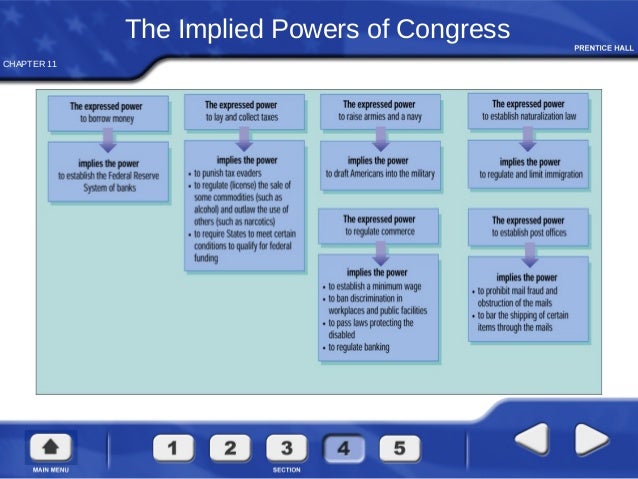
- Declare war.
- Levy taxes.
- Regulate commerce.
- Mint currency.
- Control immigration.
- Establish bankruptcy legislation.
- Punish counterfeiters.
- Create a national post office.
What are 10 powers of Congress?
the enumerated powers of congress. 1 of article 1 section 8. power to tax and spend. 2 of article 1 section 8. power to borrow money. 3 of article 1 section 8. power to regulate commerce. 4 of article 1 section 8. power for naturalization and to regulate bankrupcy. 5 of article 1 section 8.
What are the enumerated powers if Congress?
Congress has authority over financial and budgetary matters, through the enumerated power to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts and excises, to pay the debts and provide for the common defense and general welfare of the United States.
What are the most important powers of Congress?
What are the most important enumerated powers of Congress? The Congress shall have Power To lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defence and general Welfare of the United States; but all Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States; ArtI.
What are 3 examples of implied powers?
Examples of Implied Powers. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. 1. Income Tax. 2. Getting rid of the penny. 3. Military Draft.

What were the implied powers of Congress in the 1940s?
In recent decades, the U.S. Congress has used its implied powers to do the following: 1940: Establishment of mandatory army conscription for men. 1947: Creation of the Air Force. 1965: Establishment of Medicare and Medicaid.
What are the powers of Congress?
In addition to these expressed powers, the United States Congress has established its implied power to do the following: 1 Create a national bank 2 Establish a federal minimum wage 3 Establish a military draft 4 Create gun control laws in some cases
Why is the necessary and proper clause important?
Using the Necessary and Proper Clause, Congress can make the argument that new powers are necessary for the proper running of the country even if they were not originally included in the Constitution. After all, the people who wrote the Constitution clearly intended it as a living document (given the number of amendments added to it) and included the Necessary and Proper Clause with the expectation that the role of government would change over time.
What is implied power?
The phrase implied powers refers to the abilities and powers that a government branch has that are not explicitly stated in the U.S. Constitution but are suggested to be applicable in some or all cases. This implied powers definition is contrasted with the idea of expressed powers, which are the powers that are described in detail in the Constitution or other documents. For instance, the U.S. Congress has the expressed power to collect taxes. As a result of this expressed power, it also has the implied power to punish tax evasion and to determine which items are taxed more heavily than others.
What was the significance of McCulloch v. Maryland?
Maryland was an 1819 court case in which the state of Maryland attempted to impose a tax on the national bank and also questioned the validity of a national bank as an extension of the Necessary and Proper Clause. The Supreme Court had to decide whether the bank was legitimate and whether a state had the right to impose a tax on it.
Why are implied powers clear?
Some implied powers are clear because they naturally follow expressed powers. For instance, the expressed power of Congress to raise an army implies the power to establish a military draft if needed. However, many examples of implied power actually come from a very specific expressed power as listed in the Constitution.
What are the two types of congressional powers?
There are two types of congressional power in the United States: expressed power, which is detailed in Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution, and implied power, which includes the Necessary and Proper Clause (which allows Congress to create any law needed to serve the country) and extensions of other expressed powers.
What are implied powers?
The implied powers of Congress are not described in the Constitution, but provide a way to carry out the powers that are specifically stated in the Constitution. Learn about the definition & real-world examples of implied powers of Congress. Updated: 10/11/2021
What are the powers of Congress?
Constitution describes the actual powers of Congress. These powers are called expressed powers (sometimes called delegated or enumerated powers); they are, quite literally, 'expressed' in the document. They are listed, all 27 of them, and they include some clearly important obligations. Some are very concrete: Congress has the power to declare war, for instance, or to levy and collect taxes. Some, however, are less clear. For example, Congress is given the power to 'To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes.' This is pretty straightforward as far as whose commerce the Congress gets to regulate. But what, exactly, is commerce? And what does it mean to regulate it?
What does the need and proper clause mean?
The very existence of the 'necessary and proper' clause indicates that the Framers knew the government would change and take on additional obligations. But the existence of implied powers was one thing; actually saying so was another. It took a Supreme Court case to bring the concept of implied powers to life.
What is the last listed power of Congress?
The last listed power of Congress is much more vague than the Commerce clause. It says that Congress has the power 'to make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof.' Simply put, this means that Congress can make any law it sees as 'necessary and proper' in order to carry out its expressed powers.
Who has the power to raise an army?
For instance, Congress has the power to raise an army and if Congress deems it 'necessary and proper' that this army should be filled with a national draft, it would have the power, under this clause, to pass a law establishing one.
What did Maryland try to tax?
In 1819, the state of Maryland tried to tax an institution of the federal government, the Bank of the United States. The Bank's existence is a great example of implied powers: the Constitution doesn't say that Congress has the right to establish a bank, but its defenders claimed that one was necessary to carry out the Congress' power to collect taxes. So the Supreme Court had to decide: can a state tax a federal bank? And did Congress have the right to create one?
Why did the government use the implied powers clause?
Using the expressed powers as a guide, the government would be able to use the “necessary and proper” clause to meet the ever-expanding needs of the American people.
What is the implied power?
Implied powers are created from Clause 18 in Article 1, Section 18 of the U.S. Constitution. This clause is called the “necessary and proper” clause or “elastic clause.”. It states:
Why is the elastic clause controversial?
While the wording of the elastic clause was meant to make the Constitution timeless, it can lead to controversy because of differences in interpretation and the power it creates. For more, look at the reserved powers under the 10th Amendment.
What is the difference between implied and inherent powers?
The difference between implied and inherent powers is where you will find them. You will not find inherent powers established in the Constitution. That is because inherent powers are those that the government needs to be able to get their job done right. This can include acquiring land or regulating immigration.
Why does the fact that this clause expands the others creates issues?
Additionally, the fact that this clause expands the others creates issues, because questions arise as to where that power stops. This generates controversy from the limitations of the articles and the power they create.
What is the government's power to regulate commerce?
Using their power to regulate commerce, collect taxes, raise an army and establish post offices, to name a few, the government has enacted the following: The U.S. government created the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) using their power to collect taxes.
Which clause is the regulation of tobacco and alcohol under?
Regulation of tobacco and alcohol falls under the implied powers in the commerce clause.
Which section of the Constitution mentions the implied powers of Congress?
The Constitution makes mention of the implied powers of Congress in Article I , Section VIII. Specifically, this section, referred to as the “ necessary and proper clause ,” notes that:
What are implied powers?
Implied Powers. The term “implied powers” refers to those powers of the U.S. government that the Constitution does not refer to by name. Instead, the government assumes the Constitution affords them these powers based on prior decisions related to them, which established precedent. An example of implied powers is Congress passing laws restricting ...
What is the difference between implied powers and express powers?
The difference between implied powers and express powers is that the Constitution does not spell out exactly what implied powers are. However, it does discuss express powers in Article I. Implied powers are those powers that are “necessary and proper” for Congress to be able to fulfill its ...
What are some examples of implied powers?
One of the famous examples of implied powers involving the U.S. Supreme Court is the case of McCulloch v. Maryland. The Court decided this case in 1819. Here, the United States government needed to pay off the debt that the nation acquired during the War of 1812.
What are some examples of implied powers versus express powers?
Issue patents. An example of implied powers versus express powers is the way in which officials collect taxes. Congress has the express power to collect taxes. It also has the implied power to create an agency – the Internal Revenue Service –and entrust it to handle the collection of taxes.
Why does the Constitution include the "necessary and proper" clause?
Therefore, by including the “necessary and proper clause ,” they covered their bases insofar as allowing the government to act as it sees fit, within reason. This is why the government often relies on the doctrine of implied powers when creating and passing new laws.
What are implied powers?
Other powers not specifically listed in Section 8, but assumed to exist , are called “ implied powers .". Not only does the Constitution define Congress' powers in relation to the judicial and executive branches, it also places limits on it concerning power delegated to the individual states.
Which clause of the Constitution gives Congress the power to act?
In addition to the explicit powers enumerated in Section 8 of the Constitution, Congress also has additional implied powers derived from the Necessary and Proper Clause of the Constitution, which permits it,
Which case enumerated the power of Congress to regulate interstate commerce?
Through the Supreme Court’s many interpretations of the Necessary and Proper Clause and the Commerce Clause—the enumerated power to regulate interstate commerce—such as McCulloch v Maryland, the true range of the lawmaking powers of Congress extends far beyond those enumerated in Section 8.
Which is more important, Congress or the enumerated power?
Of all the powers of Congress, none is more important than its enumerated power to make laws.
What is the Congress?
Congress is one of three co-equal branches of the federal government, along with the judicial branch, represented by the courts, and the executive branch, represented by the presidency. The powers of the United States Congress are set forth in Article I, Section 8 of the United States Constitution .
How long does the House of Representatives serve?
Congressional representatives are elected to two-year terms, and the Speaker of the House is second in line to succeed the president after the vice president .
What is the Senate responsible for?
The Senate is responsible for confirming presidential appointments of Cabinet members, federal judges, and foreign ambassadors. The Senate also tries any federal official accused of a crime, once the House determines that a trial is in order.
Which clause of Article I is the source of the implied powers of Congress?
The final clause of Article I, Section 8—known as the “Necessary and Proper Clause” is the source of the implied powers of Congress .
What is the power of Congress?
The powers of Congress are limited to those specifically listed in Article I, Section 8 and those determined to be “necessary and proper” to carry out those powers. The Article’s so-called “necessary ...
What is the purpose of the necessary and proper clause?
The Article’s so-called “necessary and proper” or “elastic” clause creates the justification for Congress to exercise several “ implied powers ,” such as the passage of laws regulating the private possession of firearms . In addition, Article III Section 3 of the Constitution grants Congress the power to assess punishment for the crime of treason, ...
Why is the Commerce Clause important?
Over the years, Congress has relied on the Commerce Clause to pass environmental, gun control, and consumer protection laws because many aspects of business require materials and products to cross state lines. However, the scope of the laws passed under the Commerce Clause is not unlimited.
What is the legislative branch?
The Legislative Branch. Robert Longley is a U.S. government and history expert with over 30 years of experience in municipal government and urban planning. Article I, Section 8 of the U.S. Constitution specifies the “expressed” or “enumerated” powers of Congress. These specific powers form the basis of the American system ...
What is Clause 8?
Clause 8: To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries;
What is the purpose of clause 3?
Clause 3: To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes; Clause 4: To establish a uniform Rule of Naturalization, and uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States;
