What foods increase prostaglandins?
What trimester of pregnancy marks the return of the inflammatory response as well as prostaglandins?
- Bananas. …
- Sunflower Seeds. …
- Ginger. …
- Pineapple: remember that alcohol is contraindicated for cramps so stay away from the piña coladas!
What are some effects of prostaglandins in the body?
Some of their functions include: 1
- Vasodilation and vasoconstriction (the opening and closing of blood vessels)
- Bronchoconstriction (the constriction of air passageways)
- Blood clotting
- Uterine contractions
- Fever
- Maintenance of tissues such as the stomach lining
Are prostaglandins good or bad?
Studies have shown the more prostaglandin inflammation you have, the worse your menstrual cramps can be, which is known as dysmenorrhea. What Do Prostaglandins Do? While all this menstrual cramp talk may make you think all prostaglandin functions are bad, they are actually very necessary and protective of your health.
What do prostaglandins do in inflammation?
Prostaglandins play a key role in the generation of the inflammatory response. Their biosynthesis is significantly increased in inflamed tissue and they contribute to the development of the cardinal signs of acute inflammation.
How do prostaglandins affect the body?
What are the effects of prostaglandins?
What are prostaglandins made of?
How do prostaglandins help with bleeding?
What is the role of prostaglandins in pregnancy?
What are the health problems that can result from too many prostaglandins?
Why are protaglandins unique?
See 4 more
About this website

What is the main function of prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins play a key role in the generation of the inflammatory response. Their biosynthesis is significantly increased in inflamed tissue and they contribute to the development of the cardinal signs of acute inflammation.
What does prostaglandin do in inflammation?
Inflammation and pain They know prostaglandins can have a variety of inflammatory effects, including causing vasodilation, promoting fevers, and recruiting cells involved in allergic reactions. Doctors have also identified the prostaglandin type PGE2 as causing redness, swelling, and pain.
What is the effect of prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins play a key role in inflammation by contributing to the development of redness, swelling, heat, and pain. Excess production of prostaglandins due to inflammation may lead to: Arthritis. Heavy menstrual bleeding.
What foods are high in prostaglandins?
These foods contain arachidonic acids, which instigate the production of cramp-causing prostaglandins....FOODS:Bananas. ... Sunflower Seeds. ... Ginger. ... Pineapple: remember that alcohol is contraindicated for cramps so stay away from the piña coladas!
What causes prostaglandins to be too high?
High levels of prostaglandins are produced in response to injury or infection and cause inflammation, which is associated with the symptoms of redness, swelling, pain and fever. This is an important part of the body's normal healing process.
What are the 9 function of prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins play a role in the following reproductive functions: 1) conception; 2) luteolysis; 3) menstruation; and 4) parturition. It has also been proposed that Prostaglandin A may be the natriuretic hormone, the circulating hormone which controls sodium reabsorption by the kidney.
What are examples of prostaglandin?
Types of prostaglandinsXalatan (latanoprost)Zioptan (tafluprost)Travatan Z (travoprost)Lumigan (bimatoprost)Vyzulta (latanoprostene bunod)
Why does prostaglandin cause pain?
High concentrations of prostaglandins cause pain by direct action upon nerve endings. More typically, however, at low concentrations, they markedly increase sensitivity to pain. The pain threshold may be so altered that even normally painless stimuli may be painful.
Where are prostaglandins found?
Prostaglandins are found in most tissues and organs. They are produced by almost all nucleated cells. They are autocrine and paracrine lipid mediators that act upon platelets, endothelium, uterine and mast cells. They are synthesized in the cell from the fatty acid arachidonic acid.
How can I increase my prostaglandin naturally?
“This is validated by data from large epidemiological population studies, which have shown that the intake of fish or fish oil supplements, and other foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids promote the production of these types of prostaglandins.”
What vitamins reduce prostaglandins?
With its antioxidant properties, vitamin E reduces phospholipid peroxidation and inhibits the release of arachidonic acid and its conversion to prostaglandins. Therefore, it can play a significant role in relieving the severity of dysmenorrhea [6,7,8,9,10].
Does magnesium reduce prostaglandins?
Taken daily, magnesium may prevent dysmenorrhea (menstrual cramps) in some people (1). It works by relaxing the smooth muscle of the uterus and by reducing the prostaglandins that cause period pain (1,8).
Do prostaglandins reduce inflammation?
Despite the clinical efficacy of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, prostaglandins may function in both the promotion and resolution of inflammation.
Are prostaglandins anti-inflammatory?
Long regarded as proinflammatory molecules, prostaglandins (PGs) also have anti-inflammatory effects.
Do prostaglandins cause vasoconstriction or vasodilation?
Prostaglandins are powerful, locally-acting vasodilators and inhibit the aggregation of blood platelets. Through their role in vasodilation, prostaglandins are also involved in inflammation.
What is the mechanism of action of prostaglandins?
Mechanism of Action [2] The COX-1 enzyme produces basal amounts of prostaglandins, while chemical mediators induce the COX-2 isoform to increase prostaglandins production. Prostaglandins are highly lipophilic molecules that enter cells via a special prostaglandin transporter called PGT (prostaglandin transporter).
How Prostaglandins Cause Painful Periods + What to Do About It
Nearly every woman has experienced menstrual cramps at some point during her period. What most women don’t know is there are hormone-like substances known as prostaglandins that are behind these intense, and sometimes debilitating cramps.
How Prostaglandins Impact Inflammation and Pain - Verywell Health
Dangerous COX-2 Inhibitors . You may remember Vioxx and Bextra, the once-promising pain relievers that were pulled from the market in 2004. They only inhibited the COX 2 enzyme and were known as COX 2 inhibitors.
Prostaglandins - Reproduction, Inflammation & Other Conditions
These natural chemicals in the body play a role in reproduction, as well as in promoting and resolving inflammation. Prostaglandins are natural chemicals in the body with hormone-like qualities.
Prostaglandins in the menstrual cycle of women. A review
The changes of concentrations of prostaglandins (PG) are cyclic in the uterine tissues and related to steroid ovarian hormones. The role in normal menstruation is presumably related to a local haemodynamic effect. PGF2 alpha vasoconstricts the endometrial vessels during menstruation and contracts th …
Prostaglandins and Inflammation - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC)
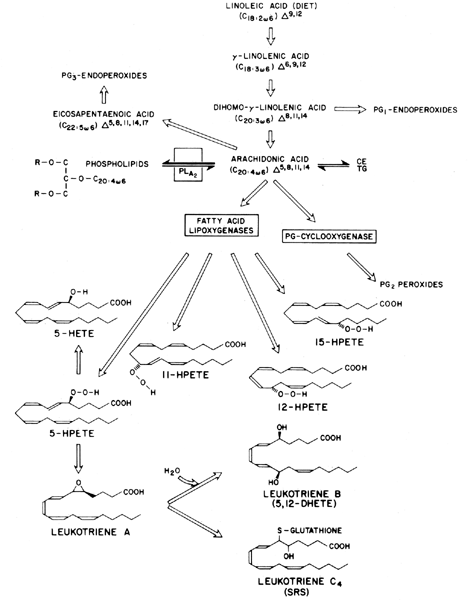
Biosynthesis of Prostaglandins. Prostaglandins and thromboxane A 2 (TXA 2), collectively termed prostanoids, are formed when arachidonic acid (AA), a 20-carbon unsaturated fatty acid, is released from the plasma membrane by phospholipases (PLAs) and metabolized by the sequential actions of prostaglandin G/H synthase, or cyclooxygenase (COX), and respective synthases.
How do prostaglandins work?
Most prostaglandins act locally; for instance, they are powerful locally acting vasodilators. Vasodilation occurs when the muscles in the walls of blood vessels relax so that the vessels dilate. This creates less resistance to blood flow and allows blood flow to increase and blood pressure to decrease. An important example of the vasodilatory action of prostaglandins is found in the kidneys, in which widespread vasodilation leads to an increase in the flow of blood to the kidneys and an increase in the excretion of sodium in the urine. Thromboxanes, on the other hand, are powerful vasoconstrictors that cause a decrease in blood flow and an increase in blood pressure.
What is a prostaglandin?
prostaglandin, any of a group of physiologically active substances having diverse hormonelike effects in animals. Prostaglandins were discovered in human semen in 1935 by the Swedish physiologist Ulf von Euler, who named them, thinking that they were secreted by ...
How do thromboxanes and prostacyclins work?
Thromboxanes and prostacyclins play an important role in the formation of blood clots. The process of clot formation begins with an aggregation of blood platelets. This process is strongly stimulated by thromboxanes and inhibited by prostacyclin. Prostacyclin is synthesized in the walls of blood vessels and serves the physiological function of preventing needless clot formation. In contrast, thromboxanes are synthesized within platelets, and, in response to vessel injury, which causes platelets to adhere to one another and to the walls of blood vessels thromboxanes are released to promote clot formation. Platelet adherence is increased in arteries that are affected by the process of atherosclerosis. In affected vessels the platelets aggregate into a plaque called a thrombus along the interior surface of the vessel wall. A thrombus may partially or completely block (occlude) blood flow through a vessel or may break off from the vessel wall and travel through the bloodstream, at which point it is called an embolus. When an embolus becomes lodged in another vessel where it completely occludes blood flow, it causes an embolism. Thrombi and emboli are the most common causes of heart attack (myocardial infarction). Therapy with daily low doses of aspirin (an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase) has had some success as a preventive measure for people who are at high risk of heart attack.
What is the role of arachidonic acid in cell membranes?
In response to many different stimuli, including various hormonal, chemical, or physical agents, a chain of events is set in motion that results in prostaglandin formation and release.
What is the synthesis of prostaglandins?
Synthesis of prostaglandins. The prostaglandins are made up of unsaturated fatty acids that contain a cyclopentane (5-carbon) ring and are derived from the 20-carbon, straight-chain, polyunsaturated fatty acid precursor arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is a key component of phospholipids, which are themselves integral components of cell membranes.
How much do prostaglandins affect blood pressure?
Prostaglandins are very potent; for example, in humans some affect blood pressure at concentrations as low as 0.1 microgram per kilogram of body weight. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities.
What enzyme catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid from phospholipid molecules?
These stimuli, either directly or indirectly, result in the activation of an enzyme called phospholipase A 2. This enzyme catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid from phospholipid molecules. Depending on the type of stimulus and the enzymes present, arachidonic acid may diverge down one of several possible pathways.
What is the function of prostaglandins in the body?
Prostaglandins are made at sites of tissue damage or infection, where they cause inflammation, pain and fever as part of the healing process. When a blood vessel is injured, a prostaglandin called thromboxane stimulates the formation of a blood clot to try to heal the damage; it also causes the muscle in the blood vessel wall to contract ...
Where are prostaglandins produced?
Unlike most hormones, which are produced by glands and transported in the bloodstream to act on distant areas of the body, the prostaglandins are produced at the site where they are needed. Prostaglandins are produced in nearly all cells and are part of the body’s way of dealing with injury and illness. Prostaglandins act as signals ...
What happens if my levels of prostaglandins are too high?
High levels of prostaglandins are produced in response to injury or infection and cause inflammation, which is associated with the symptoms of redness, swelling, pain and fever. This is an important part of the body’s normal healing process.
How many different receptors are there for prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins carry out their actions by acting on specific receptors; at least eight different prostaglandin receptors have been discovered. The presence of these receptors in different organs throughout the body allows the different actions of each prostaglandin to be carried out, depending on which receptor they interact with.
How are protaglandins broken down?
Prostaglandins are very short-lived and are broken down quickly by the body. They only carry out their actions in the immediate vicinity of where they are produced; this helps to regulate and limit their actions.
What is the first step in the process of making prostaglandins?
The chemical reaction that makes the prostaglandins involves several steps; the first step is carried out by an enzyme called cyclooxygenase. There are two main types of this enzyme: cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2.
Which hormone is responsible for regulating the contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the gut and the airways?
Prostaglandins are also involved in regulating the contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the gut and the airways.
Why are prostaglandins used in medicine?
Because of prostaglandins' important role in initiating and perpetuating inflammation, numerous drugs have been developed over the years to counter their actions. Doctors consider these drugs effective and they're relatively inexpensive, as well.
What is the process of producing prostaglandins?
As part of the natural healing process , your body produces prostaglandins at the sites of infection or tissue damage. 1 . Numerous drugs and dietary changes have been researched to counter the negative effects of prostaglandins. Nine OK / Getty Images.
What is the role of prostaglandins in spinal deformity?
He specializes in spinal deformity and complex spinal reconstruction. Prostaglandins are hormones that exert a lot of influence over key physiological processes in your body —including pain levels and inflammation.
Why do protaglandins not last long?
Prostaglandins don't last long—they carry out their function, and then the body breaks them down. That helps limit their activity, which is a good thing. When levels get too high, it can result in excess inflammation and pain.
Is anti-prostaglandin diet good for chronic pain?
Anti-Prostaglandin Diet. It is well known that inflammation is at the root of a number of modern-day diseases, including chronic pain. It's also well known that taking medication to address the ills associated with inflammation may come with side effects, some of which can be quite serious.
Can prostaglandins be taken over the counter?
While many of these medications are available over-the-counter, that doesn't mean they're without side effects. Long-term use carries certain risks, as well.
How do prostaglandins affect the body?
Prostaglandins have significant effects, but they also have limitations. They usually have a short half-life, so they don’t last long in the body. For this reason, they can only affect cells that are close by. That’s why they’re present throughout the body to exert the following effects.
What are the effects of prostaglandins?
They know prostaglandins can have a variety of inflammatory effects, including causing vasodilation, promoting fevers, and recruiting cells involved in allergic reactions. Doctors have also identified the prostaglandin type PGE2 as causing redness, swelling, and pain.
What are prostaglandins made of?
Prostaglandins are compounds in the body made of fats that have hormone-like effects. They’re interesting because they can have different effects depending on the receptors where they attach. Some known effects include uterine cramping and increased sensitivity to pain. Researchers have even created artificial prostaglandins for use in medication ...
How do prostaglandins help with bleeding?
In addition, prostaglandins also influence blood clotting to prevent bleeding. They also help dissolve clots when a person is healing.
What is the role of prostaglandins in pregnancy?
forming platelets into a cluster or breaking them up. opening or closing up airways. contracting or relaxing smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. causing uterine contractions in pregnancy and when not pregnant. As you can see, prostaglandins play a variety of roles in the body.
What are the health problems that can result from too many prostaglandins?
Complications. Too many or too few prostaglandins in the body can cause health complications. Known problems with too many prostaglandins include arthritis and menstrual cramping. Conditions that can result from too few prostaglandins include glaucoma and stomach ulcers.
Why are protaglandins unique?
Prostaglandins are unique compounds because they have hormone-like effects. That is, they influence reactions in the body when they’re present in certain tissues.