
What are ependymal cells made of?
Ependymal cells are clearly defined as a subtype of glial cells because they are nonneuronal cells in the brain that are derived from neuroectoderm. They are made up of ependymocytes, choroid plexus epithelial cells, tanycytes, and Müller cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells.
What are cells called that have nuclei?
Only the cells of advanced organisms, known as eukaryotes, have a nucleus. Generally there is only one nucleus per cell, but there are exceptions, such as the cells of slime molds and the Siphonales group of algae. Simpler one-celled organisms (prokaryotes), like the bacteria and cyanobacteria, don’t have a nucleus.
What cells are in both plant and animal cells?
- The plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and contain well developed cellular organelles.
- The cell membrane, cytoplasm, chromosomes, and mitochondria are the structures that are present in both the plant and the animal cells.
- The cell wall and chloroplast are present only in the plant cell.
What cell types are derived from stem cells?
Types of Adult Stem Cells:
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (Blood Stem Cells)
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Neural Stem Cells
- Epithelial Stem Cells
- Skin Stem Cells
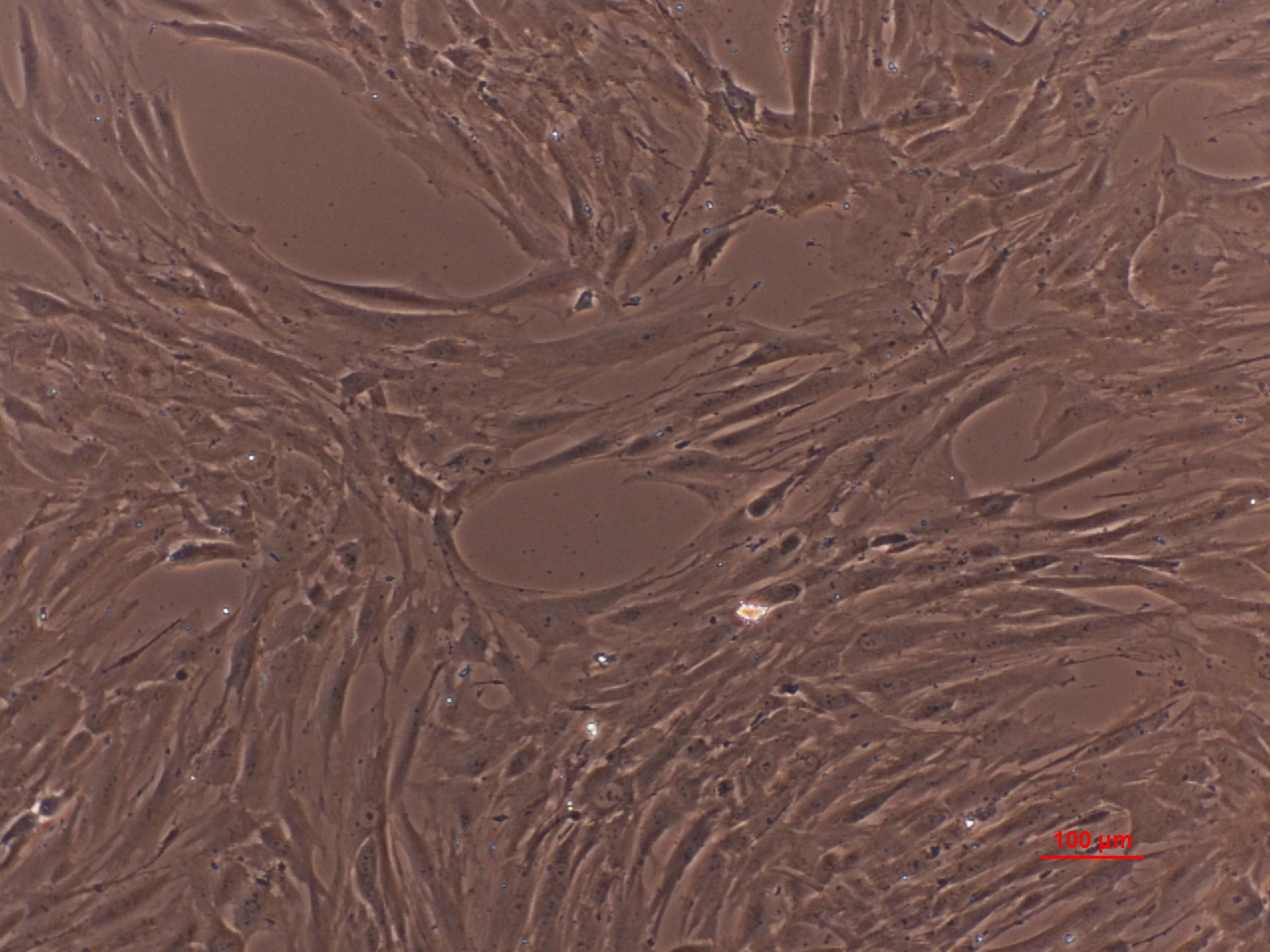
What is the definition of a mesenchymal cells?
(meh-ZEN-kih-mul) Refers to cells that develop into connective tissue, blood vessels, and lymphatic tissue.
What tissue has mesenchymal cells?
Mesenchymal Stem Cells In the case of MSCs, the lineage-committed cells can generate a variety of specialized mesenchymal tissues including bone, cartilage, muscle, marrow stroma, tendon, ligament, fat, and a variety of other connective tissues (Caplan, 1994).
What is the difference between stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells?
MSCs (also known as Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stromal Cells or Medicinal Signalling Cells) are an example of tissue or 'adult' stem cells. They are 'multipotent', meaning they can produce more than one type of specialized cell of the body, but not all types.
What is mesenchymal tissue made of?
Mesenchyme is a type of animal tissue comprised of loose cells embedded in a mesh of proteins and fluid, called the extracellular matrix.
Where are mesenchymal cells most commonly found?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are adult stem cells traditionally found in the bone marrow. However, mesenchymal stem cells can also be isolated from other tissues including cord blood, peripheral blood, fallopian tube, and fetal liver and lung.
What is the difference between epithelial and mesenchymal cells?
Epithelial cells are specialized cells, which line cavities, organs, and vessels in the body. In contrast, mesenchymal cells are unspecialized cells, which are capable of differentiating into any type of cells in the body at any time.
What is the function of mesenchymal cells?
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent stem cells found in bone marrow that are important for making and repairing skeletal tissues, such as cartilage, bone and the fat found in bone marrow. With age and disease, MSCs predominantly convert into lipid-accumulating fat cells.
What are the 4 types of stem cells?
Stem cellsEmbryonic stem cells.Tissue-specific stem cells.Mesenchymal stem cells.Induced pluripotent stem cells.
Do adults have mesenchymal cells?
Sources. MSCs are present not only in fetal tissues but also in many adult tissues with few exceptions. Efficient population of MSCs has been reported from bone marrow [10].
What develops from the mesenchyme?
The mesenchyme develops into the tissues of the lymphatic and circulatory systems, as well as the musculoskeletal system. This latter system is characterized as connective tissues throughout the body, such as bone, and cartilage. A malignant cancer of mesenchymal cells is a type of sarcoma.
What type of tissue is mesenchyme?
Mesenchyme, or mesenchymal connective tissue, is a type of undifferentiated connective tissue. It is predominantly derived from the embryonic mesoderm, although may be derived from other germ layers, e.g. mesenchyme derived from neural crest cells (ectoderm).
What is the difference between parenchyma and mesenchymal?
The key difference between parenchyma and mesenchymal cells is that the parenchyma cells cannot differentiate whereas the mesenchymal cells are capable of differentiating. There are different types of cells in multicellular organisms that are necessary for various biological functions.
What type of tissue is mesenchyme?
Mesenchyme, or mesenchymal connective tissue, is a type of undifferentiated connective tissue. It is predominantly derived from the embryonic mesoderm, although may be derived from other germ layers, e.g. mesenchyme derived from neural crest cells (ectoderm).
Where are mesenchymal cells found quizlet?
Mesenchyme is located only in the umbilical cord.
What cells are found in connective tissue proper?
The common cell types in connective tissue include: fibroblasts, mast cells, plasma cells, macrophages, adipocytes, and leukocytes.
Where does mesenchyme come from?
Mesenchyme is an embryonic precursor tissue that generates a range of structures in vertebrates including cartilage, bone, muscle, kidney and the erythropoietic system. Mesenchyme originates from both mesoderm and the neural crest, an ectodermal cell population, via an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Overview
Structure
While the terms mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) and marrow stromal cell have been used interchangeably for many years, neither term is sufficiently descriptive:
• Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue that is derived from the mesoderm and that differentiates into hematopoietic and connective tissue, whereas MSC…
Location
Function
Clinical significance
Research
History
Controversies