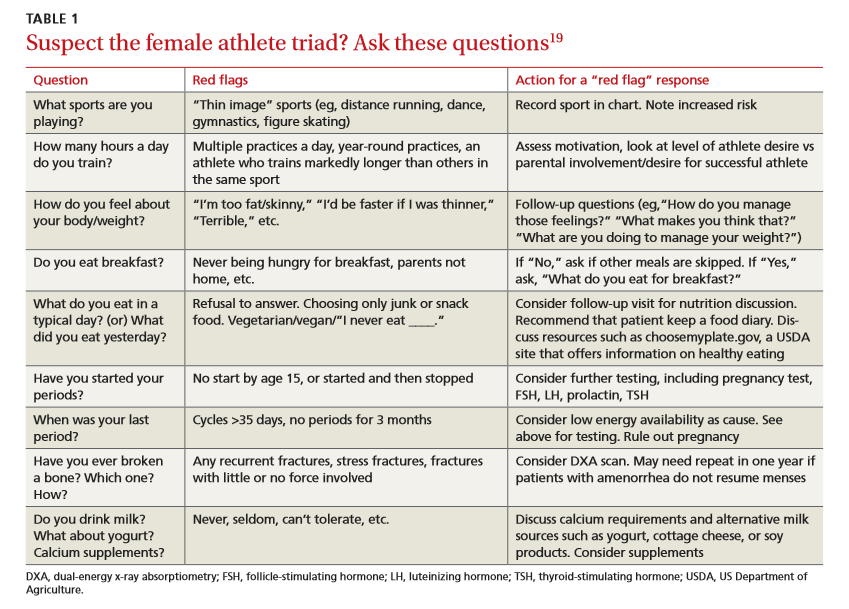
Percentage of Adults Reporting Selected Modifiable Risk Factors, Ontario, 2014 [1]
| RISK FACTOR | DEFINITION | AGE RANGE | PERCENTAGE |
| Current smoking | Adults who report smoking daily or occas ... | ≥20 years | 18.7% |
| Alcohol consumption | Adults who report drinking alcohol in ex ... | ≥19 years | 8.2% |
| Obesity | Adults with a body mass index (BMI)≥ 30 ... | ≥18 | 26.8% |
| Physical activity | Adults who are moderately active or acti ... | ≥18 | 51.5% |
Why are 5 key risk factors modifiable?
They are modifiable because they can, in theory, be changed. These 5 key modifiable risk factors are associated with the risk of developing cancer and other chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease):
Are there modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM)?
Modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus - Non-Pharmacological Interventions to Reduce the Risk of Diabetes in People with Impaired Glucose Regulation: A Systematic Review and Economic Evaluation - NCBI Bookshelf Obesity is the main risk factor for T2DM,74 but the mechanisms for this association are poorly understood.
Is heart disease modifiable or non-modifiable?
While some of those are non-modifiable risk factors, or out of your control, the majority of them are modifiable risk factors, or in your control. The even better news is that you can lower your risk of developing heart disease through lifestyle changes.
Are there modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer disease?
A growing body of evidence has identified potential modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD) ( 1 – 3 ).
How can you tell if a factor is modifiable or Nonmodifiable?
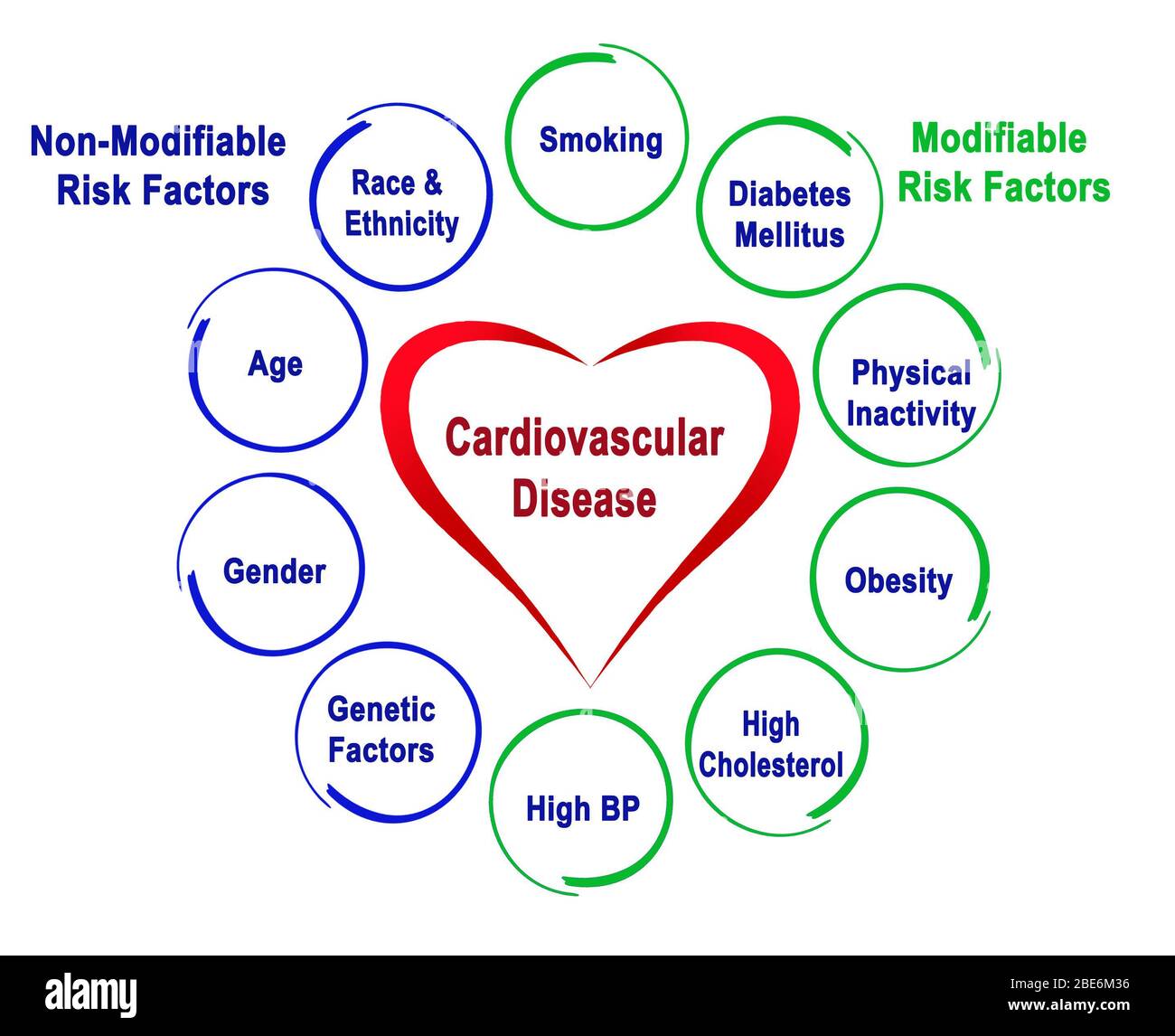
Non-modifiable cardiovascular disease risk factors are those that cannot be changed. These include a person's age, ethnicity and family history (genetics cannot be changed), among other factors. Modifiable cardiovascular disease risk factors are those that can be reduced or controlled with altered behavior.
What are the six modifiable health risk factors?
The 2009 World Health Organization report on global health risks identifies hypertension, smoking, raised glucose, physical inactivity, obesity and dyslipidaemia, in that order, as being the top six modifiable global mortality risk factors.
What are 5 non-modifiable risk factors?
Non-Modifiable Risk FactorsAge.Gender.Family history.Ethnicity.
What is not modifiable?
: not modifiable : unalterable, inflexible these variations from custom are illogical, incomprehensible, and unmodifiable — Science News Letter.
What is an example of a modifiable risk factor?
Modifiable risk factors include: smoking high blood pressure diabetes physical inactivity being overweight high blood cholesterol. The good news is that the effect of many risk factors can be changed (you cannot change the risk factor, only its effect).
What is non-modifiable factors?
Non-modifiable risk factors are factors that cannot be changed or adjusted, hence they are out of our control. These include: Genetics. Having a family history of high BP means that someone within your immediate family has been diagnosed with high BP before the age of 60 years.
What is modifiable and non-modifiable factors?
Risk factors are either modifiable, meaning you can take measures to change them, or non-modifiable, which means they cannot be changed.
What are modifiable determinants of health?
Applying this categorization to health disparities, conceptualizations of the root causes of health disparities emphasize the most modifiable determinants of health: the physical and social environment, psychology and health behaviors, socioeconomic position and status, and access to and quality of healthcare.
Is age a modifiable risk factor?
Age is not considered to be a modifiable risk factor but, unfortunately, it outranks all those that are—eg, lipids, blood pressure, and smoking—as a predictor of clinical events.
What are modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors?
Risk factors are conditions that increase your risk of developing a disease. Risk factors are either modifiable, meaning you can take measures to change them, or non-modifiable, which means they cannot be changed.
What are the 4 modifiable risk factors for chronic disease?
The CDC identifies four main preventable risk factors in contributing to chronic disease: tobacco use, poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, and alcohol use. As a physician, it's important to keep an eye on trends in these risk factors, in addition to counseling your patients on prevention.
What are modifiable health determinants?
Modifiable health determinants are those that a person can exert some control over, such as peers and education; whereas non-modifiable health determinants are those that are not able to be changed or controlled, for example, genetic factors (age and gender), family history and race.
What is a modifiable health behaviors?
The daily modifiable lifestyle behaviors most significantly associated with healthy outcomes were: eating a low-fat diet, engaging in aerobic exercise, maintaining a nonsmoking status, and obtaining adequate sleep.
What are modifiable factors?
Modifiable factors encompass nutrition, weight, exercise, smoking and sedentary behavior is the likes of it. Nutrition remains one of the critical factors least attended to. Healthy eating comprises limiting the intake of foods with saturated fats, excess sugars and salts while increasing consumption of fruits, cereals, nuts, lean meat, fish, eggs, ...
What are the factors that affect health?
These include individual factors like skills, knowledge, attitude; socioeconomic factors like income and education; environmental factors like location and access to health facilities as well as technology.
Why do people have immune deficiency?
Immune deficiency may arise through inherent defects in immune function, but is much more commonly due to secondary causes, including infection, drug therapy, malignancy and ageing. Factors like family, media, ethnicity and religion influence the social construct of health .
What are the consequences of mutations?
The consequence of an individual mutation depends on various factors, including the mutation type, the nature of the gene product and the position of the variant in the protein. Mutations can have profound effects or subtle effects on gene and cell function.
How much physical activity is needed to improve mental health?
The recommended physical activity- minimum 30 minutes of moderate intensity physical activity on at least 5 days per week is quite basic and can be incorporated to the daily routine.3.
October 29th was World Stroke Day
Almost a month later, the impact and awareness it created is still fresh in our mind.
High blood pressure (or Hypertension)
High blood pressure, which is experienced by more than 2/3 of individuals over age 65, is often considered the most important modifiable risk factor for stroke. While high blood pressure often has no symptoms, a quick test at your doctor’s office can determine if you are at risk.
Diet
Nearly half of strokes may be linked to poor diet and small improvements can make a substantial difference in reducing your risk. The American Heart Association recommends focusing your diet around vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, plant-based proteins, lean animal proteins, and fish.
Physical Inactivity
Physical inactivity is linked to a number of poor health effects, including stroke. To reduce your risk, the American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity (or 75 minutes of vigorous activity) each week. Exercise can take on many different forms. Find your favorite way to move and stick to it!
Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce your risk of stroke. Being overweight contributes to many other risk factors of stroke – including high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. If maintaining a healthy weight is challenging, talk to your health care team about a weight management plan.
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (or AF) is the most common type of abnormal heart rhythm and individuals with atrial fibrillation are 5 times more likely to have a stroke. With proper medical management of atrial fibrillation, the risk of AF-related strokes can be substantially decreased.
Smoking
It is estimated that smoking contributes to 15% of all stroke deaths per year and individuals that smoke 20 cigarettes per day are 6 times more likely to have a stroke. Quitting smoking will reduce your risk of stroke (as well as other important diseases).
Heart Disease vs. Cardiovascular Disease
Heart disease and cardiovascular disease are terms often used synonymously together, however they couldn’t be more distinct. All heart diseases are cardiovascular disease, yet not all cardiovascular diseases are heart disease. Let me explain.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Heart disease is caused by a combination of non-modifiable and modifiable factors. The non-modifiable and modifiable risk factors of heart disease are similar in men and women, however the signs of heart disease are not as recognizable in women as they are in men.
How to Lower Your Risk of Heart Disease
It’s never too late to take care of your heart and lower your modifiable risk factors of heart disease. By making lifestyle changes such as exercising more, changing your diet, losing weight, and relieving stress, you can lower your number of modifiable risk factors for heart disease.
Article Sources
Know Your Risk for Heart Disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021.
Get wellness tips, exclusive offers, and more recipes directly to your inbox regularly!
Join The Myers Way® movement that has helped over 1.2 MILLION people in 120+ countries. When you sign up, you’ll receive a full-color, 59-page eBook filled with delicious, simple recipes that will tempt your taste buds.