In lake and pond ecosystems many include light, nutrients, oxygen, pH, temperature, and turbulance. There are many different kinds of biotic factors in lakes. Biotic factors are defined as any living organism that affects the way the ecosystem works.
What are the 6 abiotic factors in an ecosystem?
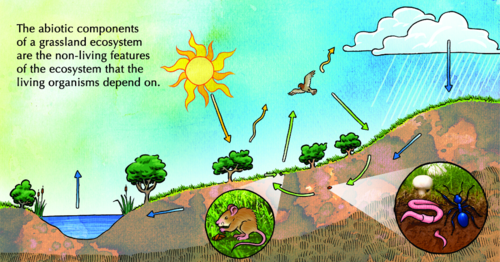
giving an example. Label the diagram below with some examples and units of measuremen of abiotic factors. The abiotic or non-living factors in an ecosystem include: temperature, turbidity, pH, dissolved oxygen, nitrate levels and phosphate levels.
What are some examples of biotic factors in an ecosystem?
State a few examples of biotic resources.
- Plants
- Animals
- Fungi
- Bacteria
What are 10 biotic factor?
What are 10 biotic factors in an ecosystem? Biotic factors include animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, and protists.Some examples of abiotic factors are water, soil, air, sunlight, temperature, and minerals.
What are three biotic factors?
Types of Biotic Factors
- Producers. Producers – also known as autotrophs, from the Greek words “auto” for “self” and “troph” for “food” – are organisms that make their own food using inorganic materials and ...
- Consumers. Consumers, also called “heterotrophs,” are organisms that eat other living organisms in order to obtain energy.
- Decomposers. ...

What are 3 abiotic factors found in a pond?
Some abiotic factors of a pond ecosystem are – water, temperature/sunlight, salinity, nutrients, pH of soil, carbon dioxide, oxygen.
What is pond biotic or abiotic?
A pond or lake ecosystem includes biotic (living) plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (nonliving) physical and chemical interactions. Pond and lake ecosystems are a prime example of lentic ecosystems.
What is abiotic in a pond?
Abiotic component Abiotic factors are non-living factors that can have an impact on the ecosystem The main factors of ponds include water quality, temperature, light, soil, and seasonal change. Water is an important abiotic factor. The quality of water is crucial for living organisms in the pond.
What are the 5 biotic factors?
Like all ecosystems, aquatic ecosystems have five biotic or living factors: producers, consumers, herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and decomposers.
Is algae biotic or abiotic?
BioticAnswer: Biotic: fish, plants, algae, bacteria. Abiotic: salt, water, rocks, sediment, trash.
What is the ecosystem of a pond?
A pond is a type of aquatic ecosystem. The autotrophic components of a pond are algae, phytoplankton and aquatic plants, zooplankton, amphibians and fish are the major consumers. Fungi, bacteria are the decomposers. Abiotic factors constitute water, organic and inorganic nutrients and the soil at the bottom.
What eats algae in a pond?
Fish that clean ponds by eating algae and other debris include the common pleco, the mosquitofish, the Siamese algae eater and the grass carp. Be careful with carp, koi and other bottom feeders. While they eat algae, they can also make your pond look dirty.
Is wind a biotic factor?
Abiotic factors are the non-living parts of an environment. These include things such as sunlight, temperature, wind, water, soil and naturally occurring events such as storms, fires and volcanic eruptions. Biotic factors are the living parts of an environment, such as plants, animals and micro-organisms.
Is soil biotic or abiotic?
Soil is composed of both biotic—living and once-living things, like plants and insects—and abiotic materials—nonliving factors, like minerals, water, and air. Soil contains air, water, and minerals as well as plant and animal matter, both living and dead.
What are biotic factors in water?
A biotic factor is a living organism that shapes its environment. In a freshwater ecosystem, examples might include aquatic plants, fish, amphibians, and algae. Biotic and abiotic factors work together to create a unique ecosystem. Learn more about biotic factors with this curated resource collection.
What are the 3 types of biotic factors?
Producers, consumers, and decomposers are the three broad categories of biotic components.
Is grass biotic or abiotic?
bioticGrass is a biotic component of the environment. Biotic factors are the living components of an ecosystem.
Is water abiotic or biotic?
Abiotic factorsAbiotic factors are non-living things that "live" in an ecosystem that affect both the ecosystem and its surroundings. Some examples of Abiotic factors are the sun, rocks, water, and sand. Biotic factors are living organisms that affect other living organisms.
What are 2 abiotic factors?
An abiotic factor is a non-living part of an ecosystem that shapes its environment. In a terrestrial ecosystem, examples might include temperature, light, and water. In a marine ecosystem, abiotic factors would include salinity and ocean currents.
What animal live in a pond?
Fish, turtles, and snails live in the water. Ducks and other birds live above the water. Other animals live near ponds. Those animals include frogs, beavers, and muskrats.
Is grass biotic or abiotic?
bioticGrass is a biotic component of the environment. Biotic factors are the living components of an ecosystem.
What are abiotic factors in ponds?
Abiotic factors of a pond are all elements that are in or that affect the ecosystem of a pond other than the living, or biotic, factors . Abiotic factors vary by pond and include a wide range of components such as temperature, stratification, density, oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, salinity, and calcium and nitrogen levels.
How do abiotic factors affect ponds?
Changes to abiotic factors can be subtle or catastrophic and can affect what plants and animals are able to live and thrive in the pond. As the ecosystem is altered because of changes in the abiotic factors, some die out while others change and adapt to the new environment.
Why is density important in a pond?
Density is an important abiotic factor because it affects the amount of light that passes through the water, and therefore what type of plants and other biotic factors can survive at various depths. Some abiotic factors may be suspended in the water while others may be in the sediment at the bottom of the pond.
