Some examples of chytrids include:
- Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis: Causes chytridiomycosis, an amphibian disease
- Synchytrium endobioticum: Causes potato wart when it comes into contact with crops
- Olpidium brassicae: Parasitic plant fungus
- Polyphagus euglena: Algae parasite
- Rhizophydium harderi: Fungi found in freshwater and ocean water
How many Chytridiomycota are there?
The class Chytridiomycetes has over 750 chytrid species distributed among ten orders.
What are most chytrids?
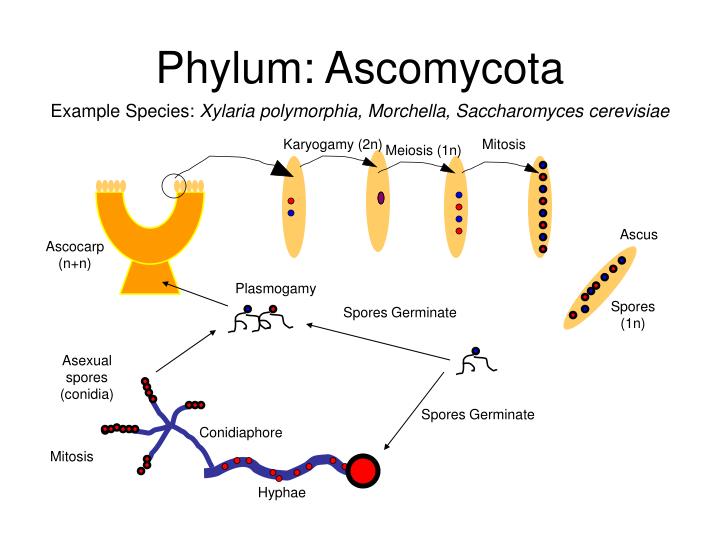
Most chytrids are unicellular; a few form multicellular organisms and hyphae, which have no septa between cells (coenocytic). They reproduce both sexually and asexually; the asexual spores are called diploid zoospores. Their gametes are the only fungal cells known to have a flagellum.
Where do you find Chytridiomycota?
Chytridiomycota, a phylum of fungi (kingdom Fungi) distinguished by having zoospores (motile cells) with a single, posterior, whiplash structure (flagellum). Species are microscopic in size, and most are found in freshwater or wet soils. Most are parasites of algae and animals or live on organic debris (as saprobes).
Why are Chytridiomycota important to humans?
Because Chytridiomycota often feed on decaying organisms, they are important decomposers. While this is an important function, Chytridiomycota can also have a negative impact on human produce, particularly Synchytrium endobioticum, the species that causes potato wart.
What type of fungus is chytrid?
Chytridiomycosis is caused by two species of microscopic fungi Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (“Bd”) and B. salamandrivorans (“Bsal”), which are often simply referred to as “chytrid”.
Why is Glomeromycetes important?
Members of the Glomeromycota, are responsible for forming mutualistic associations called endomycorrhizae with the roots of about 70% of the world's plants. These endomycorrhizae are also known as arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, abbreviated AMF.
What are the characteristics of Chytridiomycota?
Chytridiomycota cells are coenocytic with no distinction between individual cells. The filaments are long and tubular with a cytoplasm lining and large vacuole in the center. These single-celled organisms have branching hyphae with rhizoids and produce gametes with flagelli.
How is Chytridiomycota transmitted?
Chytrid fungus is probably transferred by direct contact between frogs and tadpoles, or through exposure to infected water. The disease may not kill frogs immediately, and they can swim or hop to other areas before they die, spreading fungal spores to new ponds and streams.
Can Chytridiomycota cause disease?
Chytridiomycosis is an infectious disease that affects amphibians worldwide. It is caused by the chytrid fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis), a fungus capable of causing sporadic deaths in some amphibian populations and 100 per cent mortality in others.
How does Chytridiomycota eat?
Chytrids are fungi in the phylum Chytridiomycota. They have motile spores and are primarily aquatic organisms. Like all fungi, chytrids live in their food and have an absorptive mode of nutrition in which they secrete digestive enzymes and absorb the breakdown products.
What are some examples of Glomeromycota?
Gigaspora...Diversispo...GeosiphonAcaulospo...Diversispo...Acaulospora morrowiaeGlomeromycota/Lower classifications
Are most chytrids Heterotrophs?
Chytrids are heterotrophs, like all fungi and like humans. Like humans they sometimes consume dead materials (i.e. are saprophytes) but also may consume living materials, in which case the chytrids may act as a parasite or predator.
How many species of chytrids are there?
There are approximately 1,000 chytrid species, in 127 genera, distributed among 5 orders. Both zoospores and gametes of the chytrids are mobile by their flagella, one whiplash per individual. The thalli are coenocytic and usually form no true mycelium (having rhizoids instead).
Are all chytrids parasitic?
There is considerable variation in the morphology and ecology of chytrids. Some are freshwater, some marine; some are parasites on plants and dipterans, while others live on decaying plants and insect parts.
What is the phylum of fungi?
phylum of fungi. ... (Show more) Chytridiomycota, a phylum of fungi (kingdom Fungi) distinguished by having zoospores (motile cells) with a single, posterior, whiplash structure (flagellum). Species are microscopic in size, and most are found in freshwater or wet soils. Most are parasites of algae and animals or live on organic debris (as saprobes).
What is the cause of amphibian chytridiomycosis?
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, fungus isolated as the cause of amphibian chytridiomycosis.…
What is the name of the parasite that causes plant diseases?
Most are parasites of algae and animals or live on organic debris (as saprobes). A few species in the order Chytridiales cause plant disease, and one species, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, has been shown to cause disease in frogs and amphibians.
Is chytridiomycota a restricted order?
The Chytridiomycota is ret ained but in a restricted sense. One of Chytridiomycota ’s traditional orders, the Blastocladiales, has been raised to phylum status as the Blastocladiomycota. Similarly, the group…. fungus: Annotated classification.
What order is Zygomycota in?
Phylum: Zygomycota – Order: Mucorales: no zoospores; produce conidia in sporangia; mycelium nonseptate; survive as zygospores; most are saprophytic but a few are weak plant pathogens causing bread molds ( Figure 13 (b)) and fruit rots ( Figures 3 (b) and 3 (c)) in storage.
How many phyla are there in the Eumycota?
The superphylum Eumycota includes eight phyla and one clade (Shearer et al. 2007; Baldauf, 2003, 2008; Gleason et al., 2017a). Four phyla (the Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota) produce only walled spores and are not considered to be zoosporic true fungi. Four phyla and one clade (the Olpidium clade, Monoblepharidomycota, Blastocladiomycota, Neocallimastigomycota, and Chytridiomycota) produce uniflagellated chemotactic zoospores or rarely amoebae during asexual reproduction and therefore are included in the zoosporic true fungi. The morphological and molecular characteristics of the four phyla of zoosporic true fungi have been reviewed thoroughly by James et al. (2014) and by Powell and Letcher (2014). We focus only on the Chytridiomycota in the next section because of the recent interest in research in evolution of ancient zoosporic fungi.
What phylum produces sexual spores?
Phylum: Basidiomycota – have mycelium, often with binucleate cells, sexual spores (basidiospores) produced externally on a clublike structure called a basidium; some of them produce several types of spores and spore-bearing structures, namely, basidiospores on basidia, spermatia in spermagonia; aeciospores in aecia; uredospores in uredia; and teliospoes in telia; rusts are very serious diseases of grain ( Figures 12 (a) and 12 (b) ), of beans and soybeans, and other crops, and of trees. Basidiomycetes also include the smuts of grain crops ( Figures 12 (a) and 12 (b) ), and the root rots, wood rots, and decays of trees ( Figures 12 (c)–12 (e)) and timber.
What kingdom is fungus?
The true fungi. Kingdom: Fungi. Phylum: Chytridiomycota – have round or limited elongated nonseptate mycelium, restricted to the host plant, and, alone among the fungi, produce motile zoospores and survive as sporangia. Cause few plant diseases, for example, wart of potato.
What causes white rot on vegetables?
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, causing the white rot or watery soft rot of vegetables ( Figures 14 (a) and 14 (b) ). Athelia ( Sclerotium) and Thanatephorus ( Rizoctonia ), causing root and stem rots of vegetables and fleshy ornamentals and soft rots of fleshy leaves and fruits.
What causes rust on cereals?
Puccinia, causing the devastating rust diseases of cereals, and other plants. Cronartium, the rust of pine trees. Gymnosporangium, the cedar-apple rust. Hemileia, the coffee rust.
What order are glomales in?
Order: Glomales: Form vascular – arbuscular mycorrhizae within roots of host plants. Phylum: Ascomycota – Recent, 2007, taxonomic studies have placed most of the 32 000 species of Ascomycetes in the subphylum Pezizomycotina.
What fungi have flagella?
The Chytrids are the only fungi that have retained flagella. They produce both gametes and diploid zoospores that swim with the help of a single flagellum. An unusual feature of the chytrids is that both male and female gametes are flagellated. The ecological habitat and cell structure of chytrids have much in common with protists.
What phylum are fungi in?
Identify characteristics and examples of fungi in the phylum Chytridiomycota
Where do chytrids live?
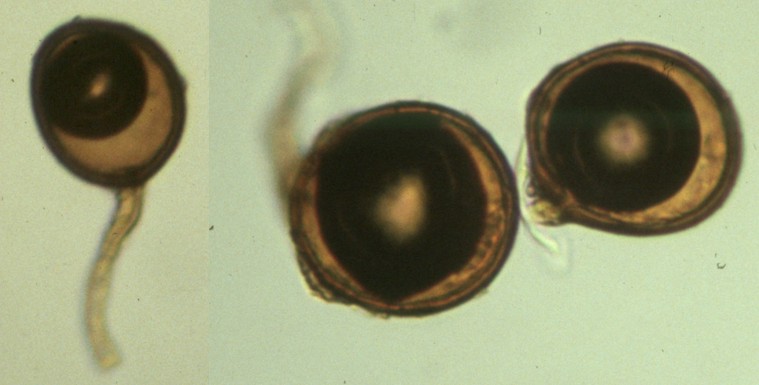
Chytrids usually live in aquatic environments , although some species live on land. Some species thrive as parasites on plants, insects, or amphibians (Figure 1), while others are saprobes. The chytrid species Allomyces is well characterized as an experimental organism.
Do chytrids have chitin?
Like all fungi, chytrids have chitin in their cell walls, but one group of chytrids has both cellulose and chitin in the cell wall. Most chytrids are unicellular; however, a few form multicellular organisms and hyphae, which have no septa between cells (coenocytic). The Chytrids are the only fungi that have retained flagella.
Is Allomyces a diploid or haploid?
Allomyces produces diploid or haploid flagellated zoospores in a sporangium. Figure 1. The chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is seen in these light micrographs as transparent spheres growing on (a) a freshwater arthropod and (b) algae.
Key Points
The first recognizable chytrids appeared more than 500 million years ago during the late pre-Cambrian period.
Chytridiomycota: The Chytrids
The kingdom Fungi contains five major phyla, which were established according to their mode of sexual reproduction or use of molecular data. The Phylum Chytridiomycota (chytrids) is one of the five true phyla of fungi. There is only one class in the Phylum Chytridiomycota, the Chytridiomycetes.