
Terms
- buffera solution composed of a weak acid and its conjugate base that can be used to stabilize the pH of a solution
- alkalinehaving a pH greater than 7; basic
- acidichaving a pH less than 7
What are some examples of pH buffers?
The pharmaceutical buffers of Clark and Lubs
- HCl + KCl (pH – 1.2 to 2.2)
- KCl + Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (pH – 2.2 to 4.0)
- NaOH + Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (pH – 4.2 to 5.8)
- NaOH + KH 2 PO 4 (pH – 5.8 to 8.0)
- H 3 BO 3 + NaOH + KCl (pH – 8.0 tp 10.0)
How does a buffer control the pH?
How does a buffer control the pH? Buffers work by neutralizing any added acid (H+ ions) or base (OH- ions) to maintain the moderate pH, making them a weaker acid or base. Thus the breaking of the buffer is its capacity, or in other words, it is the amount of acid or base, a buffer can absorb before breaking its capacity.
What is the relationship between pH and buffer?
What is the relationship between pH and buffer? pH is a fundamental scale that we use in chemistry to measure the acidity r basicity of a solution. Buffers are chemical solutions that can resist the changes in pH. Therefore, the difference between pH and buffer is that the pH is a logarithmic scale whereas a buffer is an aqueous solution.
How do buffers change pH?
capacity has a range of about 2. This means when a buffer is created, the pH can be changed by -1 by acid or +1 by base before the pH begins to change substantially. After the addition of base to raise the pH by 1 or more, most of the conjugate acid will have been depleted to try to maintain a certain pH, so the pH will be free to increase faster without the restraint of the conjugate acid. The same
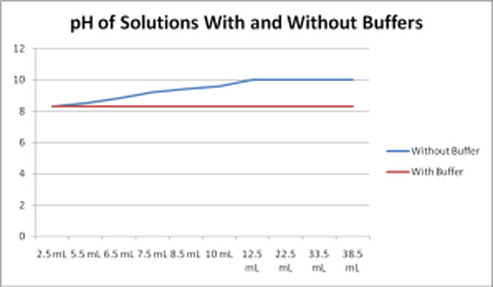
What is the key difference between pH and buffer?
A buffer is an aqueous solution that tends to withstand the change in pH, whereas pH is a logarithmic scale that we use to evaluate an aqueous solution's acidity or basicity. The main distinction between pH and buffer is this. Additionally, the pH scale is a crucial one in chemistry.
What is the difference between pH and buffer pH?
pH is a fundamental scale that we use in chemistry to measure the acidity r basicity of a solution. Buffers are chemical solutions that can resist the changes in pH. Therefore, the difference between pH and buffer is that the pH is a logarithmic scale whereas a buffer is an aqueous solution.
What is a buffer and examples?
A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. An example of a buffer solution is bicarbonate in blood, which maintains the body's internal pH.
What is a buffer simple definition?
(Entry 1 of 4) 1 : any of various devices or pieces of material for reducing shock or damage due to contact. 2 : a means or device used as a cushion against the shock of fluctuations in business or financial activity. 3 : something that serves as a protective barrier: such as. a : buffer state.
Why is pH and buffer important?
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. This is important for processes and/or reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges.
What is the purpose of a pH buffer?
PH buffers are special solutions which prevent large variations in pH levels. Every pH level produced has a specified buffer capacity and buffer range. The capacity of the buffer refers to the amount of acid or base which can be added before the pH alters substantially.
Is water a buffer?
"A buffer solution is water mixed with a chemical to give it special properties in regards to pH (acidity)....Making a pH Buffer Solution.Acid, formula, and mass (g) or volume (ml) of standard reagentConjugate base, formula, and massBuffer pHBoric acid H2B4O7 31.4 gSodium hydroxide NaOH 12.0 g12.716 more rows
Which solution is a buffer?
In chemistry, the definition of a buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acid or a base. It consists of a solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa.
Where are buffers used?
Buffer solutions are used in the manufacture of many cosmetic and personal hygiene products in order to maintain a pH that's neutral or even slightly alkaline. The buffer solution prevents the products becoming too acidic or too alkaline, as this could cause skin irritations.
What is the meaning of pH in chemistry?
pH, quantitative measure of the acidity or basicity of aqueous or other liquid solutions. The term, widely used in chemistry, biology, and agronomy, translates the values of the concentration of the hydrogen ion—which ordinarily ranges between about 1 and 10−14 gram-equivalents per litre—into numbers between 0 and 14.
What are common buffers?
Simple buffering agentsBuffering agentpKaUseful pH rangeCitric acid3.13, 4.76, 6.402.1–7.4Acetic acid4.83.8–5.8KH2PO47.26.2–8.2CHES9.38.3–10.31 more row
Is water a good buffer?
There WOULD be a very very very small concentration and H+ and OH- in it, since a value of Ka means that it does ionise in itself, but on the whole there would be MORE water molecules floating about. This is why water acts as a very poor buffer. You need the acid AND the conjugate base (salt) for a buffer to work.
What is meant by pH?
A measure of how acidic or basic a substance or solution is. pH is measured on a scale of 0 to 14. On this scale, a pH value of 7 is neutral, which means it is neither acidic nor basic. A pH value of less than 7 means it is more acidic, and a pH value of more than 7 means it is more basic.
What is the difference between acid base and buffer?
Key Points. A basic solution will have a pH above 7.0, while an acidic solution will have a pH below 7.0. Buffers are solutions that contain a weak acid and its a conjugate base; as such, they can absorb excess H+ ions or OH– ions, thereby maintaining an overall steady pH in the solution.
What does pH stand for?
potential hydrogenpH, explained The abbreviation pH stands for potential hydrogen, and it tells us how much hydrogen is in liquids—and how active the hydrogen ion is.
How do you calculate the pH of a buffer?
Our buffer pH calculator provides you with an effortless way to compute the pH of any kind of buffer solution....How to calculate the pH of a buffer solution?pH = -log₁₀(H);Ka – Acid dissociation constant;[HA] – Concentration of the acid;[A⁻] – Concentration of conjugate base; and.pKa = -log₁₀(Ka).
What is the capacity of a buffer?
The capacity of the buffer refers to the amount of acid or base which can be added before the pH alters substantially. It may also be characterized as the level of strong acid or base that needs to be added to alter the pH of a liter of solution by one pH unit.
What is buffer range?
The buffer range is the pH range where a buffer can effectively neutralize added acids and bases whilst maintaining a steady pH. This is critical for processes or reactions which need specific and stable pH ranges.
What is the pH of water?
Sometimes this is known as the potential of hydrogen in an aqueous solution. The pH of a solution is on a scale of 0-14 and is a temperature-dependent property, with water having a neutral pH of 7.47 at 0°C and 6.14 at 100°C.
Why do different buffers have different pH?
Because the different Brønsted acids involved with these buffers have different pKa's, and so they hold protons more or less tightly, different buffers are able to operate at different pH ranges. This factor, together with control over the concentrations of the components of the buffer system, allows pH to be held fairly constant at almost any value necessary.
Why do biological systems use buffers?
Even different tissues within the same organism may work best at different pH values. In order to maintain pH balance at an optimum level, biological systems employ buffers. Buffers are compounds that can either absorb or provide protons in order to keep the pH of their environment from changing. Because they need to absorb or provide protons, buffers are weak Brønsted acids or weak bases, together with their conjugates.
What does low pH mean?
A low pH actually means there are lots of protons or hydronium ions around. At low pH, the environment is very acidic. Low pH is usually associated with the presence of strong Brønsted acids. The typical pH of about 3 in the stomach is produced by dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl.
How is pH related to pKa?
pH is related to pKa. Both indices work on a logarithmic scale to avoid carrying large amounts of decimal places in very small numbers. A pH of 6, typical in many biological environments, means that the hydronium ion concentration is about 10 -6 moles/L (in which a mole is a unit used for convenient counting of nanoscopic things like molecules or ions, just like a dozen is used for counting eggs or doughnuts).
Why is pH important in biological processes?
Control of pH is very important in biological systems. Many biological processes operate at an optimum pH, and many biomoecules are stable only across a certain pH range. Proteins are particularly sensitive to conditions including pH. Changes in conditions can easily lead to proteins becoming denatured, which means the protein undergoes a shape change that severely affects its ability to function. This shape change is a conformational change, and it is brought about by changing interactions along the protein chain, including changing electrostatic interactions when different sites become protonated or deprotonated.
What happens when pH is too low?
When pH gets too low, the conjugate base, carbonate, can absorb a proton and become bicarbonate again.
What buffers maintain pH?
For instance, one of the buffers that maintain the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid (H CO) and its conjugate base, the bicarbonate ion (HCO ). Carbonic acid is formed when carbon dioxide enters the bloodstream and combines with water, and it is the main form in which carbon dioxide travels in the blood between the muscles (where it’s generated) and the lungs (where it’s converted back into water and CO, which is released as a waste product).
What is the function of buffers in biological systems?
Buffers, solutions that can resist changes in pH, are key to maintaining stable H ion concentrations in biological systems. When there are too many H ions, a buffer will absorb some of them, bringing pH back up; and when there are too few, a buffer will donate some of its own H ions to reduce the pH. Buffers typically consist of an acid-base pair, with the acid and base differing by the presence or absence of a proton (a conjugate acid-base pair).
How does H shift away from neutral?
H concentration shifts away from neutral when an acid or base is added to an aqueous (water-based) solution. For our purposes, an acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H) in a solution, usually by donating one of its hydrogen atoms through dissociation. A base, in contrast, raises pH by providing hydroxide (OH) or another ion or molecule that scoops up hydrogen ions and removes them from solution. (This is a simplified definition of acids and bases that works well for thinking about biology. You may want to visit the chemistry section to see other acid-base definitions.)
What is the pH scale used for?
The pH scale is used to rank solutions in terms of acidity or basicity (alkalinity). Since the scale is based on pH values, it is logarithmic, meaning that a change of 1 pH unit corresponds to a ten-fold change in H ion concentration. The pH scale is often said to range from 0 to 14, and most solutions do fall within this range, although it’s possible to get a pH below 0 or above 14. Anything below 7.0 is acidic, and anything above 7.0 is alkaline, or basic.
How much pH do humans need to survive?
For instance, human blood needs to keep its pH right around 7.4, and avoid shifting significantly higher or lower – even if acidic or basic substances enter or leave the bloodstream.
What is the pH of blood?
The pH inside human cells (6.8) and the pH of blood (7.4) are both very close to neutral. Extreme pH values, either above or below 7.0, are usually considered unfavorable for life. However, the environment inside your stomach is highly acidic, with a pH of 1 to 2. How does the stomach get around this problem? The answer: disposable cells! Stomach cells, particularly those that come in direct contact with stomach acid and food, are constantly dying and being replaced by new ones. In fact, the lining of the human stomach is completely replaced about every seven to ten days.
Is a solution acidic or basic?
Solutions are classified as acidic or basic based on their hydrogen ion concentration relative to pure water. Acidic solutions have a higher H concentration than water (greater than 1 × 10 M), while basic (alkaline) solutions have a lower H concentration (less than 1 × 10 M). Typically, the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is expressed in terms of pH. pH is calculated as the negative log of a solution’s hydrogen ion concentration:
What is the pH of a solution?
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. You have probably used litmus paper, paper that has been treated with a natural water-soluble dye so it can be used as a pH indicator, to test how much acid or base (alkalinity) exists in a solution. You might have even used some to make sure the water in an outdoor swimming pool is properly treated. In both cases, this pH test measures the amount of hydrogen ions that exists in a given solution. High concentrations of hydrogen ions yield a low pH, whereas low levels of hydrogen ions result in a high pH. The overall concentration of hydrogen ions is inversely related to its pH and can be measured on the pH scale (Figure 1). Therefore, the more hydrogen ions present, the lower the pH; conversely, the fewer hydrogen ions, the higher the pH.
What is the pH of water?
Thus, small changes in pH represent large changes in the concentrations of hydrogen ions. Pure water is neutral. It is neither acidic nor basic, and has a pH of 7.0. Anything below 7.0 (ranging from 0.0 to 6.9) is acidic, and anything above 7.0 (from 7.1 to 14.0) is alkaline (basic). The blood in your veins is slightly alkaline (pH = 7.4). The environment in your stomach is highly acidic (pH = 1 to 2). Orange juice is mildly acidic (pH = approximately 3.5), whereas baking soda is basic (pH = 9.0).
What is the key to keeping pH in the body?
Buffers are the key. Buffers readily absorb excess H + or OH –, keeping the pH of the body carefully maintained in the aforementioned narrow range. Carbon dioxide is part of a prominent buffer system in the human body; it keeps the pH within the proper range. This buffer system involves carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3) and bicarbonate (HCO 3–) anion.
Why is carbonic acid fleeting?
While carbonic acid is an important product in this reaction, its presence is fleeting because the carbonic acid is released from the body as carbon dioxide gas each time we breathe. Without this buffer system, the pH in our bodies would fluctuate too much and we would fail to survive.
What is the difference between high and low pH?
High concentrations of hydrogen ions yield a low pH, whereas low levels of hydrogen ions result in a high pH. The overall concentration of hydrogen ions is inversely related to its pH and can be measured on the pH scale (Figure 1). Therefore, the more hydrogen ions present, the lower the pH; conversely, the fewer hydrogen ions, the higher the pH.
Which substances give up H+?
The stronger the acid, the more readily it donates H +. For example, hydrochloric acid and lemon juice are very acidic and readily give up H + when added to water.
What happens if the pH of the body is too low?
If the pH of the body is outside of this range, the respiratory system malfunctions, as do other organs in the body. Cells no longer function properly, and proteins will break down. Deviation outside of the pH range can induce coma or even cause death.
What is the Difference Between pH and Buffer?
pH is a logarithmic scale that we use to determine the acidity or the basicity of an aqueous solution whereas, a buffer is an aqueous solution that tends to resist the change in pH. This is the key difference between pH and buffer. Moreover, the pH is a very important scale in chemistry. We can measure the pH of a solution using a pH meter or via experimental methods. Furthermore, we use the pH scale in order to determine the quality of water, soil, etc. On the other hand, the use of buffer solutions is to maintains the correct pH for enzymatic activity, in fermentation processes in industries, in setting the correct conditions for dyes, in chemical analysis, calibrating pH meters, etc. We measure the buffer capacity of a buffer using chemical analysis.
What is Buffer?
A buffer is an aqueous solution that tends to resist the change in pH. This solution contains a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. The pH of these solutions changes slightly upon addition of either a strong acid or a strong base.
What is the pH of an aqueous solution?
pH is a logarithmic scale that we use to determine the acidity or the basicity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative base 10 logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration measured in the unit mol/L. If we express it more precisely, we should use the activity of hydrogen ions instead of the concentration. The pH scale has numbers from 0 to 14. Solutions having a pH less than 7 are acidic and if the pH is higher than 7, it is a basic solution. The pH 7 indicates a neutral solution, i.e. pure water.
What happens when you add a weak acid to a system?
Then if we add some strong acid to this system, the equilibrium shifts towards the acid, and it forms more acid using the hydrogen ions released from the added strong acid.
Why do we use pH?
We can use the pH of a liquid to determine whether it is an acid or a base. It also is helpful in determining the buffering capacity of a buffer. A buffer solution contains a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. Therefore, it tends to resist changes in the pH of the solution.
Why are buffers used in fermentation?
When considering the applications of buffers, these solutions are necessary to keep the correct pH for enzymatic activity in organisms. Moreover, these are used in industries in fermentation processes, setting the correct conditions for dyes, in chemical analysis, calibrating pH meters, etc.
Is a pH of 7 acidic or basic?
Solutions having a pH less than 7 are acidic and if the pH is higher than 7, it is a basic solution. The pH 7 indicates a neutral solution, i.e. pure water. Figure 01: pH of Different Components. The equation for the determination of pH is as follows:
pH, acids, based and buffers
Acids and bases, like salts, dissociate in water into electrolytes. Acids and bases can very much change the properties of the solutions in which they are dissolved.
Glossary
molecule that donates hydroxide ions or otherwise binds excess hydrogen ions and decreases the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
What is the buffer capacity of soil?
The buffer capacity of soils is the capacity of soils to resist change. In relation to soil pH, the soil Buffer Index is a measure of the soil reservoir of basic material, which will serve to resist change in soil pH. By comparison, soil pH measures the current acid or basic condition of the soil, as the plant experiences it, ...
What is buffer index?
Buffer Index (BI) measured in the laboratory, as a part of the Oklahoma State University soil test, is an indirect estimate of the soil reservoir size for storing basic material. Because the test involves adding basic (lime-like) material to soils of pH less than 6.5 and then measuring pH again, the BI pH is larger when the reservoir is small. The two soils illustrated in Figure 2 need to be limed. The Pond Creek Silt Loam soil would have a BI value of about 6.2. About 4.2 tons of ECCE lime would be required to raise the soil pH to 6.8. The sandy soil, having the same soil pH, would have a BI value of about 6.5 and require only 2.4 tons of ECCE lime. The field calibration for BI and lime requirement is provided in Table 2.
How does soil pH change?
Because of this relationship and the large reserve of bases from soil solids, the pH does not change much from month to month or even year to year. Also, since the large reservoir on the left is shaped like a pyramid, pH can be changed more easily by liming at pH near 6 than in the very acid pH 4.5 to 5.5 range.
What pH is needed for alfalfa?
Considering a soil test result of pH 5.8 and Buffer Index 6.8, where establishment of alfalfa is intended the following steps are taken to determine lime requirement.
Why is soil pH high?
The soil pH is seldom too high (basic or alkaline) to interfere with crop production. However, when crop production declines due to high soil pH, it is usually because the pH is 8.5 or higher and water movement into the soil is drastically reduced. This problem can be corrected if the soil has good internal drainage, or it can be provided for, and the alkali salts such as sodium can be leached out. The leaching will only be possible after the required amount of gypsum has been applied. For more information on alkali soils see Fact Sheet PSS-2226, “Reclaiming Slick-Spots and Salty Soils.”
Why is pH important for soil?
Soil pH is a very important soil chemical property because it strongly influences availability of plant nutrients in the soil and can have a drastic effect on crop production. Crops vary in their tolerance, or ability to grow, in soil at very high and very low pH (see Table 1). A soil pH of 7.0 is neutral and is used as a reference ...
Does pH change month to month?
Because of this relationship and the large reserve of bases from soil solids, the pH does not change much from month to month or even year to year. Also, since the large reservoir on the left is shaped like a pyramid, pH can be changed more easily by liming at pH near 6 than in the very acid pH 4.5 to 5.5 range.
