What do the different parts of the nervous system do?
What Do the Different Parts of The Nervous System Do?
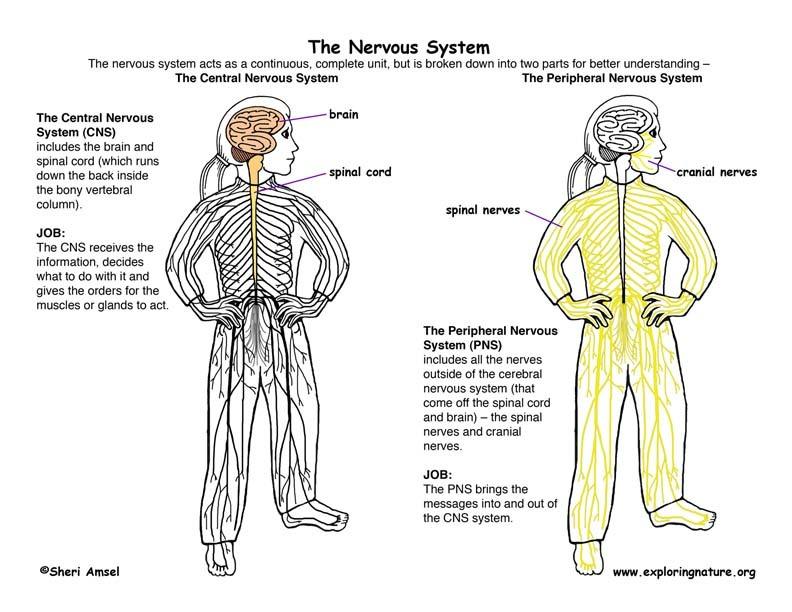
- Central Nervous System. The spinal cord directs signals from the brain to the body and is capable of controlling simple reflexes without transmitting information from the brain.
- Peripheral Nervous System. ...
- See a Neurologist. ...
Why is it important to have a healthy nervous system?
- Numbness, tingling sensation, weakness and paralysis
- Blurred vision, dimness, loss of vision
- Sudden and severe headache
- Dizziness, inability to stand or walk
- Change in behaviour or level of consciousness, confusion
- Severe nausea or vomiting
What are the 2 main subdivisions in peripheral nervous system?
Two major divisions of the nervous system. Motor, sensory. Two subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system. Motor. A nerve cell conducting impulses from the brain to the effectors. Sensory. A nerve cell receiving information and transmiting it to the brain. Afferent.
What 2 groups is the perpheral nervous system divided into?
There are two main types; spinal nerves and cranial nerves. Functionally, the PNS can be divided into the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. Both of these can be further subdivided; the former into sympathetic and parasympathetic arms and the latter into sensory and motor divisions. It might sound complicated, but it’s not.

What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
The two main parts of the nervous system are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the spinal cord and the brain, which contains 100 billion nerve cells. The peripheral nervous system is broken down into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
Which system controls the nervous system?
In the somatic nervous system, sensory information is sent to the central nervous system by the peripheral nerve fibers. The autonomic nervous system controls muscles in the vital organs and glands. The sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system and enteric nervous system are the three main parts of the autonomic nervous system .
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
The body’s nervous system is made up of two major parts, the central nervous system , and the peripheral nervous system . These two parts of the nervous system act jointly to assure your body is communicating all of its sensory information and needs. The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system each play different roles in controlling your body’s functions.
What is the somatic nervous system made of?
The somatic nervous system is made up of motor neurons and sensory neurons that help the body perform voluntary activities.
What system sends signals to and from the CNS?
Peripheral Nervous System. Nerves make up the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which works to send signals to and from the CNS, the body’s organs, muscles, and senses. The PNS is broken into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Sympathetic Nervous System. The sympathetic nervous system stimulates what is known as the fight or flight response in the body. It prepares the body’s energy for stressful or energy-exerting activities.
Which part of the brain is responsible for sensory functions, voluntary motor skills, speech, and critical thinking?
The parts of the forebrain are responsible for sensory functions, voluntary motor skills, speech, and critical thinking. It also controls homeostasis which is maintained through regulation of body temperature, blood pressure, pleasure, pain, hunger, and thirst as well as hormone production.
Which part of the brain controls the movement of the eye?
The Midbrain: The midbrain connects the forebrain and the hindbrain and carries the important job of connecting the brain to the spinal cord. It processes sounds and sights and works to control the movement of the eye.
What is the brain responsible for?
The brain processes most of the body’s sensory information and is responsible for coordinating conscious and unconscious body functions including feeling, thinking, and maintaining homeostasis, which is the body’s ability to maintain a stable environment. The brain is made up of three regions, the forebrain, the midbrain, ...
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
This article throws light upon the two main parts of nervous system. The parts are: 1. The Cerebro-Spinal Axis 2. The Nerves and Their Functions.
How many nerve cells are there in the brain?
There are approximately 14,000,000,000 nerve cells or neurons in the brain. The nerve cells are connected with one another by the synapses or the junctions between neurons.
How many spinal nerves are there?
The spinal nerves are given off from the spinal cord on either side at regular intervals. There are thirty one pairs of these nerves. Each nerve has two roots, an anterior and a posterior root, which unite with each other.
What is the spinal cord made of?
The spinal cord is composed of the grey matter and the white matter. The grey matter consisting of nerve cells lies inside and the white matter consisting of nerve-fibres, lies outside completely covering the grey matter. The spinal cord is the channel of communication from the brain and to the brain.
Where do nerve currents travel?
The former carry nerve currents from the sense-organs inward to the sensory centres in the spinal cord and the brain. The latter carry nerve currents from the motor centres in the spinal cord and the brain outward to muscles and glands.
What is the term for the cord that connects the brain to the brain?
It is prolongation of the spinal cord, called also the ‘Bulb’ or the ‘Stem’ which connects the brain with the spinal cord. It acts as a conductor between the spinal cord and the brain. All the nerve-fibres passing from the spinal cord to the brain pass through it.
Where are sensory nerves located?
The sensory nerves are the axons of sensory neurons situated in the sense-organs and other internal organs. The motor nerves are the axons of motor neurons situated in the motor centres of the spinal cord and the brain.
What are the two major parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system can be divided into two major subdivisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), shown in [link]. The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord; the PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body. In this section, we focus on the peripheral nervous system; later, we look at the brain and spinal cord.
Which divisions of the autonomic nervous system have opposite effects on various systems?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system have the opposite effects on various systems.
What is the somatic nervous system?
The somatic nervous system is associated with activities traditionally thought of as conscious or voluntary. It is involved in the relay of sensory and motor information to and from the CNS; therefore, it consists of motor neurons and sensory neurons. Motor neurons, carrying instructions from the CNS to the muscles, are efferent fibers (efferent means “moving away from”). Sensory neurons, carrying sensory information to the CNS, are afferent fibers (afferent means “moving toward”). Each nerve is basically a two-way superhighway, containing thousands of axons, both efferent and afferent.
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system is made up of thick bundles of axons, called nerves, carrying messages back and forth between the CNS and the muscles, organs, and senses in the periphery of the body (i.e., everything outside the CNS). The PNS has two major subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
Which system controls the body's internal organs and glands?
The autonomic nervous system controls our internal organs and glands and is generally considered to be outside the realm of voluntary control. It can be further subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions ( [link] ). The sympathetic nervous system is involved in preparing the body for stress-related activities; the parasympathetic nervous system is associated with returning the body to routine, day-to-day operations. The two systems have complementary functions, operating in tandem to maintain the body’s homeostasis. Homeostasis is a state of equilibrium, in which biological conditions (such as body temperature) are maintained at optimal levels.
What happens to the parasympathetic nervous system after a threat is resolved?
Once the threat has been resolved, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over and returns bodily functions to a relaxed state. Our hunter’s heart rate and blood pressure return to normal, his pupils constrict, he regains control of his bladder, and the liver begins to store glucose in the form of glycogen for future use. These processes are associated with activation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system is divided into two major parts: (a) the Central Nervous System and (b) the Peripheral Nervous System.
What are the two major divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
The nervous system can be divided into two major subdivisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), shown in Figure 1. The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord; the PNS connects the CNS to the rest ...
What are the two major subdivisions of the PNS?
The PNS has two major subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system is associated with activities traditionally thought of as conscious or voluntary. It is involved in the relay of sensory and motor information to and from the CNS; therefore, it consists of motor neurons and sensory neurons.
What happens to the parasympathetic nervous system after a threat is resolved?
Once the threat has been resolved, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over and returns bodily functions to a relaxed state. Our hunter’s heart rate and blood pressure return to normal, his pupils constrict, he regains control of his bladder, and the liver begins to store glucose in the form of glycogen for future use. These processes are associated with activation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
What is the CNS and PNS?
The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord; the PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body. In this section, we focus on the peripheral nervous system; later, we look at the brain and spinal cord. Figure 1. The nervous system is divided into two major parts: (a) the Central Nervous System and (b) the Peripheral Nervous System.
Why is the sympathetic nervous system activated?
The sympathetic nervous system is activated when we are faced with stressful or high-arousal situations. The activity of this system was adaptive for our ancestors, increasing their chances of survival. Imagine, for example, that one of our early ancestors, out hunting small game, suddenly disturbs a large bear with her cubs.
Which division of the autonomic nervous system is activated?
activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, allowing access to energy reserves and heightened sensory capacity so that we might fight off a given threat or run away to safety
What are the two major parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system can be divided into two major subdivisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), shown in. The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord; the PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body. In this section, we focus on the peripheral nervous system; later, we look at the brain and spinal cord.
Which divisions of the autonomic nervous system have opposite effects on various systems?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system have the opposite effects on various systems.
What is the somatic nervous system?
The somatic nervous system is associated with activities traditionally thought of as conscious or voluntary. It is involved in the relay of sensory and motor information to and from the CNS; therefore, it consists of motor neurons and sensory neurons. Motor neurons, carrying instructions from the CNS to the muscles, are efferent fibers (efferent means “moving away from”). Sensory neurons, carrying sensory information to the CNS, are afferent fibers (afferent means “moving toward”). Each nerve is basically a two-way superhighway, containing thousands of axons, both efferent and afferent.
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system is made up of thick bundles of axons, called nerves, carrying messages back and forth between the CNS and the muscles, organs, and senses in the periphery of the body (i.e., everything outside the CNS). The PNS has two major subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
Which system controls the body's internal organs and glands?
The autonomic nervous system controls our internal organs and glands and is generally considered to be outside the realm of voluntary control. It can be further subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The sympathetic nervous system is involved in preparing the body for stress-related activities; the parasympathetic nervous system is associated with returning the body to routine, day-to-day operations. The two systems have complementary functions, operating in tandem to maintain the body’s homeostasis. Homeostasis is a state of equilibrium, in which biological conditions (such as body temperature) are maintained at optimal levels.
What happens to the parasympathetic nervous system after a threat is resolved?
Once the threat has been resolved, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over and returns bodily functions to a relaxed state. Our hunter’s heart rate and blood pressure return to normal, his pupils constrict, he regains control of his bladder, and the liver begins to store glucose in the form of glycogen for future use. These processes are associated with activation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
What are the two major divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
The nervous system can be divided into two major subdivisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), shown in Figure 1. The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord; the PNS connects the CNS to the rest ...
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system is made up of thick bundles of axons, called nerves, carrying messages back and forth between the CNS and the muscles, organs, and senses in the periphery of the body (i.e., everything outside the CNS). The PNS has two major subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and ...
What are the two major subdivisions of the PNS?
The PNS has two major subdivisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system is associated with activities traditionally thought of as conscious or voluntary. It is involved in the relay of sensory and motor information to and from the CNS; therefore, it consists of motor neurons and sensory neurons.
What happens to the parasympathetic nervous system after a threat is resolved?
Once the threat has been resolved, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over and returns bodily functions to a relaxed state. Our hunter’s heart rate and blood pressure return to normal, his pupils constrict, he regains control of his bladder, and the liver begins to store glucose in the form of glycogen for future use. These restorative processes are associated with activation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
What is the CNS and PNS?
The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord; the PNS connects the CNS to the rest of the body. In this section, we focus on the peripheral nervous system; later, we look at the brain and spinal cord. Figure 1. The nervous system is divided into two major parts: (a) the Central Nervous System and (b) the Peripheral Nervous System.
Which system is associated with routine, day-to-day operations of the body?
parasympathetic nervous system: associated with routine, day-to-day operations of the body. peripheral nervous system (PNS): connects the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, organs and senses in the periphery of the body. somatic nervous system: relays sensory and motor information to and from the CNS.
Which system controls the internal organs and glands?
The autonomic nervous system controls our internal organs and glands and is generally considered to be outside the realm of voluntary control. It can be further subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions (Figure 2).
