
- Respiration is the process in which oxygen moves from the outside air into the body and carbon dioxide and other waste gases move from inside the body into the outside ...
- The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages called the respiratory tract. It has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
- The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx. All of these organs are involved in conduction or the movement of air into and out of the body. ...
- The lower respiratory tract includes the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, and the lungs. The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are involved in conduction. ...
- The respiratory system protects itself from potentially harmful substances in the air by the mucociliary escalator. This includes mucus-producing cells, which trap particles and pathogens in the incoming air. ...
- The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is monitored by cells in the brain. ...
What are the 10 parts of the respiratory system?
Respiratory system. The respiratory system is made up of the organs included in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. These are the parts: Nose. Mouth. Throat (pharynx) Voice box (larynx) Windpipe (trachea) Large airways (bronchi) Small airways (bronchioles) Lungs. The upper respiratory tract is made up of the: Nose. Nasal cavity. Sinuses ...
What is the two main division of the respiratory system?
The respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The organs in each division are shown in Figure 16.2. 2. In addition to these organs, certain muscles of the thorax (the body cavity that fills the chest) are also involved in respiration by enabling breathing.
What are the 5 main functions of the respiratory system?
- Major function of the respiratory system. is to supply the body with oxygen and dispose carbon dioxide but because it moves air, it also functions in speech and smell.
- Pulmonary ventilation. moving air into and out of the lungs (breathing)
- External respiration.
- Transport.
- Internal respiration.
What is a respiratory system and what does it do?
Your respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that help you breathe. This system helps your body absorb oxygen from the air so your organs can work. It also cleans waste gases, such as carbon dioxide, from your blood. Common problems include allergies, diseases or infections.
What are the two 2 main types of respiration in humans?
There are two types of Respiration:Aerobic Respiration — Takes place in the presence of oxygen.Anaerobic Respiration –Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
What are the 2 most important components in the respiratory system?
The major components of the respiratory system are the bronchi, the larger conducting airways that begin at the end of the trachea and go into the lung; the bronchioles, the more narrow airways that branch from the bronchi; and alveoli, tiny air sacs located at the end of the bronchioles where the exchange of oxygen ...
What are the types of respiratory system?
There are three major types of respiratory structures in the vertebrates: gills, integumentary exchange areas, and lungs.
What are the main parts of the respiratory system?
The main organ of the respiratory system is the lungs. Other respiratory organs include the nose, the trachea and the breathing muscles (the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles).
What are the major zones of the respiratory system?
The conducting zone consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. These structures form a continuous passageway for air to move in and out of the lungs.
What are the structures of the upper respiratory tract?
The upper respiratory tract structures are found in the head and neck and consist of the nose, pharynx, and larynx. The upper respiratory tract. 1. 2.
Where is the respiratory zone located?
Check out these free respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. The respiratory zone is found deep inside the lungs and is made up of the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli. These thin-walled structures allow inhaled oxygen (O2) to diffuse into the lung capillaries in exchange for carbon dioxide (CO2).
Where are the lower respiratory tract structures located?
The lower respiratory tract structures are located in the thorax or chest and include the trachea, bronchi, and lungs (= bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli). Please note that many authorities include the larynx with the lower respiratory tract structures.
What are the structures that make up the conducting zone?
The conducting zone consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. These structures form a continuous passageway for air to move in and out of the lungs. The conducting zone. 1.
What is the respiratory system?
Your respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that help you breathe. This system helps your body absorb oxygen from the air so your organs can work. It also cleans waste gases, such as carbon dioxide, from your blood. Common problems include allergies, diseases or infections.
What are the two parts of the respiratory system that help regulate the temperature and humidity of the air you inhale?
Your airways are a complicated system that includes your: Mouth and nose: Openings that pull air from outside your body into your respiratory system. Sinuses: Hollow areas between the bones in your head that help regulate the temperature and humidity of the air you inhale.
What are the bones and muscles that surround the respiratory system?
Some of the bones and muscles in the respiratory system include your: Diaphragm: Muscle that helps your lungs pull in air and push it out. Ribs: Bones that surround and protect your lungs and heart. When you breathe out, your blood carries carbon dioxide and other waste out of the body.
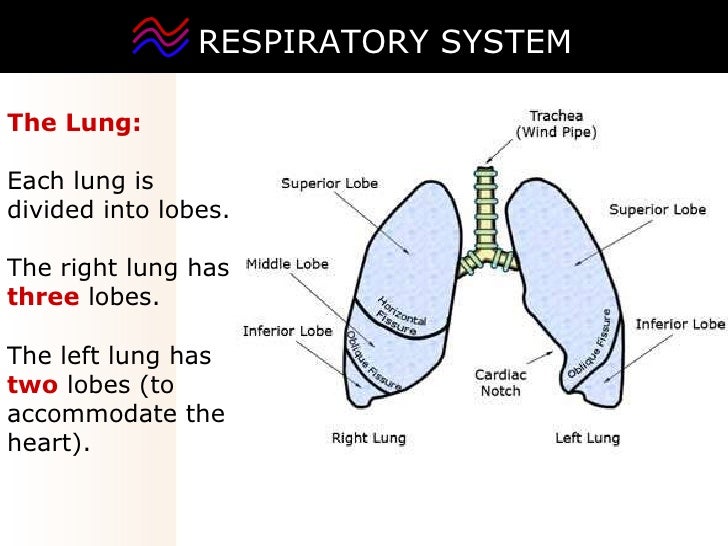
What are the lobes of the lungs?
Lung lobes: Sections of the lungs — three lobes in the right lung and two in the left lung. Pleura: Thin sacs that surround each lung lobe and separate your lungs from the chest wall. Some of the other components of your respiratory system include:
What diseases affect the respiratory system?
Disease: Respiratory disorders include lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). These illnesses can harm the respiratory system’s ability to deliver oxygen throughout the body and filter out waste gases. Aging: Lung capacity decreases as you get older.
What causes inflammation in the respiratory system?
Conditions that can cause inflammation (swelling, irritation and pain) or otherwise affect the respiratory system include: Allergies: Inhaling proteins, such as dust, mold, and pollen, can cause respiratory allergies in some people. These proteins can cause inflammation in your airways.
What are the air sacs in the lungs?
Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Bronchioles: Small branches of the bronchial tubes that lead to the alveoli. Capillaries: Blood vessels in the alveoli walls that move oxygen and carbon dioxide.
How many alveoli are there in the lungs?
These tiny air sacs are the functional units of the lungs where gas exchange takes place. The two lungs may contain as many as 700 million alveoli, providing a huge total surface area for gas exchange to take place. In fact, alveoli in the two lungs provide as much surface area as half a tennis court!
Which organ is responsible for breathing?
2. In addition to these organs, certain muscles of the thorax (the body cavity that fills the chest) are also involved in respiration by enabling breathing. Most important is a large muscle called the diaphragm, which lies below the lungs and separates the thorax from the abdomen.
How wide is the trachea?
The trachea, or windpipe, is the widest passageway in the respiratory tract. It is about 2.5 cm (1 in.) wide and 10-15 cm (4-6 in.) long. It is formed by rings of cartilage, which make it relatively strong and resilient. The trachea connects the larynx to the lungs for the passage of air through the respiratory tract. The trachea branches at the bottom to form two bronchial tubes.
What is the process of transferring gases from the body to the outside air?
Respiration is the life-sustaining process in which gases are exchanged between the body and the outside atmosphere. Specifically, oxygen moves from the outside air into the body; and water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other waste gases move from inside the body into the outside air.
What is the waste product of cellular respiration?
When cellular respiration is aerobic, it uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide as a waste product. Respiration by the respiratory system supplies the oxygen needed by cells for aerobic cellular respiration and removes the carbon dioxide produced by cells during cellular respiration.
How many lobes are there in the right lung?
These are called lobes, and they are separated from each other by connective tissues. The right lung is larger and contains three lobes. The left lung is smaller and contains only two lobes.
What is the physical process of conducting air to and from the lungs?
This is the physical process of conducting air to and from the lungs. The other process is gas exchange. This is the biochemical process in which oxygen diffuses out of the air and into the blood while carbon dioxide and other waste gases diffuse out of the blood and into the air.
