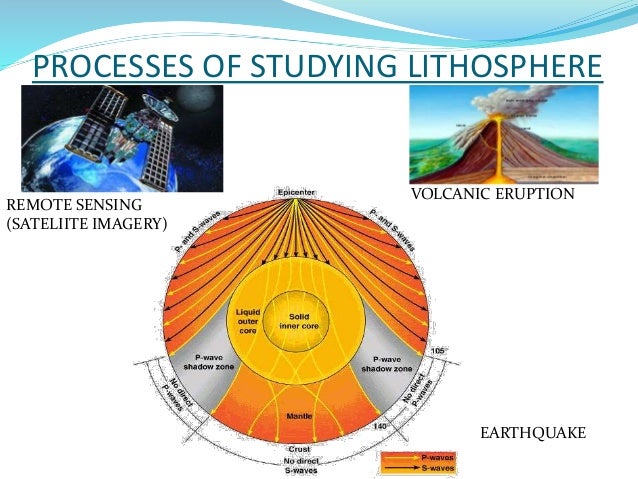
Following are some points showing the importance of the lithosphere:
- The lithosphere supplies the mother earth’s forests and grasslands and is responsible for agriculture, human settlements.
- It is a rich source of minerals such as iron, aluminum, copper, magnesium, and rocks such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
- Organic compounds such as coal, natural gas, oil, etc are biotic remains buried in the lithosphere for millions of years. ...
What are some interesting facts about the lithosphere?
- The lithosphere is important for life to exist. ...
- The shifting of tectonic plates causes the formation of mountains, volcanoes and even the continents.
- Volcanoes and earthquakes are devastating in the short term, but give rise to fertile soil and lands in the long term. ...
What does the lithosphere do for humans?
Lithosphere provide us forests, grasslands for grazing land for agriculture and human settlements and also rich source of minerals. The lithosphere contains different types of rocks such as the igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks, it helps to provide the necessary nutrients required to plants.
What is lithosphere and what does it consist of?
The lithosphere is the solid crust or the hard top layer of the earth. It consists of rocks and minerals and is covered by a thin layer of soil. It is irregular and consists of various landforms such as mountains, plateaus, plains, valleys etc.
What are the main features of the lithosphere?
What is the lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere?
- Lithosphere means land, atmosphere means air and hydrosphere means water.
- The lithosphere consists of land, soil, rocks, stones, and minerals.
- The hydrosphere consists of water bodies.
- The atmosphere contains gases and it forms a layer around the Earth.

What are found in the lithosphere?
The lithosphere consists of all the mountains, rocks, stones, top soil and sand found on the planet. In fact, it also includes all the rocks under the sea and under the surface of the Earth. The lithosphere is found all around us and we interact quite closely with it every day.
What are the 3 components of lithosphere?
The lithosphereLayers of the Earth.The 6-35 km (4-21 miles) thick lithosphere. Earth's crust. ... Lithosphere The solid part of the earth. It consists of three main layers: crust, mantle and core.The Crust Is the outermost layer of the earth. Has a depth of about 32 to 40 km.
What are the 5 examples of lithosphere?
Lithosphere examplesSedimentary rocks.Metamorphic rocks.Igneous Rocks.Granite.Seafloor.Soil.Mountains.
What are 5 facts about lithosphere?
Fact 1# The Greek Origin.Fact 2# Continental and Oceanic Lithosphere.Fact 3# Lithospheric Plates Bump and Slide.Fact 4# Heat Spikes Up Lithosphere's Elasticity.Fact 5# Tectonic Activity and Geological Events.Fact 6# Reshaping the Lithosphere.Fact 7# The Oceanic Lithosphere is Constantly Thickening.More items...
What are the types of lithosphere?
The lithosphere can be divided into two varieties: oceanic and continental. Oceanic crust is relatively thin and dense, according to Sciencing.com. The oceanic crust is mainly composed of basalt rock rich in silica and magnesium.
What are the 3 components of hydrosphere?
The collection of water on our planet—in the ocean, the ground, and the atmosphere—collectively forms the hydrosphere, making it a water-world.
What are 5 things found in the hydrosphere?
The hydrosphere includes water in oceans, lakes, streams, ponds, groundwater, glaciers and other ice forms. 5.
What rocks are found in the lithosphere?
All the three types of rock namely Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic make up the Earth's lithosphere, the outermost layer. The lithosphere is solid rock. Sedimentary rocks are the most abundant rock only on the surface of the Earth, but igneous and metamorphic are abundant deeper into the mantle.
How many layers are in the lithosphere?
There are two types of lithosphere: Oceanic: Which is associated with oceanic crust and exists in the ocean basins. Continental: This is associated with continental crust.
Where is the lithosphere?
The lithosphere is the outer solid part of the earth, including the crust and uppermost mantle.
How is the lithosphere formed?
Oceanic lithosphere forms at midocean ridges, where hot magma upwells, and then cools to form plates as the material moves away from the spreading center. As the plate cools, heat flow decreases and the seafloor deepens (Fig. 3). However, only shallow (< 1 km) measurements of lithospheric temperatures are possible.
What color is the lithosphere?
Continental crust - yellow. Inner core - red. Lithosphere - gray. Mantle - label, but do not color.
What are the components of biosphere?
Biosphere is the region of earth where life exists and interacts with the environment. It has three componets- lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere.
What are the two layers of lithosphere?
The lithosphere consists of the tectonic plates at the top of the mantle, and the crust above, which the plates move around.
What minerals make up most of the lithosphere?
The crust is made up of about 80 elements, which occur in over 2000 different compounds and minerals. However, most of the mass of the material in the crust is made up of only 8 of these elements. These are oxygen (O), silica (Si), aluminium (Al), iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), potassium (K) and magnesium (Mg).
What rocks are found in the lithosphere?
All the three types of rock namely Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic make up the Earth's lithosphere, the outermost layer. The lithosphere is solid rock. Sedimentary rocks are the most abundant rock only on the surface of the Earth, but igneous and metamorphic are abundant deeper into the mantle.
1. What is Meant by Lithosphere?
One can explain lithosphere as the outermost rocky terrain of Earth, consisting of crust and upper portion of the mantle.
2. What are the Types of Lithosphere?
You can divide lithosphere into two primary types – continental and oceanic.
3. What are the Two Layers of Lithosphere?
Crust is the top layer of lithosphere, comprising an outer rocky terrain. Upper mantle is the second layer just underneath this crust.
4. Define the lithosphere and discuss its types?
The word ‘litho’ has its origin from Greek vocabulary which literally means stone, and sphere refers to a globe. The lithosphere is basically the o...
5. What is the deepest part of the oceanic lithosphere? Why is the oceanic lithosphere denser than t...
The Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench is more than 11.5 km below sea level, rendering it the deepest part of the oceanic lithosphere. This type...
6. Why is the lithosphere imperative?
There are a number of reasons as to why the lithosphere is vital for life on Earth: The biosphere of Earth depends greatly on the rocky terrain of...
7. What lies below the lithosphere? Explain in brief?
The asthenosphere, which is the part of Earth’s mantle, is the layer that lies underneath the lithosphere. It happens to extend from about 100-700...
8. How are humans harming the lithosphere and why is there a need to preserve it?
Activities like mining, farming, urbanisation, etc., tend to harm the lithosphere. The lithosphere is the topmost crust of the Earth where the bios...
How do we know the lithosphere and asthenosphere are there?
We know the lithosphere exists because it's where we live and we can see the direct effects of plate tectonics through spectacular volcanoes and lofty mountain ranges. But how do we know what's going on below the surface?
Additional resources
Explore the most detailed map ever of the tiny magnetic signals generated by Earth's lithosphere with ESA. Tour the world's volcanoes, earthquakes, impact craters and plate tectonics with this incredibly detailed map from the United States Geological Survey.
Bibliography
Boden, David R. Geologic fundamentals of geothermal energy. CRC Press, 2016.
What is the lithosphere?
Litho is derived from a Greek word, meaning stone, while sphere signifies a globe or ball. Lithosphere is the outermost rocky surface of Earth. It comprises the upper part of Earth’s mantle and its brittle crust.
What is the key to understanding the lithosphere?
The key to understanding lithosphere definition is learning about its compositions. However, due to the uneven distribution of rocks and other materials, pinpointing all the components of lithosphere can be difficult.
What is Oceanic Lithosphere?
The portion of the upper mantle and crust present underneath the ocean and seas is termed as oceanic lithosphere. Structure of the lithosphere under the oceans can be different from continental lithosphere. Oceanic lithosphere also tends to be denser than its counterpart.
What is the outermost rocky terrain of Earth?
Ans. One can explain lithosphere as the outermost rocky terrain of Earth, consisting of crust and upper portion of the mantle.
What is the interaction between Earth's atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere?
The interaction between Earth’s atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere are crucial for life on Earth. Each of them is responsible for essential pre-requisites for life, as we know it. Vedantu’s application can help students understand lithosphere and its composition in detail.
Why is the lithosphere important?
Lithosphere is important for life to exist . Earth’s biosphere relies greatly on the presence of this rocky terrain. Tectonic plates forming lithosphere causes change, which, in turn, gave rise to life as we know it today. Shifting of tectonic plates causes the formation of mountains, volcanoes and even the continents.
Which layer of the atmosphere is present on land?
The lithosphere layer present on land is known as continental lithosphere. This type encompasses all of the continents and areas designated above sea level. Continental lithosphere comes into direct contact with the atmosphere.
What is the lithosphere?
Lithosphere, rigid, rocky outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and the solid outermost layer of the upper mantle. It extends to a depth of about 60 miles (100 km). It is broken into about a dozen separate, rigid blocks, or plates ( see plate tectonics ).
What causes the lateral movement of the plates?
Slow convection currents deep within the mantle, generated by radioactive heating of the interior, are believed to cause the lateral movements of the plates (and the continents that rest on top of them) at a rate of several inches per year. …single rigid layer, called the lithosphere.
What is the lithosphere?
A lithosphere ( Ancient Greek: λίθος [ líthos] for "rocky", and σφαίρα [ sphaíra] for "sphere") is the rigid, outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.
What are the different types of lithospheres?
Different types of lithosphere. The lithosphere can be divided into oceanic and continental lithosphere. Oceanic lithosphere is associated with oceanic crust (having a mean density of about 2.9 grams per cubic centimeter) and exists in the ocean basins.
What is the thermal boundary layer of the oceanic lithosphere?
In fact, oceanic lithosphere is a thermal boundary layer for the convection in the mantle. The thickness of the mantle part of the oceanic lithosphere can be approximated as a thermal boundary layer that thickens as the square root of time. is the age of the given part of the lithosphere.
What is the boundary between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere?
The Lithosphere-Asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress: the lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle failure, while the asthenosphere deforms viscously and accommodates strain through plastic deformation .
Why is the continental lithosphere not recycled?
Because of its relatively low density, continent al lithosphere that arrives at a subduction zone cannot subduct much further than about 100 km (62 mi) before resurfacing. As a result, continental lithosphere is not recycled at subduction zones the way oceanic lithosphere is recycled. Instead, continental lithosphere is a nearly permanent feature of the Earth.
How thick is the continental lithosphere?
Continental lithosphere. Continental lithosphere has a range in thickness from about 40 km to perhaps 280 km; the upper ~30 to ~50 km of typical continental lithosphere is crust. The crust is distinguished from the upper mantle by the change in chemical composition that takes place at the Moho discontinuity.
Which is thicker, the oceanic lithosphere or the continental lithosphere?
Oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic lithosphere consists mainly of mafic crust and ultramafic mantle ( peridotite) and is denser than continental lithosphere. Young oceanic lithosphere, found at mid-ocean ridges, is no thicker than the crust, but oceanic lithosphere thickens as it ages and moves away from the mid-ocean ridge.
What is Lithosphere?
The lithosphere is the rigid, outermost shell on Earth. It is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater. The outermost shell of a rocky planet, the crust, is defined on the basis of its chemistry and mineralogy.
Which part of the lithosphere reacts with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere through the soil-?
The uppermost part of the lithosphere that chemically reacts to the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere through the soil-forming process is called the pedosphere.
What is the outermost layer of a rocky planet?
The outermost shell of a rocky planet, the crust, is defined on the basis of its chemistry and mineralogy. This includes the crust and the uppermost mantle, which constitute the hard and rigid outer layer of the Earth.
What is Lithosphere?
It is the outermost shell of a terrestrial-type planet or natural satellite. It is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle, which compose the rigid and hard outer layer of the Earth.
What are the two types of lithospheres?
It is mainly of two types: oceanic lithosphere and continental lithosphere. The lithosphere underneath the ocean and seas is termed the oceanic lithosphere while the lithosphere layer present on land is known as the continental lithosphere.
What is the outermost shell of the Earth?
Composed of the Greek words “lithos” meaning rocky, and the word “sphaira” meaning sphere, the lithosphere is the rigid, outermost shell on earth, composed of the earth’s crust and the portion of the upper mantle.
How deep can the oceanic lithosphere go?
The oceanic lithosphere can go deeper than 100 km while the continental lithosphere is thinner and generally ranges between 35 to 50 km.
How much of the Earth's surface is covered by the continental lithosphere?
About 40% of the Earth’s surface is covered by continental lithosphere, but it also makes up about 70% of the volume of Earth’s crust. Most scientists believe that there was no continental crust originally on the Earth, but the continental crust ultimately derived from the fractional differentiation of oceanic crust. The continental lithosphere is billions of years old, much older than the oceanic lithosphere.
Which is denser, the oceanic or continental lithosphere?
The oceanic lithosphere tends to be denser than its counterpart the continental lithosphere. It thickens as it ages and moves away from the mid-ocean ridge. The oldest oceanic lithosphere is about 170 million years old.
Which sphere is responsible for the movement of tectonic plates?
The lithosphere is also responsible for the movement of tectonic plates. This shifting of tectonic plates is responsible for the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and even the continents.
What are the elements that make up the lithosphere?
Some of the elements that make up the majority of the lithosphere are silicon, iron, and magnesium with other elements like aluminum, sodium, and potassium also present.
What is the Lithosphere?
The lithosphere is the rigid, outermost layer of the Earth's rocks and minerals, which consists of the crust and upper mantle. The term "lithosphere" comes from the Greek word litho, which means "stone," and "sphere," referring to the rough shape of the Earth. Thus, it is the sphere of rocks and minerals that encases the Earth.
How does the lithosphere interact with the biosphere?
The lithosphere is an important part of the environment and interacts with all of the other spheres. The lithosphere provides the biosphere with minerals in soil or water that have been dissolved through hydrosphere-lithosphere interactions. The hydrosphere and atmosphere both play roles in weathering and erosion, which break down rocks into soil and allow the minerals to become accessible to the biosphere. The lithosphere, due to its landforms, also has an impact on the weather and how water flows. Some scientists study these interactions.
Why does the thickness of the lithosphere vary?
The thickness of the lithosphere varies because of different types of lithosphere (remember, the oceanic lithosphere is generally thinner, and the continental lithosphere is generally thicker). The depth of the lithosphere can also vary.
What are the roles of the hydrosphere and atmosphere?
The hydrosphere and atmosphere both play roles in weathering and erosion, which break down rocks into soil and allow the minerals to become accessible to the biosphere . The lithosphere, due to its landforms, also has an impact on the weather and how water flows. Some scientists study these interactions. 5:52.
What are the different types of spheres?
There are other spheres that other scientists use to describe the Earth. They include the: 1 Hydrosphere - all the Earth's water 2 Atmosphere - all the Earth's gases 3 Biosphere - all the Earth's living things
Why do volcanoes occur on continents?
Because they are so similar, each plate is forced upward. Volcanoes on continents are the result of convergence between continental and oceanic plates. As these two plates converge, the denser oceanic plate subducts and melts in the mantle, creating magma, which rises to find vents.
What is the lithosphere responsible for?
The movement of these plates is responsible for the formation of mountains and oceanic trenches, volcanic eruption, and the earthquakes. The lithosphere includes both the land area and the water bodies. The land area consists of 30% of the total area of the earth.
What are the water bodies that make up the lithosphere?
Water bodies are essential for the existence of all the living beings on the earth. The lithosphere contains the water bodies such as lakes, rivers, and oceans.
Why is the lithosphere important?
Let us see in detail why the lithosphere is important to us. The lithosphere helps to provide all the necessary nutrients required for the growth of plants. It also combines with the hydrosphere and the atmosphere to help in the growth of all the living organisms.
How many tectonic plates are there in the lithosphere?
The lithosphere also contains the different types of rocks such as the igneous, sedimentary, and the metamorphic rocks. There are mainly 15 tectonic plates in the lithosphere. They are – the North American, Caribbean, South American, Scotia, Antarctic, Eurasian, Arabian, African, Indian, Philippine, Australian, Pacific, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, ...
What is the outermost part of the Earth?
The lithosphere is the outermost part of the earth. It is subdivided into tectonic plates. The lithosphere of the earth consists mainly of the crust and the upper mantle. There are basically two types of the lithosphere, namely – Oceanic Lithosphere and Continental Lithosphere.
How much of the Earth's surface is land?
The land area consists of 30% of the total area of the earth. In the continental regions it has a thickness of 35-50 kilometers and under the ocean beds, it gets reduced to 6-12 kilometers. This outer layer of the earth has a depth of more than 100 kilometers. The lithosphere is very important to us mainly because of the abundance ...
What are the different types of metals we use in our daily lives as tools?
The various minerals present in it are iron, silver, manganese, aluminum, magnesium, calcium, and copper. Water bodies are essential for the existence of all the living beings on the earth.

Overview
A lithosphere (from Ancient Greek λίθος (líthos) 'rocky', and σφαίρα (sphaíra) 'sphere') is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineral…
Earth's lithosphere
Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the uppermost mantle. The lithosphere is underlain by the asthenosphere which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long pe…
Mantle xenoliths
Geoscientists can directly study the nature of the subcontinental mantle by examining mantle xenoliths brought up in kimberlite, lamproite, and other volcanic pipes. The histories of these xenoliths have been investigated by many methods, including analyses of abundances of isotopes of osmium and rhenium. Such studies have confirmed that mantle lithospheres below some cratons have persisted for periods in excess of 3 billion years, despite the mantle flow that acco…
See also
• Carbonate–silicate cycle
• Climate system
• Cryosphere
• Geosphere
• Kola Superdeep Borehole
Further reading
• Chernicoff, Stanley; Whitney, Donna (1990). Geology. An Introduction to Physical Geology (4th ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0-13-175124-8.
External links
• Earth's Crust, Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
• Crust and Lithosphere