
Symptoms
The causes of neutropenia include:
- Problem in the production of neutrophils in the bone marrow
- Destruction of neutrophils outside the bone marrow
- Infection
- Nutritional deficiency
Causes
Neutropenia is a condition that means that you have lower-than-normal levels of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, in your blood. This might happen due to an infection, but can result from cancer treatment. Avoiding infection is very important. What is neutropenia? Neutropenia refers to lower-than-normal levels of neutrophils in the blood.
Prevention
Introduction: Multiple studies have questioned the benefit of neutropenic diets in decreasing infections in patients with cancer, but recent surveys showed that such diets are still prescribed. In this study, we sought to evaluate the effectiveness of neutropenic diet in decreasing infection and mortality in neutropenic patients with cancer with neutropenia.
Complications
Neutropenia is often caused by blood-based conditions, blood cancers, and the corresponding medical treatments. Use of immune-suppressing medications such as steroids, monoclonal antibodies, and cyclosporine may also lead to neutropenia. Are You Neutropenic? Neutropenia can be confirmed with a full blood count (FBC) test.
What is the most common cause of neutropenia?
What does it mean to be neutropenic?
Do we still need the neutropenic diet?
What can cause neutropenia?
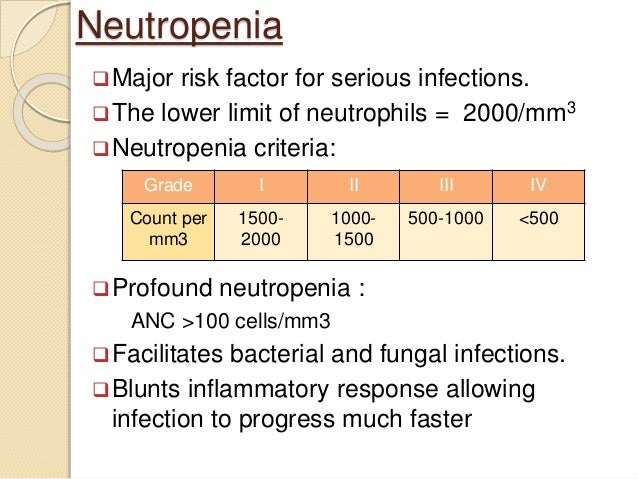
What is considered neutropenic?
In adults, a count of 1,500 neutrophils per microliter of blood or less is considered to be neutropenia, with any count below 500 per microliter of blood regarded as a severe case. In severe cases, even bacteria that are normally present in the mouth, skin, and gut can cause serious infections.
How do you know if a patient is neutropenic?
Your doctor can use these tests to diagnose neutropenia:Complete blood count (CBC). This test measures neutrophil counts. ... Antibody blood test. This test checks for autoimmune neutropenia.Bone marrow aspirate. This procedure tests bone marrow cells.Bone marrow biopsy. ... Cytogenetic and molecular testing.
What are neutropenic patients at risk for?
People who have neutropenia have a higher risk of getting serious infections. This is because they do not have enough neutrophils to kill organisms that cause infection. People with severe or long-lasting neutropenia are most likely to develop an infection.
Are all cancer patients neutropenic?
If you receive chemotherapy or radiation therapy, you may develop neutropenia because the cancer treatment prevents the production of neutrophils. Patients who have cancers that affect bone marrow, such as leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma, also may become neutropenic.
What is the main cause of neutropenia?
Nutritional deficiencies: Not having enough vitamins or minerals such as vitamin B12, folate or copper in your diet can cause neutropenia. Autoimmune deficiencies: With certain autoimmune conditions, your body makes antibodies that destroy healthy neutrophils.
Can neutropenia be fatal?
In people with severe neutropenia, infections can rapidly become serious or fatal. Even if doctors cannot diagnose a specific infection, people who have neutropenia and fever are presumed to have an infection. Such people are given antibiotics effective against common infectious organisms.
What should neutropenic patients avoid?
Avoid raw and undercooked eggs. Avoid salad bars, buffets, and potlucks. Avoid unpasteurized products, such as unpasteurized dairy items (like milk, cheese, and eggnog), as well as unpasteurized honey, juice, and cider. Avoid fresh and packaged foods that are past their “use by” and expiration dates.
How long can you live with neutropenia?
The neutropenia is most often temporary in these cases. Chronic neutropenia is defined as lasting more than 2 months. It may eventually go away, or remain as a life-long condition. Some people are born with it (congenital neutropenia), and others develop it as young children.
How do you fix neutropenia?
Approaches for treating neutropenia include:Antibiotics for fever. ... A treatment called granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). ... Changing medications, if possible, in cases of drug-induced neutropenia.Granulocyte (white blood cell) transfusion (very uncommon)More items...•
Does neutropenia mean cancer?
Neutropenia – what causes it? Neutropenia can be caused by blood cancer. It can also happen during or after cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, a stem cell transplant, or medications which suppress your immune system.
What cancers cause neutropenia?
Neutropenia can also be caused by solid tumor malignancies, if they infiltrate the bone marrow, or by certain lymphoproliferative malignancies, such as natural killer cell lymphomas (large granular lymphocytic leukemia), hairy cell leukemia, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Why do cancer patients get neutropenic?
Although chemotherapy is used to destroy cancer cells, it may also damage normal cells in the process, including neutrophils. When these infection-fighting white blood cells are used up or destroyed faster than the bone marrow can make new ones, neutropenia may result.
What is the WBC count for neutropenic precautions?
What Are Neutropenic Precautions? If your white blood cell count drops to 1,000 per mm3 or below, you are considered to be neutropenic. Until your count rises, it will be necessary for you to take additional measures to further decrease your risk for infection.
What qualifies for neutropenic precautions?
These safety measures are called neutropenic precautions. Neutropenia is a blood condition involving low levels of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell....You should avoid:raw or unwashed fruits and vegetables.raw or undercooked meat, including beef, pork, chicken, and fish.uncooked grains.raw nuts and honey.
Is 1.5 a low neutrophil count?
What is the normal number of neutrophils? The number of neutrophils that circulate in the blood stream varies a bit according to age however the usual range of normal neutrophil numbers is 1.5 – 8.0 X 10^9/l (1.5 million – 8 million neutrophils per milliliter) of blood.
When should a patient be on neutropenic precautions?
When to Start Neutropenic Precautions. If you are going through chemotherapy, you may see neutropenia start seven to 12 days after the treatment starts. You should start neutropenic precautions at this time unless your doctor tells you otherwise.