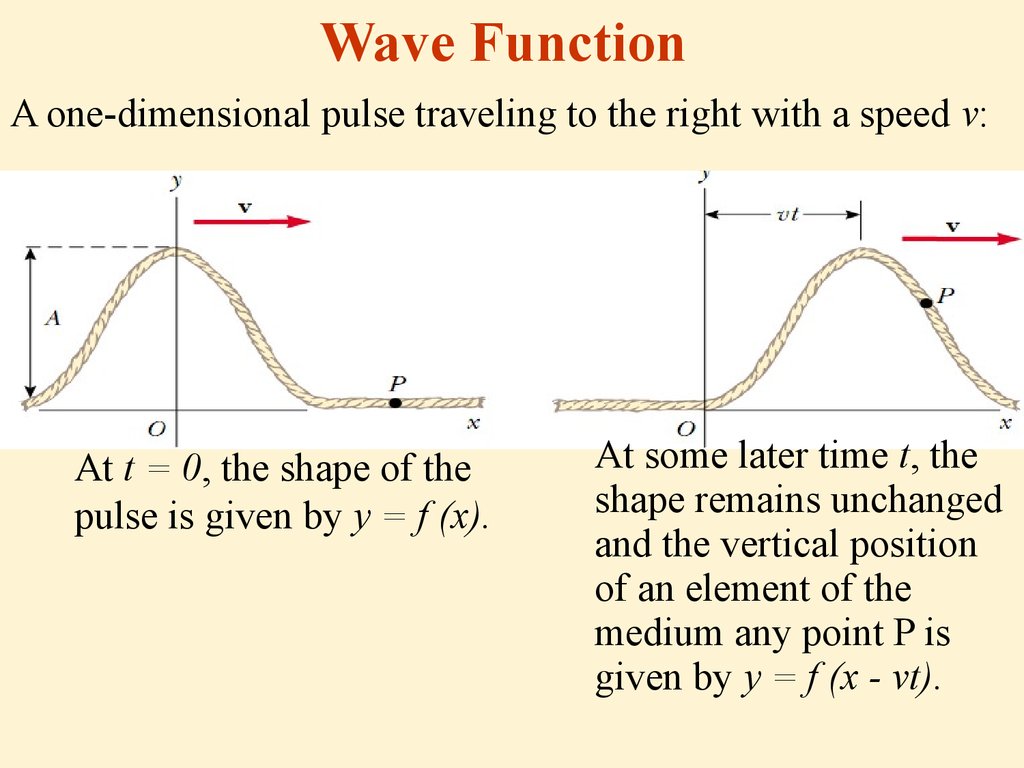
The characteristics of transverse waves are:
- Transverse waves can only pass through solids and cannot pass through liquids or gasses.
- Polarization is a phenomenon that can only be observed in transverse waves. The plane of vibration, also known as...
- When transverse waves propagate in a medium, pressure and density remain constant.
- In transverse waves, the formation o...
What are the characteristics of transverse waves?
Transverse Waves: Definition, Characteristics, Examples, Formulae
- Definition of Transverse Waves. When the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the wave.
- Characteristics of Transverse Waves. In Transverse waves, particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the velocity of the wave. ...
- Practical Examples of Transverse Waves. ...
- Important Formulae. ...
- Things to Remember. ...
Is a transverse wave the same as a sinusoidal wave?
Not necessarily. A sinusoidal wave is a wave that can be described by a single sine or cosine function. A transverse wave is a wave where the displacement of an element is perpendicular to the direction of travel. If you get your hands on a slinky, a transverse wave goes up and down or side to side, and it kind of looks like how a snake might move.
What are some real life examples of transverse waves?
- Ripples in Water Pond.
- Plucking a Guitar String.
- Earthquake (Seismic S wave)
- Tsunami Waves.
- X-Rays.
- Electromagnetic Waves.
- Oscillating String or Rope.
What are facts about transverse waves?
Similarities Between Longitudinal Wave And Transverse Wave
- Both waves are mechanical waves
- Both transport energy without transporting matter.
- Particles oscillate about their meaning position in both waves.

What are 3 main properties of a transverse wave?
Trough - The lowest part of a transverse wave. Wavelength - The distance between one crest and the next in a transverse wave. Amplitude - The height from the resting position to the crest of the transverse wave.
What are the five characteristics of a transverse wave?
Review the characteristics of periodic transverse and longitudinal waves such as wavelength, crest, trough, amplitude, expansion, and compression.
What are some properties of transverse waves Wikipedia?
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations.
What are some properties of transverse waves quizlet?
As a transverse wave moves in one direction, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of the wave, or across it. The medium moves parallel to the direction the waves are traveling. The medium moves back-and- forth in the same direction as the wave travels.
What are the properties of longitudinal and transverse waves?
In a longitudinal wave, the medium or the channel moves in the same direction with respect to the wave. Here, the movement of the particles is from left to right and forces other particles to vibrate. In a transverse wave the medium or the channel moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
What are the 4 characteristics of a wave?
No matter whether you are talking about vibrations or waves, all of them can be characterized by the following four characteristics: amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. The amplitude of a wave can be described as the maximum distance the molecules are displaced from their starting place .
What are the properties of longitudinal waves?
Characteristics of Longitudinal WavesCompression. In a longitudinal wave, compression is a region in which the particles of the wave are closest to each other.Rarefaction. Rarefaction in a longitudinal wave takes place when the particles are farthest apart from each other.Wavelength. ... Amplitude. ... Period and Frequency.
What is transverse wave in simple words?
Definition of transverse wave : a wave in which the vibrating element moves in a direction perpendicular to the direction of advance of the wave.
How do transverse waves move?
Transverse waves cause the medium to move perpendicular to the direction of the wave. Longitudinal waves cause the medium to move parallel to the direction of the wave.
What are the 8 properties of waves?
There are many properties that scientists use to describe waves. They include amplitude, frequency, period, wavelength, speed, and phase. Each of these properties is described in more detail below. When drawing a wave or looking at a wave on a graph, we draw the wave as a snapshot in time.
What are four basic properties of waves quizlet?
The basic properties of waves are amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed.
What property describes how often a wave occurs?
Wavelength describes a wave's length, and frequency describes how often it occurs. Speed describes how quickly a wave moves.
What is the sine of a transverse wave?
A simple transverse wave can be represented by a sine or cosine curve, so called because the amplitude of any point on the curve— i.e., its distance from the axis—is proportional to the sine (or cosine) of an angle. In the figure, sine curves of various amplitudes are shown.
What is longitudinal wave?
Waves come in two varieties. In a longitudinal wave the oscillating disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation. A familiar... The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Adam Augustyn, Managing Editor, Reference Content.
What are some examples of longitudinal waves?
Waves come in two varieties. In a longitudinal wave the oscillating disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation. A familiar example is a sound wave in air—the oscillating motions of the air molecules are induced in the direction of the advancing wave.…
How does a transverse wave reflect?
The way in which a transverse wave reflects depends on whether it is fixed at both ends. First, let us discuss a case where the waves are fixed at both ends. The image below shows a transverse wave that is reflected from a fixed end. When a transverse wave meets a fixed end, the wave is reflected but inverted.
What is transverse wave?
Transverse Waves. Waves are everywhere, and we can describe waves as disturbances that travel through a medium from one location to another. Waves come in many shapes and forms. While all waves share the same basic characteristic properties and behavior, some waves can be distinguished from other waves based on some observable characteristics.
What are the two ways to categorize waves?
Categorizing waves on this basis leads to two notable categories: transverse waves and longitudinal waves. A transverse wa ve is a wave in which particles move perpendicular to ...
What is longitudinal wave?
A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles move in a direction parallel to the wave propagation. In this article, our focus will be on transverse waves and their characteristics. You can check out our article on longitudinal waves to understand their characteristics.
What happens when a transverse wave meets a fixed end?
The image below shows a transverse wave that is reflected from a fixed end. When a transverse wave meets a fixed end, the wave is reflected but inverted. This swaps the peak with troughs and the troughs with peaks.
What are some examples of transverse waves?
Some examples of transverse waves are listed below: The ripples on the surface of the water. Electromagnetic waves. Stadium or a human wave. Ocean Waves. The secondary waves of an earthquake.
What is the peak of a wave?
The peak is the top point of the wave and trough is the bottom point of the wave. Refer to the diagram below for the visual representation of these terms. Following are a few important terminologies to know: Amplitude – The maximum displacement of a particle from its equilibrium position.
How are transverse waves demonstrated?
Transverse waves are often demonstrated by moving a rope rapidly up and down , although a slinky spring could also be used.
How do you know if a wave is transverse?
In transverse waves, the vibrations are at right angles to the direction of wave travel. One way to remember the movement of particles in transverse waves is to use the 'S' sound: in transverse waves the particles move from side-to-side – crossing the direction of wave travel.
What are the properties of waves?
Properties of waves. Waves transfer energy but not matter. Waves may be transverse (eg water wave) or longitudinal (eg sound wave). Wave motion can be described using the terms amplitude, wavelength, frequency and period. Part of.
How to remember the movement of particles in transverse waves?
One way to remember the movement of particles in transverse waves is to use the 'S' sound : in transverse waves the particles move from side-to-side – crossing the direction of wave travel.
What does a transverse wave look like?
When you picture a wave in your mind, you probably envision a squiggly line with peaks and valleys. This is exactly what a transverse wave looks like. It’s a moving wave that oscillates perpendicular to the direction of its propagation. Transverse waves can be electromagnetic or mechanical in nature.
What are some examples of transverse waves?
To better explain this phenomenon, we have listed a few good examples of transverse waves that people see in their everyday life. 10. Vibrations In A Guitar String.
What type of wave has the longest wavelength?
Radio Waves. Form: Electromagnetic waves. Like ripples on the water, a radio wave is a series of repeating peaks and valleys. These waves have the longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from 1 millimeter to over 100 kilometers (62 miles).
How are waves distinguished from others?
While most of them share the same behavior, some waves can be distinguished from others based on their properties . One way to characterize them is the way they move in a particular medium, which leads to two notable categories: transverse and longitudinal waves. In this article, we will be focusing on the former.
What is microwave radiation?
Like radio waves, microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation that has a wide range of applications, including radar, communications, and cooking. They are also used in modern technology, for example, in keyless entry systems, collision avoidance systems, remote sensing, and spectroscopy.
How are radioactive waves produced?
They are produced by lightning, nuclear explosions, and radioactive decay. In space, they are generated by most energetic bodies like pulsars, neutron stars, black holes, and supernova explosions. These waves are sometimes used to treat cancers in the body by destroying the DNA of tumor cells.
Why are S waves more destructive than P waves?
S-waves cannot travel through the Earth’s molten outer core, but they are usually more destructive than P-waves because they are multiple times higher in amplitude.
What are some examples of transverse waves?
Let’s analyze some daily life examples of transverse waves. 1. LightWave. Lightwave forms the most important example of a transverse wave. In case of the light waves, particles travel perpendicular to the direction of the waves. It is the visible spectrum that is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight.
What is the highest point of a transverse wave?
Transverse waves are the waves in which the particles move in a direction perpendicular to that of a wave. The highest point is called “Crest, ” and the lowest point is called “Trough.”. They can even travel in vaccum. Let’s analyze some daily life examples of transverse waves. 1.
What are electromagnetic waves?
These are the transverse waves in which the electric field and magnetic field are perpendicular to each other. 9.
What is the term for the wave that stands up and raises arms?
When a large number of spectators are attending a match or a game in a stadium, you might have noticed a metachronal rhythm achieved by successive groups of the audience when they stand, yell, or raise their arms. It is also called stadium wave or Mexican waves. 8. Electromagnetic Waves.
Which wave requires a solid medium to travel?
These S-waves are transverse waves and require a solid medium to travel. 5. Tsunami Waves. Though Tsunamis have properties of both the transverse as well as a longitudinal wave; however, it starts as a transverse wave.
Is a guitar a longitudinal wave?
The sound wave is a longitudinal wave, but the wave on the guitar is, however, a transverse wave. The particles in the string move perpendicular to the direction of the wave propagation. 4. Earthquake (Seismic S wave) The bump or rattle that we feel during an earthquake is due to seismic-S wave.