
Sensory Vs Motor Neurons
| Bases | Sensory Neurons | Motor Neurons |
| Function | When we compare motor neuron vs sensory ... | Motor Nerves are responsible for sending ... |
| Location | Dorsal root ganglion of the spinal nerve ... | Ventral root ganglion of the spinal cord ... |
| Polarity | Sensory neurons are unipolar | Motor neurons are multipolar |
| Structure/Length of the Axon | Short axon | Long axon |
What is the difference between the sensory and motor neurons?
- Sensory neurons conduct signals from sensory organs to the CNS. ...
- Sensory neurons lack distinct axons and dendrites.
- Sensory neurons possess receptors.
- The soma of the sensory neurons possesses a nucleus and other cell organelles.
What nerves are sensory and motor?
What are the 12 cranial nerves?
- I. Olfactory nerve. The olfactory nerve transmits information to the brain regarding a person’s sense of smell. ...
- II. Optic nerve. ...
- III. Oculomotor nerve. ...
- IV. Trochlear nerve. ...
- V. Trigeminal nerve. ...
- VI. Abducens nerve. ...
- VII. Facial nerve. ...
- VIII. Vestibulocochlear nerve. ...
- IX. Glossopharyngeal nerve. ...
- X. Vagus nerve. ...
How do sensory and motor nerves help us?
Sensory nerves are in charge of relaying sensory information from your body extremities to your brain and spine. Motor nerves are in charge of sending signals out from the brain and spine, telling your body when to contract its muscles and move around. Autonomic nerves are basically in charge of everything else that your body does. Things like ...
What transmits impulse between sensory and motor neurons?
What transmits signals to sensory neurons? Interneurons. Interneurons, which are found only in the CNS, connect one neuron to another. They receive information from other neurons (either sensory neurons or interneurons) and transmit information to other neurons (either motor neurons or interneurons). Which neuron transmits impulse? motor neuron
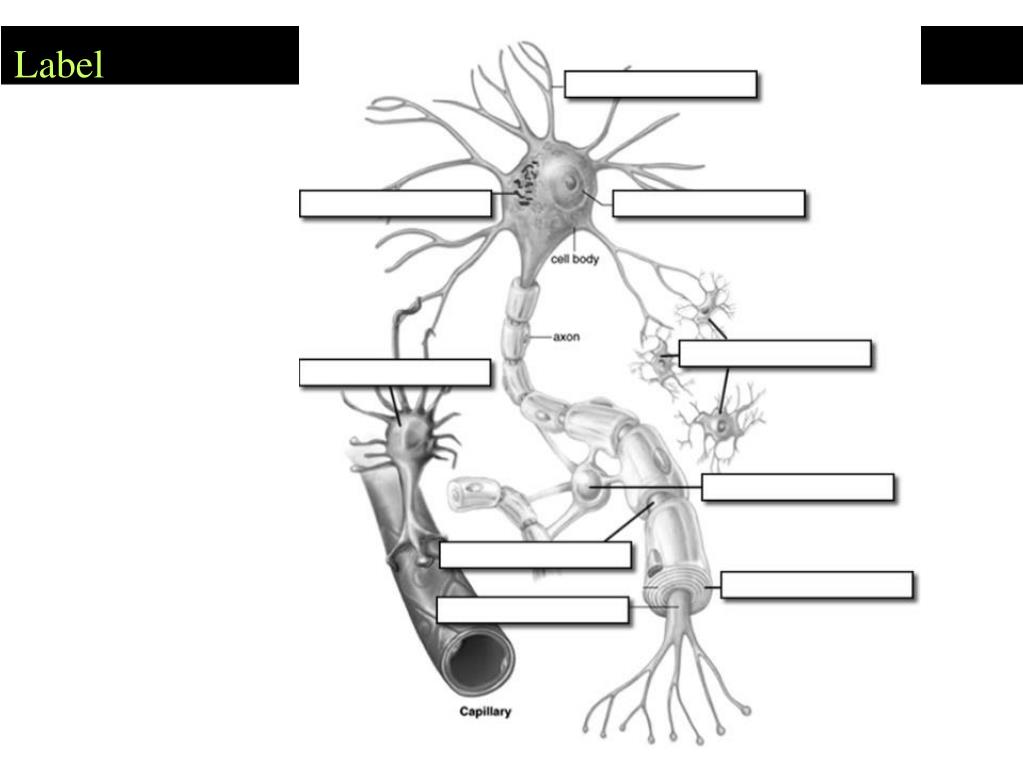
What are the function of sensory nerves and motor nerves?
Sensory nerves report information to the brain. It is a one-way communication from the body to the brain. Motor nerves respond by sending messages from the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) to the body for movement. Motor nerves send messages in the opposite direction from the CNS to the body.
What is the function of sensory and motor?
The sensory and motor systems are tightly integrated. Sensory stimulation and feedback provides important information to the brain through sensory skills like smell, touch, vision, hearing, and balance. Motor function is how your brain and body receives, and then reacts to, sensory stimulation.
What is a motor function?
any activity that results from stimulation of motor neurons, including glandular activity as well as reflexes and voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions. Also called motor behavior.
What's a motor neuron?
Motor neurons are a specialized type of brain cell called neurons located within the spinal cord and the brain. They come in two main subtypes, namely the upper motor neurons and the lower motor neurons. The upper motor neurons originate in the brain and travel downward to connect with the lower motor neurons.
Answer
sensory and motor neurons are the path way for our send organs and Brian to transfer massages. Sensory neurons transmits signals from send organs to Brian and spinal chord. Motor neurons transmute signals from brain and spinal chord to effectors life muscles.
Answer
Sensory nerve is a nerve that pass impulses from receptors toward or to the central nervous system. All the signals that receptor perceives are transferred to the central
Where do motor neurons start?
They begin in the cortex of one side of the brain, descend through the internal capsule, cross to the opposite side in the brain stem, descend through the corticospinal tract, and synapse with the lower motor neurons in the cord. The lower motor neurons receive the impulse in the posterior part of the cord and run to the myoneural junction located ...
What is the function of the motor cortex?
Motor and Sensory Functions of the Nervous System. The motor cortex, a vertical band within each cerebral hemi-sphere, controls the voluntary movements of the body.
What are the motor fibers of the spinal nerves?
All of the motor fibers of the spinal nerves represent extensions of these anterior horn cells, with each of these fibers communicat-ing with only one particular muscle fiber. The motor system is complex, and motor function depends on the integrity of the corticospinal tracts, the extrapyramidal system, and cerebellar function.
What are the two groups of motor neurons?
Upper and Lower Motor Neurons. The voluntary motor systemconsists of two groups of neurons: upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Upper motor neurons originate in the cere-bral cortex, the cerebellum, and the brain stem and modulate the activity of the lower motor neurons. Upper motor neuron fibers make up the descending motor pathways ...
Why are reflexes uninhibited?
However, because the inhibitory influences of intact upper motor neurons are now impaired , reflex (involuntary) movements are uninhibited, and hence hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, diminished or absent superficial reflexes, and pathologic reflexes such as a Babinski re-sponse occur.
Where do afferent impulses travel?
Afferent impulses travel from theirpoints of origin to their destinations in the cerebral cortex via the ascending pathways directly, or they may cross at the level of the spinal cord or in the medulla , depending on the type of sensation that is registered. Sensory information may be integrated at the level of the spinal cord or may be relayed to the brain. Knowledge of these pathways is important for neurologic assessment and for understanding symptoms and their relationship to various lesions.
Where are motor nerves located?
The motor nerve pathways are contained in the spinal cord. Some represent the pathways of the so-called extrapyramidal system, establishing connections be-tween the anterior horn cells and the automatic control centers located in the basal ganglia and the cerebellum. Others are components of reflex arcs, forming synaptic connections between ...
What is the function of sensory neuron?
When we compare motor neuron vs sensory neuron, the main function of Sensory Neurons is to send sensory signals from sensory organs to the central nervous system. Motor Nerves are responsible for sending motor commands from the central nervous system to the sensory organs to initiate actions. Location.
Where do sensory neurons originate?
Sensory neurons conduct signals from sensory organs to the CNS. Sensory Neurons arise from the dorsal root ganglion, which are specialized clusters present at the dorsal roots of the spinal cord.
Where are motor nerves located?
These neurons are located at the ventral root ganglion of the spinal cord. Motor neurons consist of long axon and multiple dendrons. They lack receptors.
Which type of neuron has receptors?
Sensory neurons possess receptors. The soma of the sensory neurons possesses a nucleus and other cell organelles. A synaptic junction with second-order sensory neurons is formed as the central branch extends from soma to the posterior horn of the spinal cord. These neurons are also known as pseudo unipolar neurons.
Where is the synaptic junction?
A synaptic junction with second-order sensory neurons is formed as the central branch extends from soma to the posterior horn of the spinal cord. These neurons are also known as pseudo unipolar neurons. In the blog, we have already explained the difference between sensory and motor nerves.
How many taste receptors are there on the tongue?
Taste receptor cells on our tongues form a group of 50 to 150. These cells respond to the chemicals present in the food and thus, form taste buds, which help us in differentiating among the food items of different tastes.
What are Sensory Neurons?
The sensory neurons are known to be located in the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord. These are the afferent neuron that helps in analyzing the stimulus which is received by the sensory organs. This stimulus further activates the sensory neuron for processing and transmitting the information.
What are Motor Neurons?
Motor neurons are a part of the spinal cord in the Nervous system in general. All the kinds of muscle movements in a human body are linked with the functioning of the motor neurons. It is responsible for carrying away the electrical and chemical signals from the Central Nervous System (CNS) towards the muscles, thus, triggering the movement.
Difference Between Sensory and Motor Neurons
The differences between Sensory and. Motor Neurons are as given below:
Things to Remember
All the types of neurons serve as an essential unit of functioning in the human body. However, they lack the tendency of regenerating or reproducing once they die.
Sample Questions
Ans. The motor neurons are of two types, the upper motor neuron, and the lower motor neuron. The upper motor neuron can be found in the motor cortex or the brainstem. They are mainly associated with the transmission of the signals which are responsible for the voluntary movement in a body.
What are sensory systems?
The sensory systems create our mental images of the external world. These representations offer us with details and cues that guide the motor systems to create movements produced by the collaborated contractions and relaxations.
Which type of neuron regulates muscle contraction?
Motor neurons that regulate muscle contractions have a cell body on one point, a long axon in the middle and dendrites on the other point. Sensory neurons have dendrites on both ends, connected with a long axon with a cell body in the middle. Interneurons, or associative neurons, bring information between motor and sensory neurons.
Which chemoreceptors are responsible for detecting alterations in oxygen concentration?
Distance chemoreceptors are essential to receiving stimuli in the olfactory system through both olfactory receptor neurons and neurons in the vomeronasal organ. Direct chemoreceptors consist of the taste buds in the gustatory system as well as receptors in the aortic bodies which identify alterations in oxygen concentration.
What are mechanoreceptors?
Mechanoreceptors. Mechanoreceptors are sensory receptors which react to mechanical forces, such as pressure or distortion. While mechanoreceptors exist in hair cells and play an essential function in the vestibular and auditory systems, most of mechanoreceptors are cutaneous and are grouped into four categories:
How do nociceptors respond to stimuli?
Nociceptors respond to possibly destructive stimuli by sending signals to the spinal cord and brain. This procedure, called nociception, generally causes the understanding of pain. They are found in internal organs, and also on the surface of the body. Nociceptors detect various type of harmful stimuli or actual damage. Those that only respond when tissues are damaged are called “sleeping” or “quiet” nociceptors.
What are the four types of receptors?
The receptors which react to the stimulus and start the procedure of sensation are commonly defined in four distinct categories: chemoreceptors, photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and thermoreceptors.
Which receptors have large receptive fields?
Rapidly adjusting receptors have small receptive fields and underlie the understanding of slip. Pacinian receptors have large receptive fields and are the predominant receptors for high-frequency vibration.
