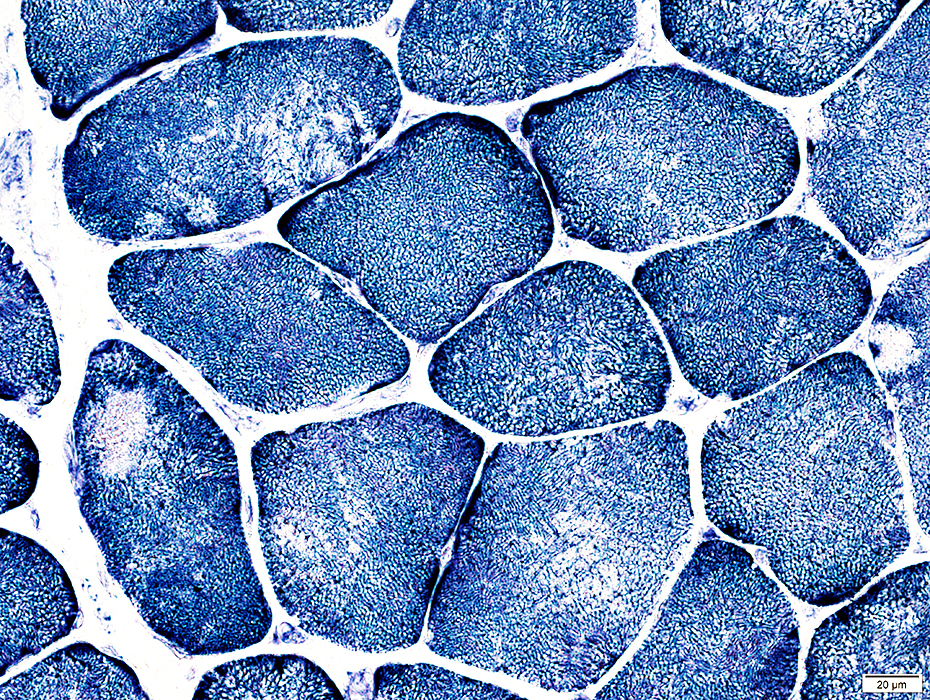
Why are red muscle fibers called slow twitch oxidative fibers?
Slow twitch fibers are also known as red fibers since they have a high oxygen content. In order to store oxygen in muscle cells the oxygen transporter myoglobin is needed. As this protein has a red colour, the muscle fibers appear also reddish.
Do muscle fibers have refractory period like nerve fibers?
Yes, muscle fibers have a refractory period because the muscle contracts due to an electrical signal from a nerve. The muscle needs to relax and reset in order to contract again. However, this refractory period is very short in skeletal muscle and a second stimulus can be sent while the muscle is still contracting, which is when we see summation of the action potentials.
What are muscle fibers arranged in bundles called?
Bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium.Muscle fibers are covered by the endomysium. Inside each skeletal muscle, muscle fibers are organized into individual bundles, each called a fascicle, by a middle layer of connective tissue called the perimysium.. Likewise, people ask, what is the arrangement of fibers in skeletal muscle?
What are red and white muscles?
Your body has two major types of muscle tissues: fast twitch and slow twitch. The fast-twitch muscle fibers are known as the white muscle, while the slow-twitch muscles fibers are known as red muscle. These two types of muscle fibers are engaged differently depending on what type of activity you are doing.
What do red muscle Fibres do?
Red muscles have slow-twitch fibers which can contract slowly for a long period of time without fatigue. They are used during aerobic exercises and as such, rely on lots of oxygen to generate energy.
What is the difference between white and red muscle fibers?
Red muscles are named so because they are dense with capillaries and are rich in myoglobin and mitochondria – which gives it a characteristic red appearance. On the other hand, white muscles have comparatively less mitochondria and myoglobin, giving the muscles a “whitish” appearance.
What type of fibers are red fibers?
Red fibers (type 1) are also known as slow-twitch fibers, and white (type 2) are called fast-twitch fibers. White, fast fibers can also be broken into two types—2A and 2B. 2A fibers sit in between the slower red fibers and the ultimate fast 2B white fibers.
Why are Type 1 muscle fibers red?
Well, arteries have more oxygen than veins do. And because of that, the color of our type 1 muscle fibers will be red because they produce more energy from oxygen than type 2 muscle fibers do. More oxygen is present in type 1, so they're red.
Are red fibers slow or fast?
Slow-twitch fibers are also called red fibers because they contain more blood-carrying myoglobin, which creates a darker appearance. Because they can provide their own source of energy, slow-twitch fibers can sustain force for an extended period of time, but they are not able to generate a significant amount of force.
What are the 3 types of muscle fibers?
The three types of muscle fiber are slow oxidative (SO), fast oxidative (FO) and fast glycolytic (FG). SO fibers use aerobic metabolism to produce low power contractions over long periods and are slow to fatigue.
What type of muscle fibers do bodybuilders have?
Type IIb muscle fibers have the fastest-contractile speed, the largest cross-sectional area, the lowest oxidative capacity, and the highest glycolytic capacity. They are ideally suited for short fast bursts of power. These muscle fibers are used in such activities as sprinting, powerlifting, and bodybuilding.
How do red muscle fibers increase?
Running, jogging, hiking, rowing, and swimming are all good ways to strengthen your slow-twitch muscles. With weight training, choose higher numbers of reps, shorter rest periods, and slower motions. When resistance training, try to lengthen the amount of time spent under tension.
What is the difference between Type 1 and type 2 fibers?
The two types of skeletal muscle fibers are slow-twitch (type I) and fast-twitch (type II). Slow-twitch muscle fibers support long distance endurance activities like marathon running, while fast-twitch muscle fibers support quick, powerful movements such as sprinting or weightlifting.
What are Type 1 and type 2 muscles?
Skeletal muscle fibers are broadly classified as "slow-twitch" (type 1) and "fast-twitch" (type 2).
What is type 2 muscle fiber?
You use type 2 muscle fibers, your “fast-twitch" muscle fibers, during short, explosive periods of physical activity. “Type 2 muscle fibers are quicker to fatigue but can produce stronger and faster bursts of power," says Joe Tatta, PT, DPT, founder of the Integrative Pain Science Institute.
What is the difference between white and red muscle fibers quizlet?
Red muscle fibers have slower twitch than white muscle fibers and they don't tire so easily.
What is the functional difference between red and white skeletal muscle fibers?
Red Muscles use more oxygen than White Muscles and this is one of the reasons why they are used in strenuous activities like exercise. They rely only on oxygen to generate energy and are thus also called slow-oxidative Muscles. They are rich in glycogen and enzymes of glycolysis which gives them the requiRed energy.
How do red fibers compare to white fibers quizlet?
Red fibers contract more slowly than white. Red fibers fatigue more slowly than white. Red fibers have fewer mitochondria than white.
Is white muscle fast or slow?
White fibers, also called fast-twitch fibers or anaerobic fibers, are used for rapid, short-term activities like fleeing from danger. These fast-twitch muscles are able to contract more quickly than the dark, slow-twitch muscles.
Which muscle fibers are red?
Thigh muscle, which is a red muscle, predominantly consists of type I muscle fibers with relatively large quantities of mitochondria and myoglobin, while breast muscle, which is white muscle, has a high ratio of type IIB muscle fibers and comparatively smaller quantities of mitochondria and myoglobin (Jayasena et al., 2015).
Which muscle type produces ATP?
One of the two main types of skeletal muscle, which contains abundant mitochondria and myoglobin. Red muscle fibres contract and fatigue more slowly than white fibres and generate ATP by aerobic catabolism of glucose and fats, utilizing myoglobin-bound O2
What is a slow twitch muscle?
slow-twitch muscle in which small dark "red" muscle fibers predominate; myoglobin is abundant and great numbers of mitochondria occur, characterized by slow, sustained (tonic) contraction. Contrast with white muscle.
Why is duck breast considered red meat?
Duck breast meat is regarded as red meat, owing to its higher concentration of red muscle fibers.
Where does the locomotive power for steady swimming come from?
His experiments show that most of the locomotive power for steady swimming comes from the fish's driveshaft - the area of the red muscle nearest the tail.
Why do muscle fibers develop?
It’s possible for muscle fibers to develop issues. This can be due to things like direct injury, a nerve condition, or another underlying health condition. Conditions affecting muscle fibers can, in turn, affect the function of a specific muscle or muscle group. Last medically reviewed on May 12, 2020.
What type of muscle fibers are striated?
This causes the muscle tissue to be striated, or have a striped appearance. Skeletal muscle fibers are classified into two types: type 1 and type 2. Type 2 is further broken down into subtypes. Type 1. These fibers utilize oxygen to generate energy for movement.
What is the skeletal muscle made of?
Skeletal muscle. Each one of your skeletal muscles is made up of hundreds to thousands of muscle fibers that are tightly wrapped together by connective tissue. Each muscle fiber contains smaller units made up of repeating thick and thin filaments.
What are the different types of muscles?
The types of muscle tissue have different functions within your body: 1 Skeletal muscle. These muscles are attached to your skeleton by tendons and control the voluntary movements of your body. Examples include walking, bending over, and picking up an object. 2 Smooth muscle. Smooth muscles are involuntary, meaning that you can’t control them. They’re found in your internal organs and eyes. Examples of some of their functions include moving food through your digestive tract and changing the sizes of your pupil. 3 Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is found in your heart. Like smooth muscle, it’s also involuntary. Cardiac muscle contracts in a coordinated way to allow your heart to beat.
What muscle is involuntary?
Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is found in your heart. Like smooth muscle, it’s also involuntary. Cardiac muscle contracts in a coordinated way to allow your heart to beat. Muscle fibers and muscles work to cause movement in the body.
What are some examples of muscle tissue?
These muscles are attached to your skeleton by tendons and control the voluntary movements of your body. Examples include walking, bending over, and picking up an object.
What causes muscle tornness?
This can happen when a muscle stretches beyond its limits or is made to contract too strongly. Some of the most common causes are sports and accidents.
Why are my muscles red?
1. These muscle fibres are dark red which is due to the presence of red haemoprotein called myoglobin. Myoglobin binds and stores oxygen as oxymyogiobin in the red fibres. Oxymyogiobin releases oxygen for utilization during muscle contraction.
Which muscle has more sarcoplasmic reticulum?
White muscles have more sarcoplasmic reticulum. 4. They depend mainly on anaerobic oxidation (glycolysis) for energy production and accumulate lactic acid in considerable amounts during strenuous work and soon get fatigued. 5. These muscle fibres have a fast rate of contraction for short periods.
Can red muscle contract without fatigue?
4. They carry out considerable aerobic oxidation without accumulating much lactic acid. Thus red muscle fibres can contract for a longer period without fatigue.
What are the two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers?
Two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers are how fast some fibers contract relative to others, and how fibers produce ATP. Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers. Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP.
What is the function of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves (and gives SO fibers their red color). All of these features allow SO fibers to produce large quantities of ATP, which can sustain muscle activity without fatiguing for long periods of time.
Why are FO fibers oxidative?
They are oxidative because they produce ATP aerobically, possess high amounts of mitochondria, and do not fatigue quickly. However, FO fibers do not possess significant myoglobin, giving them a lighter color than the red SO fibers.
Why do SO fibers have a large number of mitochondria?
The SO fibers possess a large number of mitochondria and are capable of contracting for longer periods because of the large amount of ATP they can produce , but they have a relatively small diameter and do not produce a large amount of tension. SO fibers are extensively supplied with blood capillaries to supply O 2 from the red blood cells in the bloodstream. The SO fibers also possess myoglobin, an O 2 -carrying molecule similar to O 2 -carrying hemoglobin in the red blood cells. The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves (and gives SO fibers their red color). All of these features allow SO fibers to produce large quantities of ATP, which can sustain muscle activity without fatiguing for long periods of time.
Why are FO fibers important?
They are oxidative because they produce ATP aerobically, possess high amounts of mitochondria, and do not fatigue quickly. However, FO fibers do not possess significant myoglobin, giving them a lighter color than the red SO fibers. FO fibers are used primarily for movements, such as walking, that require more energy than postural control but less energy than an explosive movement, such as sprinting. FO fibers are useful for this type of movement because they produce more tension than SO fibers but they are more fatigue-resistant than FG fibers.
What is FG fiber?
FG fibers are used to produce rapid, forceful contractions to make quick, powerful movements. These fibers fatigue quickly, permitting them to only be used for short periods. Most muscles possess a mixture of each fiber type. The predominant fiber type in a muscle is determined by the primary function of the muscle.
Which fibers produce ATP?
Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP. Fast oxidative (FO) fibers have fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration, but because they may switch to anaerobic respiration (glycolysis), can fatigue more quickly than SO fibers.
What are Red Muscles?
Red muscles are a type of skeletal muscle that is rich in mitochondrial concentration, myoglobin and blood supply. These are also called type I or slow twitch muscles because they show slow twitching and have a low rate of fatigue. These muscles work for long and do not show quick or early fatigue due to rich contents in them. Moreover, red muscles have thin muscle fibers, they have dark fibers in them and are dominantly seen due to which they give the red color appearance. Red muscles have a lot of mitochondria, but they still show slow contraction and power due to which they can perform more work. Red muscles use aerobic metabolism, so there is no accumulation of lactic acid during continuous work. These muscles have small motor units in them. A common example of red muscle is muscles of back (ex-tensors) or erector spine muscles etc.
Why do red muscles have dark fibers?
Moreover, red muscles have thin muscle fibers, they have dark fibers in them and are dominantly seen due to which they give the red color appearance. Red muscles have a lot of mitochondria, but they still show slow contraction and power due to which they can perform more work.
Why do white muscles have a low mitochondrial rate?
White muscles have a low quantity of mitochondria, but they still show a fast contraction and more power due to which they can perform less work and fatigue early. White muscles use anaerobic metabolism, so they have an accumulation of lactic acid during continuous work. These muscles have large motor units in them.
What is the white muscle?
White muscles are a type of skeletal muscle that has low mitochondrial concentration, myoglobin and blood supply. These are also called type II or fast twitch muscles because they show fast twitching and have a high rate of fatigue.
What muscle shows a slow contraction and low power?
Work. Red muscle can perform prolonged work. White muscle can perform short time work. Contraction & Power. Red muscle shows a slow contraction and low power. White muscle shows a fast contraction and more power. Fatigue & Accumulation. Red muscles show less fatigue and have a low accumulation of lactic acid.
What are the three major categories of muscles?
There are three major categories of muscles: Skeletal muscles, Cardiac muscles, and Smooth muscles. Here, skeletal muscles are further divided into red muscle and white muscle. Red muscles are the muscles in which dark bands or fibers are dominant, and they contain a large amount of myoglobin and mitochondria in it, ...
Why is the red muscle called the slow twitch muscle?
Red muscle is called type I or slow twitch muscles because they show slow twitching and have a low rate of fatigue.
What is red muscle fiber?
According to the American Council on Exercise, red muscle fibers specialize in long-duration, low-intensity movement, such as walking, standing or lifting loads below 70 percent of your maximal ability. Red fibers fatigue slowly and dominate muscle composition in the human body. Because red fibers contribute to all muscular contractions, they are easier to target with exercise. For example, any repetitive, weight-bearing action above an accustomed-to intensity produces red muscle adaptations such as growth and increased endurance, according to the National Strength and Conditioning Association.
What is the difference between white and red muscle?
White muscle experiences detraining, or loss of fitness, due to reduced physical activity at a faster rate than red muscle mass. While white muscle fitness augments ability to sustain a given activity over time -- muscular endurance -- red muscle has a greater influence on muscle size and maximal strength. Endurance adaptations can be lost quickly without regular exercise. Generally, endurance athletes focus on red muscle fitness, while strength and power athletes build white muscle fitness, the National Strength and Conditioning Association says. Non-athletes can support muscular health with weekly weight training sessions. Furthermore, muscle requires 0.8 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, regardless of fiber type, as prescribed by the National Strength and Conditioning Association. Consult a doctor before starting an exercise program.
What type of fibers are in muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue contains an array of type I and type II fibers. Alternative names for type I fibers include slow-twitch fibers or red muscle, while type II fibers are also known as fast-twitch fibers or white muscle. Although both fiber types contribute to movement, exercise intensity initiates which fiber dominates force production, according to the American Council on Exercise’s Resources for the Personal Trainer. For example, red muscle fibers initiate all movement while white fibers activate only when intensity surpasses a given level, as stated by the American Council on Exercise. Both fiber types require weight-bearing exercise for fitness enhancement.
Why are red muscles red?
Red muscles are red because of the presence of dense capillaries that are rich in myoglobin and mitochondria. One of the main difference between red and white muscle fibres is the colour which is deep red for red muscles because of myoglobin which is present in the sarcoplasm (cytoplasm) of the muscle fibre. The myoglobin present in red muscles ...
Why do red muscles use more oxygen than white muscles?
Red muscles use more oxygen than white muscles and this is one of the reasons why they are used in strenuous activities like exercise. White muscles use a lesser amount of oxygen than the red muscles. Energy generation. They rely only on oxygen to generate energy and are thus also called slow-oxidative muscles.
Why are white muscles called fast twitch?
Ans: Unlike red muscle fibres, the white muscle fibres can contract faster and this is why they are called fast-twitch fibres. These muscles have low myoglobin and low oxygen content. White muscles therefore do not depend on oxygen for their energy but get it from glycogen. This anaerobic energy generation process is faster and it helps the white muscle fibres to contract faster and stronger. White muscles tire out easily and this is the reason why the body activates them at the last.
How do red muscles get their energy?
Red muscle fibres get their energy from fat and glycogen by using oxygen. This is aerobic energy generation and since it is a lengthy process, the muscles contract slowly. Red muscles have a high tolerance for fatigue and do not tire out easily. Q2.
What are white muscles?
White Muscles. White muscles have a lesser amount of myoglobin and mitochondria and hence appear whitish. An example of white muscle is the eyeball muscle. Let’s look at the red and white muscle difference in detail below. Criteria. Red Muscles. White Muscles. Presence of Mitochondria. They are more in number in the body.
What are twitch fibres?
They are rich in glycogen and enzymes of glycolysis which gives them the required energy. Twitch-fibres. They have slow-twitch fibres that contract slowly for a long time without fatigue. They have fast-twitch fibres that contract faster for a short period and get tired soon.
Which muscle has more SR?
They have more SR than red muscle. Fatigue rate. Red muscles can perform aerobic oxidation without collecting a lot of lactic acids. This helps the red muscles to contract for a long period. White muscles perform anaerobic oxidation and in the process, they accumulate more lactic acid than the red muscles .