
Neurological The nervous system is a highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 …Nervous system
Why is it important to record neurological observations?
How to assess motor response?
How often should neurologists perform neurological assessments?
What is neurological observation?
What are the signs of increased ICP?
What is nursing assessment?
What is drowsiness in medical terms?
See 4 more
About this website
What do neurological observations tell us?
The Neurological Observation Chart provides an instant snapshot of a patient's conscious level as well as providing a comprehensive clinical assessment of a patient's neurological state and level of consciousness over a period of time, by a number of different observers, with as little variability as possible.
Why do neuro observations?
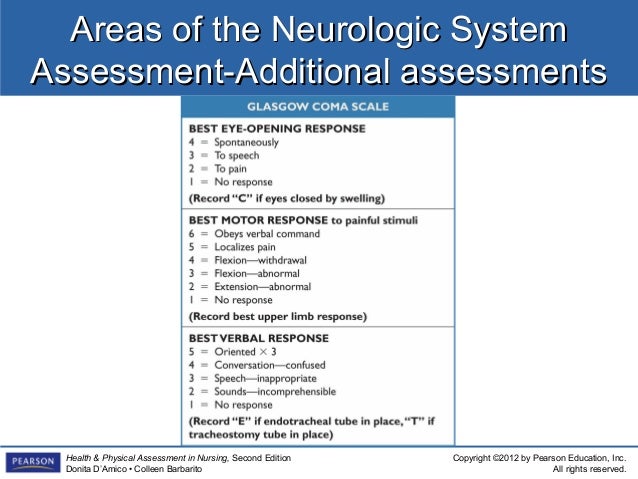
Neurological observations collect data on a patient's neurological status and can be used for many reasons, including in order to help with diagnosis, as a baseline observation, following a neurosurgical procedure, and following trauma. The most widely known and used tool is the Glasgow Coma Scale.
What is included in a neuro assessment?
A neurological (neuro) exam consists of a physical examination to identify signs of disorders affecting your brain, spinal cord and nerves (nervous system). Neurological examination is the best way for healthcare providers to check the function of your brain and nervous system.
How often are neuro observations?
Once every 12 hour shift another registered practitioner (competent in neurological observation) will routinely perform an independent set of neurological observations (fresh eyes review) on the patient to ensure consistency. This independent check should also be made when there is a change in clinical condition.
What are the 5 major areas of neurological assessment?
Mental status testing can be divided into five parts: level of alertness; focal cortical functioning; cognition; mood and affect; and thought content.
What are the 4 components of a neurological check?
There are many components to a neurological exam, including cognitive testing, motor strength and control, sensory function, gait (walking), cranial nerve testing, and balance.
What six things are assessed in the neurological exam?
The neurological exam can be organized into 7 categories: (1) mental status, (2) cranial nerves, (3) motor system, (4) reflexes, (5) sensory system, (6) coordination, and (7) station and gait.
What are some common neurological tests?
Common Neurological TestsCerebral Angiogram. Some diseases, such aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and vasculitis, affect the blood vessels of the brain. ... CT Myelogram. ... CT Scans. ... Nerve Conduction Studies. ... Nerve Conduction Velocity. ... Lumbar Puncture. ... MRI Scans. ... Neurological Examination.More items...
Why do nurses do neuro checks?
The purpose of a neurological assessment is to detect neurological disease or injury in your patient, monitor its progression to determine the type of care you'll provide, and gauge the patient's response to your interventions (Noah, 2004).
Why do nurses do neuro checks?
The purpose of a neurological assessment is to detect neurological disease or injury in your patient, monitor its progression to determine the type of care you'll provide, and gauge the patient's response to your interventions (Noah, 2004).
Why do we do neuro checks every 4 hours?
It is important that a neurological nursing assessment be performed every four hours or sooner in order to ensure continuity of care and that no adverse effects or changes have occurred.
Why do nurses do a neurological assessment?
The purpose of a neurological assessment is to detect abnormalities that may suggest brain injury, or disease. The information obtained will help determine patient care needs and the necessity for medical intervention.
What is the importance of neuro?
The nervous system not only works to produce thoughts, emotions, and behavior, but also controls important body functions, like breathing. Studying the nervous system advances understanding of our basic biology and body function.
CHA38: Neurological Observations Chart
• Observation frequency and schedule should come from specific Trust policies and guidelines eg. RCHT Policy for Prevention and Management of Falls in Hospital, Clinical Guideline for Acute Stroke, or directions
Neurological Medical Observation Chart
Author: jk6k [ 000BDB474CC2 ] Created Date: 3/30/2007 6:31:21 PM
Neurological observations in adults: Indications and required frequency
Imaging needs and (if applicable) findings If no CT head required (OR presentingmore than 48h after symptom onset AND GCS 15) If CT head indicated or decision awaited
Neurological observations 1 | Nursing Times
Subscribe for unlimited access. Over 6,000 double-blind peer reviewed clinical articles; 50 clinical subjects and 20 clinical roles or settings; Clinical articles with discussion handouts and online assessments
Performing neurological observations - PubMed
Trauma to the brain from injury or illness can cause sustained, raised intracranial pressure. In such patients, neurological observations are a fundamental aspect of nursing care and the ability to make and record such observations accurately is an essential nursing skill. Neurological observations …
Why is neurovascular status important?
Assessment of neurovascular status is essential for the early recognition of neurovascular deterioration or compromise. Delays in recognising neurovascular compromise can lead to permanent deficits, loss of a limb and even death. Neurovascular deterioration can occur late after trauma, surgery or cast application.
What happens if neurovascular status is compromised?
If neurovascular status is compromised, patients may report decreased sensation, loss of sensation, dysesthesia, numbness, tingling or pins and needles. Altered sensation may be a result of a nerve block or epidural, this should be documented in the patient’s neurovascular assessment in the flowsheet in EMR.
What is compartment syndrome?
Compartment syndrome is a serious complication of musculoskeletal injury. Compartment syndrome results from an increase in pressure inside a compartment which comprises of muscles and nerves and is enclosed by fascia, fascia is inelastic and does not expand to increased volume or pressure. When the compartment pressure increases, nerves and then muscles become compressed resulting in decreased blood flow and tissue perfusion, muscle ischemia and loss or altered sensation. Compartment syndrome is a surgical emergency to relieve the pressure or reduce volume within the compartment, which will preserve blood supply, tissue perfusion and function. Early recognition of neurovascular deterioration is crucial in limb salvage or survival.
What to do if a neurovascular observation changes?
If any changes to neurovascular observations (i.e. decrease in pulse pressure, change in limb colour or coolness of limb), escalate by notifying the treating team or catheterisation fellow. Consider need for an ultrasound conducted to confirm or rule out a thrombus.
What should be conducted on the affected limb / limbs with routine post anaesthetic observations?
Neurovascular observations, should be conducted on the affected limb / limbs with routine post anaesthetic observations and then with every set of observations.
What is the purpose of fasciotomy?
The aim of the procedure is to release pressure to improve peripheral neurovascular status and prevent long term complications.
What is the most important indicator of neurovascular compromise?
Pain. The most important indicator of neurovascular compromise is pain disproportionate to the injury. Pain associated with compartment syndrome is generally constant however worse with passive movement to extension and is not relieved with opioid analgesia.
Why is a neurological exam done?
A complete and thorough evaluation of a person's nervous system is important if there is any reason to think there may be an underlying problem, or during a complete physical. Damage to the nervous system can cause problems in daily functioning. Early identification may help to find the cause and decrease long-term complications. A complete neurological exam may be done:
What is done during a neurological exam?
During a neurological exam, the healthcare provider will test the functioning of the nervous system. The nervous system is very complex and controls many parts of the body. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, 12 nerves that come from the brain, and the nerves that come from the spinal cord. The circulation to the brain, arising from the arteries in the neck, is also frequently examined. In infants and younger children, a neurological exam includes the measurement of the head circumference. The following is an overview of some of the areas that may be tested and evaluated during a neurological exam:
What is neurology exam?
A neurological exam, also called a neuro exam, is an evaluation of a person's nervous system that can be done in the healthcare provider's office. It may be done with instruments, such as lights and reflex hammers. It usually does not cause any pain to the patient. The nervous system consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and the nerves from these areas. There are many aspects of this exam, including an assessment of motor and sensory skills, balance and coordination, mental status (the patient's level of awareness and interaction with the environment), reflexes, and functioning of the nerves. The extent of the exam depends on many factors, including the initial problem that the patient is experiencing, the age of the patient, and the condition of the patient.
How many nerves are in the nervous system?
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, 12 nerves that come from the brain, and the nerves that come from the spinal cord. The circulation to the brain, arising from the arteries in the neck, is also frequently examined. In infants and younger children, a neurological exam includes the measurement of the head circumference.
Which nerve helps with the movement of the eyes?
The patient's healthcare provider may touch the face at different areas and watch the patient as he or she bites down. Cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve). This nerve helps with the movement of the eyes. The patient may be asked to follow a light or finger to move the eyes. Cranial nerve VII (facial nerve).
Which nerve is responsible for pupil size and certain movements of the eye?
Cranial nerve III (oculomotor). This nerve is responsible for pupil size and certain movements of the eye. The patient's healthcare provider may examine the pupil (the black part of the eye) with a light and have the patient follow the light in various directions. Cranial nerve IV (trochlear nerve).
How to assess mental status?
Mental status (the patient's level of awareness and interaction with the environment) may be assessed by conversing with the patient and establishing his or her awareness of person, place, and time. The person will also be observed for clear speech and making sense while talking. This is usually done by the patient's healthcare provider just by observing the patient during normal interactions.
Why is it important to record neurological observations?
Accurate and consistent recording of neurological observations is essential to establish the patient’s neurological status and to illustrate any changes. Nurses need appropriate training in order to achieve accurate assessment.
How to assess motor response?
Motor response - this is assessed by giving the patient some simple commands, for example ‘squeeze my hand (both sides)’, ‘lift your legs up off the bed’, and ‘show your tongue’. The strength of the patient’s limbs should be noted - it is essential to observe for weaknesses. When a patient does not respond to simple commands then response to painful stimuli is assessed. There are three recognised stimuli that can be used when assessing motor response:
How often should neurologists perform neurological assessments?
If the patient’s condition is deteriorating, observations may need to be carried out as frequently as every 10-15 minutes. Clinicians’ professional knowledge and judgement will dictate the necessary timing interval for the assessment.
What is neurological observation?
Neurological observation is the collection of information on a patient’s central nervous system (consisting of the brain and spinal cord). Both medical practitioners and nurses carry out neurological assessments. They are routinely recorded in A&E and neurological wards, but may also be required in other clinical settings and situations.
What are the signs of increased ICP?
Usually the patient’s level of consciousness will have begun to deteriorate before there is any alteration in the vital signs observation. Pupillary reaction .
What is nursing assessment?
The nursing assessment includes level of consciousness, pupillary reaction, motor function and vital signs. Levels of consciousness. Consciousness can be categorised as: Full consciousness - the patient is awake, alert and aware of their surroundings;
What is drowsiness in medical terms?
Drowsiness - the patient responds slowly, sometimes without purpose, to stimuli. They may not verbally respond or, if they do, responses may be incoherent;
Introduction
Aim
- The aim of this clinical practice guideline is to outline the required neurovascular assessment to recognise early compromise and prevent permanent damage to the limb(s).
Definition of Terms
- Neurovascular: Is the structure and function of the vascular and nervous systems in combination.
- Musculoskeletal: structurally includes a combination of muscles, bones and joints.
- Capillary refill: Is an assessment of arterial blood supply return and is performed by briefly interrupting blood supply in the capillary system and timing how long it takes for the blood to …
- Neurovascular: Is the structure and function of the vascular and nervous systems in combination.
- Musculoskeletal: structurally includes a combination of muscles, bones and joints.
- Capillary refill: Is an assessment of arterial blood supply return and is performed by briefly interrupting blood supply in the capillary system and timing how long it takes for the blood to return.
- Disproportionate Pain: Pain that exceeds what is expected post injury/surgery, which is not relieved by analgesia.
Assessment
- Criteria for neurovascular assessment
Patients who require neurovascular assessment include but are not limited to: 1. Musculoskeletal trauma to the extremities 1.1. Fracture 1.2. Crush injury 2. Post-operative 2.1. Internal or external fixation or fractures 2.2. Orthopaedic surgery 2.3. Spinal surgery 2.4. Plastic surgery on extremiti… - Neurovascular assessment
A neurovascular assessment is required for each affected limb and includes assessment of 1. Pain 2. Sensation 3. Motor function 4. Perfusion (colour, temperature, capillary refill, swelling, pulses)
Documentation
- A baseline neurovascular assessment of both limbs is essential in recognising neurovascular compromise and should be documented on admission
- Neurovascular observations for both upper and lower limbs can be added into flowsheets in EMR for documentation
- Alterations in neurovascular status should be documented in flowsheets and the leading me…
- A baseline neurovascular assessment of both limbs is essential in recognising neurovascular compromise and should be documented on admission
- Neurovascular observations for both upper and lower limbs can be added into flowsheets in EMR for documentation
- Alterations in neurovascular status should be documented in flowsheets and the leading medical team should be notified immediately
- Photographs can be taken with permission/ consent from the parents/guardian and saved in the media file in EMR, to document any changes neurovascular status and allows the medical team to view prog...
Management
- Ensure affected limb is elevated to minimise the risk of compartment syndrome. Lower extremities can be elevated with pillows or using bed mechanics; upper extremities can be elevated on either a pillow, sling or box sling.
Potential Complications
- Compartment syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a serious complication of musculoskeletal injury. Compartment syndrome results from an increase in pressure inside a compartment which comprises of muscles and nerves and is enclosed by fascia, fascia is inelastic and does not expand to increas…
Discharge and Parent Information
- For patients at risk of neurovascular compromise education on neurovascular assessment is crucial. Age appropriate education should be provided to the patient, including encouragement for the patient to move their digits regularly. Educate parents on the importance of performing neurovascular assessment and why it is necessary to disturb the patient when sleeping while in …
Evidence Table
- Click here to view the Evidence Table. Please remember to read the disclaimer. The development of this nursing guideline was coordinated by Alicia Waters, CNS, Platypus Ward, and approved by the Nursing Clinical Effectiveness Committee. Updated May 2019.