3. Classification of sutures based on size (diameter)
| U.S.P. Size | COLLAGEN SUTURES | COLLAGEN SUTURES | SYNTHETIC SUTURES | SYNTHETIC SUTURES |
| Metric Size | Diameter Range | Metric Size | Diameter Range | |
| # 7 | - | - | 9 | 0.900 - 0.999 |
| # 6 | - | - | 8 | 0.800 - 0.899 |
| # 5 | - | - | 7 | 0.700 - 0.799 |
What are the types of absorbable synthetic sutures?
Most modern sutures are synthetic, including the absorbables polyglycolic acid, polylactic acid, Monocryl and polydioxanone as well as the non-absorbables nylon, polyester, PVDF and polypropylene. Also to know is, what are types of sutures?
What are indications for nonabsorbable synthetic sutures?
synthetic absorbable suture an absorbable suture produced from strands of polymers; the most commonly used materials are polyglactin 910 (Vicryl) and polyglycolic acid (Dexon); the latter is more rapidly absorbed. Synthetic absorbable sutures are absorbed by slow hydrolysis, a chemical process in which the polymer reacts with tissue fluids, causing a breakdown of the molecular …
What are the three types of suture?
Apr 05, 2018 · A natural monofilament suture. Polypropylene (Prolene). A synthetic monofilament suture. Silk. A braided natural suture. Polyester (Ethibond). A braided synthetic suture.
What is a non-absorbable suture?
Synthetic sutures: Clinical evaluation and future developments. Today's sutures are the result of a 4000-year innovation process with regard to their materials and manufacturing techniques, yet little has been done to enhance the therapeutic value of the suture itself.

What are synthetic stitches made of?
What is the difference between natural and synthetic sutures?
Is Vicryl synthetic suture?
Is silk synthetic suture?
Absorbable or non-absorbable sutures can either be synthetic or natural. Natural sutures originate from a biological source. Silk is an example of natural suture material. Synthetic sutures consist of human-made material, such as nylon.
Is stainless steel suture natural or synthetic?
What are blue sutures?
What is synthetic absorbable suture?
What is a nylon suture?
Is chromic suture absorbable?
What are Vicryl sutures?
What are Vicryl sutures used for?
What is a polyester suture?
What is an absorbable suture?
Answer. Absorbable synthetic sutures are composed of chemical polymers that are absorbed by hydrolysis and cause a lesser degree of tissue reaction after placement. Depending on the anatomic site, surgeon’s preference, and the required suture characteristics, the following types of synthetic absorbable suture may be considered including ...
How long does it take for a suture to absorb?
Absorption is minimal for 40 days and complete in 56-70 days. These sutures cause only minimal tissue reaction. These sutures are used in general soft-tissue approximation and vessel ligation. A similar suture material is made from polyglycolic acid and coated with polycaprolate (Dexon II).
What is polysorb made of?
Polysorb is a braided absorbable suture produced from a Lactomer copolymer formed via synthesis of copolymers of glycolide and lactide (in a ratio of 9 to 1). The glycolide and lactide behave differently when exposed to tissue hydrolysis.
What is a caprosyn suture?
Caprosyn is rapidly absorbing and represents the most recent innovation in the development of monofilament absorbable synthetic sutures. Caprosyn sutures are prepared from polyglytone 621, which is composed of glycolide, caprolactone, trimethylene carbonate, and lactide.
How long does it take for polyglactin 910 to absorb?
The tensile strength pf polyglactin 910 suture is approximately 65% at day 14 after implantation. Absorption is minimal for 40 days and complete in 56-70 days. These sutures cause only minimal tissue reaction.
What are the two types of sutures?
1. Absorbable and Non-absorbable suture materials. We can classify sutures into two types– those which are absorbable and will break down harmlessly in the body over time without intervention and those which are non-absorbable and must be manually removed if they are not left indefinitely.
What are sutures classified into?
Sutures are classified into different sizes based on the diameter of the thread. United States Pharmacopeia’s classification of sutures into various sizes is widely accepted across the world. The following U.S.P. and metric suture sizes chart shows the diameter range for collagen and synthetic sutures. 4.
Is a suture absorbable or non-absorbable?
As a result, absorbable sutures are often used internally; non-absorbable externally. Certain Sutures may need to be placed in a stressful environment, for example the heart (constant pressure and movement) or the bladder (adverse chemical presence) may require specialized or stronger materials to perform their role;
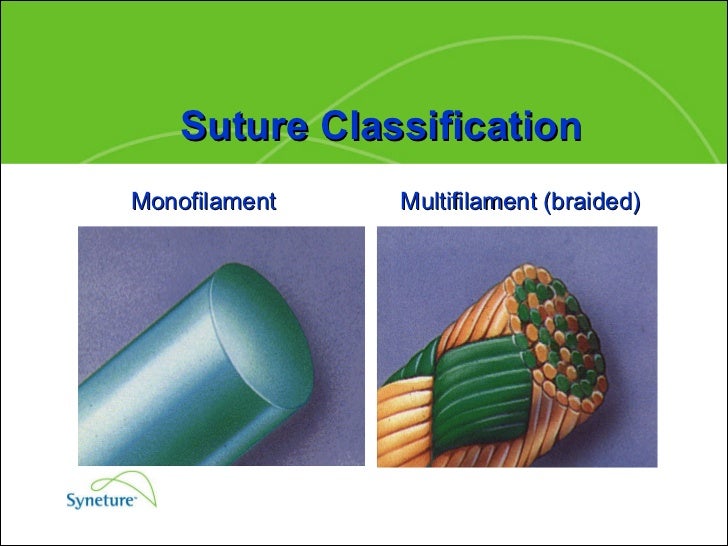
What is a multifilament suture?
Multifilament sutures are braided and often coated with various materials like silicon, wax , PTFE, polycaprolactone, calcium stearate etc. Barb sutures are monofilament sutures that have barbs or projections on the surface that can penetrate the tissues and hold them without necessitating the need for knots.
Can sutures be removed?
Suture materials which lie on the exterior of the body can be removed within minutes, and without re-opening the wound. As a result, absorbable sutures are often used internally; non-absorbable externally. Certain Sutures may need to be placed in a stressful environment, for example the heart (constant pressure and movement) or the bladder ...
What is the purpose of antimicrobial coatings?
Antimicrobial coatings like chlorhexidine, triclosan, silver ion may be given to any suture as a surface coating in addition to the regular coating materials to reduce the incidence of surgical site infection and help wound healing.
What is suture material?
Suture materials can be further categorised by their raw origin: Natural – made of natural fibres (e.g. silk or catgut). They are less frequently used, as they tend to provoke a greater tissue reaction. However, suturing silk is still utilised regularly in the securing of surgical drains.
What is surgical suture?
Surgical suture materials are used in the closure of most wound types. The ideal suture should allow the healing tissue to recover sufficiently to keep the wound closed together once they are removed or absorbed.
What is the classification of sutures?
Classification of Suture Materials. Broadly, sutures can be classified into absorbable or non-absorbable materials. They can be further sub-classified into synthetic or natural sutures, and monofilament or multifilament sutures.
How are sutures broken down?
Absorbable sutures are broken down by the body via enzymatic reactions or hydrolysis. The time in which this absorption takes place varies between material, location of suture, and patient factors.
What does the diameter of a suture affect?
The diameter of the suture will affect its handling properties and tensile strength. The larger the size ascribed to the suture, the smaller the diameter is, for example a 7-0 suture is smaller than a 4-0 suture.
What is the smallest suture?
The ideal suture is the smallest possible to produce uniform tensile strength, securely hold the wound for the required time for healing, then be absorbed. It should be predictable, easy to handle, produce minimal reaction, and knot securely.
What is a non absorbable suture?
Non-absorbable sutures are used to provide long-term tissue support, remaining walled-off by the body’s inflammatory processes (until removed manually if required). Uses include for tissues that heal slowly, such as fascia or tendons, closure of abdominal wall, or vascular anastomoses.
What are the different types of sutures?
The different types of sutures can be classified in many ways. First, suture material can be classified as either absorbable or nonabsorbable. Absorbable sutures don’t require your doctor to remove them. This is because enzymes found in the tissues of your body naturally digest them.
What is a suture used for?
Sutures are used by your doctor to close wounds to your skin or other tissues. When your doctor sutures a wound, they’ll use a needle attached to a length of “thread” to stitch the wound shut. There are a variety of available materials that can be used for suturing.
How long does it take for a suture to absorb?
For the more commonly used absorbable sutures, complete absorption times will vary: Vicryl rapide = 42 days.
What is a gut suture?
Gut – This natural monofilament suture is used for repairing internal soft tissue wounds or lacerations. The gut shouldn’t be used for cardiovascular or neurological procedures. The body has the strongest reaction to this suture and will often scar over. It’s not commonly used outside of gynecological surgery.
What is non absorbable suture?
Types of nonabsorbable sutures. Non-absorbable sutures are used to provide long-term tissue support, remaining walled-off by the body’s inflammatory processes (until removed manually if required). Uses include tissues that heal slowly, such as fascia or tendons, closure of abdominal wall, or vascular anastomoses.
What is a monofilament suture?
Monofilament suture – a single stranded filament suture (e.g nylon, PDS, or prolene). They have a lower infection risk but also have poor knot security and ease of handling. Multifilament suture – made of several filaments that are twisted together (e.g braided silk or vicryl ).
Can sutures be absorbed?
First, suture material can be classified as either absorbable or nonabsorbable. Absorbable sutures don’t require your doctor to remove them. This is because enzymes found in the tissues of your body naturally digest them.
