A typical long bone consists of the following parts:
- The diaphysis (growing between) is the shaft of a long bone — the long, cylindrical, main portion of the bone.
- The epiphyses (growing over; singular is epiphysis) are the proximal and distal ends of the bone.
- The metaphyses (between; singular is metaphysis) are the regions between the diaphysis and the epiphyses. ...
What is the process by which long bones are formed?
- Osteoprogenitor cells then convert to osteoblasts.
- Bone matrix secreted by the osteoblasts forms a bone collar. ...
- Osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, arrive and form holes in the bone collar allowing the passage of periosteal buds. ...
What are the typical parts of a long bone?
The major parts of a long bone include epiphysis, articular cartilage, diaphysis, periosteum, medullary cavity, endosteum, and marrow. What are the anatomical regions of a long bone?
What is considered a long bone?
The long bones found in the arms and hands are known as:
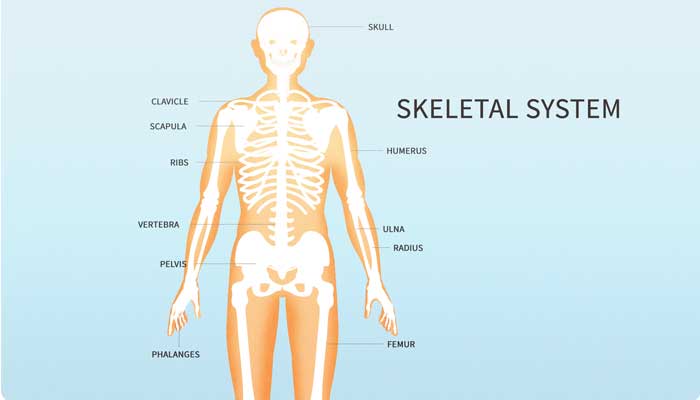
- Humerus: There are 2 humerus bones in the body (one in each arm). ...
- Radius: There are 2 radii bones in the human skeleton (one in each forearm). ...
- Ulna: There are 2 ulnae bones in the human skeleton along with the radii (one in each forearm). ...
- Metacarpals: There are 5 metacarpals in each hand (total 10) connecting the wrist to the digits in the hands. ...
What are the characteristics of long bones?
What are the characteristics of long bones?
- parts of a long bone.
- metaphysis. Part of the bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis; it contains the connecting cartilage enabling the bone to grow, and disappears at adulthood.
- diaphysis.
- distal epiphysis.
- proximal epiphysis.
- metaphysis.
What are long bones shaped like?
A long bone is one that is cylindrical in shape, being longer than it is wide.
What is unique about long bones?
Long Bones Support Weight and Facilitate Movement The long bones, longer than they are wide, include the femur (the longest bone in the body) as well as relatively small bones in the fingers. Long bones function to support the weight of the body and facilitate movement.
What are long bones made up of?
Some bones in the fingers are classified as long bones, even though they are short in length. This is due to the shape of the bones, not their size. Long bones contain yellow bone marrow and red bone marrow, which produce blood cells.
What are the 3 main parts of a long bone?
Long bones are longer than they are wide. They can be divided into three regions - epiphysis, metaphysis and the diaphysis.
How do you identify long bones?
Bones that are longer than they are wide are called long bones. They consist of a long shaft with two bulky ends or extremities. They are primarily compact bone but may have a large amount of spongy bone at the ends or extremities. Long bones include bones of the thigh, leg, arm, and forearm.
What is important about the long bone?
Long bones are hard, dense bones that provide strength, structure, and mobility. The thigh bone (femur) is a long bone. A long bone has a shaft and two ends.
What bones are long bones?
All of the bones in the arms and legs, except the patella, and bones of the wrist, and ankle, are long bones.
What do bones look like?
1:344:07How Do Bones Work? Human Skeleton Facts for Kids - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt looks a bit like jelly.MoreIt looks a bit like jelly.
How many parts does a long bone have?
two partsA long bone has two parts: the diaphysis and the epiphysis. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The hollow region in the diaphysis is called the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow marrow.
What is the structure and function of a long bone?
Long bones are hard, dense bones that provide strength, structure, and mobility. Functions of long bone: Supports soft tissue and provides attachment for skeletal muscles. Protects internal organs.
Where are most long bones found in the body?
Where are most long bones found in the body? Most long bones are found in the limbs.
What are the 5 major parts of a long bone?
List five major parts of a long bone. The major parts of a long bone include epiphysis, articular cartilage, diaphysis, periosteum, medullary cavity, endosteum, and marrow. How do compact and spongy bone differ in structure? The wall of the diaphysis is mainly composed of tightly packed tissue called compact bone.
What is the difference between long bone and short bone?
Bones can be classified according to their shapes. Long bones, such as the femur, are longer than they are wide. Short bones, such as the carpals, are approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. Flat bones are thin, but are often curved, such as the ribs.
What bones are long bones?
All of the bones in the arms and legs, except the patella, and bones of the wrist, and ankle, are long bones.
Are bones stronger than steel?
Bone is extraordinarily strong — ounce for ounce, bone is stronger than steel, since a bar of steel of comparable size would weigh four or five times as much. A cubic inch of bone can in principle bear a load of 19,000 lbs.
What are long bones called?
The long bone category includes the femora, tibiae, and fibulae of the legs; the humeri, radii, and ulnae of the arms; metacarpals and metatarsals of the hands and feet, the phalanges of the fingers and toes, and the clavicles or collar bones.
How many long bones are in the body?
There are approximately 90 long bones in the human body. They are known as clavicle, femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, meta...
What is the medical term for long bone?
The medical term for a long bone is a long osteon. The term osteon is derived from Greek language and means bone.
What are the 3 main parts of a long bone?
The three main parts of the long bone are the diaphysis and 2 epiphysis. The diaphysis is the shaft of the bone. The epiphysis are two ends superio...
What are long bones?
A long bone is any bone that is longer than it is wider. It has a shaft and two ends on it. It contains bone marrow within the shaft and a dense co...
What is the disorder of the metaphysis?
In adults, the metaphysis is instead completely ossified. There are two congenital disorders associated with long bones. Rachitis fetalis anularis is a disorder that occurs when the ends of the long bones (epiphyses) become enlarged.
What is the area between the shaft and the epiphysis of a long bone?
Long bones are thinner in the center and their diameter grows as the subject moves from the shaft to the epiphysis: The area between one end of the shaft and the adjacent epiphysis is known as the metaphysis. In children and adolescents, between the metaphysis and epiphysis is a cartilage, known as "conjugation", which represents the area of growth in length of this type of bones. In adults, the metaphysis is instead completely ossified.
Why is calcium important for fetal growth?
Calcium is an extremely important feature in an individual’s diet. Calcium intake is stored in the bones as a sort of mineral deposit, which in turn helps build stronger and healthier bones.
What is the area between one end of the shaft and the adjacent epiphysis called?
Long bones are thinner in the center and their diameter grows as the subject moves from the shaft to the epiphysis: The area between one end of the shaft and the adjacent epiphysis is known as the metaphysis.
What is bone tissue?
Bones are a form of extremely specialized connective tissue, consisting of a mix of a dense organic matrix and inorganic mineral component. They are characterized by their hardness and mechanical resistance. Bones are segments of varying shape, size and density, all of which constitute to form the skeletal system.
Which bones are considered long bones?
The femur, tibia and fibula are considered long bones in the lower limbs, and the humerus bone, ulna bone and radius bone are considered long bones in the upper limbs. The surface of long bones is covered by the periosteum, a membrane connecting the processes responsible for bone growth and callus formation in fractures.
What are the functions of long bones?
Long bones perform different functions in the human body: By interacting with the muscles and tendons, they allow movement of the limbs. They provide strength, structure and mobility to the upper and lower extremities.
What Are Long Bones in the Body?
It comprises all of the muscles and bones in the body. The bone structure consists of 206 bones in the adult human skeleton. Human babies start with about 270 bones; however, after the growth and fusion of bones during development, the human adult ends up with about 206 bones in total. There are five different types of bones in the human body: long bone, short bone, flat bones, irregular bones, and sesamoid bones. The long bones in the body will be discussed in this lesson.
What is the difference between long and wide bones?
The long bones are longer than they are wide. They contain a slight curvature to them. The shaft or the diaphysis is typically long and narrow. The ends, known as epiphysis, are present one on each end per bone. The epiphysis is broad and circular.
How many humerus bones are there in the human body?
Humerus: There are 2 humerus bones in the body (one in each arm). It makes up the arm from the shoulder to the elbow. The function of the humerus is to make up the framework for the arm and to attach the arm to the shoulders. It allows for movement of the arm while being stabilized with the rest of the body.
Where are long bones located?
The long bones grow in height or length at the epiphyseal plate. The epiphyseal plate is an area located between the diaphysis and the epiphysis on a long bone. It is composed of cartilage. There are two sides on the epiphyseal plate: one side faces the epiphysis and the other side faces the diaphysis. On the side facing the epiphysis, cartilage is grown. Whereas, on the side closer to the diaphysis, bone is grown. This is how a long bone grows.
How many metacarpals are there in each hand?
Metacarpals: There are 5 metacarpals in each hand (total 10) connecting the wrist to the digits in the hands. The function of the metacarpal bone is to form the structure of the palm and to connect the fingers to the wrist.
What are the bones of the wrist called?
As mentioned previously, the bones of the wrist are not classified as long bones. They are known as the carpals.
How many ulnae bones are there?
Ulna: There are 2 ulnae bones in the human skeleton along with the radii (one in each forearm). It shares its functions with the radius. However, it is a stable bone, while the radius allows for movement via pivoting.
What is the medullary cavity?
The medullary cavity (medulla- = marrow), or marrow cavity, is a hollow, cylindrical space within the diaphysis that contains fatty yellow bone marrow and numerous blood vessels in adults. This cavity minimizes the weight of the bone by reducing the dense bony material where it is least needed.
What is the articular cartilage?
The articular cartilage is a thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the part of the epiphysis where the bone forms an articulation (joint) with another bone. Articular cartilage reduces friction and absorbs shock at freely movable joints.
What is the growth plate in a bone?
In a growing bone, each metaphysis contains an epiphyseal (growth) plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage that allows the diaphysis of the bone to grow in length. When a bone ceases to grow in length at about ages 14–24, the cartilage in the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone; the resulting bony structure is known as the epiphyseal line.
How long does it take for a greenstick fracture to heal?
Most greenstick fractures require four to eight weeks for complete healing, depending on the break and the age of the child.
Why are greenstick fractures more common in children?
The risk of greenstick fractures is higher in young children because their bones are softer and more flexible than adult bones. In a greenstick fracture, the bone bends and cracks instead of breaking into separate pieces. Most greenstick fractures occur in children under age 10.
Why is articular cartilage not covered by periosteum?
Because articular cartilage lacks a perichondrium and lacks blood vessels, repair of damage is limited. The periosteum is a tough connective tissue sheath and its associated blood supply that surrounds the bone surface wherever it is not covered by articular cartilage.
What is the function of the periosteum?
The periosteum also protects the bone, assists in fracture repair, helps nourish bone tissue, and serves as an attachment point for ligaments and tendons.
First, what is a long bone?
Long bones are one of the five bone types that are classified by shape.
Parts of long bones
This image represents the parts of a long bone. The labels include proximal epiphysis, proximal metaphysis, diaphysis (bone shaft), distal metaphysis, distal epiphysis, and epiphyseal line (x2).
Structure of an adult human long bone
The following image gets into a little more detail regarding human long bone structure. The labels include periosteum, compact bone, nutrient artery & vein, medullary cavity, yellow bone marrow, endosteum, epiphyseal line, and spongy bone with red bone marrow.
The structure of human bones explained
Periosteum – You can think of the periosteum as a thin double-layered skin or membrane that covers the surface of all bones. The periosteum plays a crucial role in bone growth and repair. This essential membrane is attached to bones by strong collagenous fibers called Sharpey’s fibres.
Long bone images are free for educational use
If you find this information useful, then you are free to use these illustrations for educational purposes, e.g. teachers or students. While it’s not required, it would be greatly appreciated if you would link back to this page from your favorite social media account if you find this material useful.
Structure of a long bone
The long bones of an animal skeleton are typical of elongated cylindrical form with enlarged extremities. They occur in both the thoracic and pelvic limbs, acting as supporting columns and as levers. For studying the structure of a long bone, you need both the longitudinal and transverse section samples.
Example of long bones
Let’s see the example of the long bones from the dog’s appendicular skeleton. You know the appendicular skeleton of a dog consists of the bones of both thoracic and pelvic limbs. Fine, if you see the skeleton of a dog, you will find the following long bones from the thoracic and pelvic limbs –
Parts of a long bone description
You already got the basic idea of the different parts and structure of a long bone of an animal. But, in this section, I will try to describe all the parts (two or three) from a long bone with examples and labeled diagrams.
Gross structure of a long bone description
In the structure of a long bone, you might know the details of epiphysis, diaphysis, articular cartilage, compact substance, spongy substance, medullary cavity, and others. Now, I will show you the details features of these structures from the long bone of an animal.
The shaft of a long bone
You know the diaphysis is the shaft of a long bone. The length and diameter of the shaft may vary from bone to bone and even the species to species.
Structure of periosteum of the long bone
The periosteum is a membrane that invests the outer surface of the bone, except where it covers the articular cartilage. In the structure of the periosteum of a long bone, you will find specialized connective tissue. Again, the periosteum comprises two distinct layers – the outer protective fibrous layer and the inner cellular osteogenic layer.
Endosteum of a long bone
The structure of the endosteum is similar to the periosteum of the long bone but is thinner. This endosteum lines largely the medullary cavity of the long bone. Again, you will find the lining of the endosteum in the various small marrow spaces, which also contain numerous blood vessels.
What is the epiphysis made of?
The wall of the epiphysis is made of compact bone like the diaphysis and the center contains spongy bone. Spongy bone is made of many small cavities (also called medullary cavities) filled with red bone marrow. 4 Red bone marrow manufactures red blood cells and is very well connected to the circulatory system. 5 There is so much blood flow through the spongy bone, that needles inserted into the spongy bone of the humerus, of the femur, or of the sternum (not a long bone as you'll see below) can be used to administer fluid or medications just like an intravenous line. 6
What is the head of the humerus called?
The head of the humerus fits into a socket in the shoulder. That type of joint is called a ball-and-socket joint. Joints that only allow movement along one axis are called hinge joints. The wall of the epiphysis is made of compact bone like the diaphysis and the center contains spongy bone.
What is the shaft of the long bone called?
Diaphysis. The diaphysis is the shaft of the long bone, the main body. The diaphysis is a tube with a hollow center called the medullary cavity (or marrow cavity). The wall of the diaphysis is made up of compact bone, which is dense and very hard. For most of the life of a long bone, the center of the diaphysis is filled with yellow bone marrow.
Why are short bones called short bones?
Short bones are called that because they about as wide as they are long. There is no diaphysis on a short bone. It is made up of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone just like the epiphysis. Short bones also contain red bone marrow.
What is the short bone that connects the carpals to the tendons?
The carpals (wrist bones), tarsals (ankle and heel bones), and the patella (kneecap) are all short bones. Some experts consider the patella a sesamoid bone (discussed below) because it primarily provides an anchor point for tendons and ligaments.
Why do bones develop?
Sometimes, bones will develop due to friction along tendons or ligaments. Usually, these are very small bones and develop randomly between individuals. They are not named. Some anatomists consider the patella an example of sesamoid bone.
What bone is used to administer fluid?
There is so much blood flow through the spongy bone, that needles inserted into the spongy bone of the humerus, of the femur, or of the sternum (not a long bone as you'll see below) can be used to administer fluid or medications just like an intravenous line.
What is a sesamoid bone?
A sesamoid bone is a small, round bone that, as the name suggests, is shaped like a sesame seed. These bones form in tendons (the sheaths of tissue that connect bones to muscles) where a great deal of pressure is generated in a joint. The sesamoid bones protect tendons by helping them overcome compressive forces. Sesamoid bones vary in number and placement from person to person but are typically found in tendons associated with the feet, hands, and knees. The patellae (singular = patella) are the only sesamoid bones found in common with every person. Table 1 reviews bone classifications with their associated features, functions, and examples.
Where are the sesamoid bones found?
Sesamoid bones vary in number and placement from person to person but are typically found in tendons associated with the feet, hands, and knees. The patellae (singular = patella) are the only sesamoid bones found in common with every person. Table 1 reviews bone classifications with their associated features, functions, and examples. Table 1.
How many bones are there in the human body?
The 206 bones that compose the adult skeleton are divided into five categories based on their shapes (Figure 1). Their shapes and their functions are related such that each categorical shape of bone has a distinct function. Figure 1. Classifications of Bones.
What is irregular bone?
An irregular bone is one that does not have any easily characterized shape and therefore does not fit any other classification. These bones tend to have more complex shapes, like the vertebrae that support the spinal cord and protect it from compressive forces.
What is a long bone?
Long Bones. A long bone is one that is cylindrical in shape, being longer than it is wide. Keep in mind, however, that the term describes the shape of a bone, not its size. Long bones are found in the arms (humerus, ulna, radius) and legs (femur, tibia, fibula), as well as in the fingers (metacarpals, phalanges) and toes (metatarsals, phalanges).
Is a flat bone a curved bone?
The term flat bone is somewhat of a mis nomer because, although a flat bone is typically thin, it is also often curved. Examples include the cranial (skull) bones, the scapulae (shoulder blades), the sternum (breastbone), and the ribs. Flat bones serve as points of attachment for muscles and often protect internal organs.
How many bones does it take to level construction?
It takes 2,894 long bones to level Construction from 30 to 99.
What is a long bone?
A long bone is a drop from various monsters, usually those that drop big bones with some exceptions, at a universal rate of 1/400. After completion of Death to the Dorgeshuun, long bones may be sold to Barlak, in Dorgesh-Kaan, for 1,000 coins each.
How long can you be buried for prayer?
Long bones can be buried for 15.1 Prayer experience, but this is not recommended.
Does the Carpenter's Outfit apply to the Construction Experience?
He will convert all long bones in the player's inventory and bank at once. The Carpenter's Outfit will not apply to the Construction experience rewarded. This level 30 Construction requirement is not boostable. Long bones can be buried for 15.1 Prayer experience, but this is not recommended.
