What are pre-analytical errors?
Pre-analytical errors: their impact and how to minimize them MLO Med Lab Obs. 2014 May;46(5):22, 24, 26. Authors
Are 40% of errors in the laboratory pre-analytical and 40% analytical?
Pre analytical in Errors OP sample: Wrong patient identification while collection Error in listing the prescribed tests Sample mismatch during blood collection Wrong numbering of patient’s sample Patient’s not properly prepared for the test Blood sample inadequate or clotted Hemolysis of sample Misplacing of sample
Is the pre-analytical phase the most error-prone?
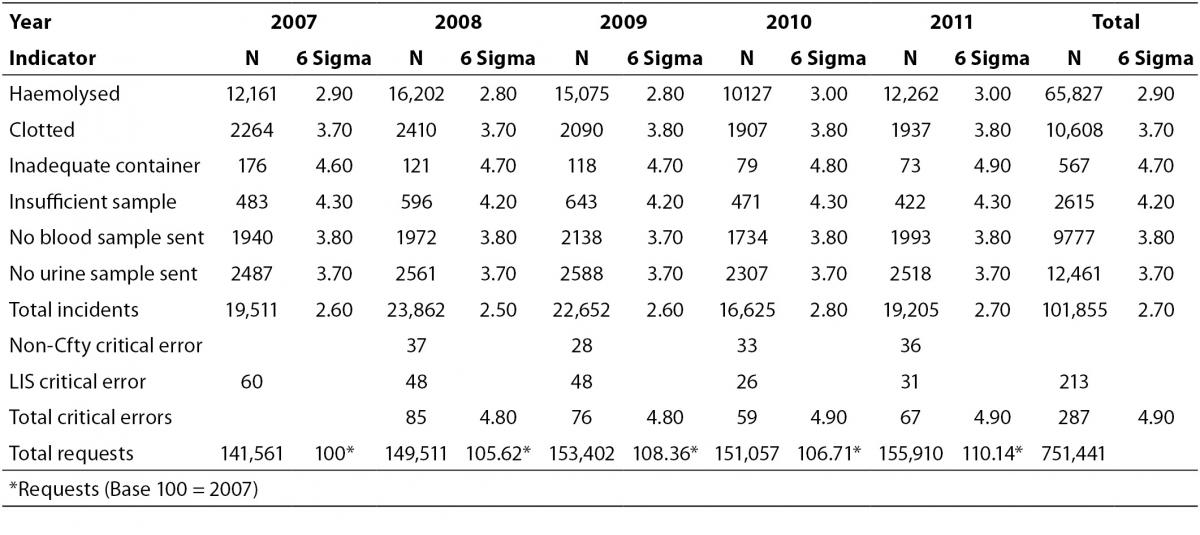
What are pre analytical errors? The most commonly reported types of pre-analytical error are: a) missing sample and/or test request, b) wrong or missing identification, c) contamination from infusion route, d) haemolysed, clotted, and insufficient samples, e) inappropriate containers, f) inappropriate blood to anticoagulant ratio, and g)
What happens when there is an error in the pre-analysis stage?
Errors in the Pre-analytical Phase. Currently, pre-analytical errors account for up to 70% of all mistakes made in laboratory diagnostics, most of which arise from problems in patient preparation, sample collection, transportation, and preparation for analysis and storage. 7 While patient preparation and sample collection (including patient and sample identification, and …

What are pre-analytical factors?
The preanalytical phase is the phase where the laboratory has no direct control on the process. Preanalytical factors that can affect results include: sample type, sampling time, sample handling, patient's preparation and the nutritional status of the patient.
What is a pre-analytical error in phlebotomy?
Preanalytic errors are errors that occur prior to the testing process. Hemolyzed specimens, clotted specimens, incorrect tube type, and inadequate tube fill can all produce preanalytic errors.
What are analytical and post analytical errors?
Postanalytical variables occur after a test result is generated. In general, suchpostanalytical errors occur with entry, manipulation, and reporting of test data. If results are written by hand or entered via keyboard, then an entry error may occur.
What does pre analytic mean?
Filters. Describing any procedure that takes place before an analysis. adjective. Describing any variable whose value can affect the outcome of a subsequent analysis.
How can preanalytical errors be prevented?
“Other measures for avoiding preanalytical errors that have proven successful are: never accept an unlabelled sample. Never allow unlabelled or mislabeled samples to be relabeled, if recollection is feasible." "Document relabeling must be approved by an attending physician, with results footnoted.
What are examples of analytical errors?
Some examples of analytical errors include equipment malfunction, procedures (i.e., standard operating procedures and assay instructions) not followed, undetected failure of quality control, sample mixups, and test interference.Nov 14, 2016
What pre-analytical errors can affect protein tests?
The most commonly reported types of pre-analytical error are: a) missing sample and/or test request, b) wrong or missing identification, c) contamination from infusion route, d) haemolysed, clotted, and insufficient samples, e) inappropriate containers, f) inappropriate blood to anticoagulant ratio, and g) ...
What is pre-analytical laboratory procedure?
Preanalytical phase comprises of test selection, patient identification, collection of the sample, handling of the sample, sorting out, pipetting and centrifugation (2, 3). Negligence in any of these steps can lead to erroneous results attributed to preanalytical phase.Mar 20, 2020
How pre-analytical errors affect the test results?
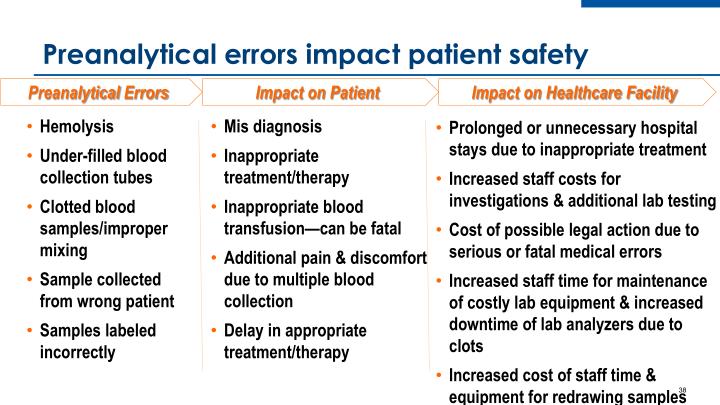
Any error during the laboratory testing process can affect patient care, including delay in reporting, unnecessary redraws, misdiagnosis, and improper treatment. Sometimes, these errors may even be fatal (e.g., acute hemolytic reaction after incompatible blood transfusion caused by an error in patient identification).May 18, 2014
Why is pre analysis important?
The preanalytic phase is an important component of total laboratory quality. A wide range of variables that affect the result for a patient from whom a specimen of blood or body fluid has been collected, including the procedure for collection, handling, and processing before analysis, constitute the preanalytic phase.
Why are pre analytical variables important?
The preanalytical phase is an important component of laboratory medicine. It includes the time from the order of test by the clinician until the sample is ready for analysis - it can account up to 70% of errors during the total diagnostic process.Sep 12, 2017
Why are pre analytical variables important to be aware of performing clinical chemistry testing?
Establishment of a quality manual addressing preanalytical variables is a prerequisite for implementing measures to recognize and control this crucial component of laboratory quality, which cannot be detected by traditional analytical quality control procedures.Apr 5, 2001
What is the pre-pre-analytical phase?
Additionally, the term “pre-pre-analytical phase” has been used for the initial part of the pre-analytical phase, focused on test selection and identification of test needed, and the term “post-post-analytical phase” has been used for the interpretation of results by the clinician.2.
How do laboratory errors affect patient care?
Clinical laboratory errors directly lead to increased healthcare costs and decreased patient satisfaction . A laboratory error is defined as any defect that occurs during the entire testing process, from ordering tests to reporting results, that in any way influences the quality of laboratory services.3 Any error during the laboratory testing process can affect patient care, including delay in reporting, unnecessary redraws, misdiagnosis, and improper treatment. Sometimes, these errors may even be fatal (e.g., acute hemolytic reaction after incompatible blood transfusion caused by an error in patient identification).3 It has been observed that diagnostic errors have led to the most prevalent type of malpractice claim in the United States.4
Why is the clinical laboratory important?
The clinical laboratory plays an increasingly important role in the patient-centered approach to the delivery of healthcare services. Physicians rely on accurate laboratory test results for proper disease diagnosis and for guiding therapy; it is estimated that more than 70% of clinical decisions are based on information derived from laboratory test results.1
When is validation necessary?
Validation is also necessary when converting from one blood collection tube to another or when switching from serum to plasma or vice versa.
What is best practice?
Best practices are just that—the best ways to approach and solve a problem. They are not ways of achieving perfection, but they can go a long way toward the goal of eliminating pre-analytical errors. Here are some recommended strategies.
How long does it take for serum to clot?
While serum is considered a cleaner specimen (i.e., free of cells and other interferences), it needs to be clotted for 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the tube used. Rapid clot blood collection tubes with thrombin-based clot activators offer a 5-minutes clotting time for serum.
What is wrong patient identification while collection?
Wrong patient identification while collection Error in listing the prescribed tests Sample mismatch during blood collection Wrong numbering of patient’s sample Patient’s not properly prepared for the test Blood sample inadequate or clotted Hemolysis of sample Misplacing of sample Delay in performing test
What is laboratory diagnostics?
Laboratory diagnostics is a fast-growing field, which provides a substantial contribution to the clinical decision making by supporting prevention, diagnosis, and therapeutic monitoring of most, if not all, human disorder. Quality and safety in diagnostic testing is, however, essential to furthering the goal of high-quality and safe healthcare, no other disciplines having such a prominent position in the patient safety solution than laboratory medicine.
What is total quality management?
The concept of total quality management encompasses all the steps involved in sample processing, beginning from test ordering to the final interpretation of results by the clinicians to reduce or eliminate the errors that may arise during the various steps. The promotion of ideal phlebotomy practices and sample transport procedures is a pre-requisite for the efficacy of laboratory functioning. The dependence on accurate laboratory results for diagnostics makes it mandatory for labs to ensure accountability and accuracy of results to negate incorrect diagnosis as a consequence of faulty reporting. A practice of keeping
What is the pre-analytical phase?
Of the three primary phases in the total laboratory testing process, the pre-analytical phase (generally defined from the time a laboratory request is made by a physician until the sample is ready for analysis) covers laboratory processes including test selection, patient biological variation, patient preparation, and specimen collection, transportation, processing, and storage. Any variation or unexpected condition change during these dynamic processes can adversely affect laboratory test results, thereby leading to patient mismanagement and compromised patient safety (see TABLE 1 ).
What are the most common interferences in laboratory testing?
Hemolysis, icterus, and lipemia are the most commonly seen interferences in laboratory testing with spectrophotometric methods. These altered results may lead to repeat testing, incorrect interpretation, wrong diagnosis, and potentially, inappropriate intervention and unfavorable patient outcomes.
What is Delta check?
The difference between a patient’s laboratory test result and a prior result found to have exceeded a predefined limit (ie, the Delta check) is a metric that should be monitored. For some parameters, where the levels are strictly regulated to maintain bodily homeostasis (eg, MCV, aPTT, sodium, potassium, hemoglobin), Delta checks should be investigated by the lab internally to first rule out specimen mislabeling, clerical error, or possible analytical error. Once a potential error is identified, a discussion between the relevant clinician (s) and a laboratory technologist to investigate possible pre-analytical errors may be initiated. These could include specimens collected from IV lines, mislabeling, or actual changes in a patient’s condition.
Why is SOP important?
Development and implementation of SOPs is integral to error prevention. Education and Training: Proper training and continuing education for all health care professionals involved in collecting, handling, preparing, and transporting patient samples is crucial to the mitigation of pre-analytical errors.
What percentage of laboratory errors are pre-analytical?
We've often heard the opinion that the Quality Control of laboratory testing isn't the biggest problem we're facing. Sometime people quote a statistic that 40% of the errors in the laboratory are pre-analytical, 40% are post-analytical, and "only" 20% are analytical. There are more "P-errors" than "A-errors", therefore, many laboratories believe they should put a higher priority on pre- and post-analytical errors than on analytical errors.
What is the most obvious error?
What's the most obvious error?#N#1. An patient sample that doesn't get to the lab.#N#2. An instrument with a systematic bias.#N#3. A test result that gets reported on the wrong patient.
What is the job of a laboratory?
The laboratory produces test results. You feed in samples, it feeds out numbers. The core job of a laboratory is to produce the correct test result. If we can't get the test results right, then we aren't doing our core job. All three types of errors need to be addressed NOW.
What is the preanalytical phase?
Preanalytical Phase. The preanalytical phase is the phase where the laboratory has no direct control on the process. Preanalytical factors that can affect results include: sample type, sampling time, sample handling, patient's preparation and the nutritional status of the patient.
What is centralized laboratory automation?
In the current landscape, centralized laboratory automation has mainly involved the integrated connectivity of the pre- and postanalytical phases of the testing process to chemistry and immunochemistry analyzers. However, integrated automation for hematology, coagulation, urinalysis, and molecular and microbiological testing is also available. For example, Sysmex Corporation and Beckman Coulter offer track-based automation for hematology and urinalysis testing, respectively. Several centralized laboratory platforms now have the capability of automated specimen handling and transport to a variety of downstream instruments. As previously discussed, open access instrumentation can facilitate more integrated laboratory automation via track extension to nonchemistry and immunochemistry analyzers manufactured by other vendors.
Why is accurate specimen identification important?
Accurate patient and specimen identification is required for providing ordering clinicians with correct results. Regulatory agencies like The Joint Commission (TJC) have made it a top priority in order to ensure patient safety. Patient and specimen misidentification occurs mostly during the pre-analytical phase:
Where should a specimen be labeled?
The specimens should be collected and labeled in front of the patient and then sent to the laboratory with the test request. Non-barcoded specimens should be accessioned, labeled with a barcode (or re-labeled, if necessary), processed (either manually or on an automated line), and sent for analysis.
What is delta check?
Delta checks are a simple way to detect mislabels. A delta check is a process of comparing a patient’s result to his or her previous result for any one analyte over a specified period of time. The difference or “delta,” if outside pre-established rules, may indicate a specimen mislabel or other pre-analytical error.
What are the steps of molecular genetics?
Like all clinical testing, molecular genetics involves several steps: pre-analytical, analytical, and post-analytical. The pre-analytical phase involves specimen collection, acquisition by the laboratory, labeling and coding, and preparation for analysis.