Symptoms
Types of Somatoform Disorders
- Somatization Disorder. Somatization disorder occurs when a person continually complains of physical symptoms when there is no physical condition present to cause the symptoms.
- Conversion Disorder. ...
- Pain Disorder. ...
- Hypochondriasis. ...
- Other Specified Somatic Symptom and Related Disorder. ...
Causes
Types of psychotic disorders
- schizophrenia. ...
- Delusional disorder. ...
- Brief psychotic disorder. ...
- schizophreniform disorder. ...
- Schizoaffective disorder. ...
- Shared psychotic disorder or “two-person madness”. ...
- Substance-Induced Psychotic Disorder. ...
- Psychotic disorder due to medical illness. ...
Prevention
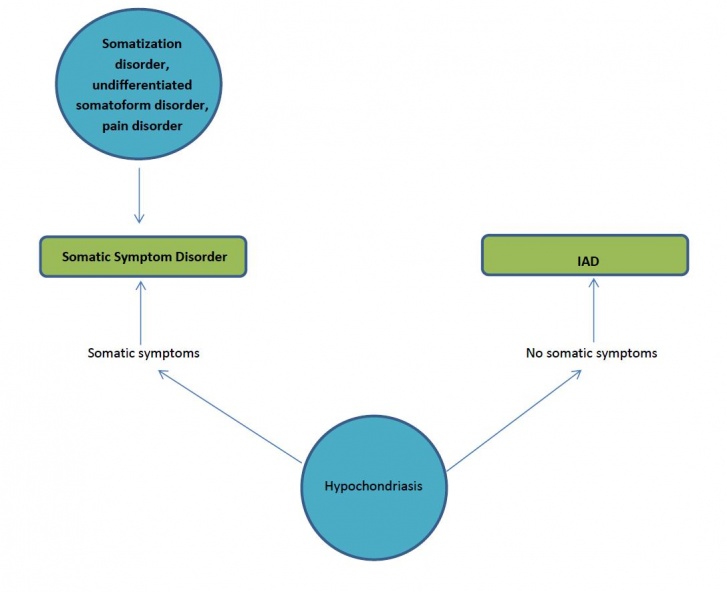
What are the two somatoform disorders as identified in the DSM-IV-TR? DSM - IV - TR somatoform disorders include somatization disorder, conversion disorder, pain disorder, undifferentiated somatoform disorder, hypochondriasis, and body dysmorphic disorder.
Complications
A negative correlation was found between depression-related symptoms and grey matter volume of the bilateral amygdala. Moreover, the severity of affective and somatic PMDD symptoms ... presence of ongoing psychiatric disorders, treatment with ...
What are the different types of somatoform disorders?
What are the different types of psychosomatic disorders?
What are two somatoform disorder?
What are somatic symptom and related disorders?
What are somatic system disorders?
Somatic symptom disorder (SSD) occurs when a person feels extreme, exaggerated anxiety about physical symptoms. The person has such intense thoughts, feelings, and behaviors related to the symptoms, that they feel they cannot do some of the activities of daily life.
How many somatic symptom disorders are there?
There are seven types of somatoform disorders where individuals present with a multitude of clinically significant symptoms that cannot be explained, including: Somatization disorder. Conversion disorder. Pain disorder.
Is somatic symptom disorder a mental illness?
Somatic symptom disorder (SSD) is a mental health condition in which a person feels significantly distressed about physical symptoms and has abnormal thoughts, feelings and behaviors in response to them. The disorder disrupts their daily functioning and quality of life.
What do all types of somatic symptom disorders have in common?
Some previously distinct somatic disorders—somatization disorder, undifferentiated somatoform disorder, hypochondriasis, and somatoform pain disorder—are now considered somatic symptom disorders. All have common features, including somatization—the expression of mental phenomena as physical (somatic) symptoms.
Is Fibromyalgia a somatic disorder?
In the wider literature, however, including non-US studies, fibromyalgia is considered to be one of a series of “medically unexplained syndromes.” These illnesses are sometimes called somatic symptom disorders (SSD) or functional somatic syndromes because the main symptoms, pain, fatigue, cognitive disturbance, and ...
What is the main cause of somatic pain?
Somatic pain occurs when pain receptors in tissues (including the skin, muscles, skeleton, joints, and connective tissues) are activated. Typically, stimuli such as force, temperature, vibration, or swelling activate these receptors.
How is somatic symptom diagnosed?
To determine a diagnosis, you'll likely have a physical exam and any tests your doctor recommends. Your doctor or other health care provider can help determine if you have any health conditions that need treatment.
Can anxiety cause somatic symptoms?
The emotional distress of anxiety is often accompanied by specific physical symptoms associated with a state of autonomic arousal, such as sweating, dizziness, and shortness of breath (most notable in patients with panic attacks), or more generalized somatic complaints, such as insomnia, restlessness, and muscle aches ...
How do you treat somatic disorders?
Cognitive behavior therapy and mindfulness-based therapy are effective for the treatment of somatic symptom disorder. Amitriptyline, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and St. John's wort are effective pharmacologic treatments for somatic symptom disorder.
How do I know if my symptoms are psychosomatic?
In addition to the somatic symptom itself (for example, pain or upset stomach), people with psychosomatic disorder often: Become angry or irritable because they believe their medical needs aren't being met. Get depressed or anxious. Visit healthcare providers frequently, often jumping from one physician to another.
What's another word for somatic?
In this page you can discover 17 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for somatic, like: corporeal, physical, bodily, fleshly, body, corporal, personal, immunologic, pathological, neurochemical and striatal.
Is somatic disorder curable?
Somatic symptom and related disorder treatment Although there is no known cure for somatoform disorders, they can be managed. Treatment focuses on helping the person who has the disorder to live as much of a normal life as possible. Even with treatment, he or she may still have some pain or other symptoms.
Which of the following is the most common somatic symptom in adults?
Pain is the most common symptom, but whatever your symptoms, you have excessive thoughts, feelings or behaviors related to those symptoms, which cause significant problems, make it difficult to function and sometimes can be disabling.
What is the difference between somatic symptom disorder and illness anxiety disorder?
Similarities and Differences with Somatic Symptom Disorder However, in Somatic Symptom Disorder there is generally a somatic expression of the complaint (e.g., back pain), whereas in Illness Anxiety Disorder, it is dominated by anxiety about having or acquiring a serious medical illness.
Is somatic symptom disorder the same as hypochondriasis?
Definition/Criteria. According to DSM-IV, somatization disorder has a specified number and type of somatic symptoms, whereas hypochondriasis is characterized by abnormal attitudes and beliefs about illness [16]. The criteria for hypochondriasis mention bodily symptoms but do not indicate what these might be.
Is somatic disorder curable?
Somatic symptom and related disorder treatment Although there is no known cure for somatoform disorders, they can be managed. Treatment focuses on helping the person who has the disorder to live as much of a normal life as possible. Even with treatment, he or she may still have some pain or other symptoms.
What is somatic symptom disorder?
Somatic symptom disorder is a disorder in which individuals feel excessively distressed about their health and also have abnormal thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in response to their symptoms. There are different subtypes of the disorder based on the patient’s complaint.
How to treat somatic symptoms?
The goal of treating somatic symptom disorder is to manage symptoms using both behavioral therapy and sometimes medications that treat the underlying anxiety and depression . Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that helps patients learn ways to change their patterns of thinking or behavior in order to change the way they feel. CBT helps patients better cope with anxiety and stress and respond to situations more effectively. If medication is prescribed, antidepressants are a common choice. Antidepressants in addition to helping mood, have been reported to help ease such symptoms as pain, fatigue, pain in joints, and sleep problems.
Why are women more likely to have somatic symptoms than men?
Women are ten times more likely to report somatic symptoms than men. This is explained by the fact that the disorder is often related to childhood abuse and trauma to which women are more often exposed then men. Somatic symptom disorder can appear in any age group.
What is the phone number for somatic symptom disorder?
Although a person with somatic symptom disorder reports symptoms, the symptoms may have no medical explanation. Appointments 866.588.2264. Appointments & Locations.
Can somatic symptoms be explained?
Although a person with somatic symptom disorder reports symptoms, the symptoms may have no medical explanation. Even when there is a medical cause, the person’s worry is out of proportion to the symptom. The distress causes the patient to visit multiple healthcare providers and to have many medical tests and unnecessary procedures.
Can you have more than one symptom?
Neurological symptoms such as headaches, movement disorders, weakness, dizziness, fainting. Digestive symptoms such as abdominal pain or bowel problems, diarrhea, incontinence, and constipation. Usually, patients report experiencing more than one symptom. Symptoms can range from mild to severe.
Can somatic symptom disorder be prevented?
Somatic symptom disorder cannot be prevented but can be treated.
What is somatic symptom disorder?
Somatic symptom disorder involves a person having a significant focus on physical symptoms, such as pain, weakness or shortness of breath, that results in major distress and/or problems functioning. The individual has excessive thoughts, feelings and behaviors relating to the physical symptoms. The physical symptoms may or may not be associated ...
Why is somatic symptom disorder not diagnosed?
A person is not diagnosed with somatic symptom disorder solely because a medical cause can’t be identified for a physical symptom. The emphasis is on the extent to which the thoughts, feelings and behaviors related to the illness are excessive or out of proportion.
Where do you go for somatic symptoms?
People with somatic symptom disorder typically go to a primary care physician rather than a psychiatrist or other mental health professional.
What is excessive thoughts?
Excessive thoughts, feelings or behaviors related to the physical symptoms or health concerns with at least one of the following: Ongoing thoughts that are out of proportion with the seriousness of symptoms. Ongoing high level of anxiety about health or symptoms.
What causes somatic symptoms?
having negative affectivity, a personality trait that involves negative emotions and poor self-image. difficulty dealing with stress.
How is somatic symptom disorder treated?
Treating somatic symptom disorder usually involves therapy, medication, or a combination of both, to improve your quality of life and relieve anxiety over your physical health.
What is the best treatment for somatic symptom disorder?
Psychotherapy. Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, is a good first step in treating somatic symptom disorder. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a particularly helpful form of psychotherapy for somatic symptom disorder. It involves working with a therapist to identify negative or irrational thoughts and patterns.
What are the characteristics of a medical condition?
Additional characteristics include: symptoms that aren’t related to any known medical condition. symptoms that are related to a known medical condition, but are much more extreme than they should be. constant or intense anxiety about a possible illness. thinking that normal physical sensations are signs of illness.
Can antidepressants help with somatic symptoms?
Antidepressant medications can also help with somatic symptom disorder and reduce anxiety. They tend to work best when combined with some form of psychotherapy. If your doctor does suggest medication, you may only need to take it temporarily.
Can somatic symptoms be improved?
Living with somatic symptom disorder. Having somatic symptom disorder can feel extremely overwhelming, but with the right therapist, and in some cases the right dose of medication, you can improve your quality of life. If you’re not sure where to start, check out this list of mental health resources.
What is somatic symptom disorder?
It is the manifestation of one or more physical symptoms accompanied by excessive thoughts, emotion, and/or behavior related to the symptom, which causes significant distress and/or dysfunction.[1] These symptoms may or may not be explained by a medical condition. The two major changes to the DSM-IV criteria included eliminating the requirement that somatic symptoms be organically unexplained and adding the requirement that certain psychobehavioral features have to be present to justify the diagnosis. The new criteria also eliminated somatization disorder, undifferentiated somatoform disorder, hypochondriasis, and pain disorder from the previous definitions. These revisions were intended to increase the relevance of SSD and its use in the primary care setting.
What percentage of the population is affected by somatic symptom disorder?
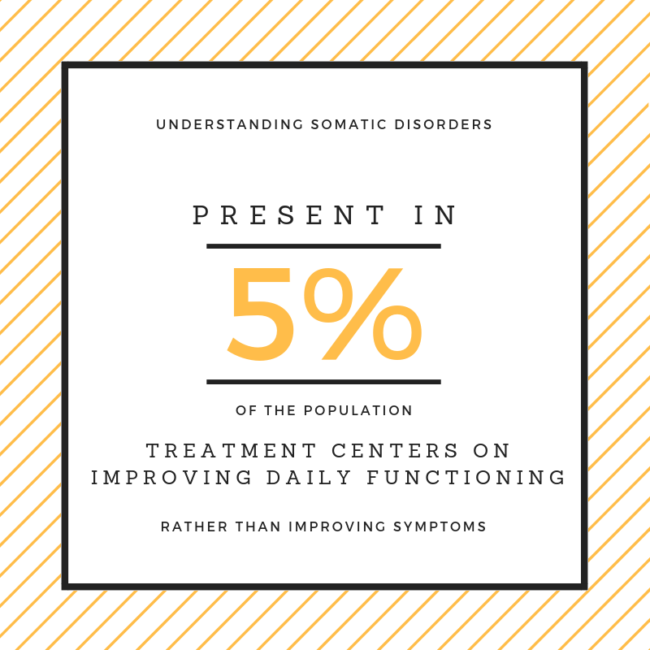
The prevalence of somatic symptom disorder (SSD) is estimated to be 5% to 7% of the general population, with higher female representation (female-to-male ratio 10:1), and can occur in childhood, adolescence, or adulthood. [1][3]The prevalence increases to approximately 17% of the primary care patient population.[4] The prevalence is likely higher in certain patient populations with functional disorders, including fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, and chronic fatigue syndrome. [5]
What is a physical exam for somatic complaints?
In addition to a thorough history, a full review of systems (not only at the location of the symptom) and a comprehensive physical exam is required to evaluate physical causes of somatic complaints. Given frequent comorbid psychiatric disease, a mental status examination should be performed, noting appearance, mood, affect, attention, memory, concentration, orientation, the presence of hallucinations or delusions, and suicidal or homicidal ideation.[8] Ultimately, the physical examination may provide a baseline for monitoring over time, assure patients that their complaints are acknowledged, and help validate the primary care provider’s concern that the patient does not have a physical medical illness. If a disease is present, the exam may provide information on severity.
How long does somatic syndrome last?
Longitudinal studies show considerable chronicity, with up to 90% of somatic syndrome disorder (SSD) cases lasting longer than 5 years. [14][15]Systematic reviews and meta-analyses have revealed that therapeutic interventions only yield small-to-moderate effect sizes. [16][17]Chronic limitation of general function, significant psychological disability, and decreased quality of life are frequently observed. [15][18]
What tests are required to rule out somatization?
If it is necessary to rule out somatization due to medical conditions, specific studies may be ordered, including but not limited to thyroid function tests, urine drug screen, limited blood studies (i.e., alcohol level), and limited radiological testing.
Is SSD a genetic disorder?
The pathophysiology of somatic symptom disorder (SSD) is unknown . Autonomic arousal from endogenous noradrenergic compounds may cause tachycardia, gastric hypermotility, heightened arousal, muscle tension, and pain associated with muscular hyperactivity in patients with SSD. There may also be a genetic component. A study of monozygotic and dizygotic twins revealed that the contribution of genetic factors to somatic symptoms was 7% to 21%, while the remaining was attributable to environmental factors.[6] Several single nucleotide polymorphisms were associated with somatic symptoms in another study. [7]
What Are Somatic Symptom Disorders?
Somatic symptom disorder (SSD) is a condition that causes a person to manifest physical symptoms that can’t be linked to any medical conditions. These symptoms often cause severe distress to a person who has the disorder. Research shows that about five to seven percent of people worldwide have somatic symptom disorder.
Symptoms of Somatic Symptom Disorders
The symptoms a person with somatic symptom disorder experiences typically varies from person to person. Symptoms range in severity, and people with this condition usually experience a range of symptoms. However, some of the most common symptoms of the disorder include: 2
Identifying Somatic Symptom Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistic Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM 5) provides the following diagnostic criteria for identifying somatic symptoms disorder:
Causes of Somatic Symptom Disorders
There’s no singular cause for SSD, as with many mental health conditions. The disorder, however, has been linked to experiencing childhood abuse and trauma.
Related Disorders
There are other mental health disorders that affect the way people view their health concerns. These disorders are similar but not the same with SSD. They are sometimes grouped and referred to as somatoform disorders.
Complications Related to Somatic Symptoms Disorders
While SSD might not result in physical medical conditions, it can severely affect the quality of your life. If it goes untreated, you can become so consumed with your perceived health problems that it starts to take a toll on your health and the relationships you have with other people.
Treatment for Somatic Symptom Disorders
Treating somatic symptoms disorder can be tricky. This is mainly because people with this condition don’t realize that their anxiety exacerbates their symptoms.
How to treat somatic symptom disorder?
Treatment strategies include medications such as antidepressants to address any underlying anxiety or depression. Effective treatment options also include cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based therapy. Somatic symptom disorder is generally a chronic condition, but research has shown that people can recover and learn strategies to minimize their distress.
Why do somatic symptoms occur?
Causes. There are multiple factors that may contribute to the development of somatic symptom disorder. Major life stress might precede the development of symptoms in some cases. People who have a negative outlook or personality are more prone to developing the condition, as well as those who have a family history of somatic symptom disorder. ...
What percentage of the population has somatic symptom disorder?
The prevalence of somatic symptom disorder is unknown, but it is estimated that 5 to 7 percent of the general population may have this condition. Females tend to report more physical symptoms than males, and it is therefore likely that the prevalence of somatic symptom disorder is higher in females.
How long does it take for a somatic symptom to go away?
Although any somatic symptom may not be continuously present, the state of being symptomatic is persistent (typically more than 6 months).
How long is a somatic symptom persistent?
Although any somatic symptom may not be continuously present, the state of being symptomatic is persistent (typically more than 6 months). article continues after advertisement.
What is excessive thoughts, feelings, or behaviors related to the somatic symptoms or associated health concerns?
Excessive thoughts, feelings, or behaviors related to the somatic symptoms or associated health concerns as manifested by at least one of the following: Disproportionate and persistent thoughts about the seriousness of one’s symptoms. Persistently high level of anxiety about health or symptoms.
Can somatic symptoms be physical?
People with somatic symptom disorder have multiple physical symptoms that cause significant distress. These symptoms can be specific (pain in a specific area) or more general (fatigue), and they may be normal bodily sensations or be the result of a medical condition.
How does a somatic disorder affect people?
However, people with a somatic symptom disorder have exceptionally intense thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in response to their symptoms. To distinguish a disorder from a normal reaction to feeling ill, the responses must be intense enough to cause significant distress to the person (and sometimes to others) and/or make it difficult for the person to function in daily life.
What are the symptoms of somatic symptom disorder?
However, in somatic symptom disorders, mental factors are expressed as physical symptoms—a process called somatization—and the person's main concern is with physical (somatic—from soma, the Greek word for body) symptoms, such as pain, weakness, fatigue, nausea, or other bodily sensations.
What is somatic symptom?
Somatic symptom and related disorders are mental health disorders characterized by an intense focus on physical (somatic) symptoms that causes significant distress and/or interferes with daily functioning. Most mental health disorders are characterized by mental symptoms. That is, people have unusual or disturbing thoughts, moods, and/or behaviors.
What is the negative effect of attitudes or behaviors on a medical condition?
Sometimes attitudes or behaviors can have a negative effect on a medical disorder that a person has—a disorder called psychological factors affecting other medical conditions. In somatic symptom disorder, people's symptoms concern and preoccupy them, worry them constantly, and/or drive them to see doctors very frequently.
What is conversion disorder?
The different responses people have define the specific disorder they have, as in the following: In conversion disorder (functional neurological symptom disorder), physical symptoms that resemble those of a nervous system disorder develop .
How do people react to somatic symptoms?
However, people with a somatic symptom disorder have exceptionally intense thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in response to their symptoms.
What is factitious disorder?
In factitious disorder, people pretend to have symptoms for no apparent external reason (such as to get time off from work). In illness anxiety disorder, people are excessively preoccupied and worried about the possibility of having or getting a serious illness.
What is a somatic symptom?
Somatic symptom disorder (SSD formerly known as "somatization disorder" or " somatoform disorder ") is a form of mental illness that causes one or more bodily symptoms, including pain. The symptoms may or may not be traceable to a physical cause including general medical conditions, other mental illnesses, ...
What are the symptoms of a neurological disorder?
For example, patients may have symptoms such as: Weakness or paralysis. Abnormal movements (such as tremor, unsteady gait, or seizures) Blindness. Hearing loss.
Why do people feel unsatisfied with SSD?
They may feel unsatisfied if there's no better physical explanation for their symptoms or if they are told their level of distress about a physical illness is excessive.
What is the best treatment for SSD?
Cognitive behavioral therapy may help relieve symptoms associated with SSD. The therapy focuses on correcting:
Can SSD cause anxiety?
Sexual symptoms. Many people who have SSD will also have an anxiety disorder. People with SSD are not faking their symptoms. The distress they experience from pain and other problems they experience are real, regardless of whether or not a physical explanation can be found.
Can SSD cause physical symptoms?
Patients who experience SSD may cling to the belief that their symptoms have an underlying physical cause despite a lack of evidence for a physical explanation. Or if there is a medical condition causing their symptoms, they may not recognize that the amount of distress they are experiencing or displaying is excessive.
