What are some examples of phase changes?
Types of phase transition
- A eutectic transformation, in which a two-component single-phase liquid is cooled and transforms into two solid phases. ...
- A metastable to equilibrium phase transformation. ...
- A peritectic transformation, in which a two-component single-phase solid is heated and transforms into a solid phase and a liquid phase.
What is needed for matter to change phase?
Section Summary
- Most substances have three distinct phases: gas, liquid, and solid.
- Phase changes among the various phases of matter depend on temperature and pressure.
- The existence of the three phases with respect to pressure and temperature can be described in a phase diagram.
What are the six different phase changes?
Six Phase Changes. STUDY. PLAY. Melting. when a substance changes from a solid to liquid. Freezing. when a substance changes from a liquid to solid. Vaporization. the phase change in which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. Condensation.
How does phase change materials (PCM) works?
Phase change materials are conceptually different, however. They operate by storing energy at a constant temperature while phase change occurs, for example from solid to a liquid, as illustrated in the center of Figure Temperature Profile of a PCM. As heat is added to the material, the temperature does not rise; instead heat drives the change ...

What are PCMs commonly used for?
PCMs are used in many different commercial applications where energy storage and/or stable temperatures are required, including, among others, heating pads, cooling for telephone switching boxes, and clothing. By far the biggest potential market is for building heating and cooling.
What are the advantages of phase change material?
PCMs provide many advantages when incorporated into products. They include energy savings, a better night's sleep, cooling and heating relief in remote locations without access to electricity, and better performing electronics. There are two kinds of heat energy: sensible and latent.
What is an example of a phase change material?
The most common example of a phase change material is water. In its solid form, water (or ice) requires a (relatively) huge amount of energy to melt, whereas liquid water will change the temperature using much less energy.
What is the significant of using phase changing materials when incorporated into clothing?
They make it possible to engineer fabrics that help regulate human body temperature. Depending on the surrounding temperature, phase change materials absorb or release heat, consequently oscillating between liquid and solid phases.
Is phase change material expensive?
Organic PCMs are typically more expensive than inorganic ones: most paraffin waxes are byproducts from oil refineries and therefore available in abundant supply but at a relatively high price ($1.88−2.00/kg); fatty acid PCMs include stearic acid ($1.43−1.56/kg), palmitic acid ($1.61−1.72/kg), and oleic acid ($1.67−1.76 ...
What is phase change material in mattresses?
Just like its name, phase change materials are substances that change from one phase – liquid, solid or vapor – to another phase depending on their temperature. A natural PCM is water/ice. When the temperature dips down to freezing (32 degrees Fahrenheit), water freezes into ice.
How do you choose a phase change material?
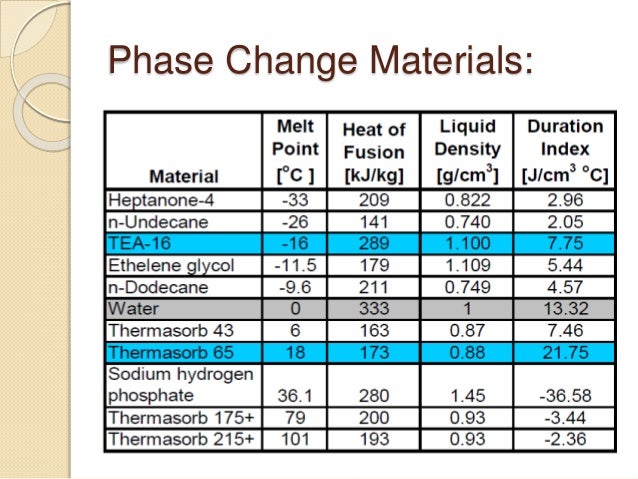
There are several factors that need to be considered when selecting a phase change material. An ideal PCM will have high heat of fusion, high thermal conductivity, high specific heat and density, long term reliability during repeated cycling, and dependable freezing behavior.
Why is a phase change important?
Phase changes can have a strong stabilizing effect on temperatures that are not near the melting and boiling points, since evaporation and condensation occur even at temperatures below the boiling point.
What are the 4 processes of phase change in materials?
Melting: the substance changes back from the solid to the liquid. Condensation: the substance changes from a gas to a liquid. Vaporization: the substance changes from a liquid to a gas. Sublimation: the substance changes directly from a solid to a gas without going through the liquid phase.
What happens to the materials that undergo phase change?
Phase change materials are latent thermal storage materials. They use chemical bonds to store and release heat. The thermal energy transfer occurs when a material changes from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a solid. This is called a change in state, or phase.
Which of the following factors causes the materials to change in its phase?
Substances can change phase — often because of a temperature change. At low temperatures, most substances are solid; as the temperature increases, they become liquid; at higher temperatures still, they become gaseous.
What is PCM made of?
Organic materials used as PCMs tend to be polymers with long chain molecules composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen. They tend to exhibit high orders of crystallinity when freezing and mostly change phase above 0°C (32°F).
What are the best phase change materials?
Paraffin waxes are the most common PCM for electronics thermal management because they have a high heat of fusion per unit weight, have a large melting point selection, provide dependable cycling, are non-corrosive and are chemically inert.
How does energy changes affect the phase and temperature of a material?
When thermal energy is added to a substance, its temperature increases, which can change its state from solid to liquid (melting), liquid to gas (vaporization), or solid to gas (sublimation).
What is the chemistry term for a phase change when a solid becomes a liquid?
The process of a solid becoming a liquid is called melting (an older term that you may see sometimes is fusion).
What is organic and inorganic PCM?
The three main PCM types defined were organic, inorganic, and eutectic PCMs. Organic PCMs primarily consist of paraffins (straight chain n-alkanes), esters, fatty acids, and alcohols (Sharma et al., 2009). Under inorganic PCMs, salt hydrates are primarily used.
What is phase change material?
When the sodium acetate solution crystallises, it becomes warm. A phase change material ( PCM) is a substance which releases/absorbs sufficient energy at phase transition to provide useful heat/cooling. Generally the transition will be from one of the first two fundamental states ...
What are the two main classes of phase change materials?
There are two principal classes of phase change material: organic (carbon-containing) materials derived either from petroleum, from plants or from animals; and salt hydrates, which generally either use natural salts from the sea or from mineral deposits or are by-products of other processes.
How does PCM work?
Unlike conventional SHS materials, however, when PCMs reach their phase change temperature (their melting point) they absorb large amounts of heat at an almost constant temperature until all the material is melted. When the ambient temperature around a liquid material falls, the PCM solidifies, releasing its stored latent heat. A large number of PCMs are available in any required temperature range from −5 up to 190 °C. Within the human comfort range between 20 and 30 °C, some PCMs are very effective, storing over 200 kJ/kg of latent heat, as against a specific heat capacity of around one kJ/ (kg*°C) for masonry. The storage density can therefore be 20 times greater than masonry per kg if an temperature swing of 10 °C is allowed. However, since the mass of the masonry is far higher than that of PCM this specific (per mass) heat capacity is somewhat offset. A masonry wall might have a mass of 200 kg/m 2, so to double the heat capacity one would require additional 10 kg/m 2 of PCM.
What is the market for PCMs?
By far the biggest potential market is for building heating and cooling. PCMs are currently attracting a lot of attention for this application due to the progressive reduction in the cost of renewable electricity, coupled with limited hours of availability, resulting in a misfit between peak demand and availability of supply. In North America, China, Japan, Australia, Southern Europe and other developed countries with hot summers peak supply is at midday while peak demand is from around 17:00 to 20:00. This creates a lot of demand for storage media.
How to increase thermal conductivity?
In this case, the basic idea is to increase thermal conductivity by adding a highly conducting solid (such as the copper mesh or graphite) into the relatively low-conducting PCM, thus increasing overall or bulk (thermal) conductivity. If the PCM is required to flow, the solid must be porous, such as a mesh.
What is PCM in science?
A phase change material ( PCM) is a substance which releases/absorbs sufficient energy at phase transition to provide useful heat/cooling. Generally the transition will be from one of the first two fundamental states of matter - solid and liquid - to the other. The phase transition may also be between non-classical states of matter, ...
Why are liquid gas transitions impractical?
Although liquid–gas transitions have a higher heat of transformation than solid–liquid transitions, liquid→gas phase changes are impractical for thermal storage because large volumes or high pressures are required to store the materials in their gas phase.
What are Phase Change Materials (PCM)?
A phase change material is a term used for any material that both absorbs and releases heat as it changes physical state, such as from a solid to a liquid, and vice-versa. As an output for this reaction, the material will typically become either warmer or cooler depending on the phase change temperature (PCT). For this reason, PCMs provide solutions for heat/cooling storage and retention, extreme weather protection and overall energy efficiency. They’re commonly found in applications such as high-efficiency appliances, clothing, and hardware materials.
What is the best material for phase change?
Some of the most preferable phase change materials are plant-based. These organic compounds are free of toxicity, typically have high latent heat capacity, and are cheaper than most paraffin PCMs. Plant-based PCMs (and some made of animal fat) are found to be more efficient than salt hydrates and paraffin, and typically have a wide range of melting points depending on the raw materials involved.
Why do we use phase change beads?
Even the fashion industry has tapped into the strategic use of phase change materials in the form of beads placed within textiles to increase the human body’s own energy efficiency.
Is PCM phase change material the same?
No two phase change materials are alike, and each application warrants its own unique solution. When deciding on the type of PCM for your project, ensure you’ve taken the following measures into consideration:
Thermal Energy Storage
Thermal energy storage refers to technology that captures heat in a medium. The system then dispenses the stored latent heat energy at a later time. For example, batteries store and dispense electrical power. Thermal energy storage systems do the same with heat.
PCMs and Thermal Engineering
Effective PCM heat sinks can store thermal energy while remaining at a relatively stable temperature themselves. Engineers often place PCMs in hermetically sealed capsules or other enclosures, which maximize their effectiveness.
Types of Phase Change Materials
An excellent PCM will score high in multiple categories. Among them are the heat of fusion, thermal conductivity, and specific heat. A good PCM will demonstrate consistent freezing behavior and stand up to repeated cycling.
Concept Group LLC
Concept Group LLC is a thermal engineering firm specializing in advanced insulation solutions for complex and demanding thermal challenges. We combine innovative engineering with expert manufacturing to develop proprietary solutions for clients across industries.
Why are phase change materials useful?
Capturing and storing energy is difficult. Phase change materials (PCMs) are ideal for use in any application where a storage and release of thermal energy is desired. PCMs act like a battery for heat energy because they absorb heat energy as they melt and can be “recharged” by cooling them until they crystallise and give the stored energy back the environment. They can store and release heat energy thousands of times without change in thermal properties.
What happens to a material when it changes from a solid to a liquid?
Phase change materials are substances that absorb and release heat energy when they change phase (known as latent heat). When a material melts , it changes from a solid phase to a liquid phase. During the phase transition, many materials are able to absorb a significant amount of heat energy. The opposite is true when the material freezes ...
What is the term for the ability of a material to absorb or release heat energy as it melts or freezes?
This is known as latent heat. Latent heat capacity is the ability of a material to absorb or release heat energy as it melts or freezes without increasing in temperature.
What is the difference between material that melts and material that absorbs heat?
Materials that melt to absorb heat are much more efficient at absorbing heat energy compared to sensible heat energy materials. This means that it takes a much smaller amount of a material to store heat energy phase change material than using a material that does not change phase.
Does phase change material store heat?
This demonstrates the powerful effect of using a phase change material to store heat energy latently rather than using sensible heat capacity.
What is phase change material?
Phase change materials (PCMs) are substances that absorb and release thermal energy during the process of melting and solidifying. When a PCM melts, it absorbs a large amount of heat (energy) from the environment. Conversely, when a PCM solidifies it releases a large amount of energy in the form of latent heat. PCMs continuously cycle through this process, making them ideal for a variety of everyday applications that require temperature management. PCMs reduce temperature swings and have the ability to maintain a specific temperature for extended periods of time.
Why are PCMs used in refrigerators?
PCMs are used in these applications because they are eco-friendly and energy-saving. Some PCM applications include: High-performance textiles and foams that provide relief from hot and cold conditions. Refrigerators and freezers that use less energy.
Why are PCMs used in electronics?
PCMs are used in these applications because they are eco-friendly and energy-saving.
First, what do we mean by Phase Change Materials?
I hear more and more people talking about Phase Change Materials. You have certainly used one already, e.g. with your portable isothermal bag (cooling bag) when you go to the beach and you want to keep your food and drinks cold. Just as you can keep things cold with a Phase Change Materials, you can also use PCMs to keep things warm.
What materials can be used as Phase Change Materials?
The next question I often get: what kind of materials are we talking about?
PCM examples: Salt, alcohol, wax and sugar
In Norway, the most typical utilisation of these mixtures are on the winter roads: salt crystals spread out on the road will mix with rainwater to lower the freezing point below 0 °C, thus preventing ice formation until the air temperature is well below zero degree Celsius.
We are especially interested in PCMs today
Phase Change Materials are gaining a lot of attention these days, because their technology readiness level (TRL) is close to commercial use for thermal energy storage; This means to absorb heat or cold when in excess, and deliver it back later when needed.
Industrial advantages of PCMs
Ideally, the goal is to store heat or cold similarly to how we store electrical energy in batteries, using charging and discharging phases. Compared to other methods to store heat, Phase Change Materials make thermal storage units more compact and can operate on a narrow temperature range, which means lower heat losses.
PCMs can help you heat up your house
One example of Phase Change Material application focuses on wood stoves. In new, modern buildings, thermal insulation is so effective that wood stoves often overheat the house. One solution is to develop a heat storage using PCMs to absorb part of this excess heat before it reaches the room and deliver the heat back also after the combustion ends.
Phase Change Materials can save energy in supermarkets
Another promising example in focus in the PCM-Eff project is the integration of a PCM-based cold accumulator in refrigerated food display cabinets such as those found in supermarkets.
What are the materials used in phase change?
There are various types of phase change materials. The most commonly used ones include salt hydrates, fatty acids, esters, and paraffin. Ionic liquids are considered to be more of the newer ones.
What happens to phase change materials?
Phase change materials, when in the process of freezing, release a large amount of energy (latent energy), also known as the energy of crystallization. On the other hand, when melted, these materials absorb an equal amount of energy from the environment.
Why are vegetable based phase change materials so popular?
Vegetable-based phase change materials are gaining popularity because of their safety and environmental benefits. Paraffin is thought to be toxic and has laxative effects when ingested. Moreover, when disposed of in a landfill, it poses environment problems. The material that makes up paraffin, long chain alkanes, will not decay for decades. On the other hand, vegetable-based phase change materials degrade within six months. Considered cost-effective, vegetable-based materials are environmentally friendly and also renewable with the capability to be microencapsulated. Biodegradable, higher latent heat, longer ignition rates, longer horizontal flame propagation rates are all the new properties that vegetable-based phase change materials have to offer.
How does phase change material help the environment?
The role of phase change materials in stabilizing the temperature of the environment is significant. A system that saves energy while providing comfort is what these products have to offer are main advantages. Even though many disadvantages still exist, research is ongoing to overcome hurdles holding back phase change materials.
What is phase change?
Phase change materials are considered to be ideal products for thermal management solutions. These materials are capable of storing and releasing thermal energy while melting and freezing, hence the name phase change.
Is paraffin a phase change material?
Paraffin is a traditional phase change material and also bears some limitations. Pure paraffin products are thought to have very high latent heats. Petroleum-based paraffin has geopolitical consequences because of the release of an excess amount of carbon which contributes to the global warming crisis.
What are Phase Change Materials?
Materials display different properties in each state of matter (solid, gas, liquid, and plasma) which can be manipulated for a multitude of purposes.
From Water to Modern Phase-Change Materials: A Brief Overview
Aside from its essential use for sustaining life, water is a phase-change material that has a long history of use in industry. This material is the most well-known phase change material, which has a melting point of 0 o C and a boiling point of 100 o C.
Vanadium Oxides
The family of vanadium oxides has been extensively researched for their phase-change characteristics. They exhibit these characteristics differently depending on stoichiometry. Of this family of materials, vanadium dioxide (VO 2) has a well-known near-room temperature metal to insulator transition.
Ternary Ge-Sb-Te
Ternary Ge-Sb-Te, or GST, is a family of chalcogenide alloys that exhibit phase-change characteristics. These materials have already found widespread commercial application in devices such as Blu-Ray and DVD-RAM players. They are key components in phase-change memory applications.
Other Uses of Phase-Change Materials
Phase-change materials have been widely explored for a multitude of devices. CrodaTherm TM 24W is a proprietary phase-change material that has the physical form of a waxy solid. It is used primarily for thermal storage and maintaining ambient temperature for applications such as HVAC systems and thermally regulated pharmaceutical packaging.
The Future
From heat storage and thermal regulation devices to reconfigurable photonics, ferroelectrics, memory devices, and other novel applications, phase-change materials, from the well-known vanadium oxide and GST families to novel materials, display great promise for next-generation applications.
References and Further Reading
Croda Energy Technologies (2022) CrodaTherm TM 24W [online] Available at:
Overview
Applications
Applications of phase change materials include, but are not limited to:
• Thermal energy storage, such as the FlexTherm Eco by Flamco.
• Solar cooking
• Cold Energy Battery
Characteristics and classification
Latent heat storage can be achieved through changes in the state of matter from liquid→solid, solid→liquid, solid→gas and liquid→gas. However, only solid→liquid and liquid→solid phase changes are practical for PCMs. Although liquid–gas transitions have a higher heat of transformation than solid–liquid transitions, liquid→gas phase changes are impractical for thermal storage bec…
Selection criteria
The phase change material should possess the following thermodynamic properties:
• Melting temperature in the desired operating temperature range
• High latent heat of fusion per unit volume
• High specific heat, high density, and high thermal conductivity
Thermophysical properties
Key thermophysical properties of phase-change materials include: Melting point (Tm), Heat of fusion (ΔHfus), Specific heat (cp) (of solid and liquid phase), Density (ρ) (of solid and liquid phase) and thermal conductivity. Values such as volume change and volumetric heat capacity can be calculated there from.
Technology, development, and encapsulation
The most commonly used PCMs are salt hydrates, fatty acids and esters, and various paraffins (such as octadecane). Recently also ionic liquids were investigated as novel PCMs.
As most of the organic solutions are water-free, they can be exposed to air, but all salt based PCM solutions must be encapsulated to prevent water evaporation or uptake. Both types offer certain advantages and disadvantages and if they are correctly applied some of the disadvantages bec…
Thermal composites
Thermal composites is a term given to combinations of phase change materials (PCMs) and other (usually solid) structures. A simple example is a copper mesh immersed in paraffin wax. The copper mesh within paraffin wax can be considered a composite material, dubbed a thermal composite. Such hybrid materials are created to achieve specific overall or bulk properties (an example being the encapsulation of paraffin into distinct silicon dioxide nanospheres for increas…
Fire and safety issues
Some phase change materials are suspended in water, and are relatively nontoxic. Others are hydrocarbons or other flammable materials, or are toxic. As such, PCMs must be selected and applied very carefully, in accordance with fire and building codes and sound engineering practices. Because of the increased fire risk, flamespread, smoke, potential for explosion when held in containers, and liability, it may be wise not to use flammable PCMs within residential or o…
Water-Based PCMS
- Water-based PCMs are typically found in cooling applications, from refrigerators and freezers to gel packs. By adding an alcohol (such as glycol or ethanol) to water to prevent supercooling, the mixture’s freezing point is greatly reduced and it can therefore be an effective material in energy saving applications that reach up to -30ºC. Water is typically only useful for its phase-changing p…
Salt Hydrate PCMS
- Salt hydrates are some of the most cost-efficient PCM solutions, and the most readily available. Salt hydrate PCMs also have an impressive latent heat storage capacity, which makes them suitable for thermal energy saving applications like space heaters. However, salt hydrate PCMs also come with their fair share of adversities to look out for. Of all the phase change materials, s…
Paraffin PCMS
- Paraffin PCMs are other favorable material options depending on the application. Paraffins offer stability in their formulation over other competing organic compounds, which makes them more durable during heating and cooling processes. They are also non-corrosive, which is a huge asset when paired with metal materials that are exposed to moisture. However, paraffin comes with s…
Plant-Based PCMS
- Some of the most preferable phase change materials are plant-based. These organic compounds are free of toxicity, typically have high latent heat capacity, and are cheaper than most paraffin PCMs. Plant-based PCMs (and some made of animal fat) are found to be more efficient than salt hydrates and paraffin, and typically have a wide range of melting...
Thermal Energy Storage
- Thermal energy storage refers to technology that captures heat in a medium. The system then dispenses the stored latent heat energy at a later time. For example, batteries store and dispense electrical power. Thermal energy storage systems do the same with heat. Phase change materials are popular components in thermal energy storage systems. There ...
PCMS and Thermal Engineering
- Effective PCM heat sinks can store thermal energy while remaining at a relatively stable temperature themselves. Engineers often place PCMs in hermetically sealed capsules or other enclosures, which maximize their effectiveness. Absorbing heat via PCM is a straightforward concept. However, effective system designs demand engineering expertise. It is vital to select th…
Types of Phase Change Materials
- An excellent PCM will score high in multiple categories. Among them are the heat of fusion, thermal conductivity, and specific heat. A good PCM will demonstrate consistent freezing behavior and stand up to repeated cycling. Melt temperature, weight, corrosionresistance, and cost are other considerations. To identify an ideal PCM, engineers must weigh the relative impor…