...
Panic disorder and agoraphobia
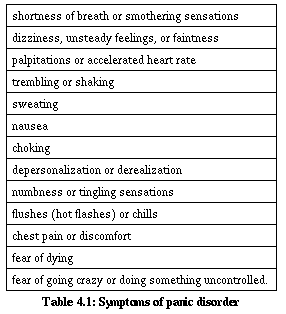
- Rapid heart rate.
- Trouble breathing or a feeling of choking.
- Chest pain or pressure.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness.
- Feeling shaky, numb or tingling.
- Excessive sweating.
- Sudden flushing or chills.
- Upset stomach or diarrhea.
Symptoms
Treatment - Agoraphobia
- Self-help techniques and lifestyle changes. Learning more about agoraphobia and its association with panic disorder and panic attacks may help you control your symptoms better.
- Psychological therapies. If your symptoms do not respond to self-help techniques and lifestyle changes, your GP may suggest trying a psychological therapy.
- Medicine. ...
Causes
Little by little, agoraphobia can be overcome. It takes time and a lot of patience. As I found great assistance from many understanding people in support groups, so can you. This is one time the person with this disorder must learn to turn to someone trusted to help them through.
Prevention
Agoraphobia is a type of mental illness that is classified under panic disorders. Panic disorders are mental illnesses that manifest through experiences of intense fear and panic attacks. People with this condition avoid situations or places that induce panic attacks. Most people with agoraphobia like to stay at home for fear of developing panic attacks when they enter environments that trigger the reaction.
Complications
What Causes a Panic Attack with Agoraphobia?
- Genetics. The specific cause of panic attacks is unknown. However, some evidence suggests that there may be a genetic aspect involved.
- Stress. Stress may also play a role in bringing on the disorder. Many people first experience attacks while going through intensely stressful periods.
- Development of Attacks. Panic attacks tend to come on with no warning. ...
How do you treat agoraphobia?
Can agoraphobia go away?
Is agoraphobia a mental illness?
What causes agoraphobia panic disorder?

What are the symptoms of a person with agoraphobia?
The physical symptoms of agoraphobia can be similar to those of a panic attack and may include:rapid heartbeat.rapid breathing (hyperventilating)feeling hot and sweaty.feeling sick.chest pain.difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)diarrhoea.trembling.More items...
Which is the best example of agoraphobia?
1 For example, a person with agoraphobia may avoid driving a car, leaving the comfort of home, shopping in a mall, traveling by airplane, or simply being in a crowded area.
What can trigger agoraphobia?
a traumatic childhood experience, such as the death of a parent or being sexually abused. experiencing a stressful event, such as bereavement, divorce, or losing your job. a previous history of mental illnesses, such as depression, anorexia nervosa, or bulimia. alcohol misuse or drug misuse.
What happens to your body when you have agoraphobia?
The symptoms and signs of agoraphobia may include: anxiety in response to being away from an environment that feels 'safe' panic attack including symptoms such as breathlessness, sweating, dizziness, fast heart rate, choking sensations, nausea, and feelings of extreme fear or dread.
What is the best medication for agoraphobia?
An SSRI called sertraline is usually recommended for people with agoraphobia.
What helps agoraphobia?
Coping and supportStick to your treatment plan. Take medications as directed. ... Try not to avoid feared situations. ... Learn calming skills. ... Avoid alcohol and recreational drugs. ... Take care of yourself. ... Join a support group.
Is agoraphobia a severe mental illness?
Agoraphobia can involve a combination of fears, other feelings, and physical symptoms. These can all vary from mild to severe. Some people can manage agoraphobia symptoms by following a routine. For others, it can be severely debilitating.
How is agoraphobia diagnosed?
A diagnosis of agoraphobia can usually be made if: you're anxious about being in a place or situation where escape or help may be difficult if you feel panicky or have a panic attack, such as in a crowd or on a bus. you avoid situations described above, or endure them with extreme anxiety or the help of a companion.
What is an agoraphobic lifestyle?
Agoraphobia is a fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult or that help wouldn't be available if things go wrong. Many people assume agoraphobia is simply a fear of open spaces, but it's actually a more complex condition. Someone with agoraphobia may be scared of: travelling on public transport.
Does agoraphobia qualify for disability?
Given this situation, you may have often wondered if suffering from agoraphobia makes you eligible for disability benefits from the Social Security Administration (known as SSDI benefits). The short answer is that, yes, you can qualify for disability due to agoraphobia.
What is agoraphobia the fear of?
What is agoraphobia? Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder that causes intense fear of becoming overwhelmed or unable to escape or get help. Because of fear and anxiety, people with agoraphobia often avoid new places and unfamiliar situations, such as: Open or enclosed spaces.
What part of the brain does agoraphobia affect?
In the panic disorder/agoraphobia spectrum, several studies appear to converge on effects in the amygdala, ACC, insula, and lateral prefrontal cortex, but also for occipital brain areas.
What is agoraphobia?
Agoraphobia is a fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult or that help wouldn't be available if things go wrong. Many people assume agoraphobia is simply a fear of open spaces, but it's actually a more complex condition. Someone with agoraphobia may be scared of: travelling on public transport.
What are the types of agoraphobia?
Types of AgoraphobiaParanoid agoraphobia.Claustrophobia.Disorganized agoraphobia.Catatonic agoraphobia.Enochlophobia.
Is agoraphobia a disorder?
Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder that causes intense fear of becoming overwhelmed or unable to escape or get help. Because of fear and anxiety, people with agoraphobia often avoid new places and unfamiliar situations, such as: Open or enclosed spaces. Crowds.
What is an example of a social phobia?
You may have social anxiety if you: worry about everyday activities, such as meeting strangers, starting conversations, speaking on the phone, working or shopping. avoid or worry a lot about social activities, such as group conversations, eating with company and parties.
What are the causes of agoraphobia?
However, there are several factors that are known to increase your risk of developing agoraphobia. These include having: depression. other phobias, such as claustrophobia and social phobia. another type of anxiety disorder, such as generalized anxiety disorder or obsessive compulsive disorder.
How many people have agoraphobia?
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) estimates that 0.8 percent of American adults have agoraphobia. About 40 percent of cases are considered severe. When the condition is more advanced, agoraphobia can be very disabling.
What is agoraphobia in a heart attack?
a fear of the consequences of panic attacks, such as having a heart attack or losing control. a change in your behavior as a result of the panic attacks. You won’t be diagnosed with agoraphobia if your symptoms are caused by another illness. They also can’t be caused by substance abuse or another disorder.
Why do people with agoraphobia have panic attacks?
People with agoraphobia may experience panic attacks whenever they enter a stressful or uncomfortable situation, which further enhances their fear of being in an uncomfortable situation.
What is it called when you are afraid of being in a car?
People with agoraphobia are typically: afraid of being in places where it would be difficult to escape, such as a car or elevator. Agoraphobia often coincides with panic attacks. Panic attacks are a series of symptoms that sometimes occur in people with anxiety and other mental health disorders.
What is the disorder that causes people to avoid places and situations that might cause them to feel trapped?
Agoraphobia is a type of anxiety disorder that causes people to avoid places and situations that might cause them to feel: trapped. helpless.
How is aoraphobia diagnosed?
Agoraphobia is diagnosed based on symptoms and signs. Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms, including when they started and how often you experience them. They’ll ask questions related to your medical history and family history as well. They may also perform blood tests to help rule out physical causes for your symptoms.
What Are the Symptoms of Agoraphobia?
Agoraphobia is the persistent and extreme fear of spaces that are usually outside of the home. Common symptoms include:
How to help agoraphobia?
Psychotherapy. Psychotherapy has been found to be helpful in treating agoraphobia. Specifically, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has proven very effective. Cognitive behavioral therapy involves addressing the fears, thinking patterns, and behaviors that contribute to the disruption of your daily life.
What is the disorder that is associated with panic disorder?
Another study found that people with panic disorder and agoraphobia were also frequently diagnosed with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). 5
What is the fear of spaces outside of the home?
Agoraphobia is the persistent and extreme fear of spaces that are usually outside of the home. Common symptoms include:
How long does agoraphobia last?
In addition, for a diagnosis of agoraphobia, the symptoms must be persistent, lasting at least six months. Avoidant behavior is another part of the diagnostic criteria for agoraphobia. A person with avoidant behavior steers clear of the object or situation they fear as well as anything they associate with their fear.
What is the best medicine for agoraphobia?
Doctors commonly prescribe antidepressants to treat agoraphobia, as well as to treat related conditions like panic disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. 8
How to ride a bus without fear?
Then, you could work your way up to walking to the bus stop and returning home. You might take a short bus ride, eventually riding for longer amounts of time until you are able to ride the bus without fear.
What are the symptoms of agoraphobia?
Symptoms of agoraphobia relating to behaviour include: avoiding situations that could lead to panic attacks, such as crowded places, public transport and queues. being housebound – not being able to leave the house for long periods of time. needing to be with someone you trust when going anywhere.
How do you know if you have agoraphobia?
The physical symptoms of agoraphobia can be similar to those of a panic attack and may include: rapid heartbeat. rapid breathing (hyperventilating) feeling hot and sweaty. feeling sick. chest pain. difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) diarrhoea. trembling.
Why do people with agoraphobia have physical symptoms?
However, many people with agoraphobia rarely experience physical symptoms because they deliberately avoid situations that make them anxious.
What are the symptoms of panic attacks?
Cognitive symptoms may include fear that: a panic attack will make you look stupid or feel embarrassed in front of other people. a panic attack will be life threatening – for example, you may be worried your heart will stop or you'll be unable to breathe.
What does it mean when you stare at someone?
a fear of being left alone in your house (monophobia) a general feeling of anxiety or dread.
Can you force yourself to confront uncomfortable situations?
Some people are able to force themselves to confront uncomfortable situations, but they feel considerable fear and anxiety while doing so.
Can someone with agoraphobia leave the house?
For example, someone with severe agoraphobia may be unable to leave the house, whereas someone who has mild agoraphobia may be able to travel short distances without problems. The symptoms of agoraphobia can be broadly classified into 3 types: physical. cognitive. behavioural.
What are the symptoms of agoraphobia?
Cognitive symptoms are fears associated with the physical symptoms of agoraphobia. They include: Fear that you will experience a life-threatening panic attack. Fear that you are losing your mind or sanity. Fear that you may be unable to control yourself in public. Fear that people will stare at you.
How to diagnose agoraphobia?
To diagnose agoraphobia, a doctor will start by asking you about your symptoms and your behaviors. They may also perform a physical exam and order lab tests to rule out other conditions, such as an overactive thyroid ( hyperthyroidism ), which can cause similar symptoms as a panic attack.
What is agoraphobia?
Agoraphobia may prevent you from going to work, keeping in touch with your friends and family, or running errands.
Why do people get agoraphobia?
Causes of agoraphobia. Some people with agoraphobia experience panic attacks or anxiety before they develop agoraphobia. Then, they have a panic attack somewhere public and associate panic with that location. Some people inherit genes that make them more likely to experience agoraphobia. In some cases, a stressful or traumatic event can bring on ...
What is the fear of being outside?
Agoraphobia is a fear of being outside or of being in a situation from which escape would be impossible. Symptoms include anxiety, fear, disorientation, rapid heartbeat, diarrhea, or dizziness. Treatment may incorporate psychotherapy, self-exposure to the anxiety-causing situation, and medications such as SSRIs, benzodiazepines, and beta-blockers.
What are some examples of places that cause anxiety in people with agoraphobia?
Examples of places that cause anxiety in people with this condition include: Public transportation. Shopping malls. Parking lots. Movie theaters. When people with agoraphobia are in public, they may feel anxiety and panic. They may avoid certain places or have a hard time leaving the house at all.
What is the best treatment for agoraphobia?
People living with agoraphobia may benefit from exposure therapy, a type of therapy in which you gradually face your fears until you no longer experience them. Cognitive behavioral therapy ( CBT) is also a treatment for agoraphobia.
How do you know if you have agoraphobia?
Your provider may diagnose agoraphobia if you meet specific standards developed by the American Psychiatric Association. To have a diagnosis of agoraphobia, a person must feel extreme fear or panic in at least two of the following situations:
How many people with agoraphobia are symptom free?
About a third of people with agoraphobia overcome the disorder and become symptom-free. Another half learn to manage their symptoms better but still have some anxiety.
What is the disorder that causes fear?
Agoraphobia. Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder that causes excessive fear of certain situations. Some people may even resist leaving home. With medication, cognitive behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes, patients can overcome the disorder and participate in things they enjoy. The earlier the condition is diagnosed, ...
What are the risk factors for agoraphobia?
Risk factors for developing agoraphobia include: Having panic attacks or other phobias. Experiencing stressful life events, such as the death of a loved one, being attacked, or being abused. Having a nervous or anxious nature. Responding to panic attacks with excess fear and apprehension. Having a relative with agoraphobia.
How many people have agoraphobia?
About 1% to 2% of adults in the United States have been diagnosed with agoraphobia. Roughly 2% of adolescents experience it. Agoraphobia is more common among women. It usually starts before age 35.
Why do people with agoraphobia avoid new places?
Because of fear and anxiety, people with agoraphobia often avoid new places and unfamiliar situations, such as: Open or enclosed spaces. Crowds. Places outside your home. Public transportation. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
What is the treatment for aoraphobia?
Agoraphobia treatment usually involves a combination of treatment methods: therapy, medication and lifestyle changes.
