
Key Takeaways: How Magnets Work
- Magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field.
- The two sources of magnetism are electric current and spin magnetic moments of elementary particles (primarily electrons).
- A strong magnetic field is produced when the electron magnetic moments of a material are aligned. ...
Full Answer
Do magnets really work?
The study also revealed the anti-inflammatory effects of magnets. Thus, the magnetic effect not only helped to boost blood circulation but also decreased the swelling. Although, these beneficial effects of magnets are yet to be proved in human trials, there is hope that further research may soon report the positive impact of magnets on humans.
How do magnets work at the physical level?
Key Takeaways: How Magnets Work
- Magnetism is a physical phenomenon by which a substance is attracted or repelled by a magnetic field.
- The two sources of magnetism are electric current and spin magnetic moments of elementary particles (primarily electrons).
- A strong magnetic field is produced when the electron magnetic moments of a material are aligned. ...
What is a magnet and how does it work?
This article explains how permanent magnets work. The working principle of a permanent magnet is related to its atomic structure. Most materials are composed of molecules, molecules are composed of atoms, and atoms are composed of nuclei and electrons. Inside the atom, electrons keep spinning and rotate around the nucleus.
How are magnets used to make objects?
- Toys: Given their ability to counteract the force of gravity at close range, magnets are often employed in children's toys, such as the Magnet Space Wheel and Levitron, to amusing ...
- Refrigerator magnets are used to adorn kitchens, as a souvenir, or simply to hold a note or photo to the refrigerator door.
- Magnets can be used to make jewelry. ...

What is a magnet and how does it work?
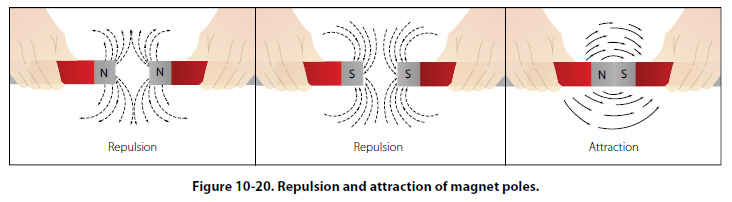
All magnets have north and south poles. Opposite poles are attracted to each other, while the same poles repel each other. When you rub a piece of iron along a magnet, the north-seeking poles of the atoms in the iron line up in the same direction. The force generated by the aligned atoms creates a magnetic field.
What are magnets answer?
An object which is capable of producing magnetic field and attracting unlike poles and repelling like poles.
How do magnets work explained for kids?
Magnets produce lines of magnetic force which leave a magnet from its north pole and re-enters the magnet at the south pole. When two magnets are placed together one magnet's north pole will attract the other's south pole. However, two north poles or two south poles will always repel each other.
How do magnets work on earth?
If you have a rotating electric current, it will create a magnetic field. On Earth, flowing of liquid metal in the outer core of the planet generates electric currents. The rotation of Earth on its axis causes these electric currents to form a magnetic field which extends around the planet.
What is a magnet class 6?
Magnets are the naturally occurring substances with the property of attracting iron. A magnet. It is found that naturally occurring rocks have the property of attracting small pieces of iron. Hence, they are called as natural magnets. They are permanent magnets in nature.
What is a magnet class 6 question answer?
Answer: Solution: The substances which have the property of attracting iron are called magnets.
What are magnets for grade 1?
A magnet is a rock or a piece of metal that can pull certain types of metal toward itself. The force of magnets, called magnetism, is a basic force of nature, like electricity and gravity. Magnetism works over a distance. This means that a magnet does not have to be touching an object to pull it.
What is a magnet for Grade 3?
A magnet is an object that can attract some metals like iron. Static electricity can also attract objects without touching them, but it works a bit differently. It can attract and repel due to electrical charges.
What is a magnet Grade 7?
Magnetism is the force that pulls (attracts) or pushes (repels) an object which contains metal towards, or away from, a magnet. A magnet has an area around it over which it can exert a force on objects. The further away the object is from the magnet, the weaker the force. This area is called the magnetic field.
What are uses of magnet?
What are 5 uses of magnets?A magnet is used in a compass to show the direction.Powerful magnets are used to lift objects.Magnets are used in generators and motors.Prevents corrosion in a water heater. ... Magnets are used in medical equipment.
What is magnet made of?
Magnets are made of a group of metals called ferromagnetic metals. Nickel and iron are examples of these metals. Metals such as these are unique in their ability to be magnetized uniformly.
What is a magnet in science?
A magnet is an object that creates a magnetic field: This field is invisible, but it's responsible for the most obvious property of a magnet: the ability to attract some materials, like iron, and attract or repel other magnets.
What is a magnet class 4?
A magnet is a rock or a piece of metal that can pull certain types of metal toward itself. The force of magnets, called magnetism, is a basic force of nature, like electricity and gravity. Magnetism works over a distance. This means that a magnet does not have to be touching an object to pull it.
What is magnet short?
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets.
What is in a magnet?
Most permanent magnets contain iron, nickel, or cobalt. Alnico is an alloy made up of aluminium, nickel and cobalt. A strong permanent magnet can be made from Alnico alloys. Consumer electronics and industrial applications use them extensively.
What is a magnet for Grade 3?
0:213:46Magnets and Magnetism | Magnets Video for Kids - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou surprised it's not a magical instrument it's a magnet a magnet is a rock or a piece of metalMoreYou surprised it's not a magical instrument it's a magnet a magnet is a rock or a piece of metal that can pull certain kinds of metal. Towards itself the force of magnets is called magnetism.
Why is the earth’s magnetic field important?
Without Earth’s magnetic field, life on the planet would eventually die out. That's because we would be exposed to high amounts of radiation from t...
Are humans electromagnetic?
Humans can generate their own electromagnetic fields. This can be explained due to the presence of small electric currents running in the body (gen...
Are magnets harmful to the body?
Whether the magnetic field of a magnet is harmful to the human body depends on its strength. Scientists agree that magnets under 3000 Gauss are har...
Can magnets damage my Macbook?
Magnets can damage a Macbook. This is because the data on your computer’s hard disk can be erased due to the magnetization of a nearby magnet. If t...
What is magnetic inductance?
Magnetic inductance is defined as a property that allows any material (such as iron) to temporarily acquire magnetic properties when placed near an...
How do magnets work?
Magnets work because they contain what are called magnetic domains – little bits of matter that are magnetically polarized north to south. In most metals, these point in every direction and cancel each others magnetic fields. In a magnet, they are all aligned in more or less the same direction, so the overall objects acts like one big magnetic domain.
How do magnets lose their attraction?
On the other hand, magnets can lose their attraction if you randomize the direction of the domains within it, by heating it up to a high temperature or by bashing it enough times.
What is the property of a magnet?
This magnetic field is responsible for the property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials and attracts or repels other magnets.
What are the materials that are attracted to a magnet?
Materials that can be magnetized such as iron and steel, which are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic. Although ferromagnetic materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances that respond weakly to a magnetic field cannot be attracted by a magnet, are called non-magnetic materials, such as rubber, plastic, wood, glass and even some metals such as aluminium, copper and gold.
How does an electric current affect the magnetic field?
If you introduce electric current, the domains will start to line up with the external magnetic field. The more current applied, the higher the number of aligned domains. As the external magnetic field becomes stronger, more and more of the domains will line up with it. There will be a point where all of the domains within the iron are aligned with the external magnetic field (saturation), no matter how much stronger the magnetic field is made. After the external magnetic field is removed, soft magnetic materials will revert to randomly oriented domains; however, hard magnetic materials will keep most of their domains aligned, creating a strong permanent magnet.
How do magnets work?
If you've read How Electromagnets Work, you know that an electrical current moving through a wire creates a magnetic field. Moving electrical charges are responsible for the magnetic field in permanent magnets as well. But a magnet's field doesn't come from a large current traveling through a wire -- it comes from the movement of electrons.
Why do magnets attract?
This is because magnets attract materials that have unpaired electrons that spin in the same direction. In other words, the quality that turns a metal into a magnet also attracts the metal to magnets. Many other elements are diamagnetic -- their unpaired atoms create a field that weakly repels a magnet.
How do temporary magnets produce magnetic fields?
Temporary or soft magnets produce magnetic fields while in the presence of a magnetic field and for a short while after exiting the field. Electromagnets produce magnetic fields only when electricity travels through their wire coils. Iron filings (right) align along the magnetic field lines of a cubical neodymium magnet.
How do iron filings work?
Iron filings line up along the magnetic fields of four small magnets. After removing the magnet, the filings will continue to have their own weak magnetic fields. To make a magnet, all you have to do is encourage the magnetic domains in a piece of metal to point in the same direction.
What is the magnet in the office?
Around the office, the magnet became an object of curiosity and the subject of impromptu experiments. Its uncanny strength and its tendency to suddenly and noisily jump from unwary grips to the nearest metal surface got us thinking. We all knew the basics of magnets and magnetism -- magnets attract specific metals, and they have north and south poles. Opposite poles attract each other while like poles repel. Magnetic and electrical fields are related, and magnetism, along with gravity and strong and weak atomic forces, is one of the four fundamental forces in the universe.
How to make a magnet?
To make a magnet, all you have to do is encourage the magnetic domains in a piece of metal to point in the same direction. That's what happens when you rub a needle with a magnet -- the exposure to the magnetic field encourages the domains to align. Other ways to align magnetic domains in a piece of metal include: 1 Placing it a strong magnetic field in a north-south direction 2 Holding it in a north-south direction and repeatedly striking it with a hammer, physically jarring the domains into a weak alignment 3 Passing an electrical current through it
Why do cows need magnets?
Magnets can also protect the health of animals. Cows are susceptible to a condition called traumatic reticulopericarditis, or hardware disease, which comes from swallowing metal objects. Swallowed objects can puncture a cow's stomach and damage its diaphragm or heart. Magnets are instrumental to preventing this condition. One practice involves passing a magnet over the cows' food to remove metal objects. Another is to feed magnets to the cows. Long, narrow alnico magnets, known as cow magnets, can attract pieces of metal and help prevent them from injuring the cow's stomach. The ingested magnets help protect the cows, but it's still a good idea to keep feeding areas free of metal debris. People, on the other hand, should never eat magnets, since they can stick together through a person's intestinal walls, blocking blood flow and killing tissue. In humans, swallowed magnets often require surgery to remove.
What Is a Magnet?
A magnet is any material capable of producing a magnetic field. Since any moving electric charge generates a magnetic field, electrons are tiny magnets. This electric current is one source of magnetism. However, the electrons in most materials are randomly oriented, so there is little or no net magnetic field. To put it simply, the electrons in a magnet tend to be oriented the same way. This happens naturally in many ions, atoms, and materials when they are cooled, but isn't as common at room temperature. Some elements (e.g., iron, cobalt, and nickel) are ferromagnetic (can be induced to become magnetized in a magnetic field) at room temperature. For these elements, the electrical potential is lowest when the magnetic moments of the valence electrons are aligned. Many other elements are diamagnetic. The unpaired atoms in diamagnetic materials generate a field that weakly repels a magnet. Some materials don't react with magnets at all.
What is the force produced by a magnet?
The force produced by a magnet is invisible and mystifying. Have you ever wondered how magnets work ?
Why is nuclear magnetic moment weaker than electronic magnetic moment?
The nuclear magnetic moment is much weaker than the electronic magnetic moment because although the angular momentum of the different particles may be comparable, the magnetic moment is inversely proportional to mass (mass of an electron is much less than that of a proton or neutron).
What are the two sources of magnetism?
The two sources of magnetism are electric current and spin magnetic moments of elementary particles ( primarily electrons). A strong magnetic field is produced when the electron magnetic moments of a material are aligned. When they are disordered, the material is neither strongly attracted nor repelled by a magnetic field.
Is nickel ferromagnetic or diamagnetic?
Some elements (e.g., iron, cobalt, and nickel) are ferromagnetic (can be induced to become magnetized in a magnetic field) at room temperature. For these elements, the electrical potential is lowest when the magnetic moments of the valence electrons are aligned. Many other elements are diamagnetic. The unpaired atoms in diamagnetic materials ...
Do magnets have a magnetic field?
However, the electrons in most materials are randomly oriented, so there is little or no net magnetic field. To put it simply, the electrons in a magnet tend to be oriented the same way. This happens naturally in many ions, atoms, and materials when they are cooled, but isn't as common at room temperature.
How do magnets work?
It starts with matter – physical substances which make up all objects in the universe – and the microscopic atoms which make up matter.
What are magnets used for?
From magnetic clips and push pins – good for use in the kitchen, classroom or office – to heavy duty retrieving, separating and welding magnets designed for use in manufacturing shops. Magnets have a variety of applications.
What is the second strongest permament magnet?
Samarium Cobalt. A second type of rare earth magnet, it is composed of samarium, cobalt and iron. Samarium Cobalt (SmCo) magnets have high resistance to demagnetization, good temperature stability and are the second strongest permament magnets available.
What is the strongest magnet?
Neodymium magnets (NdFeb, NIB, Neo), also known as “rare earth magnets,” are composed of neodymium, iron, boron and transition metals. Despite their small size, these magnets are incredibly powerful and are the strongest magnetic material available.
What are ceramic magnets made of?
Ceramic (Ferrite) Magnets. Composed of strontium carbonate and iron oxide, ceramic (ferrite) magnets are one of the popular types of magnet, partly due to their cost-efficiency. They can be manufactured in the forms of discs, rings, blocks, cylinders and sometimes arcs. Ceramic magnets have a variety of applications, including speakers, ...
What is an alnico magnet?
Alnico Magnets. Alnico magnets are made primarily from (Al), (Ni) and (Co), hence al-ni-co. Alnico magnets are available in a variety of shapes and sizes and are very temperature stable. They produce a strong magnetic field and are commonly known for their popularity as red horseshoe or bar magnets.
How many poles does a magnet have?
Magnets are objects made with specific elements, creating a magnetic field. All magnets have at least two poles – north and south – with the magnetic field lines exiting the north end and re-entering at the south end of the magnet. Every magnet retains a north and south pole, regardless of size, even if it has been broken into multiple pieces.
What type of magnet is created when a current of electricity moves through a coil of wire?
Another type of manmade magnet is the electromagnet. Electromagnets are created when a current of electricity moves through a coil of wire. The coil is magnetic as long as it is receiving the electrical current. But pull the plug on the electricity, and you’ll pull the plug on the magnetism, too.
What are the materials that make up magnets?
There is a group of materials known as ferromagnetic materials. This group includes iron, cobalt, nickel, and some alloys of rare earth elements (mainly neodymium and samarium).
What is a permanent magnet?
These are referred to as permanent magnets. Some will only be magnetic when in the presence of an external magnetic field, such as from a permanent magnet. These “temporary” magnets are called soft magnets. *Permanent magnets can lose their strong magnetism when heated to a Curie Temperature.
Can you make your own magnet?
While you’d need highly specialized machinery to create most manmade magnets, you can create your own simple electromagnet or conduct in-depth electromagnet projects at home or in school!
Is lodestone a magnet?
Lodestone, a naturally magnetized piece of magnetite, attracts iron, so it is technically a magnet. There are some fun stories about the ancient discoveries and uses of magnetite and lodestone on our blog. The rest of the magnets we see today are created—manmade. There is a group of materials known as ferromagnetic materials.
Memes Used As A Defense Mechanism: The Western World Watches As Russia Invades Ukraine
The ongoing Russian-Ukrainian Conflict has escalated this week after Putin recognized Russian-backed regions Donetsk and Luhansk as part of his country.
Kanye West's 'DONDA 2' Release Concert And Livestream Event Has Several Highlight Moments As It Trends Online
Kanye West's highly anticipated sequel Donda 2 had a listening party in Miami in which a concert performance was given to the track list before the album drops. Between the celebrity cameos and sound issues, the night and livestreamed performance became
Official Russian Government Accounts On Social Media Continue Posting Memes And Constant Trolling As Troops Invade Ukraine
The Russian government's social media presence as of late has been characterized by a lot of trolling and memery, coinciding with the country's recent aggressive foreign policy.
What Is A Magnet?
The Magnetic Dipole and Magnetism
- The atomic magnetic dipole is the source of magnetism. On the atomic level, magnetic dipoles mainly are the result of two types of movement of the electrons. There is the orbital motion of the electron around the nucleus, which produces an orbital dipole magnetic moment. The other component of the electron magnetic moment is due to the spindipole magnetic moment. Howev…
The Atomic Nucleus and Magnetism
- The protons and neutrons in the nucleus also have orbital and spin angular momentum, and magnetic moments. The nuclear magnetic moment is much weaker than the electronic magnetic moment because although the angular momentum of the different particles may be comparable, the magnetic moment is inversely proportional to mass (mass of an electron is much less than t…
Sources
- Cheng, David K. (1992). Field and Wave Electromagnetics. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. ISBN 978-0-201-12819-2.
- Du Trémolet de Lacheisserie, Étienne; Damien Gignoux; Michel Schlenker (2005). Magnetism: Fundamentals. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-22967-6.
- Kronmüller, Helmut. (2007). Handbook of Magnetism and Advanced Magnetic Materials. Joh…
- Cheng, David K. (1992). Field and Wave Electromagnetics. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. ISBN 978-0-201-12819-2.
- Du Trémolet de Lacheisserie, Étienne; Damien Gignoux; Michel Schlenker (2005). Magnetism: Fundamentals. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-22967-6.
- Kronmüller, Helmut. (2007). Handbook of Magnetism and Advanced Magnetic Materials. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-02217-7.