
What is the difference between P and S waves?
What Are Some Differences Between P & S Waves?
- Wave Speeds. P waves travel faster than S waves, and are the first waves recorded by a seismograph in the event of a disturbance.
- Type of Wave. Primary waves are made up of compression waves, also known as push-pull waves. ...
- Travel Capability. ...
- Wave Sizes. ...
Are P waves faster than S waves?
Since P waves are faster than S waves, the larger the arrival time difference between the two waves is, the farther that location is from the epicenter. where {eq}t_S {/eq} and {eq}t_P {/eq} are the arrival times of S and P waves at the seismometer, respectively, and x is the distance traveled.
What are the different types of P waves?
- Normal P Wave Size
- Duration <120ms (3mm)
- Amplitude <2.5mm
What is the difference between P wave and S wave?
P Wave
- Body Waves
- P waves and S waves
- P waves. P waves, or Primary waves, are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph. ...
- S waves. S waves, or secondary waves, are the second waves to arrive during an earthquake. ...
- Difference between s waves and p waves. d=t (S-P).10 Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about Physics-related concepts.
What are S waves in an earthquake?
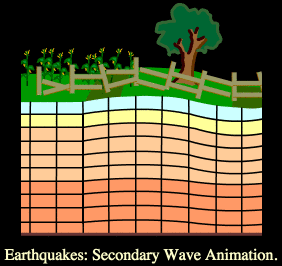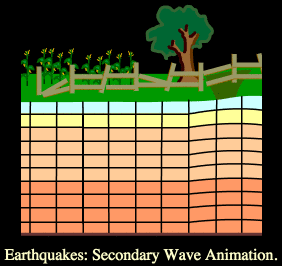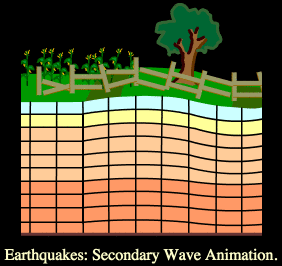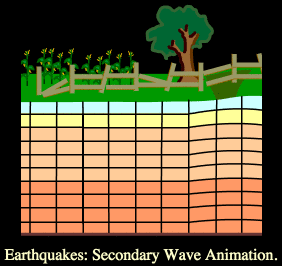
An S wave, or shear wave, is a seismic body wave that shakes the ground back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is moving.
What are P waves short answer?
What are P waves? P waves are the first waves that are detected by a seismograph. They are the fastest seismic waves and can travel through gases, liquids, or solids.
How do P waves travel through an earthquake?
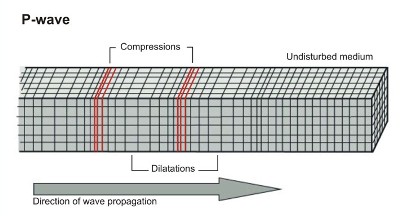
In a P wave, the rock particles are alternately squished together and pulled apart (called compressions and dilatations), so P waves are also called compressional waves. These waves can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. P waves can travel through the liquid outer core. An S wave is a different beast.
Can You Feel P waves in an earthquake?
P-waves are generally too subtle to be felt by humans, although seismographs will pick them up. But some animals may be able to detect P-waves before the S-waves arrive. This would give them less than two minutes' notice for any quake near enough to affect them.
What happens during P waves?
The P wave represents the electrical depolarization of the atria. In a healthy person, this originates at the sinoatrial node (SA node) and disperses into both left and right atria.
What is difference between P and S waves?
P waves can travel through liquid and solids and gases, while S waves only travel through solids. Scientists use this information to help them determine the structure of Earth. For example, if an earthquake occurs on one side of Earth, seismometers around the globe can measure the resulting S and P waves.
Why do P waves arrive first?
The direct P wave arrives first because its path is through the higher speed, dense rocks deeper in the earth. The PP (one bounce) and PPP (two bounces) waves travel more slowly than the direct P because they pass through shallower, lower velocity rocks. The different S waves arrive after the P waves.
Which is more destructive P or S waves?
An earthquake also causes secondary or shear waves, called S waves. These travel at about half the speed of P waves, but can be much more destructive. S waves move the earth perpendicularly to the direction the wave is traveling.
What are the characteristics of P waves?
Seismic P waves are also called compressional or longitudinal waves, they compress and expand (oscillate) the ground back and forth in the direction of travel, like sound waves that move back and forth as the waves travel from source to receiver. P wave is the fastest wave.
Do P waves cause damage?
P waves are compressional waves that do not produce much damage. They can move through any type of material and travel at almost twice the speed of S waves. High frequency P waves do not weaken, or "attenuate," as rapidly as S waves so they retain higher frequencies when they arrive at seismic stations.
Which wave causes most damage in earthquake?
Rayleigh waves cause both vertical and horizontal ground motion. These can be the most destructive waves as they roll along lifting and dropping the ground as they pass.
What are the 3 types of earthquake waves?
There are three basic types of seismic waves – P-waves, S-waves and surface waves. P-waves and S-waves are sometimes collectively called body waves.
What are S waves for kids?
S waves are seismic wavesTwo types of seismic waves. S waves and P waves are the two types of seismic waves produced by all earthquakes. ... Shear waves. ... Where shear waves travel. ... Travel speed through the crust. ... Moving through the mantle. ... Body waves. ... Outer and inner core of the Earth.
What type wave is P wave?
compressional waveA P wave, or compressional wave, is a seismic body wave that shakes the ground back and forth in the same direction and the opposite direction as the direction the wave is moving.
What are primary waves kids?
Primary waves are P waves that arrive at recording stations first. They are the fastest waves produced by an earthquake. S waves are produced by all earthquakes. S waves arrive a short time after P waves at recording stations.
Who discovered P waves?
Inge LehmannIt's thanks to a pioneering scientist named Inge Lehmann — who would have turned 127 today — that scientists know that inner core exists. According to the American Museum of Natural History, Lehmann made her discovery while studying a type of seismic shock wave called Primary waves, or P-waves.
What is an earthquake?
An earthquake is the trembling or shaking of the Earth when multiple tectonic plates suddenly slip past each other.
What are seismic waves?
The waves or bursts of energy that propagate through the Earth and instigate earthquakes are called seismic waves.
What are the two types of seismic waves?
Body waves and surface waves are the two types of seismic waves.
What are the two types of body waves?
P waves and S waves are the two types of body waves.
What are P waves?
P waves are the first waves that are detected by a seismograph. They are the fastest seismic waves and can travel through gases, liquids, or solids.
What are the two types of earthquake waves?
Earthquake waves are of two kinds namely the body waves and surface waves. Body waves are produced due to the discharge of energy at the focus and it progresses in all directions traveling through the body of the earth, hence, the name is body waves. When interacted with the surface rocks, these body waves generate a new collection ...
Where do earthquake waves occur?
Earthquake Waves – Important Points. Most of the earthquakes take place near the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean. Throughout the world, there are around 5, 00,000 earthquakes every year, though only 100 cause destruction. Earthquakes last only for a few seconds but they cause heavy loss of life and property.
How do earthquakes generate waves?
The earthquakes generate waves on the surface of the earth and these are designated as seismic waves, these waves can be recorded by an apparatus called the seismograph. The instrument comprises a vibrating rod/a pendulum, which starts fluctuating when tremors occur, a pen that is attached to the vibrating system records the seismic waves on a paper which passes under it. By studying these waves, specialists can construct a complete map of the earthquake, as shown below. They can also determine its potential to cause destruction.
What is the term for the study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth?
Seismology is an experimental examination of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth/ other planet-like bodies. A recording of earth movement as a function of time is termed a seismogram. A seismologist is a specialist who researches seismology.
What instrument is used to measure seismic waves?
Q.1 The instrument used to measure the seismic waves is known as. Ans.1. The seismic waves are registered by an instrument called the seismograph.
What is the shadow zone in a seismograph?
The earthquake waves which are not reported in the seismo-graphs, such zones are called the ‘shadow zone’.
Which waves are more damaging to the Earth's crust?
The surface waves are the last to arrive on the seismograph. The L-waves are more damaging as they cause displacement of rocks, and henceforth, the breakdown of structures occurs.
What is a P wave?
A P wave ( primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology.
What does the P wave stand for?
The name P wave can stand for either pressure wave (as it is formed from alternating compressions and rarefactions) or primary wave (as it has high velocity and is therefore the first wave to be recorded by a seismograph). The name S wave represents another seismic wave propagation mode, standing for secondary or shear wave.
How do seismic waves travel through the interior of the Earth?
P waves travel through the fluid layers of the Earth's interior, and yet they are refracted slightly when they pass through the transition between the semisolid mantle and the liquid outer core. As a result, there is a P-wave " shadow zone " between 103° and 142° from the earthquake's focus, where the initial P waves are not registered on seismometers. In contrast, S waves do not travel through liquids.
Why is the S wave velocity negligible in the outer core?
Velocity of seismic waves in the Earth versus depth. The negligible S-wave velocity in the outer core occurs because it is liquid, while in the solid inner core the S-wave velocity is non-zero.
What direction does a P wave travel?
In isotropic and homogeneous solids, a P wave travels in a straight line longitudinal; thus, the particles in the solid vibrate along the axis of propagation (the direction of motion) of the wave energy. The velocity of P waves in that kind of medium is given by
What is the shadow zone of an earthquake?
As a result, there is a P-wave " shadow zone " between 103° and 142° from the earthquake's focus, where the initial P waves are not registered on seismometers. In contrast, S waves do not travel through liquids.
How fast is a P wave?
Typical values for P wave velocity in earthquakes are in the range 5 to 8 km/s. The precise speed varies according to the region of the Earth's interior, from less than 6 km/s in the Earth's crust to 13.5 km/s in the lower mantle, and 11 km/s through the inner core. Velocity in Common Rock Types. Rock Type.
What are the P waves?
P waves. P waves, or Primary waves, are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph. P waves are the fastest seismic waves and can move through solid, liquid, or gas. They leave behind a trail of compressions and rarefactions on the medium they move through. P waves are also called pressure waves for this reason.
How to understand P waves?
To understand P waves, we have to first look into the basics of seismology and seismic waves. The waves of energy that travel through the earth and cause earthquakes and related phenomena are seismic waves. There are two types of seismic waves : 1 Body waves 2 Surface waves
What are the two types of seismic waves?
There are two types of seismic waves : Body waves. Surface waves. Body waves are the waves that can travel through the layers of the earth. They are the fastest waves and as a result, the first waves that seismographs can record. Body waves can move through all states of matter including rocks and molten lava.
Can shear waves move through solids?
They are compression waves. They are shear waves. Can move through solids and liquids. Can only move through solids. Shake the medium in the direction in which they are propagating. Shake the medium in the direction perpendicular to which they are moving.
What are P and S Waves?
Primary (P) and secondary (S) waves are two types of waves caused by earthquakes. They are defined based on when they arrive and are felt on the surface. P waves, or primary waves, arrive first while S waves, or secondary waves, arrive second. Both waves cause the ground to shake when an earthquake occurs. S waves cause more intense shaking than P waves and are typically much more destructive.
Why are P waves called primary waves?
P waves are called primary waves because they are the first waves to arrive at any location after an earthquake.
How to make a compressional wave?
These can be created at home by using a spring or slinky with fixed ends. If one person gathers a few coils and compresses them at one end before releasing them, then a compressional wave will travel from one end of the spring to the other.
What is the first wave to be felt on the surface after an earthquake?
Body waves are the first waves to be felt on the surface after an earthquake. Since they can move through deep layers of rock, they follow a shorter ray path than a surface wave. A ray path is the direction the wave follows as it propagates away from the locus (or origin) through the Earth.
How fast does a P wave move?
This is due to the fact that the outer core is a liquid and the shear modulus (or rigidity) is zero. The P- wave increases in speed to about 11 km/s when it passes into the solid inner core.
How does a mechanical wave travel?
A mechanical wave is a wave that must travel through a medium, such as the ground or air. The energy of a mechanical wave is transferred from one molecule to another as it propagates (or travels) through its medium. They differ from electromagnetic waves, which can travel through a vacuum.
Where are P waves felt?
Due to the difference in speed through a liquid, P waves are refracted within the outer core and leave something known as a Shadow Zone on the Earth's surface. The P wave shadow zone is the area on the surface where no P waves are felt or measured after the occurrence of an earthquake. This zone is located at angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees from the earthquake location.
How do P waves travel?
P waves travel away from the focus of an earthquake where the rocks first fractured by compressing and expanding the rocks as they travel through solids, liquids and gases. P waves travel through all parts of the Earth.
What type of waves do earthquakes produce?
Every earthquake produces P waves and S waves but only larger earthquakes produce Love waves and Rayleigh waves. These are the four major types of seismic waves. How seismic waves move through the Earth, USGS.
How fast do Rayleigh waves travel?
speed of surface waves. The Rayleigh waves travel slightly slower at 7800 miles per hour while circling the globe. These waves circle the Earth sometimes for more than a week after a great earthquake. Scientists say it is something like vibrations in the ringing of a bell.
What type of waves are created when energy builds up in rocks and they fracture?
Seismic waves. Earthquake waves are seismic waves that are created when energy builds up in rocks and they fracture. Scientists estimate there are several million earthquakes each year. Every earthquake produces P waves and S waves but only larger earthquakes produce Love waves and Rayleigh waves. These are the four major types of seismic waves.
What is the difference between S waves and S waves?
s waves. S waves are transverse waves. S waves travel in a motion similar to a rope held tight at one end while the other end is lifted rapidly back and forth. S waves only travel through solids and do not travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth.
What are the two types of seismic waves formed during earthquakes?
Body waves and surface waves are the two types of seismic waves formed during great earthquakes. P waves and S waves are called body waves because they travel through the body of the Earth.
How do love waves move?
Love waves are transverse waves. Love waves move back and forth in the direction they are traveling. Take a slinky and lay it on a table and make waves that move through the slinky as you move it back and forth. This is similar to the action of Love waves.
What is an earthquake?
An earthquake is what happens when two blocks of the earth suddenly slip past one another. The surface where they slip is called the fault or fault plane. The location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts is called the hypocenter, and the location directly above it on the surface of the earth is called the epicenter.
Why does the earth shake when there is an earthquake?
The energy radiates outward from the fault in all directions in the form of seismic waves like ripples on a pond. The seismic waves shake the earth as they move through it, and when the waves reach the earth’s surface, they shake the ground and anything on it, like our houses and us!
How do scientists measure the size of earthquakes?
The size of an earthquake depends on the size of the fault and the amount of slip on the fault, but that’s not something scientists can simply measure with a measuring tape since faults are many kilometers deep beneath the earth’s surface. So how do they measure an earthquake? They use the seismogram recordings made on the seismographs at the surface of the earth to determine how large the earthquake was (figure 5). A short wiggly line that doesn’t wiggle very much means a small earthquake, and a long wiggly line that wiggles a lot means a large earthquake. The length of the wiggle depends on the size of the fault, and the size of the wiggle depends on the amount of slip.
Is there such a thing as earthquake weather? Can some animals or people tell when an earthquake is about to hit?
If weather does affect earthquake occurrence, or if some animals or people can tell when an earthquake is coming, we do not yet understand how it works.
What waves are used to destroy earthquakes?
The destruction caused by earthquakes is primarily done by these waves. S waves also called secondary waves and shear waves, are the second waves to hit the seismographs. They are transverse waves, which means that the motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
What are seismic waves?
Seismic waves are like those ripples which can travel through the inside of the earth, as well as on the surface. P waves, S waves, and Surface waves. Based on the medium they travel in, earthquake waves can be classified under two categories: Body waves. Surface waves.
How fast do P waves travel?
These arrive after P waves. These waves travel in the speed range of 1.5-13 km/s. These waves are almost 1.7 times slower than P waves. These waves travel in a linear direction. These waves travel in a transversal direction. These waves can travel through solid, liquid, and gas. These waves travel through only solids.
Where do earthquake waves originate?
They originate at the epicenter of the earthquake and travel through the earth at amazing speeds. There are two types of body waves namely, Surface waves are those waves that travel on the surface of the earth. The destruction caused by earthquakes is primarily done by these waves.
Which waves can only travel through solids?
S waves can only travel through solids and scientists have been successful to map the interior of the earth by studying the routes of these waves. P waves or Primary waves are the first waves to hit the seismographs when an earthquake strikes.
Answer
This is why S-waves arrive as secondary waves at the Earth's surface. There is another importantdifference between P-waves and S-waves. Although both can pass through solid rock, only P-waves can also pass through gases and liquids.
Answer
P waves (aka primary waves) are the fastest waves. It's a seismic body wave that shakes the ground back and forth in the same direction and the opposite direction as the direction the wave is moving.
Seismograph
Types of Earthquake Waves
- Earthquake waves are of two kinds namely the body waves and surface waves. 1. Body waves are produced due to the discharge of energy at the focus and it progresses in all directions traveling through the body of the earth, hence, the name is body waves. 2. When interacted with the surface rocks, these body waves generate a new collection of waves named “surface waves”. These wav…
Diagram For Better Understanding of P, S, and L Earthquake Waves Shadow Zone
- The earthquake waves are recorded on seismo-graphs placed at far-off positions. Though there exist some particular regions where the waves are not reported, such unreported zones are called the ‘sh...
- It was recognized that seismographs positioned at any distance within 105° from the epicenter, marked the arrival of both P and S-waves. However, the seismographs placed beyo…
- The earthquake waves are recorded on seismo-graphs placed at far-off positions. Though there exist some particular regions where the waves are not reported, such unreported zones are called the ‘sh...
- It was recognized that seismographs positioned at any distance within 105° from the epicenter, marked the arrival of both P and S-waves. However, the seismographs placed beyond 145° from epicenters...
- Thus, a zone within 105° and 145° from the epicenter was recognized as the shadow zone for both kinds of waves.
- The complete zone beyond 105° does not receive S-waves. The shadow zone of the S-wave is much greater than that of the P-waves.
Earthquake Waves – Important Points
- Most of the earthquakes take place near the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean.
- Throughout the world, there are around 5, 00,000 earthquakes every year, though only 100 cause destruction.
- Earthquakes last only for a few seconds but they cause heavy loss of life and property.
- They bring changes to the surface of the earth.
Overview
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at any affected location or at a seismograph. P waves may be transmitted through gases, liquids, or solids.
Nomenclature
The name P wave can stand for either pressure wave (as it is formed from alternating compressions and rarefactions) or primary wave (as it has high velocity and is therefore the first wave to be recorded by a seismograph). The name S wave represents another seismic wave propagation mode, standing for secondary or shear wave.
Seismic waves in the Earth
Primary and secondary waves are body waves that travel within the Earth. The motion and behavior of both P and S waves in the Earth are monitored to probe the interior structure of the Earth. Discontinuities in velocity as a function of depth are indicative of changes in phase or composition. Differences in arrival times of waves originating in a seismic event like an earthquake as a result of …
Propagation
In isotropic and homogeneous solids, a P wave travels in a straight line longitudinal; thus, the particles in the solid vibrate along the axis of propagation (the direction of motion) of the wave energy. The velocity of P waves in that kind of medium is given by
In typical situations in the interior of the Earth, the density ρ usually varies much less than K or μ, so the velocity is mostly "controlled" by these two parameters.
See also
• Earthquake warning system
• Lamb waves
• Love wave
• S wave
• Surface wave
External links
• Animation of a P wave
• P-wave velocity calculator
• Purdue's catalog of animated illustrations of seismic waves
• Animations illustrating simple wave propagation concepts by Jeffrey S. Barker