What is a sampling method in research?
Sampling is the selection of a subset of the population of interest in a research study. In the vast majority of research endeavors, the participation of an entire population of interest is not possible, so a smaller group is relied upon for data collection.
What are the 5 main types of sampling?
Non-Probability Sampling Types Non-probability Sampling methods are further classified into different types, such as convenience sampling, consecutive sampling, quota sampling, judgmental sampling, snowball sampling. Here, let us discuss all these types of non-probability sampling in detail.
What are different sampling methods?
Methods of sampling from a populationSimple random sampling. ... Systematic sampling. ... Stratified sampling. ... Clustered sampling. ... Convenience sampling. ... Quota sampling. ... Judgement (or Purposive) Sampling. ... Snowball sampling.
What are the three main sampling methods?
Sampling TechniquesSampling helps a lot in research. ... Probability Sampling.Simple Random Sampling: Every element has an equal chance of getting selected to be the part sample. ... For example: Random selection of 20 students from class of 50 student. ... Stratified Sampling.Cluster Sampling.· Single Stage Cluster Sampling.More items...•
What are the 4 sampling strategies?
Four main methods include: 1) simple random, 2) stratified random, 3) cluster, and 4) systematic. Non-probability sampling – the elements that make up the sample, are selected by nonrandom methods. This type of sampling is less likely than probability sampling to produce representative samples.
What are the 4 types of samples?
There are 4 types of random sampling techniques:Simple Random Sampling. Simple random sampling requires using randomly generated numbers to choose a sample. ... Stratified Random Sampling. ... Cluster Random Sampling. ... Systematic Random Sampling.
What is the best sampling method?
We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling.
What are the 4 types of random sampling?
There are four primary, random (probability) sampling methods – simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
What are the types of qualitative research sampling?
In this section, we briefly describe three of the most common sampling methods used in qualitative research: purposive sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling.
Why sampling is used in research?
Samples are used to make inferences about populations. Samples are easier to collect data from because they are practical, cost-effective, convenient, and manageable.
What is importance of sampling in research?
Studies are conducted on samples because it is usually impossible to study the entire population. Conclusions drawn from samples are intended to be generalized to the population, and sometimes to the future as well. The sample must therefore be representative of the population.
What is meant by sample method What are its uses?
Sampling is a process in statistical analysis where researchers take a predetermined number of observations from a larger population. The method of sampling depends on the type of analysis being performed, but it may include simple random sampling or systematic sampling.
What are the 4 types of random sampling?
There are four primary, random (probability) sampling methods – simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.
What are the 4 types of Probability sampling?
There are four commonly used types of probability sampling designs:Simple random sampling.Stratified sampling.Systematic sampling.Cluster sampling.
What are the 4 types of non-probability sampling?
Types of non-probability samplingConvenience sampling.Quota sampling.Self-selection (volunteer) sampling.Snowball sampling.Purposive (judgmental) sampling.
What are the types of random or Probability sampling?
In simple random sampling (SRS), each sampling unit of a population has an equal chance of being included in the sample. ... Systematic sampling means that there is a gap, or interval, between each selected unit in the sample.More items...•
What are the different types of sampling?
The selection of an appropriate technique for choosing participants is very much important. As the sampling procedure could have a significant influence on research outcomes. It is very much important to make the right selection of samples to draw valid conclusions.
What is the drawback of non random sampling?
But the biggest drawback of this technique is that you cannot make assumptions about the entire population.
Why is random sampling important?
It is very much important for you to make sure that the population which you have selected represents the entire population. There are some tools such as random number generator which you can utilize for applying the simple random sampling method.
What are the drawbacks of sampling?
But the main drawback of this method of sampling is that you can ensure that the sample is representative of all the students in university.
Why is selection of an appropriate method for sampling important?
It has been summarised from the above article is that selection of an appropriate method for sampling is important to draw a valid conclusion. Another fact which has been found is that the size of the population and objective of research helps in selecting the best sampling technique.
Why use sample size calculator?
The main benefit of using the sample size calculator is that you can make assumptions about the population exactly.
Which sampling technique is more suitable for exploratory research?
The non-probability sampling technique is considered to be more suitable for performing Exploratory and Qualitative research. In both qualitative and exploratory research the main objective of the researcher is to test theories related to the broad population.
What is convenience sampling?
Therefore, this method is quick, inexpensive, and convenient. It is called convenient sampling as the researcher selects the sample elements according to their convenient accessibility and proximity [3,6]. For example: assume that we will perform a cohort study on Egyptian patients with Hepatitis C (HCV) virus. The convenience sample here will be confined to the accessible population for the research team. Accessible population are HCV patients attending in Zagazig University Hospital and Cairo University Hospitals. Therefore, within the study period, all patients attending these two hospitals and meet the eligibility criteria will be included in this study.
What is the generalizability of clinical research?
The generalizability of clinical research findings is based on multiple factors related to the internal and external validity of the research methods. The main methodological issue that influences the generalizability of clinical research findings is the sampling method. In this educational article, we are explaining the different sampling methods in clinical research.
What are the two types of sampling methods?
There are two major categories of sampling methods (figure 1): 1; probability sa mpling methods where all subjects in the target population have equal chances to be selected in the sample [1,2] and 2; non-probability sampling methods where the sample population is selected in a non-systematic process that does not guarantee equal chances for each subject in the target population [2,3]. Samples which were selected using probability sampling methods are more representatives of the target population.
How to do multistage sampling?
A list of all clusters is made and investigators draw a random number of clusters to be included. Then, they list all individuals within these clusters, and run another turn of random selection to get a final random sample exactly as simple random sampling. This method is called multistage because the selection passed with two stages: firstly, the selection of eligible clusters, then, the selection of sample from individuals of these clusters. An example for this, if we are conducting a research project on primary school students from Iran. It will be very difficult to get a list of all primary school students all over the country. In this case, a list of primary schools is made and the researcher randomly picks up a number of schools, then pick a random sample from the eligible schools [3].
Why is the sample selection method criticized?
male/female ratio = 2/1) and therefore, they judge the sample to be suitable for representing the population. This method is widely criticized due to the likelihood of bias by investigator judgement [5].
When to use sampling frame?
This method is used when the whole population is accessible and the investigators have a list of all subjects in this target population. The list of all subjects in this population is called the “sampling frame”. From this list, we draw a random sample using lottery method or using a computer generated random list [4].
When to use the survey method?
This method is used when the population cannot be located in a specific place and therefore, it is different to access this population. In this method, the investigator asks each subject to give him access to his colleagues from the same population. This situation is common in social science research, for example, if we running a survey on street children, there will be no list with the homeless children and it will be difficult to locate this population in one place e.g. a school/hospital. Here, the investigators will deliver the survey to one child then, ask him to take them to his colleagues or deliver the surveys to them.
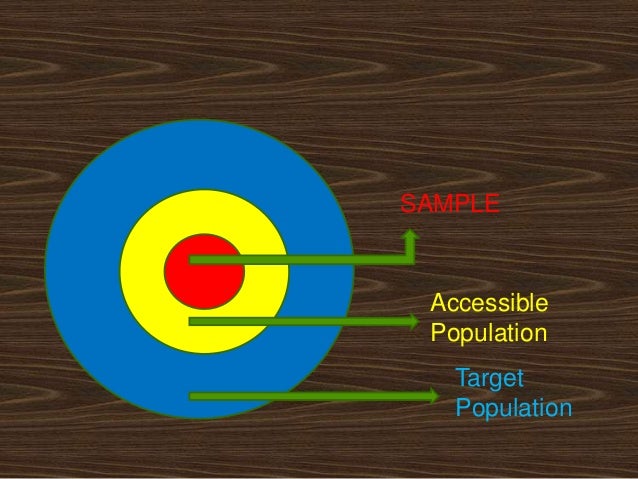
What is the Difference between Population and Sample?
Before starting with the sampling methods, it is important to understand the difference between sample and population.
What is stratified sampling?
Stratified sampling is a random selection of the participants by dividing them into strata and randomly selecting the participants from each level.
Why are some errors in the sampling frame possible?
Sometimes some errors are also possible in the sampling frame due to its discrepancy in selecting samples.
What is the method used to select participants?
The method you apply for selecting your participants is known as the sampling method. It helps in concluding the entire population based on the outcomes of the research.
What is cluster sampling?
It is a kind of sampling where the population is converted into the sub-groups called clusters. These sub-groups or clusters are then selected randomly as a sample. The selected group should have all the characteristics of other groups.
What is it called when a sample is not random?
It is known as probability sampling. If the selection is not random, it’s considered non-probability sa mpling.
How to find fixed period interval?
The fixed period interval can be calculated by dividing the sample size by the respective population size.
What are the sampling methods or Sampling Techniques?
In Statistics, the sampling method or sampling technique is the process of studying the population by gathering information and analyzing that data. It is the basis of the data where the sample space is enormous.
What is Non-Probability Sampling?
The non-probability sampling method is a technique in which the researcher selects the sample based on subjective judgment rather than the random selection. In this method, not all the members of the population have a chance to participate in the study.
What are the different types of probability sampling?
Probability Sampling methods are further classified into different types, such as simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and clustered sampling. Let us discuss the different types of probability sampling methods along with illustrative examples here in detail.
What are the two types of sampling methods?
In Statistics, there are different sampling techniques available to get relevant results from the population. The two different types of sampling methods are:: 1 Probability Sampling 2 Non-probability Sampling
How is stratified sampling done?
In a stratified sampling method, the total population is divided into smaller groups to complete the sampling process. The small group is formed based on a few characteristics in the population. After separating the population into a smaller group, the statisticians randomly select the sample.
What is the method of chance selection?
In simple random sampling technique , every item in the population has an equal and likely chance of being selected in the sample. Since the item selection entirely depends on the chance, this method is known as “ Method of chance Selection ”. As the sample size is large, and the item is chosen randomly, it is known as “ Representative Sampling ”.
What is snowball sampling?
The snowball sampling is also known as chain-referral sampling technique. In this method, the samples have traits that are difficult to find. So, each identified member of a population is asked to find the other sampling units. Those sampling units also belong to the same targeted population.
What are the two types of sampling methods?
There are two basic types of sampling methods: Probability sampling. Non-probability sampling.
Why is probability sampling the most popular way of a selecting a sample?
It is also the most popular way of a selecting a sample because it creates samples that are very highly representative of the population.
What is the difference between probability sampling and non-probability?
The key difference between non-probability and probability sampling is that the first one does not include random selection. So, let’s see the definition.
What is probability sampling?
This type of sampling method gives all the members of a population equal chances of being selected.
What is snowball sampling?
It is a methodology where researcher recruits other individuals for the study.
How to calculate sampling interval?
This interval, known as the sampling interval, is calculated by dividing the entire population size by the desired sample size.
Why is sampling important in marketing research?
The main goal of any marketing or statistical research is to provide quality results that are a reliable basis for decision-making. That is why the different types of sampling methods and techniques have a crucial role in research methodology and statistics. Your sample is one of the key factors that determine if your findings are accurate.
