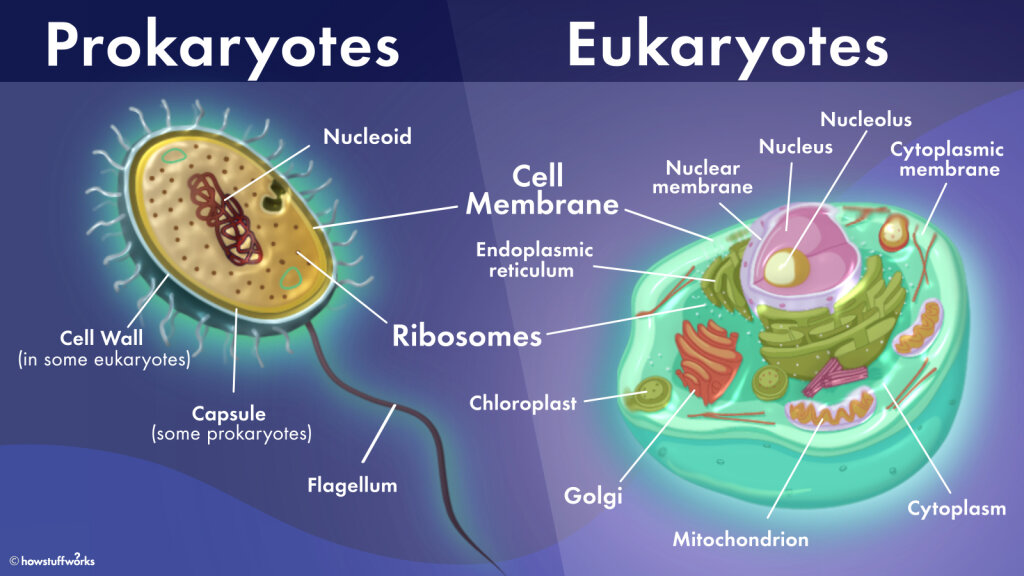
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes | |
| Type of Cell | Always unicellular | Unicellular and multi-cellular |
| Cell size | Ranges in size from 0.2 μm – 2.0 μm in d ... | Size ranges from 10 μm – 100 μm in diame ... |
| Cell wall | Usually present; chemically complex in n ... | When present, chemically simple in natur ... |
| Nucleus | Absent. Instead, they have a nucleoid re ... | Present |
What kinds of organisms have prokaryotic cells?
May 05, 2020 · Examples of Eukaryotic Cells: Animals such as cats and dogs have eukaryotic cells. Plants such as apple trees have eukaryotic cells. Fungi such as mushrooms have …
What are 2 examples of prokaryotes?
6 rows · Fungi, plants, and animals are made of eukaryotic cells (eukaryotes). Prokaryotic cells do ...
What are some examples of organisms that are prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Examples of eukaryotic cells. Neuron; Euglena; Amoeba; Red blood cell; Paramecium; Examples of prokaryotic cells. Eubacteria; Spirochetes; Mycoplasmas; Blue-green algae; Methanogens
Are prokaryotes more complex than eukaryotic cells?
Examples of prokaryotic cells: The cells of; a germ, paramecium, amoeba, bacillus, diatom, streptococcus, Pseudomonas(basically any microorganism or plant you can think of) …

What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells?
- E. coli (Escherichia Coli Bacterium)
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
- Bacillus anthracis.
- Bacillus cereus.
What are 4 examples of eukaryotic cells?
- Plant cell.
- Animal cell.
- Fungi.
- Amoebae.
What are 3 examples of prokaryotic cells?
What are 2 examples of prokaryotic cells?
What are 10 examples of eukaryotes?
- Animal cells. (Humans, Dog, cat)
- plant cells.
- fungi. (Yeast, Rhizopus, mushrooms)
- algae. (Golden Algae, Brown algae)
- Protozoa. (Amoeba, Rhizopoda)
- Eukaryotic Cell: • Eukaryotic cells are the cells, which contains nucleus in them. •
What are 5 examples of eukaryotes?
- Animals such as cats and dogs have eukaryotic cells.
- Plants such as apple trees have eukaryotic cells.
- Fungi such as mushrooms have eukaryotic cells.
- Protists such as amoeba and paramecium have eukaryotic cells.
- Insects have eukaryotic cells.
- Humans are composed entirely of eukaryotic cells.
What are 2 examples of eukaryotic cells?
All animals, plants, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic cells. Their cells are organized into compartmentalized structures such as nuclei, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and Golgi bodies.Mar 1, 2021
What are 3 examples of eukaryotes?
What are 10 examples of prokaryotic cells?
- Escherichia coli bacterium.
- Streptococcus bacterium.
- Sulfolobus acidocaldarius archeobacterium.
- streptococcus pyogenes.
- lactobacillus acidophilus.
- Cyanobacteria.
- Archaea.
What are 4 examples of prokaryotic cells?
- Escherichia Coli Bacterium (E. coli)
- Streptococcus Bacterium.
- Streptomyces Soil Bacteria.
- Archaea.
What is an eukaryotic cell and what is an example of one?
Is a tree eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
The most obvious difference between them is that prokaryotes have no nuclei, but there are four major differences between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell: No prokaryotic cell has a nucleus; every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells have no mitochondria;
What is the nucleus of an eukaryotic cell?
The word eukaryote comes from two Greek roots, eu (good, well), and karyon (nut, kernel), so a eukaryote has a well-defined or “good” nucleus (kernel) in its cells.
How do prokaryotic cells recycle nutrients?
Facts About Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotes help recycle nutrients by decomposing dead organisms. Bacteria in the intestines and mouths of all higher animals help with the digestion of food. The DNA of a prokaryotic cell is tightly coiled in a ‘nucleoid,’ which is not a true nucleus since it has no membrane.
Which type of cell has intracellular structures?
Intracellular structures are common to both types of cells. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have:
Which type of cell has circular DNA?
Prokaryotic cells have circular strands of DNA; eukaryotic cells have multiple molecules of double-stranded, linear DNA.
Where do eukaryotes store DNA?
Eukaryotic cells store chromatin (DNA and proteins) in a gel-like fluid called the nucleoplasm, inside the nucleus.
Why do all living things use cellular organization?
All living organisms use cellular organization to create structures to conduct life processes. Cells organize into tissues, which organize into organs, which organize into amazing life forms like plants, fungi, dogs, ducks, and people.
Which kingdoms are made up of eukaryotic cells?
Within this membrane are the chromosomes that store the organism’s genetic information. All organisms in the animal kingdom, plant kingdom, fungi, and protist kingdom are made up of eukaryotic cells. For instance: the protista plasmodium, the animal cells present in a lobster, the plant cells present in a jacaranda.
Which type of cell does not have a nucleus?
Prokaryotic cells. They do not have a defined nucleus and lack a nuclear membrane. Its genetic material is scattered in the cytoplasm, barely gathered in an area called the nucleoid. Bacteria and archaea are the two types of organisms with prokaryotic cells. For instance: methanogenic archaea or pseudomonas bacteria.
How do haploid cells reproduce?
They reproduce through mitosis (two genetically identical daughter cells originate from a progenitor cell) and meiosis (four genetically different haploid cells arise from a diploid progenitor cell).
What is the nucleus of a human cell?
The nucleus of a eukaryotic human cell stores its genetic information.
Do plants have a cell wall?
Plant cells have a cell wall composed of cellulose. Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
What are some examples of prokaryotic cells?
Some examples of prokaryotic cells are as follows: Azotobacter vinelandii.
What are eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells occur in protists, plants, fungi and animals to include humans. They have a membrane that separates their nucleus from the cytoplasm. They are generally larger with a size of 10-100 um. Included in these are Euglena, dinoflagellates, Plasmodium (causes malaria), amobeas and many more.
What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
The distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is considered to be the most important distinction among groups of organisms. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not.
Which is larger, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
A typical eukaryotic cell is always larger than a prokaryotic cell, for example hepatocytes have a diameter of 20-30 µ as compared to 1-2 µ for bacteria. Eukaryotic cells are present in all multicellular organisms, both plants and animals.
Where do prokaryotic cells live?
Prokaryotic cells occur in bacteria and in archaea. Archaea are single-celled organisms that are not bacteria. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Rather they have a nucleoid area that is not separated from the rest of the cell by a membrane. They typically have a much smaller genome than do eukaryotic cells. They reproduce asexually by binary fission. They are generally small with a size commonly of 1-5 um (micrometer). However, the Epuloiscium fishelsoni, which lives in the surgeonfish, is an extreme example that is about 1/2 millimeter long. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a pathogen that cau
Which organisms have a nucleus?
Archaea. Bacteria. Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) Contrary to prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes. In eukaryotic cell, all the intracellular components such as , DNA, RNA, proteins and metabolites are located in separate cellular compartment.
What are the two domains of prokarya?
Prokarya include the two domains bacteria (streptococcus, E.coli, cyanobacteria) and archaea (euryarchaeota, crenarchaeota, nanoarchaeota).
Which is smaller, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Scientists speculate that these organisms gave rise to the eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are comparatively smaller and much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus.
What is the meaning of eukaryotic cell?
The term “ Eukaryotes ” is derived from the Greek word “ eu “, (meaning: good) and “ karyon ” (meaning: kernel), therefore, translating to “ good or true nu clei .”. Eukaryotes are more complex and much larger than the prokaryotes. They include almost all the major kingdoms except kingdom monera.
What are the structures that help in cellular respiration?
It is also one of the smallest components within the cell. Some prokaryotic cells contain special structures called mesosomes which assist in cellular respiration.
What is the nucleus of a cell?
The nucleus contains DNA, which is responsible for storing all genetic information. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Within the nucleus exists the nucleolus, and it plays a crucial role in synthesising proteins. Eukaryotic cells also contain mitochondria, which are responsible for the creation of energy, which is then utilized by the cell.
Which type of cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the smallest part of a cell?
Right below the protective coating lies the cell wall, which provides strength and rigidity to the cell. Further down lies the cytoplasm that helps in cellular growth, and this is contained within the plasma membrane, which separates the interior contents of the cell from the outside environment. Within the cytoplasm, ribosomes exist and it plays an important role in protein synthesis. It is also one of the smallest components within the cell.
What are the biotic components of the environment?
Biotic components of the environment include all forms of life from minute bacteria to towering giant Sequoias. However, at the microscopic level, all living organisms are made up of the same basic unit – the cell.
