
Difference between Spontaneous and Induced Mutation
| Spontaneous Mutation | Induced Mutation |
| Spontaneous mutations occur naturally an ... | Induced mutations occur due to physical ... |
| Occurs due to slippage in natural proces ... | Induced by mutagens |
| Caused due to replication error, tautome ... | Caused due to base modification, base an ... |
| E.g. sickle cell anaemia | E.g. skin cancer due to prolonged exposu ... |
How mutations may be induced?
Mutations may be induced by many agents called mutagens. These may be chemical mutagens and radiations, e.g., X-rays, y-rays and UV rays. Mutations are created at molecular level by altering the base in nuleotides.
When does a spontaneous mutation occur?
These spontaneous mutations can occur when one strand of the DNA template loops out and becomes displaced during replication, or when DNA polymerase slips or stutters during replication. If a loop occurs in the template strand during replication, DNA polymerase may miss the looped out nucleotides, and a small deletion in the new strand will be introduced.
What are induced mutations caused by?
Induced mutations are induced by known factor- such as-physical (ionizing irradiation, ultraviolet light), chemical and biological mutagens (bacteria and viruses). Mechanism of induced mutation: Induced mutations occurs by at least three different mechanisms.
Can mutations occur spontaneously?
Some acquired mutations occur spontaneously and randomly in genes. Other mutations are caused by environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals or radiation. Mutations occur throughout the natural world.
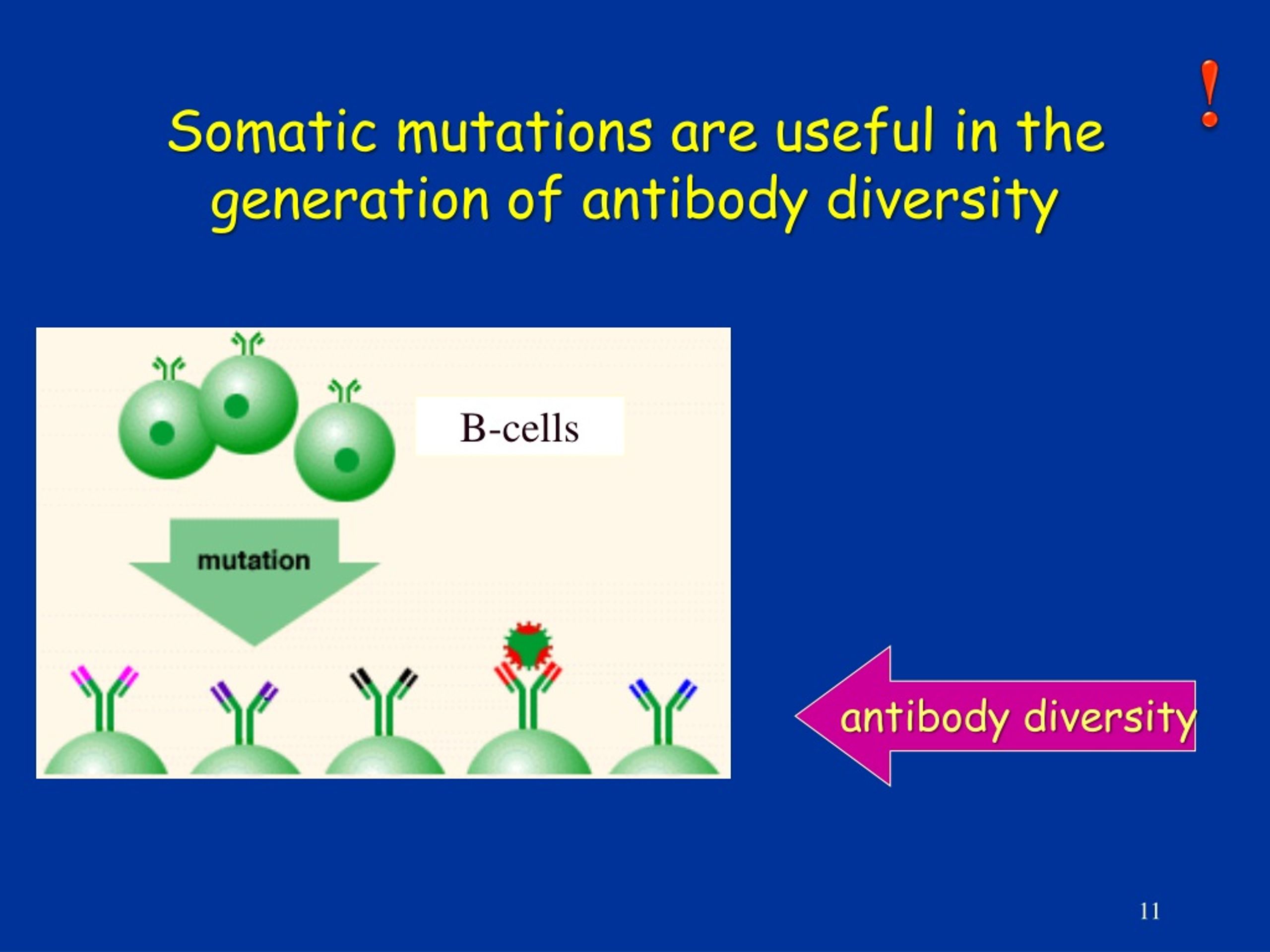
What causes spontaneous and induced mutations?
Spontaneous mutations, as the name suggests, are mutations that occur randomly due to errors in the replication of DNA, which is a natural biological process. They do not occur as a result of stimuli or environmental factors. Induced mutations occur when DNA is exposed to an agent that causes mutations.
What is the most common cause of spontaneous mutations?
Spontaneous mutations are derived from various sources, including errors made during replication of undamaged template DNA, mutagenic nucleotide substrates, and endogenous DNA lesions.
What are the causes of induced mutation?
Induced mutations on the molecular level can be caused by:Chemicals. Hydroxylamine. Base analogs (e.g., Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU)) ... Radiation. Ultraviolet light (UV) (including non-ionizing radiation). Two nucleotide bases in DNA—cytosine and thymine—are most vulnerable to radiation that can change their properties.
What are 3 examples of causes of mutation?
Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents. Mutations may be spontaneous in nature.
What is an example of a spontaneous mutation?
Examples of spontaneous mutation are pink eyes, brown coat, or piebald coat traits in house mice and a wild animal born naturally with black eyes instead of typical green eyes.
What causes a spontaneous mutation in a gene quizlet?
Spontaneous mutations are a result of an error in DNA replication or mobile genetic elements. Induced mutations are caused by agents that damage DNA in some way.
What do you mean by spontaneous and induced mutation?
Spontaneous mutations occur naturally and mainly due to error in replication. Induced mutations occur due to physical or chemical agents. Occurs due to slippage in natural processes. Induced by mutagens. Caused due to replication error, tautomeric shift, transposable genetic elements, unequal cross overs, etc.
What are the types of spontaneous mutations?
All types of mutations are produced spontaneously, i.e., base substitutions, frameshifts, insertions and deletions.
What is the difference of spontaneous and induced mutation?
Spontaneous mutations are produced by naturally occurring mutagenic agents such as electric currents, atomic particles and rays, temperature, variations, etc. whereas induced mutations are produced by subjecting organism artificially to mutagens such as gamma rays, X-rays, neutrons, ultraviolet rays, etc.
What are 3 ways a mutation can occur in the DNA?
There are three types of DNA Mutations: base substitutions, deletions and insertions.
What are the two types of causes of mutations?
Mutations result either from accidents during the normal chemical transactions of DNA, often during replication, or from exposure to high-energy electromagnetic radiation (e.g., ultraviolet light or X-rays) or particle radiation or to highly reactive chemicals in the environment.
What causes mutations quizlet?
Mutations can be caused by environmental agents such as ultraviolet light (sunshine), nuclear radiation, or certain chemicals. Other times, mutations occur when a cell copies its DNA during replication in preparation for cell division.
What is responsible for spontaneous mutation?
Spontaneous mutations are "the net result of all that can go wrong with DNA during the life cycle of an organism" (Glickman et al., 1986). Thus, the types and amounts of spontaneous mutations produced are the resultant of all the cellular processes that are mutagenic and those that are antimutagenic.
What is the most common cause of genetic mutations?
Environmental factors (also called mutagens) that could lead to a genetic mutation include: Chemical exposure. Radiation exposure. Smoking.
How common are spontaneous mutations?
Data from several studies on eukaryotic organisms shows that in general the spontaneous mutation rate is 2-12 x 10-6 mutations per gamete per gene.
What is the main cause of spontaneous mutations in an organism's genetic material?
Mutations in DNA occur for different reasons. For example, environmental factors, such as exposure to ultraviolet radiation or certain chemicals, can induce changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can also occur because of hereditary factors.
What is the use of induced mutation?
Geneticists utilize induced mutation to create mutants that help understand the effects of mutation on the phenotype of cells. It is also employed...
What is induced mutation?
An induced mutation is the type of mutation that occurs once an organism's DNA is exposed to a mutagen. Mutagens can be physical or chemical agents.
What is an example of induced mutation?
An example of induced mutation is a change of sex cell genes. The exposure of the gonads to mutagens such as radiation leads to mutation of the sex...
What causes a spontaneous mutation?
Spontaneous mutation occurs naturally with no known cause. However, it may arise from the activities of a normal cell, such as errors that occur du...
What is spontaneous mutation in microbiology?
A spontaneous mutation is a type of mutation that occurs naturally, in the absence of mutagens. Mutagens are agents that cause mutation, such as x-...
What is the difference between spontaneous and induced mutations?
Thus, spontaneous mutations are unpredictable changes in the DNA caused due to errors in replication , whereas, induced mutations are caused by physical, chemical or biological agents.
What is Spontaneous Mutation?
Spontaneous mutations are caused by the non – repaired errors that take place during the DNA replication process. These errors can either lead to transitions between nucleotide bases or transversions between bases. The transition of bases results when a purine ( adenine) is replaced by another purine base ( guanine) or a pyrimidine base ( thymine) is replaced by another pyrimidine ( cytosine ). Transversion of bases refers to the replacement of purine base by a pyrimidine base and vice versa. Spontaneous mutations are caused mainly due to chemical mutagens such as intercalating agents, alkylate guanidine, nitric oxide and radiation types such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, etc. The rate of a spontaneous mutation varies rapidly, and diseases caused due to spontaneous mutations mainly arise from chromosomal aberrations caused by the mutation.
What are the two main categories of mutations?
Mutations are mainly divided into two main categories based on the causation of the mutation. They are Spontaneous Mutations and Induced Mutations. Spontaneous Mutations are the mutations that are unpredictable and occur due to errors in replication of DNA.
What are mutations in DNA?
Mutations are referred to as changes in the DNA sequence of an organism that would result in a phenotypic change, either beneficial or harmful. Mutations can also be silent mutations that will not affect the phenotype. Mutations have contributed much towards the evolution of species. Mutations are mainly divided into two main categories based on the causation of the mutation. They are Spontaneous Mutations and Induced Mutations. Spontaneous Mutations are the mutations that are unpredictable and occur due to errors in replication of DNA. Induced mutations are the mutations that are caused by known physical, chemical or biological agents. These mutations are caused due to exposure to these agents, resulting in a change in DNA sequences. The key difference between spontaneous and induced mutations is the causative agents of these mutations. Thus, spontaneous mutations are unpredictable changes in the DNA caused due to errors in replication, whereas, induced mutations are caused by physical, chemical or biological agents.
What type of cancer is caused by induced mutation?
Specific cancer types such as skin cancers caused due to induced mutation arose due to continuous exposure to radiation.
Which radiation type is more prone to mutations?
Thus, workers who are dealing with harmful chemicals and heavy metals, radiation types such as x – rays are more prone to induced mutations. Figure 01: Skin Cancer. These type of mutations can be prevented by creating awareness on mutagens are by using proper safety precautions when handling the mutagens.
Can mutations be predicted?
Therefore, in induced mutations, the cause of the mutation can be predicted. These mutations also result in transitions and transversions of bases. The occurrence of the mutation depends on the dose of the mutation and the frequency of direct or indirect exposure to the mutagen. Therefore, individuals who are exposed to mutagens frequently are more ...
