Scientists have identified 16 essential nutrients and grouped them according to the relative amount of each that plants need:
- Primary nutrients, also known as macronutrients, are those usually required in the largest amounts. They are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Secondary nutrients are those usually needed in moderate amounts compared to the primary essential nutrients. The secondary nutrients are calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
- Micro- or trace nutrients are required in tiny amounts compared to primary or secondary nutrients. Micronutrients are boron, chlorine, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc.
What are the primary nutrients of plants?
Primary nutrients are nutrients that are required by plants in larger quantities than other nutrients. The primary nutrients include nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), and potassium (K). Deficiency of these elements limits plant health, yield, and growth, therefore these nutrients are the three most essential elements supplied by fertilizers.
What are the essential nutrients and their functions?
Six Basic Nutrients and Their Functions
- Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are a major energy source. ...
- Proteins. Skin, muscle and bones depend on dietary protein for normal growth, development and maintenance. ...
- Lipids. You may think of lipids, or fats, as dietary enemies, but they are as necessary to the body's normal functioning as the other essential nutrients.
- Vitamins and Minerals. ...
- Water. ...
What are the micronutrients needed by plants?
What are the micronutrients needed by plants?
- Supplied by air and water: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen.
- Macronutrients: nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium.
- Secondary Nutrients: calcium, magnesium, sulfur.
- Micronutrients: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), and zinc (Zn).
What are the essential nutrients for plant growth?
- The primary nutrients are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. You may be most familiar with these three nutrients because they are required in larger quantities than other nutrients. ...
- The intermediate nutrients are sulfur, magnesium, and calcium. ...
- The remaining essential elements are the micronutrients and are required in very small quantities. ...

What is plant nutrition?
Plant nutrition. Nutrition may be defined as the supply and absorption of chemical compounds required for plant life, growth, and metabolism. It is the process of absorption and utilization of essential elements for plant growth and reproduction. Arnon (1954) has defined the following criteria/objectives for the essentiality of any nutrient:
What are the main sources of nutrients for plants?
Chief sources of nutrients to plants are clay and humus of soil. Nutrients such as NH4+, Ca++ k+, Mg+, etc., are held on clay particles in an exchangeable and available form for use by plants. Soil organic matter serves as the principal storehouse for the supply of anions such as H2PO4-or SO4– to the plants.
How do plants get nutrients?
Plants obtain nutrients in the following ways: 1 From the soil solution. i.e., the free water in soil containing dissolved salts. 2 From exchangeable ions on the surface of tiny particles of soils and organic matter called “humus” particles, respectively. 3 From readily decomposable minerals. 4 Through the tiny openings on the surface of leaves, called “stomata.’ 5 Chief sources of nutrients to plants are clay and humus of soil. 6 Nutrients such as NH4+, Ca++ k+, Mg+, etc., are held on clay particles in an exchangeable and available form for use by plants. 7 Soil organic matter serves as the principal storehouse for the supply of anions such as H2PO4-or SO4– to the plants.
What can absorb foliar-applied nutrients through the cuticle of bark?
Cuticle: Woody perennials and shrubs can absorb foliar-applied nutrients through the cuticle of bark.
What is the definition of macronutrients?
1. Major or macronutrient: Those nutrients required by plants in concentrations exceeding 1000 ppm (0.1%) are termed major or micronutrients. The term ‘macro’ refers to the amount used (usually 50mg/ kg or more in the plant body) and essential. Primary nutrients: C, H, O, N, P, K are the primary elements that are essential for seed germination ...
What are the secondary nutrients?
Secondary nutrients: They are secondary because they are needed only to grow (secondary growth). They are Ca, Mg and S. 2. Minor or micronutrients: The elements required by plants in a concentration less than 100 ppm are termed minor or macronutrients. They are also called “trace elements.”.
What is the role of nutrient in plant metabolism?
Thus, an essential plant nutrient may be defined as “an element so crucial for a specific metabolic activity that in its absence the plants cannot continue to grow or complete their life cycle, and it cannot be substituted by another element.
How many nutrients are needed for a plant to grow?
Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper crop development. Each is equally important to the plant, yet each is required in vastly different amounts. These differences have led to the grouping of these essential elements into three categories; primary (macro) nutrients, secondary nutrients, and micronutrients.
What are the primary nutrients in a crop?
Primary (macro) nutrients are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. They are the most frequently required in a crop fertilization program. Also, they are need in the greatest total quantity by plants as fertilizer.
Macronutrients
1. Nitrogen (Nitrate or Ammonium are both typically used) 2. Potassium (Potassium Nitrate or Potassium Sulfate are most commonly used. Potassium Chloride is also used) 3. Phosphorous (Phosphates containing Ammonium and Potassium are commonly used. Also, Phosphoric Acid) 4. Calcium (Calcium Nitrate) 5. Magnesium (Magnesium Sulfate) 6.
Micronutrients
7. Iron (Numerous forms are used: Ferrous Sulfate, Ferric Sulfate, Ferric Chloride, Iron Ammonium Sulfate) 8. Copper (Copper Sulfate) 9. Zinc (Zinc Sulfate) 10. Chlorine (Chlorine does not usually have to be added to the solution, since it is already present in most water) 11. Boron (Boric Acid, Solubor, Borax) 12. Cobalt (Cobalt Nitrate)
Atmospheric Elements
Oxygen Plants need to take in Oxygen for their normal respiration, generally taken in at night, though they do not release it until daylight during photosynthesis.
Macronutrients: Found in most starter fertilizers
Nitrogen Key component of photosynthesis, as well as a building block of DNA, RNA, and the plants proteins. Vital during periods of rapid growth.
Micronutrients: Just as important as Macro nutrients, though needed in smaller doses
Manganese Chlorophyll production Pollen germination and production Cell growth and pathogen resistance in the root zone
1. Macronutrients
These nutrients are absorbed in greater amount from the soil. These include hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and Sulfur.
2. Micronutrients
Boron, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, zinc and chlorine are known as micronutrients. These nutrients are absorbed by plants in very small amounts from the soil. That’s why they are called micronutrients. But micronutrients are also as essential as macro-nutrients for plant growth and completion of life cycle.
Forms of nutrients in which they are absorbed by plants from the soil
Plants absorb nutrients from the soil in the form of a solution through their roots. Some nutrients are absorbed by plants alone and some in combination as shown in the following table-
Jitendra rathore
Hello friends, I am Jitendra Rathore, Author & Founder of "New Agri India". I am graduate in agriculture. I love to share proper knowledge related to agriculture with the people.
What are the five essential nutrients that plants need?
A very few plants need five other nutrients: cobalt, nickel, silicon, sodium, and vanadium. Each essential nutrient affects specific functions of plant growth and development (Table 1). Plant growth is limited by the nutrient that is in the shortest supply (Fig. 1).
What are the nutrients that plants need?
A very few plants need five other nutrients: cobalt, nickel, silicon, sodium, and vanadium.
How do plants get nutrients?
Plants take in almost all of the essential nutrients through their roots. The exception is carbon, which is taken in through leaf pores, or stomata. Two types of organisms living in the soil help the roots take up nutrients: 1 Microorganisms, or microbes, break down organic compounds into inorganic compounds in a process called mineralization. 2 Fungi enable some plants to take up phosphorus by increasing the size of the roots and providing more soil-to-root contact.
How to tell if soil has nutrient problems?
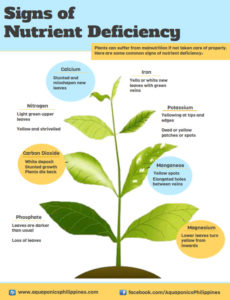
It is hard to tell whether the soil has a nutrient problem just by looking at the plants. Symptoms vary by nutrient and plant species. Common symptoms include: Little or no growth. Dead tissue at the leaf tips, on the leaf edges, or within the leaves. Yellow or dead leaves on one part of the plant only.
What happens if a plant doesn't have a nutrient?
A plant that lacks an essential nutrient cannot complete its life cycle—the seed may not germinate; the plant may not be able to develop roots, stems, leaves, or flowers properly; or it may not be able to produce seeds to create new plants. Often the plant itself will die.
What is the essential nutrient?
To be used by a plant, an essential nutrient must be broken down into its basic form. The nutrient must be in the form of either a positively charged ion (cation) or a negatively charged ion (anion). A plant cannot use organic compounds, such as those in manure or dead leaves, until they are broken down into their elemental or ionic forms.
What are the primary nutrients?
They are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and potassium.
What is the primary nutrient needed for a plant?
Primary nutrients need to be supplied as part of an NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) fertilizer. Some plants have different NPK requirements, and each stage of the growth cycle (such as root development or flowering) may have different NPK needs as well.
How many nutrients do plants need to grow?
Plants need 16 essential nutrients to grow, and they can be put into four major groups:
What is a hydroponic nutrient mix?
A hydroponic nutrient mix is a water-based mixture of all the stuff plants need to thrive in your hydroponic system.
What is nitrogen in plants?
Nitrogen (N) is a major component of several essential compounds, such as chlorophyll and amino acids. It promotes structural and vegetative growth of stems and leaves.
How many parts are in a complete nutrient mix?
There are three parts to a complete nutrient mix:
What is potassium in plants?
Potassium (K) regulates the opening and closing of stomata during photosynthesis. It promotes general plant growth.
What is the building material of leaves, roots, and stems?
Carbon (C) is the primary building material for leaves, roots, and stems. Oxygen (O) is an essential part of glucose production, which is used for energy in nutrient uptake by roots. Hydrogen (H) aids in proton gradients, which are essential for the electron transport chain in photosynthesis, and is part of nearly every compound.
PRIMARY (MACRO) NUTRIENTS
Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) are the most frequently required in a crop fertilization program.
SECONDARY NUTRIENTS
Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S) are required in lesser amounts than macronutrients, but each is equally important to the crop.
MICRONUTRIENTS
Boron (B), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn), Iron (Fe), Chloride (CI) and Molybdenum (Mo) are used in minute amounts but are just as important to plant growth and development as the major nutrients. Some micronutrients control the uptake of major nutrients and key processes.
What is Plant Nutrition?
Every living thing needs nutrients for its survival and so do plants. These nutrients facilitate the life cycle of the plant and its growth. There are 16 such nutrients, which the plant might need, and out of these sixteen, nine are essential and the other seven are required by the plants but in the absence of the remaining seven, the plant would not die. The nutrients can be further classified into the following:
How many elements are needed for plant growth?
Plant growth is solely dependent on 17 different elements. The presence of all these chemical elements in perfect proportion is primarily responsible for the healthy growth of a plant. As a gardener, you must know about these 17 essential elements. All these elements have been classified into specific categories.
What are the secondary nutrients in plants?
The Secondary Nutrients consist of Magnesium (Mg), Sulfur (S), and Calcium (Ca) which though are required in smaller amounts are required by the plant for various reasons. Magnesium is a part of Chlorophyll pigment without which Photosynthesis would not be possible and the plant would fail to prepare food and energy.
What is the most important component of the cell wall?
Boron is an important component of the cell walls. Besides sit also helps in the transportation of sugar and cell division. Manganese helps in the building of Chloroplasts and it also activates enzymes. Iron also helps in photosynthesis and enzyme reactions. It also helps in the synthesis of chlorophyll.
Why is zinc important for plants?
These nutrients are required in very small quantities as the name suggests. Zinc has a huge role to play in the stimulation and activation of enzymes; therefore it is required though in a small amount for the proper functioning of the plant. Copper is also important for Photosynthesis and it a part of various enzymes.
What are the primary nutrients in fertilizer?
Primary Nutrients – Air and Water Macronutrients. Consist of Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), and Hydrogen (H) along with Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). The latter three are commonly found in most fertilizers and the former are found in air and water from the atmosphere.
What are the three elements that are essential to plant life?
Some essential elements are primarily derived from fertilizers . Nitrogen (N), Potassium (K), and Phosphorus (P) are three elements.