Examples of Lever Simple Machine
- Nut Cracker. A nutcracker is a prominent example of a second-class lever simple machine. ...
- Seesaw. Seesaws demonstrate the working of a first-class lever simple machine in the simplest possible way. ...
- Scissors. ...
- Plier. ...
- Stapler. ...
- Wheelbarrow. ...
- Human body. ...
- Broom. ...
- Hammer. ...
- Balance Scale. ...
- Nut Cracker. A nutcracker is a prominent example of a second-class lever simple machine. ...
- Seesaw. Seesaws demonstrate the working of a first-class lever simple machine in the simplest possible way. ...
- Scissors. ...
- Plier. ...
- Stapler. ...
- Wheelbarrow. ...
- Human body. ...
- Broom.
What are some examples of a first class lever?
- Transferring where the force is applied to where it acts
- Changing the distance over which the force is applied or the speed with which it is applied
- Changing the direction of the applied force to that of the acting force
- Increasing the magnitude of the acting force over that of the applied force
What kind of simple machine is a lever?
They are the:
- Lever
- Wheel and axle
- Pulley
- Inclined plane
- Wedge
- Screw
How are the 6 types of simple machines work?
Work is performed by applying a force over a distance. These six simple machines create a greater output force than the input force; the ratio of these forces is the mechanical advantage of the machine. All six of the simple machines listed here have been used for thousands of years, and the physics behind several of them were quantified by the Greek philosopher Archimedes (ca. 287–212 BCE).
What are the 7 Simple Machines?
Seven Simple Machines synonyms, Seven Simple Machines pronunciation, Seven Simple Machines translation, English dictionary definition of Seven Simple Machines. n. Any of numerous basic devices that alter the magnitude or direction, or both, of an applied force, traditionally including the lever, wedge, inclined...
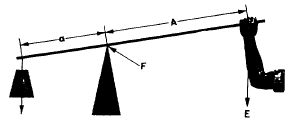
What is an example of a lever simple machine?
The Load (nail) and Fulcrum are close to each other which makes it easier to remove a nail with the hammer. Wheelbarrows, fishing rods, shovels, brooms, arms, legs, boat oars, crow bars, and bottle openers are all examples of levers. Levers may be one of the most used simple machine.
What are some examples of levers?
Examples of levers in everyday life include teeter-totters, wheelbarrows, scissors, pliers, bottle openers, mops, brooms, shovels, nutcrackers and sports equipment like baseball bats, golf clubs and hockey sticks. Even your arm can act as a lever.
What are 3 levers examples?
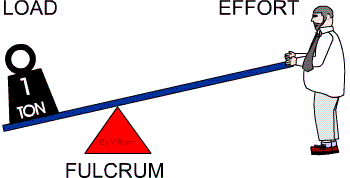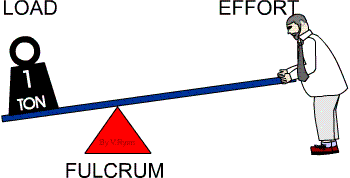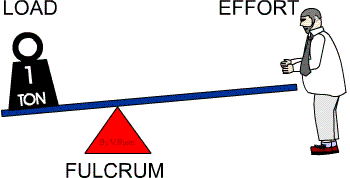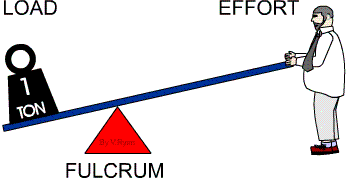
Other examples of first class levers are pliers, scissors, a crow bar, a claw hammer, a see-saw and a weighing balance. In summary, in a first class lever the effort (force) moves over a large distance to move the load a smaller distance, and the fulcrum is between the effort (force) and the load.
What are the 3 types of levers simple machines?
There are three types of lever.First class lever – the fulcrum is in the middle of the effort and the load.Second class lever – the load is in the middle between the fulcrum and the effort.Third class lever – the effort is in the middle between the fulcrum and the load.
What are 10 examples of a lever?
Examples of Lever Simple MachineNut Cracker. A nutcracker is a prominent example of a second-class lever simple machine. ... Seesaw. Seesaws demonstrate the working of a first-class lever simple machine in the simplest possible way. ... Scissors. ... Plier. ... Stapler. ... Wheelbarrow. ... Human body. ... Broom.More items...
What are 5 examples of a lever found in your home?
Lever Simple Machine Examples at Homebalance scale.bottle opener.broom.claw end of a hammer.door.fishing rod.handheld garlic press.handheld juicer.More items...
Is a pencil a lever?
Other Class 3 levers include: spoons, pencils, golf clubs, canoe paddles, the human arm, catapult and hoe. Tweezers and tongs each have two Class 3 levers.
What are some levers in your house?
Household leverspair of scissors or hole punch and scrap paper.clothes peg.nutcrackers and nuts in their shell e.g. almonds.claw hammer and small nails hammered into a piece of wood.Stapler and paper to staple.Tweezers or tongs.Chopsticks.
Are scissors a lever?
The "fulcrum" is the point on which the lever turns or balances. In the case of a fork, the fulcrum is the fingers of your hand. Scissors are really two levers put together. The handle on the toilet flusher is commonly called a fixed lever.
Is a light switch a lever?
A light switch, scissors, garage gate, broom, toaster handle, oven or refrigerator door are examples of a lever.
How is a hammer a lever?
A hammer acts as a third-class lever when it is used to drive in a nail: the fulcrum is the wrist, the effort is applied through the hand, and the load is the resistance of the wood.
What is a class 2 lever examples?
In a Class Two Lever, the Load is between the Force and the Fulcrum. The closer the Load is to the Fulcrum, the easier the load is to lift. Examples include wheelbarrows, staplers, bottle openers, nut cracker, and nail clippers.
What are some examples of levers?
Some examples of levers include more than one class, such as a nut cracker, a stapler, nail clippers, ice tongs and tweezers. Levers may be one of the most used simple machine.
What are levers in everyday life?
Examples of levers in everyday life include teeter-totters, wheelbarrows, scissors, pliers, bottle openers, mops, brooms, shovels, nutcrackers and sports equipment like baseball bats, golf clubs and hockey sticks. Even your arm can act as a lever.
How is a lever used today?
Examples of levers in everyday life include teeter-totters, wheelbarrows, scissors, pliers, bottle openers, mops, brooms, shovels, nutcrackers and sports equipment like baseball bats, golf clubs and hockey sticks. Even your arm can act as a lever.
What are the 10 simple machines?
The simple machines are the inclined plane , lever, wedge, wheel and axle, pulley, and screw.
Is a hammer a lever?
A hammer acts as a third-class lever when it is used to drive in a nail: the fulcrum is the wrist, the effort is applied through the hand, and the load is the resistance of the wood.
Are scissors a lever?
Examples include see-saws, crow bars, hammer claws, scissors, pliers, and boat oars. The claw end of a hammer, along with the handle, is a Class 1 Lever. The fulcrum is the point where the scissor blades are joined together. The force or effort is the end or handle of the scissors.
Is a door handle a lever?
The door handle has only a lever handle which operates this latch. Pushing the handle down rotates the spindle, operating the tubular latch mechanism inside the door, allowing it to be opened. The lever latch handle is easy to install and use, and is available in a variety of styles and finishes.
What is a lever in the body?
A lever is a rigid rod (usually a length of bone) that turns about a pivot (usually a joint). In our bodies bones act as lever arms, joints act as pivots, and muscles provide the effort forces to move loads. There are four parts to a lever – lever arm, pivot, effort and load. In our bodies: bones act as lever arms.
How does a lever system work?
Lever Systems. The operation of most skeletal muscles involves leverage – using a lever to move an object. A lever is a rigid bar that moves on a fixed point called the fulcrum, when a force is applied to it. The applied force, or effort, is used to move a resistance, or load.
What are some examples of levers?
Some examples of levers include more than one class, such as a nut cracker, a stapler, nail clippers, ice tongs and tweezers. Other levers, called single class levers include the claw end of a hammer. When pulling a nail, the nail is the Load, the Fulcrum is head of the hammer, and the Force is at the other end of the handle, which is the Beam.
What is a lever?
Levers Examples. Levers. A lever could be something as simple as a wooden board with a ridge that freely rotates or moves on a pivot. The most common and popular lever can be found in many playgrounds: a see-saw or teeter-totter.
How does a lever work?
How it works: If one end of the lever is pushed down, the force will lift the other end. If the other end has a load on top of it , it will be easier to move the load. The lever makes the work easier. Think of a boy and girl on a see saw.
What are the parts of a lever?
All levers have four basic parts: Beam- The lever, a wooden plank or metal bar resting on the fulcrum. Fulcrum- the pivot or the turning point. Force- the effort or input needed to move the beam and load. Load- the item or object being moved or lifted on the plank.
What is lever machine?
The lever is a type of simple machine. Learn about the different classes of levers and how they provide mechanical advantage. Simple machines are mechanical devices that are used to make work easier. Combinations of two or more simple machines working together are called compound machines. These machines create systems for different kinds ...
What are some examples of first class levers?
If the fulcrum is closer to the effort, then more effort is needed to move the load a greater distance. A teeter-totter, a car jack, and a crowbar are all examples of first class levers. First class levers are very useful for lifting large loads with little effort.
What is a Lever?
A lever is a simple machine made of a rigid beam and a fulcrum. The effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. The fulcrum is the point on which the beam pivots. When an effort is applied to one end of the lever, a load is applied at the other end of the lever. This will move a mass upward. Levers rely on torque for their operation. Torque is the amount of force required to cause an object to rotate around its axis (or pivot point).
What are the basic parts of a lever?
Basic parts of a lever showing the locations of the beam, fulcrum, effort and load (© 2019 Let’s Talk Science).
What is the mechanical advantage of a lever?
A lever provides mechanical advantage. Mechanical advantage refers to how much a simple machine multiplies an applied force. The location of the effort, load, and fulcrum will determine the type of lever and the amount of mechanical advantage the machine has. The farther the effort is away from the fulcrum, the easier it is to move the load.
Where is the load located in a second class lever?
In a second class lever, the load is located between the effort and the fulcrum. When the fulcrum is closer to the load, then less effort is needed to move the load (©2020 Let’s Talk Science).
Do machines have motors?
When you hear the word “machine” do you automatically think of something with a motor, like a forklift or a washing machine? Machines do not have to have motors. In fact, a machine is any device that transmits or modifies force.
What is a Lever?
A lever is simply a plank or ridged beam that is free to rotate on a pivot. It is perfect for lifting or moving heavy things. It is a useful simple machine, and you can find them everywhere. Good examples of levers include the seesaw, crowbar, fishing-line, oars, wheelbarrows, and the garden shovel.
How does a lever work?
A lever makes work easier by both increasing your input force and changing the direction of your input force.
What are the parts of a lever?
Parts of a lever. Levers have four important parts — the bar or beam, the fulcrum (the pivot or the turning point), effort (or force), and the load. The beam is simply a long plank. It may be wood, metal, or any durable material. The beam rests on a fulcrum (a point on the bar creating a pivot). When you push down one end ...
What is the mechanical advantage of a class one lever?
The mechanical advantage is more if the Load is closer to the fulcrum. Examples of Class One Levers include seesaws, boat oars, and crowbar. In this class, the Load is between the Effort and the Fulcrum. The mechanical advantage is more if the load is closer to the fulcrum.
Is the fulcrum of a lever always the same?
The parts of the lever are not always in the same arrangement. The load (L), fulcrum (F), and effort (E) may be at different places on the plank. In this class, the Fulcrum is between the Effort and the Load. The mechanical advantage is more if the Load is closer to the fulcrum.
What is a lever in a machine?
A lever is a simple machine that involves a bar or board moving on a pivot point. The pivot point on a lever is called a fulcrum. Looking at a see-saw on a playground, the fulcrum is placed between the two people on the see-saw. There are three categories of a lever based on the position of the fulcrum compared to where the force is being applied and the load rests.
What are the three basic types of simple machines?
The three most basic simple machines are inclined planes, levers, and pulleys. The following table shows a brief description and examples of the three types before more fully defining each one in the following sections.
How many newtons does a single pulley produce?
A single pulley cuts the workload in half. So if a force of 50 newtons is applied to the rope, the output will be 100 newtons. With a system of pulleys, the mechanical advantage changes by the addition of each pulley. So a double pulley system would have a MA of 2, so the amount of input would reduce to 25 newtons to produce 100 newtons of force.
What is a pulley?
Pulleys are simple machines that are used to transmit energy and motion. A pulley contains a wheel that holds a flexible rope, chain, cord, or belt and can either move or turn objects. While the pulley is considered a simple machine, it has more parts than the inclined plane and the lever. The wheel on the pulley has to have a groove where the rope or other flexible material can sit without slipping off. This groove is called a sheave. Pulleys can also be fixed or loose. The pulley on a flagpole is loose, which allows the wheel to pivot around giving the person pulling the rope flexibility to move.
What is an elevator pulley?
Elevators: Elevators utilize a pulley system with a motor. The motor pulls on wires that are running through pulleys putting far less strain on the motor than directly pulling up the heavy elevator car.
What is a pulley that is fixed to a garage door opener called?
When the pulley is fixed into place and cannot move, it's called a belt drive . The pulley that is fixed to a garage door opener uses a belt drive . It doesn't pivot around because the opener machine itself doesn't move.
Why are pulleys simple machines?
Pulleys are simple machines because they have very few parts and are used to lessen the workload. Most pulleys are designed to lift or pull objects.
