Specialized connective tissues are the tendons, ligaments, bone, cartilage, blood and adipose In biology, adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immun…Adipose tissue
Why do tissues become specialized?
The specialized cells can perform a certain function within the body. The cell specialization occurs in two stages of a multicellular organism. During the embryonic development, cell specialization occurs mainly due to cell signaling of cytoplasmic determinants. During adult development, the stem cells become specialized to various types of stem cells mainly due to the regulation of gene expression.
What are specialized cells and tissues?
TISSUE: Cells are the smallest, structural and functional unit of an organism, which is characteristically microscopic. Tissues are the distinct types of material consisting of specialized cells and their products. Found in both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Found only in multicellular organisms. Are microscopic. Are macroscopic.
What are the 4 types of tissues and their functions?
Types of tissues
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Nervous tissue.
What are specialized cells in the human body?
- Epithelial Cells. These cells are tightly attached to one another.
- Nerve Cells. These cells are specialized for communication.
- Muscle Cells. These cells are specialized for contraction.
- Connective Tissue Cells.
What is specialized tissue?
The definition of specialized cells are cells with unique structures and functions in the body. Specialized cells work together in groups to form different tissue types, such as muscle tissue or nervous tissue. Tissues work together to form organs that perform a specific function in the body.
What are the specialized tissues in human body?
There are four main types of specialized tissue in the human body; epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscular.
How many specialized tissues are there?
Overview. There are 4 basic types of tissue: connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
What is an example of a specialized cell?
Examples of specialized animal cells include nerve cells, sperm cells, egg cells, muscle cells, ciliated cells, and red blood cells. Specialized cells possess adaptations, special structures and features, which make them adapted to a particular function.
What are the 4 main types of tissues and their functions?
Epithelial tissues act as coverings controlling the movement of materials across the surface. Connective tissue integrates the various parts of the body and provides support and protection to organs. Muscle tissue allows the body to move. Nervous tissues propagate information.
What are the 4 main functions of tissues?
1 Functions of tissuessecretion.movement.strength.excretion.communication.
What are the 7 Specialised cells?
Specialised animal cells have components that allow them to complete a specific purpose. Specialised animal cells include red blood cells, sperm, eggs, nerve cells, muscle cells, ciliated cells, and villi.
Do all animals have specialized tissues?
All animals are eukaryotic, multicellular organisms, and almost all animals have specialized tissues.
Do animals have specialized tissues?
Animals, besides Parazoa (sponges), are characterized by specialized tissues such as muscle, nerve, connective, and epithelial tissues.
What does Specialised mean in biology?
(biology) the structural adaptation of some body part for a particular function; cell differentiation in the developing embryo.
How many types of specialized cells are there?
200 different typesYour body contains over 200 different types of specialized cells. Each type is adapted to do a particular job well and has developed special features to do it.
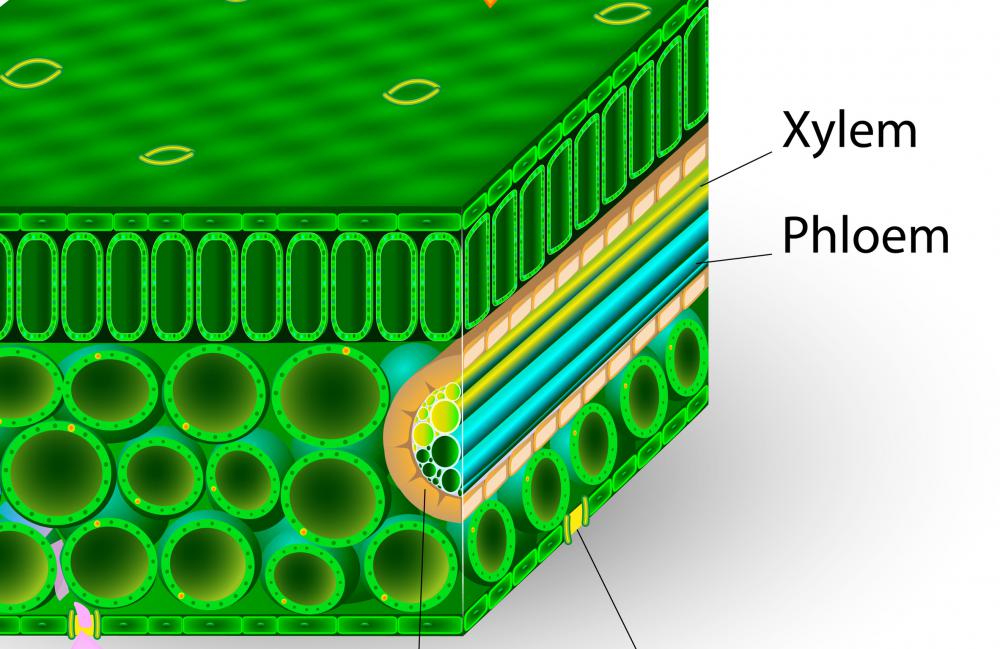
What are 5 specialized plant cells?
The specialised plant cells include parenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, xylem cells and phloem cells.
What is the most important tissue in the human body?
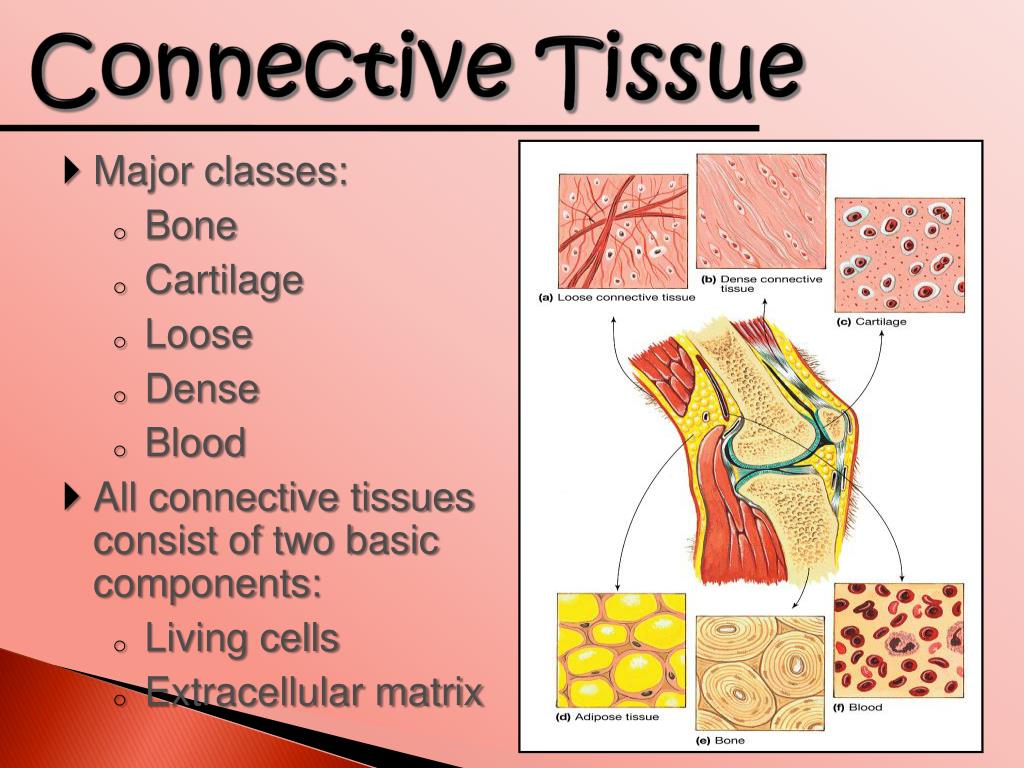
Connective tissueConnective tissue is the most abundant tissue type in our body. It connects other cells and tissues together. It is typically found in our bones, cartilage, adipose, collagen, blood and many other areas in our body. This shows that connective tissue is very important in providing support and protection in our body.
Which organ has all 4 tissue types?
The four types of tissues are exemplified in nervous tissue, stratified squamous epithelial tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, and connective tissue in small intestine.
What are the 3 tissue types in the heart?
The wall of the heart separates into the following layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. These three layers of the heart are embryologically equivalent to the three layers of blood vessels: tunica adventitia, tunica media, and tunica intima, respectively.
What are three connective tissues?
Connective tissue can further be broken down into three categories: loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue.
What Kind of Specialized Tissues Are There in the Body?
While scientists know the human body contains trillions of cells, exactly how many cell types make up the body is still an active field of study. The most recent estimate notes that there are at least 200 unique cell types in the human body, at least based on appearance. Some scientists think that estimate is low, though, and new cell types are still being discovered regularly.
What is cell specialization?
That's where cell specialization comes in. Cell specialization allows new cells to develop into a range of different tissues, all of which work together to make living organisms function as a whole. The process of cell specialization – exactly how cells develop into their diverse forms – is complex.
How are stem cells separated?
There are different types of stem cells, separated by how many tissues they can develop into. The stem cells found in an embryo, for instance, can develop into any tissue type – which is how you go from a single stem cell to a fully formed human baby.
Why are stem cells unique?
Stem cells are a unique type of cell, because, while they're immature cells without any specialization, they can follow a developmental "blueprint" to develop into the thousands of unique cell types found throughout your body. There are different types of stem cells, separated by how many tissues they can develop into.
What is the circulatory system?
Your circulatory system is one of the ones you're most likely to cover in biology class – so now's the time to get to know it! Your circulatory system is made up of a series of blood vessels – arteries, veins and capillaries – as well as a few specialized blood cell types: 1 Red blood cells: These red, disc-shaped cells are the ones responsible for carrying oxygen throughout your body. They contain hemoglobin, a special protein that can bind to the oxygen from the air you breathe, and then release it back into the tissues that need it. 2 White blood cells: Need help fighting off a cold or flu? Your white blood cells are there to help you! White blood cells make up a key component of your immune system. They help your body identify dangerous pathogens, and destroy them to keep you from getting too sick. 3 Platelets: The smallest cell type within your blood, platelets play a key role in blood clot formation. Once platelets sense damage or torn tissue, they start to clump together, forming a blood clot to slow or stop the bleeding.
Why is differentiation important in cells?
Differentiation allows developing cells to take on unique structures, and it allows the cell to carry out specialized functions.
What are the cells that help you?
Your white blood cells are there to help you! White blood cells make up a key component of your immune system. They help your body identify dangerous pathogens, and destroy them to keep you from getting too sick. Platelets: The smallest cell type within your blood, platelets play a key role in blood clot formation.
What are the different types of tissue?
There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
Which tissue is involved in the diffusion of ions and molecules?
Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and molecules.
What is the function of epithelial cells?
In addition, specialized epithelial cells function as receptors for special senses (smell, taste, hearing, and vision). Epithelial cells are numerous, exist in close apposition to each other, and form specialized junctions to create a barrier between connective tissues and free surfaces. Free surfaces of the body include the outer surface of internal organs, lining of body cavities, exterior surface of the body, tubes and ducts. The extracellular matrix of epithelial tissue is minimal and lacks additional structures. Although epithelial tissue is avascular, it is innervated.
How many types of muscle tissue are there?
Muscle tissue is easily distinguishable by its highly organized bundles of cells. Although there are three types of muscle tissue with unique cell morphologies, the fiber bundles of each tissue type are arranged in parallel oriented on the long axis and are distinct from surrounding connective tissue.
What are the free surfaces of the body?
Free surfaces of the body include the outer surface of internal organs, lining of body cavities, exterior surface of the body, tubes and ducts. The extracellular matrix of epithelial tissue is minimal and lacks additional structures. Although epithelial tissue is avascular, it is innervated.
Is muscle tissue elastic or extensible?
Muscle tissue. Muscle tissue is both extensible and elastic, in other words, it can be stretched and returned to its original size and shape. The cells of muscle tissue are unique in that they are contractile, or capable of contraction. This contraction is a result of sliding actin and myosin filaments.
Is epithelial tissue avascular or avascular?
Epithelial tissue is a highly cellular tissue that overlies body surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands. It is avascular but innervated. Epithelial cells exist in close apposition, forming a barrier between connective tissues and free surfaces. Their surfaces face basally, apically and laterally, with each having distinctive features. Specialized epithelial tissue also exists.
What Does It Mean for a Cell to Be Specialized?
If a cell is specialized, it has unique structures that allow it to carry out its function in the body. All cells start as stem cells, which are cells that can become many other types of cells. They go through a process called differentiation to become specialized. During differentiation, different environmental cues trigger changes in protein synthesis inside the cell. Different genes are turned on or off through gene regulation; this creates different proteins, and thus structure and function for the cell.
How many types of specialized cells are there in the human body?
There are over 200 different types of specialized in the human body. Specialized cells are important because they carry out specific functions that allow the body to maintain homeostasis.
What is the name of the specialized cells of the nervous system?
Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system.
What are some examples of cells specialized for reproduction?
Sperm and eggs are examples of cells specialized for reproduction.
Why are neurons different from skin cells?
However, neurons in our brain are very different from skin cells because neurons turn on genes needed for their job and thus make neuronal proteins, and skin cells turn on epithelial genes to make proteins required for their job.
What are the two types of reproductive cells?
Reproductive cells are those used for sexual reproduction. There are two main types of reproductive cells, sperm, and eggs . Sperm cells are specialized to have a shape that allows them to be aerodynamic and swim through the reproductive tract to fertilize an egg. They are also packed with mitochondria to provide the energy necessary to power the flagella for swimming. Egg cells are specialized to contain the organelles needed for a new cell to form after fusion.
How do organs work together?
Organs work together to form organ systems, groups of organs that perform a function for the body. Some examples of organ systems include the digestive system, which breaks down food and absorbs nutrients, and the cardiovascular system, which delivers oxygen and nutrients all over the body. Organ systems work together to support the entire organism.
What are the organs that come together to form tissues?
Specialized cells group together to form tissues. Tissues then form organs like the heart, stomach, or skin. Organs also come together to form systems such as the respiratory system or digestive system. These systems come together to form our bodies.
What is the body made of?
Your body is an amazing feat of engineering! It includes miles of nerve fibers and blood vessels, many feet of digestive system, a strong skeletal framework, and a protective covering. Even more amazing is the fact that all of this is created using only one type of component: the cell.
What Are Blood Cells?
Three types of blood cells exist in our circulatory system: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Each different type of blood cell is specialized, or carries out a different function. This is an example of how specialization can even occur within cells that are already specialized within a particular system of the body.
What are the cells that make up the nervous system called?
Nerve cells are called neurons . They bundle together to form a rope-like structure that branches throughout our bodies to form our nervous system. Neurons are found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Their job is to send messages through an electrical impulse.
What is the tail of a sperm cell?
The body of the sperm cell contains a large number of mitochondria, which produce large amounts of energy for the cell. The tail, called a flagellum, allows the sperm cell to travel to reach the egg cell.
How many types of cells are there in the human body?
This makes sense given that every part of our body is made up of them, but not all cells are the same. In fact, our bodies are made up of over 200 types of specialized cells. Being specialized means that even though they are similar, cells differ in size, shape, or function depending on their role in our bodies.
Which cell carries oxygen?
Red blood cells, for instance, specialize in carrying oxygen throughout the body. Instead of a nucleus, they have a large amount of a protein called hemoglobin that binds with the oxygen. Reproductive cells include the sperm cell and egg cell.
