Posted on : 26-11-2017 Posted by : Admin
- METHODS OF LOCOMOTION IN PROTOZOANS Basically there are four known methods by which the protozoans move 1. Amoeboid movement 2. Swimming movement 3. ...
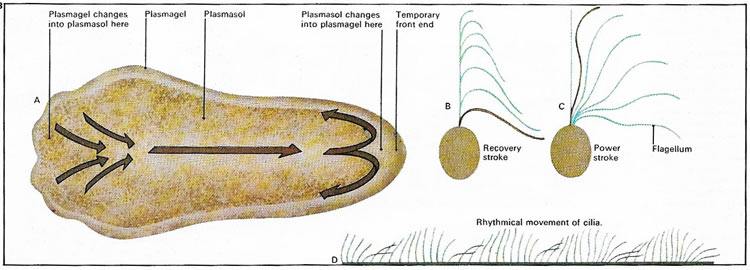
- AMOEBOID MOVEMENT This type of locomotion is also called as pseudopodial locomotion. ...
- METABOLIC MOVEMENT In protozoans a pellicle is present in the ectoplasm which is composed of proteinaceous strips supported by dorsal and ventral microtubules. ...
- SWIMMING MOVEMENT ...
How do protozoa perform locomotion?
The Protozoa perform locomotion in four different ways, each with a particular type of locomotory organelles, and each characteristic of a different class of the phylum. The ways are: 1. Amoeboid Movement 2. Flagellar Movement 3. Ciliary Movement 4. Metabolic Movement. Mode # 1. Amoeboid Movement:
What are the modes of locomotion in protists?
The following points highlight the five modes of locomotion in Protists. The modes are: 1. Pseudopodial Locomotion 2. Flagellar Locomotion 3.
What are the different types of movement of protozoon?
Ciliary Movement 4. Peristaltic Movement. Type # 1. Pseudopodial Movement: Some protozoon’s move with the help of pseudopodia. Pseudopodia are blunt, fingerlike temporary protrusions of the cytoplasm. These may be variously shaped. Large numbers of pseudopodia are present on the body surface of some individuals.
What are the different modes of locomotion in plants?
The modes are: 1. Pseudopodial Locomotion 2. Flagellar Locomotion 3. Ciliary Locomotion 4. Wriggling Locomotion 5. Locomotion by Mucilage Propulsion. Mode # 1. Pseudopodial Locomotion: It is slow creeping type of locomotion which is performed with the help of protoplasmic outgrowths called pseudopodia.
What are the 3 methods of locomotion seen in protozoans mention examples for each?
Types of Locomotion in ProtozoaLocomotion by pseudopodia. I. This type of locomotion is seen in animals that do not have a set structure for mobility and are amorphous. ... Locomotion by flagella. I. These are found in flagellated protists. ... Locomotion by cilia. I. ... Wriggling locomotion or Sporozoan movement. I.
What are the 4 methods of locomotion of protists?
In Protists, the important mechanism of locomotion is through the use of different structures such as pseudopodia, flagella, cilia, wriggling and locomotion through mucilage propulsion.
What methods of motility do protozoans use?
They are motile and can move by: Cilia - tiny hair like structures that cover the outside of the microbe. They beat in a regular continuous pattern like flexible oars. Flagella - long thread-like structures that extend from the cell surface.
How many types of locomotion organs are there in protozoa?
Locomotory organelles found in protozoa are -Pseudopodia, Flagella, Cilia and Myonemes.
What are the 3 types of locomotion found in protists?
Biologists generally categorize protists according to their Mode of movement, or locomotion. All protists can travel through water by one of three methods: cilia, flagella, or pseudo/axopodia.
What are the 3 types of motility that protists have?
Motility of Protists Protists have three types of appendages for movement. As shown in Figure below, they may have flagella, cilia, or pseudopods (“false feet”). There may be one or more whip-like flagella. Cilia are similar to flagella, except they are shorter and there are more of them.
What are the 3 main types of protozoans?
There are three major categories of protozoa: the flagellates, the amoebae, and the ciliates. The flagellates are the smallest of the protozoa and move by means of one to several flagella.
What is the method of motility of Paramecium?
Protists use various methods for transportation. (a) Paramecium waves hair-like appendages called cilia to propel itself. (b) Amoeba uses lobe-like pseudopodia to anchor itself to a solid surface and pull itself forward. (c) Euglena uses a whip-like tail called a flagellum to propel itself.
What are the 4 types of protozoans?
For our purposes, there are only 4 groups of protozoa that will be covered here: these groups are separated by motility and cell structure.Amebas (representative: Ameba proteus)Flagellates (representative: Trypanosoma, Euglena)Ciliates (representative: Paramecium)Apicomplexa (representative: Plasmodium)
Which is the Locomotory organ of class of protozoa?
The locomotory organs of protozoa are cilia, flagella and pseudopodia.
How are protozoa classified depending on their organ of locomotion?
Protozoa can be divided into four phyla based on their locomotion: Mastigophora, Sarcodina, Ciliophora, and Sporozoa. Members of the phylum Mastigophora move about by using one or more whiplike flagella.
Which protozoa has no organ of locomotion?
ParapodiaSuch a locomotion process is not found in protozoans. Thus, the correct answer is option 'D'. Parapodia.
What are modes of locomotion?
Animal locomotion, in ethology, is any of a variety of methods that animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flying, hopping, soaring and gliding.
Which list includes four types of animal-like protists?
There are four main types of animal-like protists; these are the amoeba, the flagellates, the ciliates, and the sporozoans.
What are the different organs for locomotion of protozoans give examples of organisms for each?
Locomotory Organs in ProtozoaCellular extensions like Pseudopodia (Eg: Amoeba)Pellicular contractile structures like Myonemes (Eg: Euglena and Sporozoans)Locomotory organelles like Flagella (Eg: Paramecium) and Cilia (Eg: Euglena)
Which protists use flagella for locomotion?
Zooflagellates are a third type of protists. They are animal-like and move by using flagella. Flagella are whip-like structures that spin quickly, working like a boat's propeller to move the organism through water.
What are the four types of locomotion in protozoa?
In this article we will discuss about the four main types of locomotion in protozoa. The types are: 1. Pseudopodial Movement 2. Flagellate Movement 3. Ciliary Movement 4. Peristaltic Movement. Type # 1. Pseudopodial Movement: Some protozoon’s move with the help of pseudopodia.
How does pseudopodium move?
The pseudopodium is fixed on the support by some adhesive secretion and the protoplasm of the body gradually flows into it. As to the mechanism of pseudopodia movement, the most accepted view is change of viscosity (Hyman). It states that sol-gel conversion initiates movement in the protoplasm.
What is the pseudopodia of a polystomella?
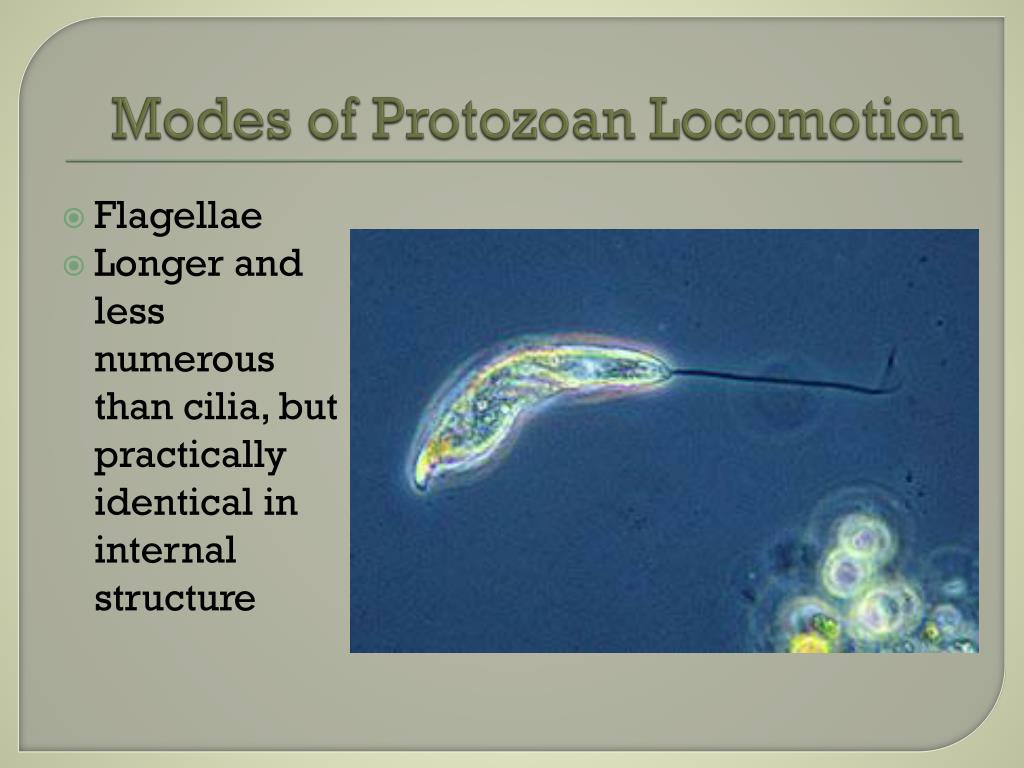
In Polystomella, the pseudopodia are known as reticulopodia (branching). Type # 2. Flagellate Movement: Certain protozoon’s move with the help of flagella. Flagella are whip-like structures in the formation of which cytoplasm takes part. These are usually 2-4 in number.
Which subphylum has locomotory organelles?
The members of the subphylum Sarcodina possess pseudopodia in the adult stage but, in the early stages, some of them bear flagella, which is the characteristic locomotory organelles of the subphylum Mastigophora.
What is the function of flagella?
The most plausible mechanism, as suggested by Lowden’s; is that the basic function of a flagellum is to produce rotation of the organism on its major axis, along with a mechanism which directs the animal. Type # 3. Ciliary Movement:
How do protozoa perform locomotion?
The ways are: 1. Amoeboid Movement 2. Flagellar Movement 3. Ciliary Movement 4. Metabolic Movement.
How do protozoa move?
The Protozoa possessing myonemes move by contraction of the body or stalk. Some flagellate (Euglena) perform wriggling or peristaltic movements by a wave of contraction and expansion passing over their body. Such movements have been termed euglenoid or metabolic movements.
What is the flagellum held out rigidly with slight concavity in the direction of stroke?
In the effective stroke the flagellum is held out rigidly with slight concavity in the direction of stroke. In the recovery stroke, however, flagellum is strongly curved and is brought forward again. Due to such flagellar action, the animal moves forward.
How fast do cilia move?
Thus, the animal moves forward in a spiral manner and the speed of movement are 400 to 2000µ per second. Ciliates are the fastest moving protozoans. The movement of cilia is controlled by the myonemes (neuronemes) present in the ectoplasm.
Which type of locomotion is a short, blunt pseudopodium in which endoplasm flows?
The ectoplasm protrudes out to form a short, blunt pseudopodium in which endoplasm flows. This type of locomotion is of lobose type in which a number of pseudopodia are formed in one direction or only one pseudopodium is formed. The latter is called of limax type.
What is the movement of an amoeboid?
Amoeboid Movement: It takes place with the help of finger-like pseudopodia which arise from the cytoplasm of the organism from any part of the body and may be withdrawn. In the pseudopodia cytoplasm flow in the direction of movement (locomotion) and thus, the organism moves forward.
How many processes are involved in the amoeboid movement?
The amoeboid movement involves four processes which occur simultaneously:
What are the three modes of locomotion?
Protozoans exhibit diverse modes of locomotion across the various groups, but the modes of locomotion can be broadly divided into flagellar, ciliary, and amoeboid movement . Only the ciliates among the three major motility groups of protozoans, however, represent a truly monophyletic group (or single evolutionary line). (Some non-ciliates, such as those of group Opalinata, possess cilia-like organelles that are fundamentally different from true cilia.) In contrast, flagella and pseudopodia are present in a wide variety of distantly related taxa.
How do amoeboids move?
Amoeboid movement is achieved by pseudopodia and involves the flow of cytoplasm as extensions of the organism. The process is visible under the light microscope as a movement of granules within the organism. The basic locomotory organelle is the pseudopodium. The way in which movement is effected can vary slightly among groups but generally involves the polymerization of cytoskeletal proteins ( actin and myosin) at the leading edge of the pseudopod, followed by the flow of cytoplasmic material into the vacancy produced through the polymerization process. The flow of cytoplasm provides the momentum necessary to propel the organism further in its direction of movement. Additional forces driving the amoeboid movement involve the “eupodium,” which extends into a potential substrate for a grab-like traction, similar to a tank tread. Pushing force is also generated in the posterior end of the organism by contractions of the cytoskeletal proteins.
How does the cilium work?
The cilium performs work against the viscous force of the water during both the effective and the recovery strokes. To be effective, each cilium must beat in a coordinated manner with its neighbouring cilia. A synchronized beat is passed along a ciliary row by means of a hydrodynamic linkage between the cilia.
How many pairs of microtubules are in the flagellum?
The structure of the eukaryotic flagellum consists of a cylinder ( axoneme) made up of a pair of central microtubules surrounded and joined by cross-bridges to a circle of nine pairs of microtubules. This “nine-plus-two” arrangement of the microtubules in the axoneme is surrounded by cytoplasm and ensheathed in cell membrane.
Where is the hydrogenosome found?
The hydrogenosome is found in the trichomonads, hypermastigotes, and some euglenids. Hydrogenosomes are thought to have evolved from mitochondria.
Which group of organisms are associated with sulfide-containing sediments?
One ecological group of ciliates (e.g., Metopus, Plagiopyla, and Caenomorpha) is associated with sulfide-containing sediments. The sulfur ciliates harbour endosymbiotic and ectosymbiotic bacteria, which may take the metabolic end products released by the ciliates and reutilize them for growth and energy-yielding processes. Similar to other anaerobic protozoans, these ciliates are believed to have reverted from an aerobic metabolism to an anaerobic lifestyle in order to exploit a specialized ecological niche.
Is anaerobic anaerobe an obligate symbiont?
Those eukaryotes that are anaerobic often are either parasites or obligate symbionts of multicellular organisms that have evolved from aerobic ancestors.
What are the different types of locomotion in protozoa?
The above describe organ beat in a different way causing different types of movement in protozoans, so protozoans have several types of movement such as amoeboid, flagellar, ciliary, and metabolic movement . Some of the protozoans movements are described here –.
Which protozoan has a central axial rod covered by adhesive and granular adhesive cytoplasm?
These are some-how straight, and each axopodium has a central axial rod covered by adhesive and granular adhesive cytoplasm. Example- Actinosphaerium. 2. Flagella. Flagella are the locomotory organ of flagellate protozoans, such as Trypanosoma, Euglena. Flagella are thread-like out projection on the body covering.
What is the name of the Pseudopodia with the filamentous structure?
b- Filopodia. Pseudopodia with the filamentous structure are called filopodia, these are usually tapering at the base and pointed at the tip. Filopodia are composed of only ectoplasm only. Example- Euglypha.
What is lobopodia in protozoa?
It is lobe-like pseudopodia with a round end, as in Amoeba. It moves by pressure flow mechanisms. Lobopodia is found in Amoebic protozoan.
Why do animals move in a spiral?
It might be because cilia do not beat directly straight, beating is somehow obliquely toward the right and might be cilia at oral groove beat more obliquely and vigorously away from the mouth. This combined effect causes swimming movement in the animal.
Which organisms have amoeboid movement?
Sarcodina, certain Mastigophora, and Sporozoa have characteristic amoeboid movement. The process of amoeboid movement is done by pseudopodia formations, pseudopodia are formed by streaming flow of cytoplasm in the direction of movement.
How does cilia work?
In each oscillation, there is a fast effective stroke followed by the recovery stroke, like flagellar movement. During effective stroke cilia expel the water in the backward direction like an oar of the boat, and in response if this effective stroke water propels the animal in the forward direction. During recovery stroke, cilia come in forward direction ready for next effective stroke. Cilia neither beat simultaneously nor independently, cilia beat progressively in a characterized wave-like manner.
What is the type of locomotion called?
AMOEBOID MOVEMENT. This type of locomotion is also called as pseudopodial locomotion. Here locomotion is brought about by the pseudopodia. It is the characteristic of rhizopod protozoans like Amoeba proteus and Entamoeba histolytica.
Where are pellicles found in protozoa?
In protozoans a pellicle is present in the ectoplasm which is composed of proteinaceous strips supported by dorsal and ventral microtubules. In many protozoans these protein strips can slide past one another, causing wriggling motion. This wriggling motion is called as metaboly or metabolic movement. This movement is mainly caused by the change in the shape of the body.
How do amoeba attach to the substratum?
Amoeboid locomotion can be explained in the following steps: Step 1: Initially Amoeba attaches itself to the solid substratum by the plasma lemma at the temporary anterior end . Step 2: Then the hyaline layer of the ectoplasm at the anterior end forms a thickened hyaline cap.
What is the basis of action of protein molecules?
Basis of action of protein molecules: Sol gel theory . Amoeboid locomotion is brought about by the protein molecules (actin and myosin) present in the cytoplasm. Goldacre and Lorsch explained the phenomenon of gelation and solation based on the folding and unfolding of these protein molecules.
How does the flagellum move?
A flagellum pushes the fluid medium at right angles to the surface of its attachment, by its bending movement. The bending movement of flagellum is made by the sliding of microtubules past each other with the help of dynein arms. The dynein arms show a complex cycle of movement with the energy provided by ATP. These dynein arms attaché to the outer microtubule of an adjacent doublet and pull the neighboring doublet. As the result the doublets slide past each other in opposite direction. The arms release and attach a little farther on the adjacent doublet and again pull the neighboring doublet.
How does the cilia move?
The beating of the cilia can be reversed to move backwards when a Paramoecium encounters any undesirable object in its path. The ciliary movement is coordinated by infraciliary system though neuromotor center called as motorium present near the cytopharynx in the ciliates like Paramoecium. The infraciliary system together with motorium form neuromotor system which helps in coordination of the beating of the cilia. Ciliary movement is the fastest locomotion in protozoans.
What is the step 10 of the plasmagel tube?
Step 10: The contraction of the plasmagel at the trailing end causes hydraulic pressure on the sol and makes the plasmosol flow forward continuously in the plasmagel tube.
What is the movement of an amorphous protist?
Amoeboid movement is an amorphous (without shape) movement, as these protists have no defined motile structures. Amoeboid movement utilizes psuedopodia (or membrane projections that fill with cytoplasm, resulting in pulling or rolling the rest of their body forward'), otherwise known as protoplasmic flow.
What is the name of the organism that travels through water?
All protists can travel through water by one of three methods: cilia, flagella , or pseudo/axopodia.
What is the axopodia?
Another type of 'podia' are axopodia, which are basically pseudopodia with a microtubule core, resulting in a rod-like structural core covered by a membrane and surrounded by cytoplasmic fluid. Axopodia are found in protists known as Heliozoa and are used in a similar fashion to the protoplasmic flow of pseudopodia.
What do cilia do?
Ciliates, such as the little paramecium pictured here, are the largest of the bunch. Each has little hair-like projections, called cilia, trailing off of its pellicle, a membrane surrounding the organism. The protists uses the cilia to rhythmically beat against its fluid environment. You could think of cilia as like thousands of little oars that the organism coordinates for movement. Ciliates, being the largest of the three protists, tend to feed on the other two type of protists (as well as bacteria), which they collect in their oral groove (or mouth) and engulf. They can also use their cilia to create a small current, which allows the protists to essentially sit back while their food comes to them.
What is the difference between a protist and an eukaryote?
Lesson Summary. Protists are eukaryotes that do not belong to the animal, plant, or fungi kingdoms and are often defined by the way they move. Eukaryotes are organisms with membrane bound organelles that includes a nucleus.
Is a protist an eukaryote?
But in general, a protist is considered a eukaryote and that does not belong to the animal, plant, or fungi kingdoms being composed of some very diverse organisms, such as protozoans, unicellular algae, ...
What is the mode of locomotion?
Mode # 1. Pseudopodial Locomotion: It is slow creeping type of locomotion which is performed with the help of protoplasmic outgrowths called pseudopodia. Pseudopodial locomotion occurs in sarcodines and slime moulds.
What type of locomotion does Flagella have?
Flagella show whip-like movement. They usually beat independently. This type of locomotion occurs in dinoflagellates (e.g., Gonyaulax), euglenoids (e.g., Euglena) and zoo-flagellates (e.g., Leishmania).

Locomotory Organelles in Protozoa
II. Method of Locomotion
- The above describe organ beat in a different way causing different types of movement in protozoans, so protozoans have several types of movement such as amoeboid, flagellar, ciliary, and metabolic movement. Some of the protozoans movements are described here –
References and Sources
- A Text-Book of Zoology Invertebrates by R.L. Kotpal tenth edition.
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780126569766501499
- 1% – https://www.notesonzoology.com/protozoa/modes-of-locomotion-in-protozoa-microorganisms-zoology/9164
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudopods