The midbrain becomes the secondary brain vesicle called the diencephalon while the hindbrain becomes the mesencephalon, metencephalon and myelencephalon.
What is the development of primary and secondary brain vesicles?
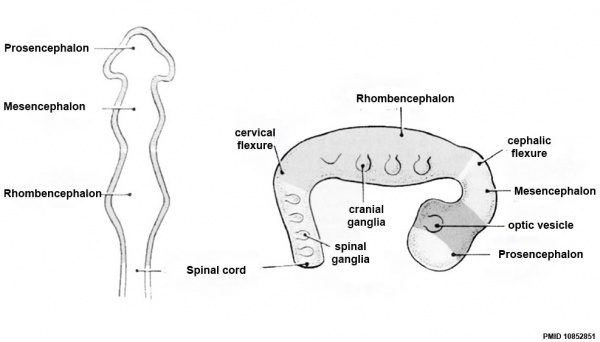
7-Development of primary and secondary brain vesicles. The cerebrum and brainstem arise from the rostral neural tube. These regions expand and constrict to form the three primary brain vesicles: Forebrain/Prosencephalon, Midbrain/Mesencephalon, and Hindbrain/Rhombencephalon. As development continues, the three primary vesicles give rise...
What are the vesicles of the brain?
brain v's, primary the three earlier subdivisions of the embryonic neural tube, including the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. brain v's, secondary the four brain vesicles formed by specialization of the forebrain and of the hindbrain in later embryonic development. chorionic vesicle the chorion of a mammal.
What are the V's of the brain?
brain v's, primary the three earlier subdivisions of the embryonic neural tube, including the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. brain v's, secondary the four brain vesicles formed by specialization of the forebrain and of the hindbrain in later embryonic development. chorionic vesicle the chorion of a mammal. encephalic v's brain vesicles.
What happens during the vesicle stage of neural development?
During these early vesicle stages, the walls of the neural tube contain neural stem cells in a region called the neuroepithelium or ventricular zone. These neural stem cells divide rapidly, driving growth of the early brain, but later, these stem cells begin to generate neurons through the process of neurogenesis.
What are primary and secondary brain vesicles?
Initially there are three primary brain vesicles: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon. These develop into five secondary brain vesicles – the prosencephalon is subdivided into the telencephalon and diencephalon, and the rhombencephalon into the metencephalon and myelencephalon.
What are the 3 primary vesicles of the brain?
Abstract. It is widely held that three primary brain vesicles (forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain vesicles) develop into five secondary brain vesicles in all vertebrates (von Baer's scheme).
What is the function of brain vesicles?
In summary, the primary vesicles help to establish the basic regions of the nervous system: forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. These divisions are useful in certain situations, but they are not equivalent regions. The midbrain is small compared with the hindbrain and particularly the forebrain.
What is a primary brain vesicle?
one of the three initial divisions of the neural tube, the primary vesicles include the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon.
How many secondary brain vesicles are there?
five secondary brain vesiclesIt is widely held that three primary brain vesicles (forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain vesicles) develop into five secondary brain vesicles in all vertebrates (von Baer's scheme).
What are the five brain vesicles?
As development continues, the three primary vesicles give rise to five secondary brain vesicles: Telencephalon, Diencephalon, Mesencephalon, Metencephalon, and Myelencephalon.
At which stage of development do the secondary brain vesicles occur?
At 5 weeks, they further develop into the secondary brain vesicles, and there are 5 of them: The prosencephalon partitions into the telencephalon and diencephalon.
Which component of the brain do each vesicle develop into?
Recall that during embryonic development the brain is initially composed of three primary vesicles: Forebrain, Midbrain, and Hindbrain. These vesicles ultimately become five brain divisions: Telencephalon, Diencephalon, Mesencephalon (midbrain), Metencephalon, and Myelencephalon.
Which brain vesicle gives rise to the midbrain?
mesencephalonThe mesencephalon gives rise to the midbrain structures, and the metencephalon the pons and cerebellum.
Which primary and secondary brain vesicles ultimately become the structure that contains the 3rd ventricle?
The various brain vesicles give rise to the following adult structures: The telencephalon develops into the cerebrum and lateral ventricles. The diencephalon forms the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, and third ventricle.
What are the three primary brain vesicles that form from the neural tube quizlet?
The neural tube becomes 3 "primary" brain vesicles in a 4-week embryo:Prosencephalon ("forebrain")Mesencephalon ("midbrain")Rhombencephalon ("hindbrain")
How can I remember the vesicles of my brain?
Three primary vesicles: Forebrain is a pro. Prosencephalon - future forebrain. M for midbrain, mesencephalon. Mesencephalon - future midbrain.
What is the primary brain vesicle of the cerebellum?
The neural tube forms three primary brain vesicles....Development of Brain.Primary vesiclesSecondary vesiclesAdult structuresHindbrain vesicle (rhombencephalon)MetencephalonPons and cerebellumMyelencephalonMedulla3 more rows•Aug 14, 2006
What are the three primary brain vesicles that form from the neural tube quizlet?
The neural tube becomes 3 "primary" brain vesicles in a 4-week embryo:Prosencephalon ("forebrain")Mesencephalon ("midbrain")Rhombencephalon ("hindbrain")
How can I remember the vesicles of my brain?
Three primary vesicles: Forebrain is a pro. Prosencephalon - future forebrain. M for midbrain, mesencephalon. Mesencephalon - future midbrain.
Which of the primary brain vesicles keeps its original name in the mature brain?
B. The term mesencephalon means "midbrain." As it develops from a primary brain vesicle to a secondary brain vesicle and finally an adult brain structure, it retains its name--the midbrain.
What is the ovoid sac formed by the closure of the auditory pit in the early embryo?
auditory vesiclea det ached ovoid sac formed by closure of the auditory pit in the early embryo, from which the percipient parts of the inner ear develop.
Where are optic vesicles located?
optic vesicle's Hollow, spherical neuroectodermal protrusions, one on each side of the forebrain. They are derived from the optic pits after closure of the embryonic neural tube. They subsequently invaginate to form the optic cup. The surface ectoderm overlying the optic vesicles invaginates to form the lens vesicle and eventually the crystalline lens. Syn.primary optic vesicle. See anophthalmia; optic cup; ectoderm; optic pit.
What is a small bladder?
1. A small bladder or sac containing liquid. 2. A small elevation on the skin containing fluid, usually serous fluid. 3. Any structure that has the appearance of 1 or 2 above.
What is a small elevation?
2. A small (that is, less than 1.0 cm in diameter), circumscribed elevation of the skin containing fluid.
What are the three subdivisions of the embryonic neural tube?
brain v's, primarythe three earlier subdivisions of the embryonic neural tube, including the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
What does "sac" mean in medical terms?
1.a small bladder or sac containing liquid.
Where does the lens vesiclea vesicle form?
lens vesiclea vesicle formed from the lens pit of the embryo, developing into the crystalline lens.
What is the brain vesicle?
Brain vesicles are the bulge-like features of the early development of the neural tube in vertebrates. Vesicle formation begins shortly after anterior neural tube closure at about embryonic day 9.0 in the mouse and the fourth ...
How long does it take for a zebrafish to develop brain vesicles?
In zebrafish and chicken embryos, brain vesicles form by about 24 hours and 48 hours post-conception, respectively. Initially there are three primary brain vesicles: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon.
Where are neural stem cells located?
During these early vesicle stages, the walls of the neural tube contain neural stem cells in a region called the neuroepithelium or ventricular zone. These neural stem cells divide rapidly, driving growth of the early brain, but later, these stem cells begin to generate neurons through the process of neurogenesis.
