in women?
Fibroadenomas arise from breast lobules and are the most common solid benign masses in women younger than age 30 years. Once diagnosed, fibroadenomas may remain stable in 80% of cases, regress in about 15%, and grow in 5% to 10%. Fibroadenomas are benign, although cancer can occur within a fibroadenoma. Women with a specific histologic diagnosis of complex fibroadenomas have cysts or histologic elements other than the fibroadenoma and have a small increased risk of future breast cancer, as described by DuPont and colleagues. Fibroadenomas may be single or multiple and are called giant fibroadenomas if larger than 8 cm.
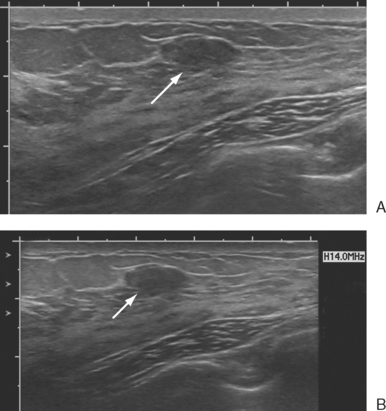
Can a sonographer see a fatty lobule?
If unsure if an ultrasound finding represents a fatty lobule, the sonographer can place a skin marker over the ultrasound finding and repeat the mammogram (see Fig. 5-9O to Q ). If the finding is a fatty mass, there should be only fat under the skin marker.
What are the different types of breast tissue?
Female breasts contain different types of fatty, fibrous, and glandular tissue: glandu lar tissue includes the breast lobes and breast ducts. fibrous, or supportive or connective, tissue is the same tissue that ligaments and scar tissue are made of.
How many glands are there in the breast?
Embedded in the breast’s fatty and fibrous tissue are 15 to 20 glands called lobes, each of which has many smaller lobules, or sacs, that produce milk. Lobules are arranged in clusters, like bunches of grapes. Ducts are thin tubes that carry milk to the nipple.
What is the name of the tissue that fills the space between glandular and fibrous tissue?
fatty tissu e fills in the spaces between glandular and fibrous tissue and largely determines your breast size. Doctors refer to all non-fatty tissue as fibroglandular tissue. There are also bands of supportive, flexible connective tissue called ligaments, which stretch from the skin to the chest wall to hold the breast tissue in place.
What is the function of lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs that help fight infection and are found throughout the body. They produce and filter a colorless fluid called lymph, which contains white blood cells known as lymphocytes (immune cells involved in defending against infections and such diseases as cancer).
Where are lymph nodes located?
Clusters of lymph nodes near the breast are located in the armpit ( known as axillary lymph nodes), above the collarbone, in the neck, and in the chest. Back to top.
Can you have dense breasts?
But anyone — regardless of age or breast size — can have dense breasts. A doctor will tell you that your breasts are dense if most of the tissue seen on your mammogram is fibrous or glandular breast tissue. These tissue types appear thicker and denser than fatty tissue and will show up white on a mammogram.
Where are the ducts located in the breast?
Ducts are thin tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The nipple is located in the middle of the areola, which is the darker area surrounding the nipple. Breast cancers can form in the ducts and the lobes.
How many lobes are there in a breast?
A healthy female breast is made up of 12–20 sections called lobes. Each of these lobes is made up of many smaller lobules, the gland that produces milk in nursing women. Both the lobes and lobules are connected by milk ducts, which act as stems or tubes to carry the milk to the nipple.
What is the tissue in the breast called?
Adipose Tissue. The female breast is mostly made up of a collection of fat cells called adipose tissue. This tissue extends from the collarbone down to the underarm and across to the middle of the ribcage. As a woman ages, especially once she reaches menopause, the breast tissue contains more adipose (fatty) tissue.