
Lymphatic watersheds The body is divided into lymph territories that allow drainage of the lymph flow from specific body regions to specific regional lymph nodes. The deep vessels do not cross between watersheds (areas of collection); however, there are some superficial vessels that cross the watershed boundaries and thereby divert lymph fluid from one quadrant to another when there are conditions of overload.
How do you clean your lymphatic system?
This Lymphatic Cleanse Can Balance Your Whole Body In 5 Simple Steps
- Detox your environment. The lymph must deal with the body's "waste products" that are produced internally like dead cells as well as toxins that are introduced from the external ...
- Stay hydrated. Lymph fluid is about 95 percent water and becomes thicker and less fluid when you are dehydrated. ...
- Incorporate red and raw foods. ...
- Move your lymph naturally. ...
How do I know if my lymphatic system is clogged?
The following are the common symptoms of a congested lymphatic system:
- – Breast swelling or soreness with each cycle;
- – Dry skin;
- – Mild rash or acne;
- – Hypersensitivity
- – Rings get tight on fingers;
- – Soreness and/or stiffness in the morning;
- – Feeling tired;
- – Bloating / Holding on to water;
- – Itchy skin;
- – Weight gain and extra belly fat;
How to cure blocked swollen lymph nodes?
Home remedies to treat swollen lymph nodes:
- A warm, wet cloth put on the area can help relieve pain.
- Pain from swollen lymph nodes behind the ear can be relieved with advil, aspirin, or tylenol.
- Rest is always recommended when you feel run down, or your immune system is compromised.
- Fungus and bacteria can be treated with a daily glass of apple cider vinegar.
When should I worry about swollen lymph nodes?
When should I worry about a big lymph node? Let us check it out in the office if: if the lymph node is painful to the touch. if the skin over it is hot or red. if there is pus draining from the skin around the lymph node. if the child has other concerning symptoms, like unexplained fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, etc. if there are lots of big lymph nodes, instead of just one How long will the big lymph node last? Sometimes weeks to months.
What is lymphatic pooling?
The pooling lymph or blood stretches the vessels and cysts, making the lymphatic malformation grow larger. If it's close to the skin surface, it can look bruised. As a lymphatic malformation grows, it may put pressure on nearby body parts, such as the eyes, trachea (windpipe), or blood vessels.
What are the 2 types of lymphatic drainage?
There are two types of lymphatic drainage which may be used to treat lymphoedema – manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) and simple lymphatic drainage (SLD). Lymphatic draining techniques provide regular stimulation of the lymph vessels under the skin.
What is lymphatic drainage and why is it important?
Lymphatic drainage massage, also known as manual lymphatic drainage, relieves swelling that happens when medical treatment or illness blocks your lymphatic system. Lymphatic drainage massage involves gently manipulating specific areas of your body to help lymph move to an area with working lymph vessels.
How do you explain lymphatic drainage?
Lymphatic drainage massage is a form of gentle massage that encourages the movement of lymph fluids around the body. The fluid in the lymphatic system helps remove waste and toxins from body tissues. Some health conditions can cause lymph fluid to build up.
What drains lymphatic fluid?
The lymphatic system is a network of delicate tubes throughout the body. It drains fluid (called lymph) that has leaked from the blood vessels into the tissues and empties it back into the bloodstream via the lymph nodes.
What drains lymph from most of the body?
The lymphatic system is a network of very small tubes (or vessels) that drain lymph fluid from all over the body. The major parts of the lymph tissue are located in the: bone marrow. spleen.
How do I drain my lymphatic myself?
Place you hand on your collarbone. Move your hand down your chest in half circles toward your underarm. Massage your chest to help reduce swelling. This massage will move the lymph fluid from your neck and chest to your underarm lymph vessels and nodes.
What causes poor lymphatic drainage?
Primary lymphoedema is caused by alterations (mutations) in genes responsible for the development of the lymphatic system. The faulty genes cause the parts of the lymphatic system responsible for draining fluid to not develop properly or not work as they should.
How can I naturally drain my lymph nodes?
Below are 10 ways to help create flow in your lymphatic system and remove toxins from your body.Exercise. Regular exercise is key for a healthy lymphatic system. ... Alternative Treatments. ... Hot and Cold Showers. ... Use Dry Brushing. ... Drink Clean Water. ... Avoid Wearing Tight Clothes. ... Breathe Deeply. ... Eat Foods That Promote Lymph Flow.More items...•
Where does lymphatic drainage occur?
Extra fluid from tissue in the body drains into and flows through small lymph vessels. This fluid is filtered through the lymph nodes, and drains back into the bloodstream. There are lymph nodes throughout your body, but mainly in the neck, armpits, groin and tummy (abdomen).
What happens to your body after a lymphatic drainage?
After the Session You will notice feeling better by about 50 percent, then hours after the massage, 90 percent better. You will also likely feel incredibly rejuvenated, which will last even for days after your session.
What is the 2 lymphatic system?
The Lymphatic System Consists of Two Main Parts: The Vessel Network and the Nodes and Organs.
What are the 2 major structures of the lymphatic system?
The two major lymphatics of the body include the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct. The right duct drains most of the right upper quadrant whereas the thoracic duct drains the lower body including the extremities and abdomen. To ensure that fluid does not flow backward, all lymphatic have one-way valves.
What are the 2 types of lymphatic tissue and where are they found?
There are two primary lymphatic organs: the red bone marrow and the thymus gland. The development of white blood cells (haemopoesis) was covered briefly in the section on blood. Both T-cell and B-cells are 'born' in the bone marrow.
What are the 2 functions of the lymphatic system?
It produces and releases lymphocytes (white blood cells) and other immune cells that monitor and then destroy the foreign invaders — such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi — that may enter your body. Transports and removes waste products and abnormal cells from the lymph.
When should I call my doctor about an issue with my lymphatic system?
Call your doctor if you experience fatigue (extreme tiredness) or have unexplained swelling that lasts more than a few weeks or interferes with your daily activities .
What is the lymphatic system?
Overview. The lymphatic system is a network of tissues, vessels and organs that work together to move lymph back into your your bloodstream. The lymphatic system is part of your immune system.
What system collects excess fluid from cells and tissue throughout the body?
Maintains fluid levels in your body: As just described, the lymphatic system collects excess fluid that drains from cells and tissue throughout your body and returns it to your bloodstream, which is then recirculated through your body.
How to check if lymphatic system is working?
To see if your lymphatic system is working as it should, your doctor may use imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI. These tests allow your doctor to see blockages in your lymphatic system.
Which ducts are used to collect lymph?
Collecting ducts: Lymphatic vessels empty the lymph into the right lymphatic duct and left lymphatic duct (also called the thoracic duct). These ducts connect to the subclavian vein, which returns lymph to your bloodstream. The subclavian vein runs below your collarbone.
How much plasma does the body use?
Some 20 liters of plasma flow through your body’s arteries and smaller arteriole blood vessels and capillaries every day. After delivering nutrients to the body’s cells and tissues and receiving their waste products, about 17 liters are returned to the circulation by way of veins. The remaining three liters seep through the capillaries and into your body’s tissues. The lymphatic system collects this excess fluid, now called lymph, from tissues in your body and moves it along until it's ultimately returned to your bloodstream.
Where are lymph nodes located?
A few of the more familiar locations of lymph nodes are in your armpit, groin and neck. Lymph nodes are connected to others by the lymphatic vessels.·.
What is lymphatic insufficiency?
Lymphatic insufficiency occurs from a decrease in reabsorption or a decrease in transport capacity of the lymphatic system. It can be primary malformation of the lymph system or an acquired condition due to obstruction or damage to the system ( TABLE 5-1 ).
What causes secondary lymphedema?
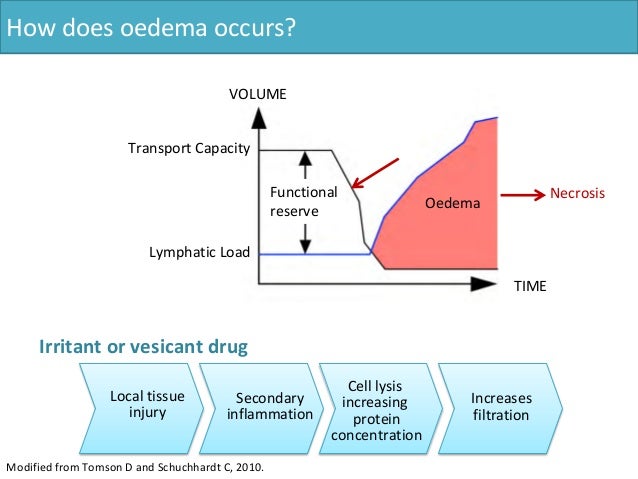
A frequent cause of secondary lymphedema is chronic venous insufficiency ( FIGURE 5-16 ). 5, 6 The sequence of events is as follows: The venous system becomes compromised and cannot accommodate the normal amount of venous flow. The lymphatic system, when healthy, can compensate because it can increase its rate of lymphangion contraction up to 10 times its resting volume and transport the fluid normally carried by the venous system. 1 For edema to develop in patients with chronic venous insufficiency, one of two scenarios must occur. Either the lymphatic and venous load exceeds the maximum transport capacity of the lymphatic system or the lymphatic system becomes impaired and cannot transport the usual fluid load. The lymphatic impairment may be caused by incompetent lymphatic valves due to distended vessels. 7, 8
What is primary lymphedema?
Primary lymphedema is a result of congenital malformations of the lymphatic system, although the consequences may not be observed in the early years ( FIGURES 5-13 and 5-14 ). Secondary lymphedema is a result of acquired damage to the lymph vessels or nodes and subsequent impaired reabsorption and/or transportation of lymphatic fluid ( FIGURE 5-15 ). Refer to TABLE 5-1 for more details of both types.
What is lymphedema mobilization?
Lymphedema is a chronic inflammatory condition that develops as a result of lymphatic insufficiency.
What is lymph node anatomy?
Lymph node anatomy A greater number of afferent vessels bring fluid to a lymph node and a lesser number of efferent vessels leave the lymph node. This anatomical arrangement permits a slower rate of lymph transport through the lymph nodes and thus allows time for the immune system to phagocytose bacteria, waste products, and dead cells. For individuals with cancer who undergo a lymph node dissection, the rate of flow through the regional lymph node is automatically decreased. This sets the stage for potential lymphatic congestion in the affected quadrant and may lead to lymphedema.
Why is my lower leg orange?
Secondary lymphedema due to trauma The tight, orange-peel texture of the lower leg skin is a result of lymphedema that has developed after a lateral ankle injury. Any trauma that disrupts the lymphatic flow, limits joint range of motion, and alters gait cycle can result in lymphedema formation.
Which lymphatic system has specific drainage routes to regional lymph nodes?
Full-body lymphatic system The superficial network of lymphatic vessels have specific drainage routes to regional lymph nodes.
How much does a De la Heart lymphatic drainage tool cost?
It's De la Heart's Lymphatic Drainage Body Tool ($29) —which the company graciously gifted to me for this story, full disclosure—with some jojoba oil to help the tool glide over your skin.
What to expect during lymphatic drainage?
What to Expect During a Lymphatic Drainage. If someone is giving you a lymphatic drainage massage, prepare to definitely feel them working on you —it’s not a Swedish massage, it’s definitely deeper. But also, expect to feel lighter when it’s over and to look more contoured.
How to do MWH?
“Think [about moving] up the limbs, [so] up the arms from the wrist to the armpit, and then down the torso to eliminate extra fluid and toxins in the body.
Why is it important to improve the immune system?
Improves the immune system due to the important elimination of toxins
Does Wood massage at home?
At home, just like with the lymphatic massage Wood did on herself (and what you’ll see me do on myself below), you’ll notice similar results to having a professional work on you, but, in my opinion, there is less of an immediate contoured effect. This is mainly because you won’t be able to work as deep on yourself as someone else would. The biggest difference: As Wood mentioned in her video, while at-home lymphatic drainage is easy and accessible, it’s always more fun to have someone massage you because you’re not doing any of the work!
Is lymphatic drainage dangerous?
Since you’re promoting proper lymph movement—something your body is meant to do naturally—there is little risk with lymphatic drainage. However, you want to make sure you’re doing it properly. Always moving the lymph toward your heart with upward motions, and then downward motions on your belly toward your groin.
Is it important to raise a glass of water after lymphatic drainage?
Sure, they may not be as visible to someone else, but I’m not doing it for anyone else—just me. So, with that said, I’m raising a tall glass of water (as I mentioned, it’s important to stay hydrated after you do any form of lymphatic drainage) and cheers to new, at-home routines that can make you feel good about yourself as we all stay home and stay safe.
