
Structure of Proteins
- ] Primary Protein Structure. The primary structure is the unique formation and order in which the amino acids (the building blocks) combine and link to give us a protein molecule.
- ] Secondary Protein Structure. After the sequencing of amino acids, we now move on to the secondary structure. ...
- ] Tertiary Structures. ...
- ] Quaternary Structure. ...
Full Answer
What are the different types of protein structure?
Protein Structure: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quatemary Structures
- Primary Structure. There are 20 different standard L-α-amino acids used by cells for protein construction. ...
- Secondary Structure. ...
- Tertiary Structure. ...
- Quaternary Structure. ...
- Protein Stability. ...
- Protein Structure Analysis. ...
- Protein Structure Stability Analysis. ...
What is the basic unit of protein structure?
Proteins are very large molecules composed of basic units called amino acids. In addition to containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen amino acids contain nitrogen. Protein molecules are large, complex molecules formed by one or more twisted and folded strands of amino acids. Proteins are highly complex molecules that are actively involved in the ...
What determines the shape of a protein?
What Determines the Structure of a Protein?
- Electrostatic Forces. Different amino acids are identified based on the presence of a variety of functional groups. ...
- Hydrogen Bonding Forces. Hydrogen bonding represents another type of molecular interaction occurring between hydrogen and molecules containing oxygen or nitrogen.
- Hydrophobic Forces. ...
- Disulfide Bonds. ...
What best describes the structure of a protein molecule?
Structure of Proteins
- ] Primary Protein Structure. The primary structure is the unique formation and order in which the amino acids (the building blocks) combine and link to give us a protein molecule.
- ] Secondary Protein Structure. After the sequencing of amino acids, we now move on to the secondary structure. ...
- ] Tertiary Structures. ...
- ] Quaternary Structure. ...
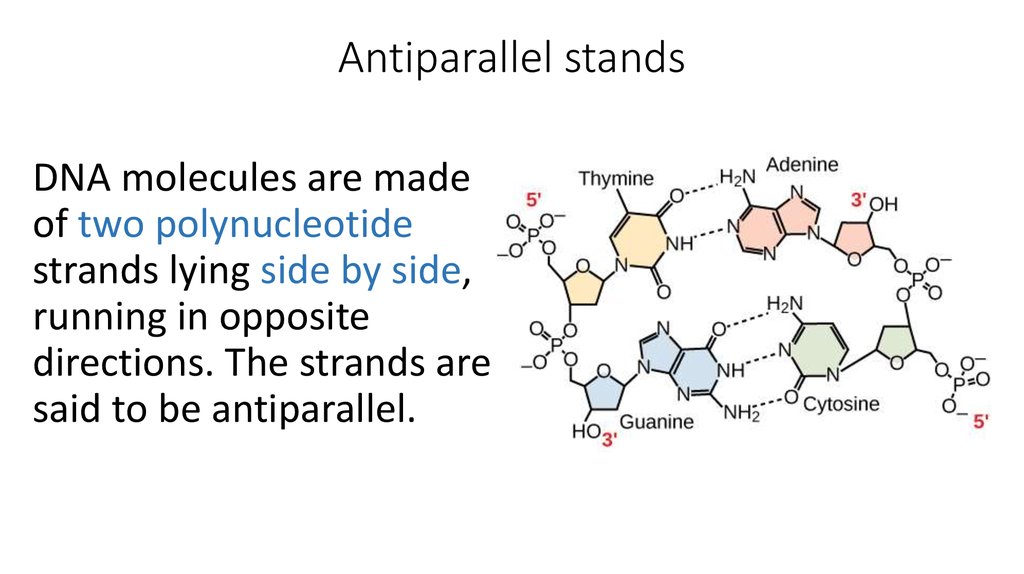
What are the protein structure?
Protein structures are made by condensation of amino acids forming peptide bonds. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure. The secondary structure is determined by the dihedral angles of the peptide bonds, the tertiary structure by the folding of protein chains in space.
What are the 4 protein structures?
The complete structure of a protein can be described at four different levels of complexity: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure.
What is protein structure and function?
Proteins are built as chains of amino acids, which then fold into unique three-dimensional shapes. Bonding within protein molecules helps stabilize their structure, and the final folded forms of proteins are well-adapted for their functions.
What are the 3 structure of protein?
A protein's primary structure is defined as the amino acid sequence of its polypeptide chain; secondary structure is the local spatial arrangement of a polypeptide's backbone (main chain) atoms; tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional structure of an entire polypeptide chain; and quaternary structure is the ...
How many protein structures are there?
four differentProteins are macromolecules and have four different levels of structure – primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary.
Why is protein structure important?
Why does a protein's shape matter? A protein's structure allows it to perform its job. For instance, antibodies are shaped like a Y. This helps these immune-system proteins bind to foreign molecules such as bacteria or viruses with one end while recruiting other immune-system proteins with the other.
What is an example of a structural protein?
Myosin, collagen and keratin are all examples of structural proteins. Myosin is the major constituent of muscles, collagen is majorly present in connective tissue, and keratin is an integral part of hair and outer layers of skin.
What is primary secondary and tertiary structure of protein?
Primary structure of a protein is the linear sequence of amino acids, the secondary structure of a protein is the folding of the peptide chain into an α-helix or β-sheet while the tertiary structure is the three-dimensional structure of a protein.
What are types of proteins?
There are seven types of proteins: antibodies, contractile proteins, enzymes, hormonal proteins, structural proteins, storage proteins, and transport proteins.
What is primary and secondary structure of protein?
The primary structure is comprised of a linear chain of amino acids. The secondary structure contains regions of amino acid chains that are stabilized by hydrogen bonds from the polypeptide backbone. These hydrogen bonds create alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheets of the secondary structure.
What are the 4 levels of protein structure quizlet?
The shape of a protein can be described by four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary.
What are the 4 stages of protein folding?
There are four stages of protein folding, primary, secondary, tertiary and quarternary. The secondary structure is the protein beginning to fold up. It can have two types of structure: the alpha helix, a coil shape held by hydrogen bonds in the same direction as the coil.
What are the four levels of protein structure How do they differ?
The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure.
Why are the four levels of protein structure important?
Each separate sequence has a unique order that conveys a very unique function. If you were to change one single arrangement of the chain, then that chain would have a completely different function. Protein function can be jeopardized or lost completely if sequence is out of order.
What makes up protein structure?
A protein’s primary structure refers to the amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain. Peptide bonds that are made during the protein biosynthes...
What are the 4 stages of protein structure?
Four levels of structure of proteins. The principal, secondary, tertiary and quaternary levels of protein structure are the four stages. To fully u...
What is the process of protein folding?
The folding of proteins is the mechanism through which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. Both molecules of protein...
How proteins are formed?
Amino acids form a polypeptide, In another words when amino acids bound by a sequence of peptide bonds , leads to formation of proteins. The polype...
Is DNA a protein?
DNA is often associated with proteins in the nucleus called histones, but DNA itself is not a protein. No. DNA is a nucleic acid consisting of phos...
What stabilizes protein structure?
Hydrogen bonding in the polypeptide chain and between amino acid “R” groups helps to preserve protein structure by keeping the protein in the form...
What determines protein structure?
In the polypeptide chain, the main structure of a protein relates to the amino acid sequence. The primary structure is bound together by peptide bo...
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The linear sequence of amino acids within a protein is called the primary structure of the protein. A sequence of just twenty amino acids, each of...
Introduction
Have you ever wondered why egg whites go from clear to opaque when you fry an egg? If so, this section is for you!
Primary structure
The simplest level of protein structure, primary structure, is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. For example, the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, A and B, shown in diagram below.
Secondary structure
The next level of protein structure, secondary structure, refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone.
Tertiary structure
The overall three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide is called its tertiary structure. The tertiary structure is primarily due to interactions between the R groups of the amino acids that make up the protein.
Quaternary structure
Many proteins are made up of a single polypeptide chain and have only three levels of structure (the ones we’ve just discussed). However, some proteins are made up of multiple polypeptide chains, also known as subunits. When these subunits come together, they give the protein its quaternary structure.
Denaturation and protein folding
Each protein has its own unique shape. If the temperature or pH of a protein's environment is changed, or if it is exposed to chemicals, these interactions may be disrupted, causing the protein to lose its three-dimensional structure and turn back into an unstructured string of amino acids.
Explore outside of Khan Academy
Do you want to learn more about protein structure and folding? Check out this scrollable interactive from LabXchange.
What Are Proteins Made Of?
Proteins are polymers, meaning they are large molecules made up of many smaller molecules. The small molecules that make up proteins are called amino acids.
Different Types of Protein Structure
The structure of proteins is directly related to their function and may be primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary.
Classes of Protein Structure
The function of a protein depends heavily on its final structure. Tertiary and quaternary proteins are both functional proteins with a 3D structure. However, the type of structure can vary significantly between different proteins.
What is Protein Denaturation?
Proteins are only functional so long as they keep their 3D structure. If they are unfolded and lose their shape, they will no longer be functional.
Protein Structure Definition
Proteins are nothing but biological polymers. They are polymers of amino acids joined together by amino acids. You must know that amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. It means that proteins have a chain-like structure, where amino acids are the primary ingredient.
Primary Protein Structure
The primary structure of a protein refers to a unique formation and sequence in which amino acids get combined. They all get linked together to produce a protein molecule. The primary structure is responsible for giving particular properties to protein.
Secondary Protein Structure
This secondary protein structure gives a unique shape to the protein. It’s where the peptide backbone of a protein structure gets folded onto itself. The folding of the polypeptide chains occurs because of the interaction between the carboxyl group and amine groups of the peptide chains.
Tertiary Protein Structure
Tertiary structure is responsible for the formation and 3-D shape of the protein. As amino acids form bonds during secondary structure, they give out shapes such as helices and sheets. Further, the structure can coil or fold randomly, and that’s what you call the tertiary structure of proteins.
Quaternary Protein Structure
The spatial arrangement of two or more peptide chains leads you to a quaternary protein structure. You should know that proteins don’t necessarily need to have a quaternary structure. Also note that primary, secondary, and tertiary structures of proteins are available in all-natural proteins. But, that’s not the case for quaternary structure.
Analysis of Protein Structure
The complexities of a protein structure do make the elucidation process of a complete protein structure extremely difficult, even with the most advanced analytical equipment. An amino acid analyzer can be used to determine which amino acids are present and their molar ratios.
Table of Contents
Classification of Proteins Primary Structure of Protein Secondary Structure of Protein Tertiary Structure of Protein Quaternary Structure of Protein
Define Protein Structure
Protein structure is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds.
Related Topics
Let us see how a peptide bond is established from the following reaction:
Classification of Proteins
Based on the molecular shape, proteins can be classified into two types.
1. Primary Structure of Protein
The Primary structure of proteins is the exact ordering of amino acids forming their chains.
3. Tertiary Structure of Protein
This structure arises from further folding of the secondary structure of the protein.
4. Quaternary Structure of Protein
The spatial arrangement of various tertiary structures gives rise to the quaternary structure. Some of the proteins are composed of two or more polypeptide chains referred to as sub-units. The spatial arrangement of these subunits with respect to each other is known as quaternary structure.
Receptor-Receptor Interactions
Francesca Fanelli, ... Francesco Raimondi, in Methods in Cell Biology, 2013
Protein Stability
Protein structures are stabilized by various interactions, including hydrophobic, hydrogen bonding, electrostatic, and van der Waals. On the basis of the importance of hydrophobic interactions, long-range contacts, and conservation of residues among proteins, Gromiha et al.
Fluorescence spectroscopy
Protein structures are mainly the combined clusters of 20 amino acid permutations in a three-dimensional space. Correlation between the protein three-dimensional structures and their functions holds an essential importance in the field of computational drug discovery. Therefore, the knowledge of native protein structures is of utmost importance.
Homologous Protein Detection
Xuefeng Cui, Yaosen Min, in Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 2019
Drug Discovery Technologies
Protein structures can be modeled using the primary amino acid sequence and a structure template (high-resolution three-dimensional structure of a homologous protein).
Functional Cell Biology
Protein structure and function is dictated by the protein amino acid sequence. Proteins similar in amino acid sequence fold into structures that are similar and often have similar function. However, the overwhelming complexity of protein sequences and structures makes it difficult to identify some pattern in the apparent disorder.
Biological Database Searching
Nor A. Nor Muhammad, in Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 2019
Structure of Proteins
Protein is made up of amino acids. Each amino acid is an organic molecule consisting of a central carbon atom attached to an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom and a variable side chain (R group). There are 20 amino acids common to most proteins and fewer common ones. The general structure of an amino acid looks like this:
Classification of Proteins
Proteins can be classified according to their composition, structure, and function. Let us look at them one by one.
Deficiency of Proteins
Deficiency of proteins occurs when one does not get enough proteins from the diet to meet the body’s requirements. Protein deficiency may lead to serious health complications. A severe form of protein deficiency leads to a disease called Kwashiorkor. It is common in Central Africa and South Asia, and 30% of children suffer.
Summary
As we have seen, all the biological functions of proteins and their importance to our body functions are very high. Proteins carry out various tasks in our bodies. From growth, cell repair to immunity, many more functions is carried out by proteins. They are important for children, teens, and pregnant women.
FAQs
Q.1. What is protein? Ans: Protein is one of the most important macronutrients of our diet. It is a macromolecule with a complex structure and diverse biological functions.
Protein Structure Definition
- Proteins are nothing but biological polymers. They are polymers of amino acids joined together by amino acids. You must know that amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. It means that proteins have a chain-like structure, where amino acids are the primary ingredient. The term structure, when it is used in relation to proteins, goes on to h...
Primary Protein Structure
- The primary structure of a protein refers to a unique formation and sequence in which amino acids get combined. They all get linked together to produce a protein molecule. The primary structure is responsible for giving particular properties to protein. Depending on the side-chain substituent, an amino acid can be classified into being acidic, basic or neutral. Although twenty …
Secondary Protein Structure
- This secondary protein structure gives a unique shape to the protein. It’s where the peptide backbone of a protein structure gets folded onto itself. The folding of the polypeptide chains occurs because of the interaction between the carboxyl group and amine groups of the peptide chains. Secondary protein structure gives out two types of shapes; they are α-helix and β-pleate…
Tertiary Protein Structure
- Tertiary structure is responsible for the formation and 3-D shape of the protein. As amino acids form bonds during secondary structure, they give out shapes such as helices and sheets. Further, the structure can coil or fold randomly, and that’s what you call the tertiary structure of proteins. When the structure gets disturbed, the protein becomes denatured. Such a protein gets chemica…
Quaternary Protein Structure
- The spatial arrangement of two or more peptide chains leads you to a quaternary protein structure. You should know that proteins don’t necessarily need to have a quaternary structure. Also note that primary, secondary, and tertiary structures of proteins are available in all-natural proteins. But, that’s not the case for quaternary structure. Thus, when a particular protein has th…
Analysis of Protein Structure
- The complexities of a protein structure do make the elucidation process of a complete protein structure extremely difficult, even with the most advanced analytical equipment. An amino acid analyzer can be used to determine which amino acids are present and their molar ratios. The sequence of the protein can then be analyzed by means of peptide mapping, and the use of Edm…